Technology for searching documentary information on the Internet
Similar essays:
Characteristics of search engines: essence, tasks, basic components; Main settings. Global search engines, their advantages and disadvantages; features of the legal system - Garant. Strategy and methodology of professional information retrieval.
General principles for organizing information retrieval on the Internet. Directory Search information resources and using search engines. Rules for the search for information regarding the accounting of current liabilities and settlements with buyers and customers.
Kabardino-Balkarian State University College Information technologies and Economics Abstract "Internet Search Systems"
Viewer Internet explorer as an extension of the Explorer program, oriented to work not only with file system this computer, but also with Internet Web documents. Features of the PixGrabber picture viewer application program.
2. Search engines and machines on the Internet. Let us turn to the history of the emergence of the Internet, which was created in connection with the need to share information resources distributed between various computer systems. Most early applications, including FTP and ...
The structure of reference and search systems of the Internet, the work of search engines. Comparative review reference search engines (Gopher, WAIS, WWW, AltaVista, Yahoo, OpenText, Infoseek). Search robots, the most popular reference search engines.
Knowing the basic concepts and terms allows you to conduct an in-depth search using keywords that most accurately describe the topic. In this case, it is necessary to distinguish between simple, advanced and contextual search techniques.
The characteristics of information search methods on the Internet, namely, using hypertext links, search engines and special tools. Analysis of new Internet resources. The history and description of Western and Russian-language search engines.
The World Wide Web is a collection of information resources connected by telecommunications and based on the hypertext representation of data scattered around the world. The World Wide Web is also designated as WWW.
Search is vital for users, with it they work with complex websites. The best websites offer a simple search box on home page and abandon advanced search and use of the search framework.
Typology of search methods. Direct search using hypertext links. Search technology using search engines. Compilation and execution of queries to search engines.
The technology of hyperlinks contained in WWW documents and processed by programs for accessing WWW servers is the main difference between WWW that allows users to quickly navigate the Internet.
What is the Internet. A brief history of the Internet. The main protocols on the Internet and search in them. The World Wide Web. Search engines in Russia.
The Internet has provided us with easy and quick access to a large number of information materials, the ability to both read, save, print these materials, and ourselves to post useful, and maybe useless information on the network.
The study of the types of connection (permanent on a leased line, session telephone Dial-up), access to information, types of services (interactive, direct, deferred reading) and search engines (Lycos, AltaVista, Yahoo, OpenText, WAIS) on the Internet.
The history of the emergence and development of the Internet, especially its humanitarian and technical aspects. Application of the World Wide Web - "World Wide Web". Key aspects of WWW technology, the specifics of its use for creating educational resources.
The concept of the Internet system, usage, network size, number of subscribers and users. Search engines, an approach to collecting information about Internet resources. Modern search engines. Work with resource catalogs, saving information on the Internet.
Internet Search Technologies
Every year, the volume of the Internet increases at times, so the probability necessary information increases dramatically. The Internet unites millions of computers, many different networks, the number of users increases by 15-80% annually. And, nevertheless, more and more often when accessing the Internet, the main problem is not the lack of information sought, but the ability to find it. As a rule, an ordinary person, for various reasons, cannot or does not want to spend more than 15-20 minutes searching for the answer he needs. Therefore, it is especially important to correctly and competently learn, it would seem, a simple thing - where and how to look in order to receive the DESIRED answer. To find the information you need, you need to find its address. To do this, there are specialized search engines (index robots (search engines), thematic Internet directories, meta-search systems, people search services, etc.). This master class reveals the basic technologies for searching for information on the Internet, provides general features of search tools, considers structures search queries for the most popular Russian-language and English-language search engines.
Web technology World Wide Web (WWW) is considered a special technology for the preparation and placement of documents on the Internet. WWW includes web pages, electronic libraries, catalogs, and even virtual museums! With such an abundance of information, the question arises sharply: “How to navigate in such a huge and large-scale information space?” Search tools come to the rescue of this problem. Search tools are special software whose main purpose is to provide the most optimal and high-quality information search for Internet users. Search tools are hosted on special web servers, each of which performs a specific function:
Analysis of web pages and recording the results of analysis at one or another level of the search server database.
Search for information at the request of the user.
Providing a convenient interface for searching information and viewing the search result by the user.
The methods of work used when working with certain search tools are almost the same. Before proceeding to discuss them, consider the following concepts:
The search tool interface is presented in the form of a page with hyperlinks, a query string (search bar) and query activation tools.
Search Engine Index is information basecontaining the result of the analysis of web pages, compiled according to certain rules.
Request is keyword or a phrase that the user enters into the search bar. For the formation of various queries, special characters ("", ~), mathematical symbols (*, +,?) Are used.
The information retrieval scheme is simple. The user types a key phrase and activates the search, thereby receiving a selection of documents for a formulated (given) request. This list of documents is ranked according to certain criteria so that at the top of the list are those documents that most closely match the user's request. Each of the search tools uses different criteria for ranking documents, both when analyzing search results and when creating an index (filling the index database of web pages). Thus, if you specify a query in the search bar for each search tool of the same design, you can get different results search. It is of great importance for the user which documents will appear in the first two or three dozen documents according to the search results and how much these documents meet the user's expectations. Most search tools offer two search methods - simple search (simple search) and advanced search (advanced search) using a special request form and without it. Consider both types of search using the example of an English-language search engine. For example, AltaVista is conveniently used for arbitrary queries, “Something about online degrees in information technology”, while the Yahoo search tool allows you to receive world news, information about exchange rates or weather forecasts.
Mastering the criteria for refining the query and advanced search techniques allows you to increase the efficiency of the search and quickly find the necessary information. First of all, you can increase the search efficiency by using the logical operators (operations) Or, And, Near, Not, mathematically x and special characters. Using operators and or symbols, the user associates keywords in the desired sequence to get the most relevant search result. [ 9 ]
Internet resources in the global network are becoming more and more and more difficult to find the necessary information every day. Therefore, all market participants in modern search engines already have the impression that today's search technologies are outdated and that the concept of search itself needs to be changed. AT currently Google is still the undisputed leader in search - 47% of all Internet users choose this service, then Yahoo! and MSN - 21 and 13% of hits, respectively, that is, in general more than 80% of the world's inhabitants prefer these particular search engines. None of the three main search engines can boast of a high degree of loyalty among their regular users: almost 71% of those who searched on Yahoo! also sometimes visit one of the other two services - Google or MSN Search, 70% Of those who searched on MSN, they also tried their luck in a particular competitive search engine. Seeing such dissatisfaction with search results, the creators of search engines try to improve their search engines and try to apply new search technologies. So, the so-called self-constructor was launched on the Google portal, where users of this search engine can customize the search process as they wish. For example, if the user is interested in the weather, he can see the weather widget in his city. And the way to display news, display stock exchanges and many other useful things can be customized in accordance with your interests. Naturally all similar settings the user can only use while he is authorized on the site of the search engine. With the advent of this technology, Google’s site was in many ways ahead of its competitors - the oldest portals Yahoo Internet ! and MSN.
The purpose of the module is to get an idea of \u200b\u200bthe basic principles of the functioning of Internet search engines, to study technologies effective search information resources.
Search task statement
Consider the formulation of the search problem. To do this, we need to answer three questions: what to look for (what sources of information); where to search (the location of these sources) and how to search (what tools to use for this).
Sources of information on the Internet
We single out the main sources of information presented on the Internet. It:
- wWW documents
- articles in newsgroups and mailing lists;
- files in file libraries
- directories of address information about organizations and people (e-mail, address, phone);
- articles in thematic databases, encyclopedias.
Placement of information sources on the Internet
Now we will answer the question of where these sources of information are located. These are such popular Internet resources asWWW newsgroups, mailing lists andFTP -servers. Currently, the main place for posting information inInternet is the world wide web.
Search method
Of course, you can search for information sources “manually”, starting from any starting address and clicking on the necessary links. You can find addresses from specialized magazines on computer science and the Internet, use directories called Yellow Pages with categorized addresses of companies and institutions. Such manuals are available in paper form or on CD-ROM. However, to effectively search for information in such a volatile space as the Internet, it is necessary to learn how to use special tools, the purpose of which is to collect data on global information resources computer network and provide users with a service quick search.
Information Retrieval Systems (IPS). Definition
Thus, we come to the concept of an autonomous search tool - information retrieval system.
IPS is a system that provides the search and selection of necessary data in a special database with descriptions of information sources (index) based on the information retrieval language and relevant search rules.
The main task of the IPS
The main task of any IPS is to search for information in accordance with the information needs of the user, formed in the form of a request. It is very important as a result of the search that you don’t lose anything, that is, find in the index all the documents related to the request (completeness of the search) and not find anything superfluous (accuracy of the search). Therefore, a qualitative characteristic of the search procedure is introduced - relevance.
Relevance is the relevance of search results to a formulated query.
Key IPS indicators for WWW
Next, we will mainly consider IPS for the World Wide Web (WWW ) The main indicators of IPS forWWW are spatial scale and specialization.
On a spatial scale, IPS can be divided into local, global, regional and specialized. Local search engines can be designed to quickly search pages on a single server scale. Regional IPSs describe the information resources of a particular region, for example, Russian-language pages on the Internet. Global search engines, unlike local ones, strive to describe the resources of the entire information space of the Internet as fully as possible.
In addition, IPSs can specialize in finding various sources of information, such as documentsWWW , files, addresses, etc.
The main tasks of designing IPS for WWW
Let us consider in more detail the main tasks that developers of the IPS should solve. As follows from the definition, IPA forWWW they search in their own database (index), which contains the result of the description of distributed information sources. So, first you need to describe information resources and create an index. Building an index begins by defining an initial setURL sources of information. Then the indexing procedure is performed.
Indexing - a description of the sources of information and the construction of the index.
Index is a special database for the effective search for the described information resources.
In some information retrieval systems, the description of information sources is carried out by the personnel of the IPS, that is, by the people who make up a brief annotation for each resource. Then, as a rule, the described resources are sorted by topics (compilation of a thematic catalog). Of course, a description compiled by man will be adequate to the source. True, in this case, the indexing procedure takes a considerable period of time, therefore, the generated index has, as a rule, a limited amount. But the search in such a system can be carried out as easily as in the thematic catalogs of libraries.
In the IPS of another type, the procedure for describing information resources is automated. To do this, a special robot program is being developed that bypasses resources using a certain technology, describes them (indexes them) and analyzes links from the current page to expand the search area. How can a document describe a program? Most often, a list of words that appear in the text and other parts of the document is simply compiled, taking into account the frequency of repetition and the location of the word, that is, a peculiar weight coefficient is assigned to the word depending on its significance. For example, if the word is in the titleWeb -pages, the robot will assign it a higher coefficient. Since the description is automated, the time spent is small, and the index can be very large in size.So with the next challenge for the second type of IPS is the development of an indexing robot.
An indexer robot is a program that serves to scan the Internet and keep the index database up to date.
For search in systems of this type the user needs to learn how to make queries, in the simplest case consisting of several words. Then the IPS will search in its index for documents whose descriptions contain words from the query. To conduct a better search, it is necessary to develop a special query language for the user. Depending on the features of constructing the index model and the supported query language, a search mechanism and an algorithm for sorting the results are developed.
Since the index is significant, the number of documents found may be quite large. Therefore, it is extremely important how the search engine searches and sorts its results.
Essential appearance search engine, which appears before the user, so one of the tasks is to develop a convenient and beautiful interface.
Finally, the presentation of search results is extremely important, because the user needs to learn as much as possible about the source of information found in order to make the right decision about the need to visit it.
Work with IPS for WWW
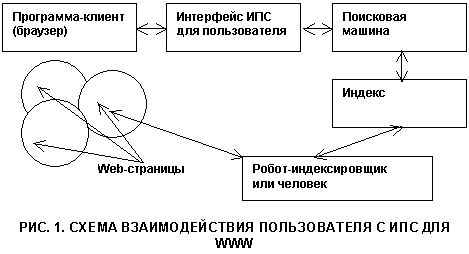
Consider a generalized scheme of user interaction with the information retrieval system for the World Wide Web WWW (Fig. 1.). Using a standard client program for the World Wide Web (browser), the user connects to the IPS at its address and formulates a search request.
The main component of the IPS is a search engine that searches the index for links to information resources and provides search results to the user.
As mentioned earlier, the search is carried out in a special database called an index. The architecture of the index is designed so that the search is as quick as possible, and you can use efficient algorithms for sorting search results. Ideally, search results should be sorted so that the most relevant links are at the top of the list.
Key Indexing Sources for WWW Documents
As you know, a Web page is a complex document consisting of many elements. When describing such a document by a robot program, it is necessary to take into account in which part of the Web page the given word occurred. Indexing Sources for DocumentsWWW usually are:
- web page title (Title);
- headings of various levels (H 1 -H 6);
- annotation (Description);
- keyword lists (KeyWords);
- hypertext links
- full texts of documents.
Search engines that describe the entire text of a WWW document are called full-text.
Features and indexing procedures
During the indexing procedure, vocabulary is often normalized (reduction of the word to the basic form). Some uninformative words, such as conjunctions or prepositions, are not indexed. Each IPS has its own list of so-called stop words that are ignored during the indexing process. In systems with highly variable languages, for example, Russian, morphology is taken into account. Taking into account morphology means the ability to work with various forms of words in a particular language. It should be noted the relative complexity of the Russian language, the words of which vary in numbers, cases, gender and tenses, and often in an unexpected way (for example: goes, goes, goes, goes, etc.). All existing IPS, taking into account the morphology of the Russian language, use the “Grammar Dictionary of the Russian Language” compiled by Andrei Anatolyevich Zaliznyak. The dictionary includes 90,000 entries, each word gives information about whether it is mutable, and how exactly it bends or conjugates.
WWW Search Tools
From the above it follows that the main tools for finding information inWWW are iPS. However, there are search tools on the Internet that differ fundamentally from the IPS discussed above. In general, the following search tools forWWW : search engines, metasearch systems ( search services) and accelerated search programs (search agents).
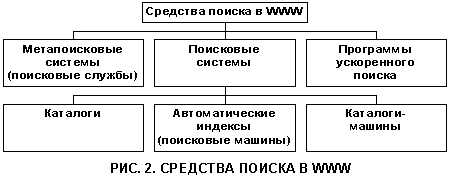
The central place rightfully belongs to search engines, which in turn are divided into directories, automatic indexes (search engines) and directories-machines. Only search engines almost fully possess the capabilities and properties of IPS.
Directory - search systemin which the description of the resources is carried out by personnel (people). Then, the described resources are sorted by topics (compilation of a thematic catalog).
Search engine (Search Engine) - a search system that uses a robot program to automate the procedure for describing information resources.
Recently, systems have started appearing on the World Wide Web that automatically search in two indexes at once (catalog index and search engine index). Such systems allow you to take advantage of the search engines of both types and are called machine directories.
The fundamental difference between meta-search systems and accelerated search programs from IPS is the absence of their own index. These tools search the indexes of other search engines.
Metacrawler system (Metacrawler) - A search engine that does not have its own index, but is able to send user requests to several search engines simultaneously, then select the most relevant results, combine them and present them to the user in the form of a document with links.
The accelerated search program (Searchbots) is a program installed on the user's computer that can send a request to several search servers and sort the results, removing duplicates.
Note that most search engines are one of the components of multifunctionalInternet Sites - the so-called portals.
Portal - MultifunctionalWeb site Internet offering a variety of services: information search, free email, etc.
WWW catalogs
Consider the features of directory systems. In catalogs, a description of the sources of information is carried out by personnel, that is, by people who make a brief annotation for each resource. Then, as a rule, the described resources are sorted by topics (compilation of a thematic catalog).
The search in the catalog is very convenient and is carried out by sequentially clarifying topics. On the initial (home) page of a system of this kind you will see a list of the largest topics (categories) highlighted by the catalog staff, implemented as hypertext links. For example, Computers, Internet, Education, Art, etc. Having chosen the link to the category of the first level, you will be taken to a page with a list of subcategories, etc. Thus, without delving into the complexity of compiling queries, you can easily find sources on your chosen topic. It should be noted that the resources described in the directories are usually specialized high-quality sites.
Many directories support the ability to quickly search for a specific category or page by keywords using a local search engine.
Note that the database of links (index) of a catalog usually has a limited amount. Some directories use robots to auto update index.
The search result in the catalog is presented in the form of a list; for each resource is given short description (abstract) with a hypertext link to the source.
Addresses of famous catalogs
Among the most popular foreign catalogs, the catalog should be mentioned firstYahoo . Directories with an index size of over 2 million links include directoriesOpen Directory and LookSmart.
- Yahoo!
- Open directory
- Looksmart
Russian popular catalogs:
- Directory @ mail.ru (List.ru)
- Constellation Internet (Aport Catalog)
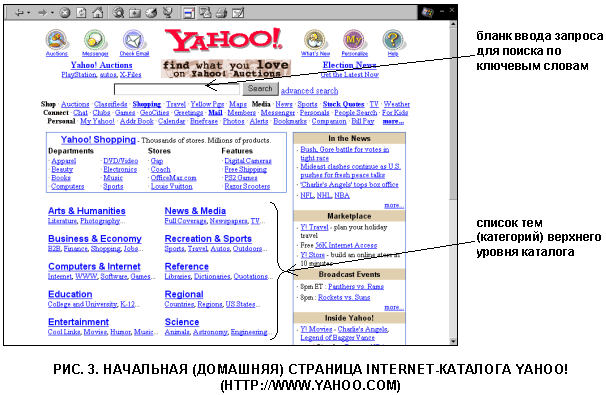
Appearance of Yahoo!
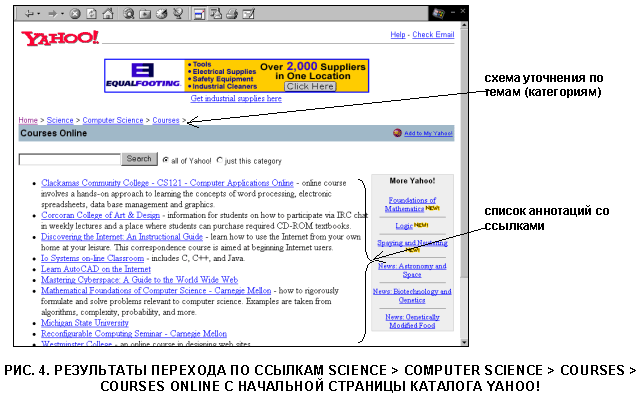
Consider the appearance home page the most popular English-language catalogYahoo (http: // www. Yahoo.com ) (Fig. 3). As usual on start page directory systems you are sure to see a list of major topics (categories). In the catalogYahoo ! It is possible to conduct a quick search using keywords using the form to enter a request. Most in a simple way A search is successive clicks on the category you need. For example, our task- find web websites dedicated toon - line courses in computer science, that is, courses conducting training throughInternet . In this case, you can select the following refinement scheme by topics: from the home page, select the Science link (Science), hereinafter Computer Science(Computer Science), then Courses (Courses) and Courses Online (Online Courses). As a result of the transitions, we get a list of annotations with the names of the corresponding pages (Fig. 4). Then, by clicking on the link that interests you, you can go to the source and study it.
Search engines
A distinctive feature of search engines is the fact that a database with information aboutWeb -pages formedand kept up to date a robot program and, as a result, has a much larger volume compared to catalog type systems. For example, search engineAltavista contains about 550 million links in the index (as of April 6, 2001).
Search in such a system is usually carried out at the request formulated by the user and consisting in the simplest case of a set of keywords. AT recent times there is a tendency sorting the contents of the index into categories, which allows you to narrow the search area and use the search ability to refine the topic.
Simple search. Generalized query generation capabilities.
Typically, search engines support two modes: simple search mode and advanced search mode. Consider the generalized possibilities of forming a query in simple search mode. You can simply enter one or more words with a space; the search for words with all kinds of endings is modeled by the * symbol at the end of the word. Many systems allow you to search for phrases or phrases, for this you need to enclose the desired fragment in quotation marks. Mandatory inclusion or exclusion of certain words is possible, implemented by the + and - signs, respectively, typed close to the keyword.
The main problem of searching for a primitively composed query (in the form of an enumeration of keywords) is that the search engine will find all pages on which these words appear in any part of the document. As a result, the number of pages found will be too large. To improve the quality of the search in the simple search mode, it is permissible to use logical operators and operators to limit the scope of the search, as well as select a specific category of documents from the list provided.
Keyword Relationship Operators
Most search engines use the following operators establishing relationships between keywords:
- AND (AND) & - mandatory presence of all keywords;
- OR (OR) | - the presence of at least one of the keywords;
- NOT! - lack of a keyword;
- NEAR ~ - A specific interval between keywords.
As an example, we give a query that can be formulated in search engine Altavista to find documents in which the word Internet is present with all kinds of endings and the phrase search for work, and the distance between them should not exceed 10 words:
internet * NEAR "job search"
Special operators
Many search engines include special operators in their query language, which allow you to search in certain areas of a document (for example, in its title) or search for a document by a known part of its address. Useful opportunity is a search for documents on the network that link to a page with the address you specified (URL). In this way, you can find on the web pages that have links to your Web site. Some systems allow you to limit your search within a specified domain.
As additional special operators, we can distinguish:
- search operators for documents with a specific graphic file;
- date limit operators;
- refinement operators for the number of words between the specified keywords;
- wordform operators;
- operators for sorting results (by relevance, freshness, old age).
Note. Unfortunately, today there is no standard for the number and syntax of supported operators for various search engines, however, attempts are being made to develop general standard. At this stage of the development of search tools, the user, referring to a particular search system, must certainly first of all get acquainted with its rules for compiling queries. Usually on the home page there is a Help link, on which you can go to the help information.
Compare the look of the search operator in the title in the search engines Altavista, Yandex, Aport:
- Altavista: title: (expression)
- Yandex: $ title (expression)
- Aport: title \u003d (expression)
Advanced (detailed, advanced) search
To write a query specifying the parameters, you need to know the language of the queries for a particular search engine. This is not very simple for the user, so many automatic indexes offer to take advantage of the so-called advanced search mode. As a rule, there is an Advanced Search link on the home page of the search engine that implements the transition to the corresponding query mode.
Advanced or detailed query mode in different systems implemented individually, but most often it is a form in which the above-mentioned operators are implemented by setting the appropriate flags or selecting parameters from the list. Thus, you have the opportunity to make a high-quality query without resorting to a complex language and numerous operators.
Submission of search results
Consider ways to present search results in search engines. Typically, the number of documents found exceeds several dozen, and in some cases can reach hundreds of thousands! Therefore, as a form of issuance, a list of links to documents of 5-10-15 units per page is compiled with the ability to go to the next group at the bottom of the page. The title andURL (address) of the document found, sometimes the system indicates in percentage the degree of relevance of the document.
In the description of the document most often contains the first few sentences or extracts from the text of the document with highlighting keywords. As a rule, the date of updating (verification) of the document, its size in kilobytes is indicated, some systems determine the language of the document and its encoding (for Russian-language documents).
Processing Search Results
What can be done with the results? If the name and description of the document meets your requirements, you can immediately go to its source by reference. It is more convenient to do this in a new window in order to be able to further analyze the results of delivery. Many search engines allow you to search in found documents, and you can refine your request by introducing additional terms. If the intelligence of the system is high, you may be offered the service of searching for similar documents. To do this, you select the document you especially like and indicate it to the system as a model. However, automating the definition of “similarity” is a very non-trivial task, and often this function may not live up to your expectations. Some search engines allow you to re-sort the results. By default, search results are sorted by relevance, but then you can choose a different sorting method (for example, by freshness, so that the latest documents found at your request are shown at the top of the list). You can save the search results as a file on local drive for further study offline.
Addresses of popular search engines
Here are the addresses of some of the most popular search engines abroad and in Russia.
Foreign search engines:
Russian search engines:
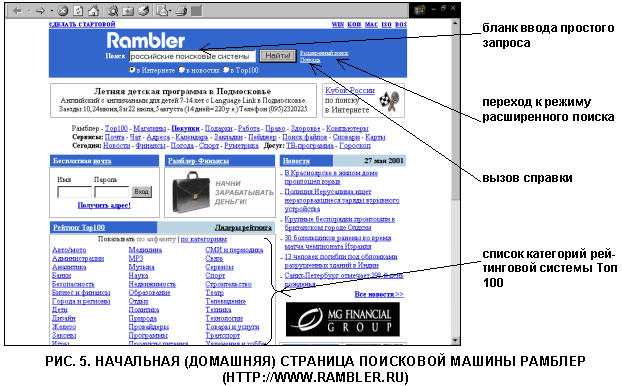
Search engine search example Rambler
Consider a search on demand for Russian prisc systems in the search engine of the Rambler portal (http://www.rambler.ru). On the home page of the search engine (Fig. 5) there is a request entry form for a simple search mode. Pay attention to the Advanced search link, which implements the transition to the advanced search mode and the Help link to call help on the rules for compiling queries.
One of the components of the portal is a system of voluntary rating of sites / pages by attendance of Rambler's Top100. This system allows server owners to determine their popularity based on a comparative assessment with other servers. On pages whose owners wish to participate in the rating system, a special counter is posted that records information about visitors to this page. Based on these data, basic site ratings are compiled by category, and a Rambler visitor can familiarize themselves with them.
Let’s compose the simplest test request, consisting of three words Russian search engines. As a result, Rambler found 75,562 documents on 11,041 sites (Fig. 6). For each page found, we see a title, the beginning of the text posted on the page, the date last update, file size, encoding and URL of the document. To refine the search results, it is possible to set the switch in the one found in the request form, enter clarifying terms in the input field and search among the documents found. In addition, you can turn to the search engine with a request to find similar pages by selecting the Find similar link, located under the description of your chosen document.
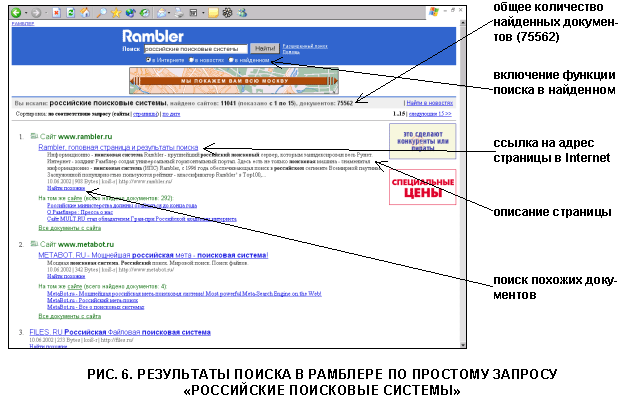
Rambler Advanced Search Mode
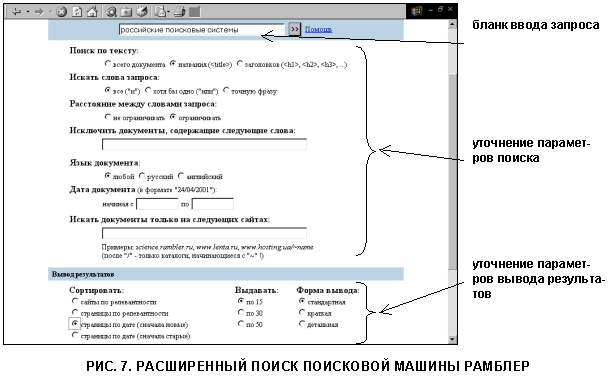
Click the Advanced Search link to go to the corresponding search mode. This mode implies the possibility of compiling a fairly complex query without using operators. You see a request input form and a series of radio buttons and fields allowing you to refine your search. For example, we need to find documents with the words Russian search engines in the page title, with a restriction on the distance between keywords and sorting results by date (Fig. 7).
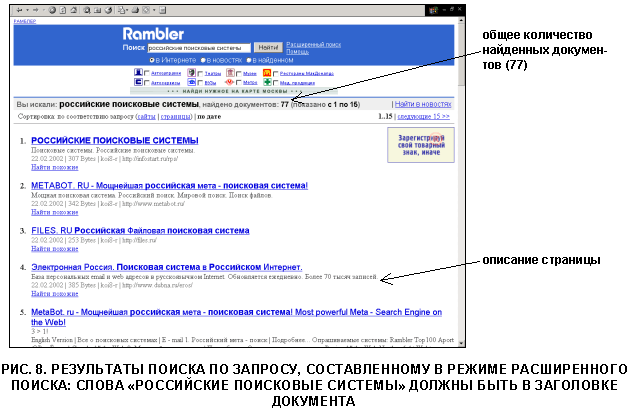
With the established restrictions, Rambler found only 77 documents, which greatly facilitates the further analysis of the results obtained (Fig. 8).
Metasearch systems (search services)
Note that various search engines describe a different number of information sources on the Internet. Therefore, you can not be limited to searching only one of the search engines. We will get acquainted with search tools that do not form their own index, but are able to use the capabilities of other search engines. These are meta-search systems (search services, Metacrawlers) that can send a user’s request to several search engines simultaneously, select a limited number of the most relevant sources of information, which are usually located at the top of the resulting list, then combine the results and present them to the user as a document with links . Advanced search capabilities in such systems mean the selection of specific search engines for the search.
Addresses of famous metasearch systems:
- Metacrawler
- Search.com
- Dogpile
Accelerated Search Programs. Definition
Finally, we consider the last search tool in the above classification - accelerated search programs or search agents (Search Agent or Searchbots).
An accelerated search program is an application installed on a user's computer and capable of:
- send requests to several search engines;
- sort search results by relevance
- delete duplicates;
- check for documents on the network.
The ease of use of this type of program is obvious, because for you there is no need to establish communication with numerous search engines and send requests to each individually. Just run on your own personal computer search agent program, make a request (you can use some refinements, for example, search in the headings of the pages you are looking for) and send it immediately to several popular search engines, previously selected from the built-in list. Some commercial versions of accelerated search programs allow you to create your own list of search engines. You can also pre-set the maximum number of links received from each system.
We give the names of some popular programs accelerated search and the addresses of their developers inInternet:
- Web ferret
- Subject Search Spider (SSSpider)
Thus, using meta-search engines and search agents, you can review the most popular and relevant sources of information indexed in various search engines.
Information Search Performance Options
After a detailed study of the main features of the tools, we turn to the problem of search efficiency. The main parameters of search efficiency are:
- full search as a ratio of the number of documents found to the total number of relevant documents;
- search accuracy - the ratio of the number of relevant documents to the total number of documents received;
- relevance of links to documents - the existence of documents found on the network at the moment;
- search speed.
Factors Affecting Search Performance
So, we found out that inInternet There are various search tools with different functionalities. The quality of the search, therefore, depends primarily on the parameters of a particular search system, for example, on the size of the index, on the search method (refinement of topics or search by query), etc. Further, when working with a specific search system, you need to have an idea of \u200b\u200bthe methods for compiling queries, and know the necessary operators.
Thus, we can distinguish the following factors affecting the effectiveness of the search:
- search engine features and capabilities;
- quality of user request wording.
Comparative Search Engine Capabilities
How can I evaluate the quality of a search tool? Search engines are usually compared by the following parameters:
- The number of pages indexed (index size).
- Index update period. This indicator affects such a parameter as the relevance of the links found. The more often the index is updated, the less often outdated links will appear in the search results.
- Delay before registration. This parameter indicates the time interval before entering the description of the Web page in the index after the request of its author.
- The number of supported operators.
- Sort by categories.
- A standard operator that combines multiple keywords by default. If the standard operator is the AND operator, the search engine will automatically search for documents on which all the entered keywords will be present. Otherwise (the OR operator), documents with all keywords and each individually will be found.
- Search for the exact phrase.
- Search by template (search for words with different endings).
- Accounting for word forms. When auto mode The system will search for word forms in documents with all its changes.
- Upper case sensitivity. If the system does not distinguish between uppercase and lowercase letters, the search results will be less quality.
- Presentation form for the results.
- Additional features: Search for articles in newsgroups, people, organizations, multimedia files, etc.
Internet Information Search Technologies
Now consider how to better prepare the user for the compilation of the request. First of all, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive lexical analysis of the information that you are going to search. Then it is advisable to compile a set of keywords (if necessary, in several languages) in the form of separate terms and phrases specific to your subject area.
Your actions:
- selection of a search tool;
- accurate wording of queries using operators supported by this search tool
- sending test requests;
- analysis of search results (by the number and relevance of links);
- if necessary, adjustment of the request;
- repeated search;
Effective Search Techniques
Based on the foregoing, we can distinguish the following methods of effective search:
- Search for general information in directory search engines. In directories, you will usually find specialized servers in your area.
- Search for highly specialized information in search engines. For a more extensive search, it is clearly not sufficient to use only catalog systems with limited number described resources. In addition, highly specialized information in directories may simply be absent. Therefore, it is necessary to search for such information in search engines with large indexes.
- Use operators or an advanced query form to narrow your search. To conduct a high-quality search, you need to familiarize yourself with the query language of a particular search engine. An effective and simple way to solve the problem of making a high-quality query is to use the advanced search mode.
- Using the search function among found resources. Most search engines support the ability to search within the results. As a rule, for this you need to enable the special checkbox Search in found and enter additional words to search again among the pages found by request.
- Using the search function for similar documents to find relevant pages according to your chosen sample.
- Use of metasearch systems and programs for accelerated information retrieval. To obtain a general overview of documents, it is advisable to use the capabilities of metasearch systems or accelerated search programs. We remind you that these search tools send your request to several search engines at once and from each system they receive some of the most relevant links.
- View the Links section on specialized sites. Authors of many specializedWeb sites accumulate their collections of links on the subject of the site. Often you will find many useful sources in these collections, saving time spent on an independent search using the tools discussed above.
- Search for answers to questions in newsgroups. If you wish, you can contact the specialized news group with a specific question about assistance. You can find the desired group using special search tools, which we will consider later.
- Subscription to specialized mailing lists. After subscribing to a specialized mailing list, you will receive an e-mail new information on the selected topics, as well as ask questions to your colleagues by subscription.
Search for articles in newsgroups
We discuss the problem of finding articles in newsgroups. In this case, search tools can be some WWW search engines that index not only the WWW space, but also articles in newsgroups, and have a special search mode in this resource. Searching for newsgroup posts published over the past six months supports, for example, the Google search server. Search wWW systems very quickly index newsgroups and contain information about articles that actually exist on the network. To search the news archives there are specialized systems, the most famous of which was the Deja system. In February 2001, Google Inc. announced the acquisition of Deja.com’s Usenet Discussion Service. So now search engine users google systems at http: // groups .google .com can also search the connected archive of the Deja system, which contains over 500 million messages indexed since 1995.
File search
Now consider the tools that allow you to search for files. Many WWW search engines provide a multimedia file search service (Altavista, Aport, ...). To do this, you do not need to know the special operators, but just go from the home page using the links Images, MP3 / Audio or Video to a special search mode. Search is carried out by a possible file name or by text in a comment on a link to a multimedia file. You can predict the name of the file, for example, an eagle file may be called eagle .gif. Or guess that the photo of Bill Gates will have the appropriate signature.
Regarding the search software, on the World Wide Web there are search Web servers with collections of shareware; some of them specialize in finding software for the Internet, others suggest finding applications for a specific operating system. These systems will ultimately lead you to a specific FTP server, from which you can download the desired software product. We should mention Archie servers, which also provide file search services on FTP servers, but using Web servers is much more convenient.
Addresses of popular servers for searching software and multimedia files:
- TuCows Collection;
- Shareware Collection CNET Shareware.com;
- Software search system for various platforms CNET Download.com;
- Search system software, computer games and multimedia files Jumbo;
- Search system for multimedia files FAST Multimedia Search;
- Russian file search system FILES.RU.
Search for address information about organizations and people
Consider search tools for finding address information. There are two ways to search: White (White) and Yellow (Yellow) search.
White-search - search for address information by a pre-known name of the addressee (name of the person or name of the organization).
Yellow-search - search for a name or title and address information by additional features (by occupation, by geographical feature).
Typically, Yellow Pages systems actually immediately include White Pages - the addressee found immediately shows his phone number and mailing address. In addition, some Yellow Pages allow you to search simply in the alphabetical list of your subscribers (white-search). On the other hand, White pages also contain yellow-search elements - in addition to setting your own name, they usually allow you to specify the name of the city, state and other data narrowing the search (which is necessary in the case of many namesakes). Perhaps that is why many on-line telephone directories that perform virtually white searches call themselves Yellow pages.
The following are the addresses of some Web systems for finding address information about people and organizations.
People Search:
- Yahoo People Search
- System
- Bigfoot System
Search for organizations:
- yellow pages section on search engines;
- http://www.yellowpages.com is a specialized server for searching in the USA and other countries.
The use of search engines in the educational process
The main areas of application of search engines in the educational process:
- search for educational portals;
- search for addresses of educational institutions on WWW;
- search study guides, encyclopedias, reference books;
- search for on-line training courses;
- search for training software.
test questions :
- Statement of the search problem. Information retrieval systems (IPS): definition and main tasks. The concept of relevance.
- Generalized structure and main components of the IPS for WWW. Concept of index. Features of the indexing procedure.
- Classification of search tools. Techniques for working with thematic catalogs.
- Search engines (automatic indexes). Simple and complex search modes.
- Generalized possibilities of query generation using operators.
- Complex (advanced) search mode. Submission and processing of search results.
- Metasearch systems (search services).
- Definition and main features of accelerated search programs (search agents).
- Search performance parameters: completeness, accuracy, relevance, speed. Factors affecting search performance. Comparative capabilities of search engines.
- Technology for finding information on the Internet. Effective Search Techniques.
- Search for articles in newsgroups. Search for files. Search for address information of organizations and people.
- Give examples of the use of search engines in DO.
Format: web document
12.07.2011 3948 0 0
Search - a process during which, in one sequence or another, the sought one is correlated with each object stored in the array.
In terms of the use of computer technology " information search "- a set of logical and technical operations with the ultimate goal of finding facts, data, documents relevant to the consumer's request.
Relevant Document - This is a document containing the required information.
Search tools
- Search engines (search engines);
- Thematic catalogs (categories);
- Specialized catalogs (online encyclopedias andreference books);
- Metasearch systems.
Thematic catalogs
Thematic catalogs are a systematic collection (selection) of links to other Internet resources. Links are organized in the form of a thematic rubricator, which is a hierarchical structure, moving along which, you can find the information you need.
Specialized Catalogs
Specialized catalogs or directories are created for individual industries and topics, for news, for cities, for addresses email etc.
Metasearch Tools
When using meta-search tools, a query is carried out simultaneously by several search engines. The search result is combined into a general list ordered by degree of relevance.
Search engines
Search engines (the most advanced search tool on the Internet) are automatic systemspolling servers connected to the global network and storing in their database information about the data available on the servers.
Search engines consist of three parts: a robot, an index, and a query processing program.
A robot (Spider, Robot or Bot) is a program that visits web pages and reads (in whole or in part) their contents.
Index - This is a data warehouse in which copies of all pages visited by robots are concentrated.
Request Processing Program - a program that, in accordance with a user’s request, “scans” the index for availability necessary information and returns links to found documents.
Search engines work in four stages:
1.Web space scan
A search engine around the clock using robots scans the available Web space and copies to itself all the pages it encounters.
2. Resource indexing
Pages discovered by search robots are processed by the request processing program and a special database called a pointer is compiled from them. The purpose of indexing is to obtain an index file with which the client’s request is processed almost instantly.
3.Search by request
The search engine receives a request from the user in the form of keywords and does not go to the Network, but to its database. The number of pages found can be very large, so before the results are sent to the client, the search results are ranked.
4.Formation of the resulting page.
The system generates a dynamic web page of framed search results.
Today, a fairly large number of search engines are known.
| http: //site/uploads/posts/2013-11/1385453618_12.jpg |
The largest and first most popular search engine, which processes 42 billion queries per month, indexes more than 25 billion web pages, can find information in 195 languages. Supports document search pDF formats, RTF, PostScript, Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel, Microsoft PowerPoint and others.
The fastest and most reliable way to search for information on the Internet is to search by URL (Universal Resours Locator).
For quick access to resources, it is enough to launch a browser program and type the familiar URL in the address bar.
For example, by typing bolohovomt.ru in the address bar, you can get to the site of the Bolokhov Engineering College
One of the most common types of searches is keyword search. Consider this type of search using the Google search engine as an example (see the video “Information Search” .mp4).
To search by keywords, you need to enter a word or several words to be searched in a special window and click on the Find button. The search engine will find in its database and display documents containing these words.
The speed of obtaining the result depends on the characteristics of the communication channels, the features of the organization of the search engine, and on the "quality" of building the request.
If the user cannot directly influence the operation of search engines, then the quality of the search query is entirely in his competence.
Simple Search Techniques
1.Word Group Search
The words “open” or “education” will give a single search for a large number of diverse links related to completely different topics, and hardly related to “open education”. Therefore, it is recommended that you add one or two keywords related to the topic you are looking for. For example, “open education” or “open education technology”. It is also necessary to narrow the scope of the question. If you need to find information about the legal system of the Guarantor, then the query “legal system of the Guarantor” will produce more suitable documents than just the “legal system”. The number of words in a group is not limited.
2.Word Form Search
In most cases, the search engine by default searches for all word forms of the language. However, you can tell the search engine not to iterate over all word forms of words from the query when searching. Many systems use an exclamation mark for this. For example, the query “! Computer” will find pages with this word without taking into account word forms
3.The role of capital letters
If the user entered as a query a keyword with capital letter, the search engine will not find pages containing this word starting with lowercase letter. therefore capital letters in the request it is recommended to use only in proper names. For example, "the city of Moscow", "Mark Thulius Cicero."
4.Wildcard Meaning
When there is no certainty that the search system correctly processes word forms (that is, when it comes, for example, to proper names or words of foreign origin), search engines allow the use of wildcards. Most often, this is the symbol "*" instead of any number of any characters to the end of the word. For example, if the user wants to find pages containing the words "Republic of Tatarstan", but also suits the Tatar Republic, then you need to submit the request "Republic of Tatar * *".
5.Accounting for reserved words
Reserved words (stop words) are those words that are not taken into account in the search. Usually they include all short words that include less than 4 letters (prepositions, conjunctions, etc.). For example, the query “we are in Italy” will find documents that include the word “Italy” or its word form.
6.Contextual Search Tools
If the keywords are in quotation marks, then the search engine should find documents in which the given phrase is present literally (search for a quote).
Advanced Search Techniques
For faster and more successful searches in search engines, various logical operators are used in conjunction with keywords. Thanks to this, it is possible to construct a query so that it will not find sites on a topic of interest, but specific pages and even individual documents. The rules for compiling complex queries on one search engine may differ from those on another, but in any case, the following basic operators will be used:
1.AND operator
Using this operator, two or more words are combined so that they are all present in the searched document. Often instead of AND they use & or +. Example: at the request of a lawyer. And the program will find documents containing both words.
2.Operator OR (OR)
Provides a search on any of the group’s words. Example: for education OR training, documents containing the word education or training will be found.
3.Logical brackets
They are used when it is necessary to control the order of logical operators. Example: at the request of Lomonosov OR (Mikhail I Vasilievich), documents containing the words Lomonosov or Mikhail I Vasilievich will be found.
4.NOT operator
It is used when it is necessary to exclude any keyword from the search results, for example, at the request of lawyers, NOT lawyers will find information about lawyers who are not lawyers.