Tablet computers with the Android operating system have a lot of advantages over devices with other platforms: the ability to change almost any settings, freely download installation files for applications, the minimum number of brakes, etc. But there is a serious drawback - fast battery consumption. This also applies to the latest innovations, the developers of which boast the increased duration of the tablet. This material describes how to get rid of the main consumer of charge - the network.
Simple instruction
Having set the goal to reduce battery consumption, the user goes into the menu and sees that a third of the battery consumes “network connection”. To be more precise, this is a GSM module. He is responsible for communications and 3G Internet. Most tablet owners prefer to use Wi-Fi, it is rarely possible to meet a user with a SIM card for this gadget. The easiest way to turn off “network connection” is to switch to “flight mode”.
This action is performed as follows:
- Go to any tablet desktop.
- Swipe (move your finger across the sensor) from the top of the screen to the bottom.
- GSM and Wi-Fi modules are active, we need to disable them. To do this, click on the "Flight Mode" function.
- After activation, the icon should light up, in the upper panel the connection and network connection will disappear.
- After this action, the wireless Internet will turn off.
- Click on the Wi-Fi icon. After this connection will become available.
Helpful advice! If you still need this module, but there is no desire to consume the battery in 2 hours, then you should try switching the tablet to 2G mode. Perform this action is only if data transfer is not important to you, that is, you do not use the InternetSIM cards.
Useful software
In older versions of Android, you may not find “flight mode”. In this case, it is recommended to use third-party software. For example, you can take the compact utility Airplane Mode Wi-Fi Tool. The peculiarity of the application is that it activates the “flight mode”, but at the same time leaves the Wi-Fi module active. If you need GSM, you will need to include it in the application. Unfortunately, the Android developers have not yet provided us with an automated option.
Sooner or later, many owners of android gadgets are faced with the issue of optimizing battery power consumption to increase battery life. According to statistics, most smartphones and tablets can work offline for 24 hours (provided that they are used in normal mode).
The reason for this situation is that modern devices are equipped with more and more powerful technical modules (display, gps, LTE), they consume a lot of energy, you can also include gluttonous applications (games), which require more and more hardware resources. In this article, we will tell you how to optimize your Android device in order to save energy and increase battery life.


Now it’s hard to imagine a person without mobile communications. Modern operators offer many services, for which you have to pay extra. Some subscribers, without suspecting it, are connected to some paid service, and it turns out only when they receive a phone bill. Therefore, the question of the operator is relevant enough for most mobile users.
To begin with, it is worth identifying the reasons why this could happen. In almost any tariff plan, in addition to free services, the package of services is also included by default, for which you are billed separately. If the subscriber does not need them, it is worthwhile to review them in advance and refuse.
In addition, the operator connects to the subscriber a “free” service, which after a certain period of time becomes paid. Most mobile users forget to disconnect it on time, and as a result it is unpleasantly surprised when they receive an invoice.
The question of how to disable the operator’s service is also of interest to those who at one time, accidentally or intentionally, connected it themselves. This usually requires sending a specific SMS message to a short number.

So, how to disable the service if you no longer need it? Universal is the way for which you need to contact the operator by calling the number that identifies customer support, and find out what services you have connected and what is their cost. If you don’t use the voiced services, you should ask to disconnect them.
Some operators provide customers with the ability to independently manage services. To do this, you need to call a special number, where using the automatic service you can do everything yourself.
For example, those who are concerned about the question of how to disable the “replace the beep” service on Megafon should go to the operator’s website, where detailed instructions on this subject are given. Or you can contact the help desk, which will also talk about it.

If you are a Beeline subscriber and don’t know how to disable the service, you can use your personal account on the operator’s website. To enter here, you need to dial the command * 110 * 09 # on the phone, after which enter the login and password into the appropriate fields. You can also disable services from this operator using the autoinformer or SMS messages. To do this, you need to call a specific number and follow the prompts of the system.
Those who are interested in how to disable the "beep" service on Megaphone can be advised to visit the operator’s office in person. If there is no time for this, you can call 0500, after which the service will be required to be disabled.
Services provided by short numbers are practically not controlled by operators. However, some content providers offer their subscribers ways to protect themselves from such fraudulent schemes, which are often quite expensive. In order to avoid connecting unnecessary services with short numbers, you need to contact your operator, who will tell you what to do next.
In 2019, mobile communications are an integral part of every person’s life. Without it, people simply can’t work or just live.
But when using it, you can encounter certain problems. One of them is the established communication restriction.
For many people, it is very important to deal with this problem as quickly and efficiently as possible, if a communication restriction is established, this means that you cannot make calls.
Such cases can occur even when there are funds on the mobile account. Therefore, it is important to know what needs to be done to solve the problem and why it arises.
 Communication restrictions can be imposed by almost every operator of MTS, Yota, Beeline, Tele2. After that, it is impossible to make outgoing calls from mobile phones, with the exception of emergency calls.
Communication restrictions can be imposed by almost every operator of MTS, Yota, Beeline, Tele2. After that, it is impossible to make outgoing calls from mobile phones, with the exception of emergency calls.
The ban is also set for sending outgoing SMS. In some cases, the restriction also blocks incoming calls to the telephone of the subscriber on whom the restriction is set.
The main reason for limiting communication is the negative balance of the subscriber’s personal account, when there is not enough money even to connect.
In this case, the mobile operator acts in accordance with the conditions specified in the contract between the user and the company, that is, blocks any outgoing calls and SMS.
This agreement is signed upon purchase of a SIM card. Few people read it carefully, but in most cases the text mentions a restriction in this case.
In addition, the reason for limiting communication may be:
- The failure of the SIM-card due to the expiration of its validity.
- In some cases, the ban can be set on the numbers of subscribers who are in roaming.
- Mobile device malfunction.
 In addition to the above reasons, some companies use the restriction service to reduce their expenses on mobile communications and do not want employees to call out of work during office hours.
In addition to the above reasons, some companies use the restriction service to reduce their expenses on mobile communications and do not want employees to call out of work during office hours.
This service works even when there is money in the account and includes the following options options:
- The restriction is carried out only within the selected office.
- White and black lists are connected.
- It is forbidden to order services from short numbers.
Subscribers choose the most suitable option themselves. The restriction of communication on the "black" list means that it is forbidden to make calls to certain numbers or entire directions.
For example, it was established that employees cannot call abroad or to other cities.
As for the "white" lists, then employees have the opportunity to call any specific areas or numbers that are allowed.
In some cases, only those numbers that are indicated by the client are entered into the “white list” by the operator. Both list options can be determined for an employee of the company individually or in groups.
 This restriction does not apply continuously, but only a certain period of time. For such a relationship, you can create a special personal schedule.
This restriction does not apply continuously, but only a certain period of time. For such a relationship, you can create a special personal schedule.
When restricting communication at the office level, the Megafon operator, at the request of the subscriber, limits the number of outgoing employees depending on their location.
So, if the subscriber leaves the office, then they cease to act. The operator can offer the customer several similar zones at the same time. In addition, it is proposed to limit the number of calls by time.
The ban on short numbers means the impossibility of all outgoing requests for various paid and free short numbers. This service is very convenient when company employees order various content.
Limiter Disabling Methods
If your number has an outgoing call restriction, you can remove the ban in several ways, depending on the reasons for blocking.
For example, if there is no money in the account, you just need to replenish it. But if there are no problems with the financial side, then all details should be clarified by the operator.
Each of them has its own hotline, where you need to call with a question. If you can’t get through, but there is coverage - in the region the connection of this provider is active, but not for everyone. Then you have to look for a branch of the operator service.
To communicate with a mobile operator, you can use the telephone. The rating of mobile operators looks like this:

It is important to consider that the restriction of communication is possible not only with mobile operators, but also with a fixed telephone.
Various methods of blocking are available to Rostelecom users. You can turn off all incoming calls, Create black and white lists for incoming and outgoing calls, or completely block telephone communications.
 The service "Password Connection" makes it possible to block outgoing calls in full or in certain directions.
The service "Password Connection" makes it possible to block outgoing calls in full or in certain directions.
To remove the communication restriction, you need to enter a password. And you can also contact the company's hotline - 8-800-100-0800.
If a person can not get through technical support, you need to visit the company branch. Practice shows that more often than not, only personal contact will help to find out the exact reason for the blocking and how to fix the problem.
Any mobile operator has a list of services that are basic and are provided to subscribers free of charge. Call restriction is included in a similar list of services from Megafon.
Activation of this option can be carried out by the subscriber independently, by entering the appropriate commands or by a support service specialist. At the same time, a fee may be charged if the service is connected through Megafon employees.
Communication restriction can be set to the following types:

To connect to any of the above prohibitions, the following conditions are necessary:
- The “call forwarding” service is activated on the subscriber’s number.
- For each type of communication, you can set only one restriction at a time.
But at the same time, the urgent question is how to disable the communication restriction Megaphone. Disabling a service is as easy as connecting it.
You just need to enter such a combination on the phone - # service code * password to manage the service #.
A similar service can be used to disable bans on call types.
 The password, which is used by default to enable or disable the ban, the user can change. This makes it possible to protect the phone from trying to control the service by other people.
The password, which is used by default to enable or disable the ban, the user can change. This makes it possible to protect the phone from trying to control the service by other people.
To enter a new password you need to use this combination - ** 03 * 330 * current password * new password #. Its validity is not limited.
But if you enter combinations to change the password, making a mistake three times, it will be impossible to use the service to establish a ban on communication. And to remove the lock you will have to visit the office of the company with a passport.
Thus, if the communication restriction is imposed by the operator, then it becomes impossible to make calls from mobile operators, except for emergency ones. In addition, sending SMS will also fail.
This problem most often occurs with a negative account balance. But the limitation of communication can be established with a positive balance.
This is often found in corporate numbers, outgoing calls to some directions may be prohibited.
An operator can apply a communication restriction if a monthly limit is set for the number of minutes that have been talked about and money spent.
Some operators offer blocking for incoming calls to phones that are in roaming. If the user cannot independently disable the service, then contact the mobile operator.
Tablet computers with the Android operating system have a lot of advantages over devices with other platforms: the ability to change almost any settings, freely download installation files for applications, the minimum number of brakes, etc. But there is a serious drawback - fast battery consumption. This also applies to the latest innovations, the developers of which boast the increased duration of the tablet. This material describes how to get rid of the main consumer of charge - the network.
Simple instruction
Having set the goal to reduce battery consumption, the user goes into the menu and sees that a third of the battery consumes “network connection”. To be more precise, this is a GSM module. He is responsible for communications and 3G Internet. Most tablet owners prefer to use Wi-Fi, it is rarely possible to meet a user with a SIM card for this gadget. The easiest way to turn off “network connection” is to switch to “flight mode”.
This action is performed as follows:
- Go to any tablet desktop.
- Swipe (move your finger across the sensor) from the top of the screen to the bottom.
- GSM and Wi-Fi modules are active, we need to disable them. To do this, click on the "Flight Mode" function.
- After activation, the icon should light up, in the upper panel the connection and network connection will disappear.
- After this action, the wireless Internet will turn off.
- Click on the Wi-Fi icon. After this connection will become available.
Helpful advice! If you still need this module, but there is no desire to consume the battery in 2 hours, then you should try switching the tablet to 2G mode. Perform this action is only if data transfer is not important to you, that is, you do not use the InternetSIM cards.
Useful software
In older versions of Android, you may not find “flight mode”. In this case, it is recommended to use third-party software. For example, you can take the compact utility Airplane Mode Wi-Fi Tool. The peculiarity of the application is that it activates the “flight mode”, but at the same time leaves the Wi-Fi module active. If you need GSM, you will need to include it in the application. Unfortunately, the Android developers have not yet provided us with an automated option.
The behavior of a phone in roaming sometimes seems not quite clear and predictable, for example, in terms of choosing a mobile network.
Let's try to understand from a technical point of view in some issues:
How does it work .
First of all, the following applies not only to phones, but to all GSM-UMTS-LTE mobile terminals - tablets, modems, routers, and so on. To understand the process, it is important that each base station has a transceiver that constantly transmits radio signals containing “system information”. System information is grouped into system messages (in the GSM network) or system blocks (in UMTS and LTE networks) that carry the information necessary for mobile stations in order to navigate in the environment and make decisions to perform certain actions when gaining access to services and work in a mobile network.
In particular, system information contains the following parameters:
Country and network code (MCC and MNC - Mobile Country Code and Mobile Network Code), which determine the ownership of a particular base station transceiver in a particular operator’s network.
The output power levels that mobile phones can use at the beginning of a communication session.
Location Area Code (LAC) - identifier of the zone (group of base stations) within the network, which are allocated for registering the location of mobile devices and distributing signal traffic.
Cell ID - identifier of a specific radio transmitter serving the sector (“cell”).
Routing Area ID - service area identifier in the packet information network.
Tracking Area ID (TAC) is a unique analogue of LAC and RAC for LTE network.
Turn on the phone and ...
So, having flown to another country, we turn on the phone to get access to mobile services.
Obviously, to access the telephone services, it is necessary to establish a communication channel with one of the base stations. To do this, the phone must search for base station signals for all supported radio access technologies and in all supported frequency ranges. It is clear that this task is quite lengthy, which may not cause the most pleasant emotions for the user, especially for models with the greatest capabilities for supported radio access technologies and frequency ranges. Therefore, standards allow manufacturers to optimize this process.
Network Code (MCC + MNC).
LAC, CellID.
In order to provide access to mobile communication services, the operator needs to make sure that these services can be provided to the subscriber - he has a subscription to these services. The key to accessing services is a (U) SIM card. Therefore, immediately after turning on the power of the mobile terminal and establishing the operating voltages for its nodes, the procedure for initializing the (U) SIM card begins, during which the phone searches for files and tries to read from them the information necessary for deciding on the choice of network and subsequent registration in the selected network.
6F7B - EF fplmn (Forbidden PLMN) - a list of "forbidden" networks
This is a small file for recording MCC + MNC codes for four networks organized in a “queue” (FIFO). When making a (U) SIM card, this file has no entries (FF value is written in all fields). When the phone receives a refusal with the reason code # 11 PLMN not allowed when trying to register on a “foreign” network, the MCC + MNC code of this network is written to this file. Then, when choosing a network for automatic registration, the terminal no longer attempts to automatically register in networks whose codes are currently in this file.
6F30 - EF plmnsel (PLMN selector)
This is one of the oldest files that affect the choice of network in roaming. It contains network codes (at least 8 MCC + MNC codes) in the priority order of their choice in roaming. This list can be created both by the user through the telephone interface and by the operator, moreover, not only in the manufacture of (U) SIM-cards, but also subsequently, downloading information “by air”.
6F60, 6F61, 6F62
6F60 - EF plmnwact (User controlled HPLMN Selector with Access Technology)
6F61 - EF oplmnwact (Operator controlled PLMN Selector with Access Technology)
6F62 - EF hplmnwact (HPLMN Selector with Access Technology)
These three files have the same structure. They can contain a list of codes (MCC + MNC) for at least 8 networks, but with additional information about the radio access technologies supported by each of the networks (GSM, GSM-Compact, UTRAN, E-UTRAN, cdma2000 HRPD, cdma20001xRTT).
This is a short file containing a number that determines the length of the interval after which the phone should try to search for a network with a high priority (home, etc.).
So what does the phone choose?
So, there comes a time when the switched-on phone after initializing the (U) SIM card, finished reading the files necessary for making a decision on choosing a network, and as a result of the search, it found signals from the base stations of mobile networks and collected the system information transmitted by them. How is a decision made about automatic network selection?
Home network (HPLMN - Home Public Mobile Network), or its equivalent, with the highest priority.
Each of the networks and its supported radio access technologies in order of priority from the 6F61 file is EF oplmnwact (Operator controlled PLMN Selector with Access Technology). If the SIM card installed in the phone does not contain files containing information about the radio access technologies supported in the listed networks, then the phone should use the list of networks from the 6F30 file - EF plmnsel (PLMN selector), and all supported radio access technologies.
Which mode of network selection, automatic or manual, is better to use in international roaming?
First of all, it should be remembered that the phone will start working in the network selection mode (automatic or manual) in which it was at the time the power was turned off. It seems like a trifle, but if you immediately automatically plug the phone into your pocket immediately after turning it on, and at home, for some reason, select the network manually (after all, other networks still wouldn’t let you in!), Then when roaming the phone will not automatically select the network, and the subscriber can remain unconnected for an indefinite time!
In addition, you need to understand that when using the phone while roaming in the manual network selection mode and subsequently there are chances to remain without communication if you are in places where the coverage of the selected operator disappears - the phone will wait for the owner’s decision to choose a network from others available in this place. Therefore, it is useful to either select one of the local networks in manual mode and wait for successful registration, or put the phone in the automatic network selection mode and make sure that it is registered in one of the local networks.
Many operators are part of groups of companies providing mobile services in several countries. Naturally, in such cases, operators are interested in subscribers receiving roaming services in partner networks. And the point here is often not so much in the desire to receive additional income from higher prices, but in the desire to leave income within the group of companies. Therefore, many operators are implementing roaming management systems (Steering of Roaming). Many, probably, turning on the phone upon arrival in the country, found a welcome text message from the operator, which contained practical recommendations on the use of voicemail, etc.
Since it has already been noted that in international roaming, in order not to be left without a connection, it is better to use automatic network selection, but you do not want to rely on the operator completely, the question arises of how a subscriber can influence the choice of network in automatic mode.
Do not be embarrassed if only one radio access technology is indicated in the list for a particular network, although it is known that the operator uses several technologies - GSM, UMTS, LTE. After the phone detects the desired network and gets access to it, it will be able to learn about the network support and other technologies from the system information transmitted by the BS, then to select the one that is optimal from the point of view of radio conditions.
It is also worth noting that manual tuning of the list of priorities for choosing networks is best done already in the country, after the operator could correct the list of preferences as you see fit. Or, at a minimum, verify that a prioritization of priorities has not changed. This is especially true when both the operator and the user use the same 6F30 file, EF plmnsel (PLMN selector), to manage priorities.
Everyone can decide this issue based on their interests, needs and preferences. Recently, Russian operators have significantly reduced prices for roaming services, or began to offer special options or packages that optimize communication costs in roaming. Of course, if you intend to communicate a lot with the owners of local numbers, then using a local operator’s SIM can be really more profitable. However, it may turn out to be inaccessible for incoming calls from the homeland - after all, not everyone knows the phone number assigned to the local SIM card, and forcing people to make international calls is not always convenient. In general, everyone solves this issue individually, based on specific conditions.
Emergency Firewall Roaming (AMR)
This concept appeared several years ago, and even now it is not very well known to a wide audience.
But in cases of natural disasters (for example, the recent flood in the Far East), serious accidents in the networks of operators (for example, when a meteorite falls in the Chelyabinsk region), a very large number of citizens are left without communication. They cannot call for help, for example, a doctor, tell relatives about their whereabouts or find out about their condition. In cases of such serious disasters, it is customary to help the victims "all over the world." It is for such cases, at the initiative of the regulator (the Ministry of Communications) or at the request of the injured operator, the inclusion of Emergency Network Roaming in the territory covered by an emergency may be allowed. In this case, subscribers get the opportunity to use the services of any of the operators whose network is available at a particular time. Unlike emergency calls (to number 112), with the AMP turned on, you can call not only the Ministry of Emergencies, but also contact relatives and friends by their usual phone numbers - mobile or wire, if they work, of course.
In such difficult situations, it is important for subscribers not to be confused and to know what needs to be done to use the networks of other operators in an emergency, because without special actions on the part of the user, their phones will not be registered in the networks of other operators in order to become available for incoming calls.
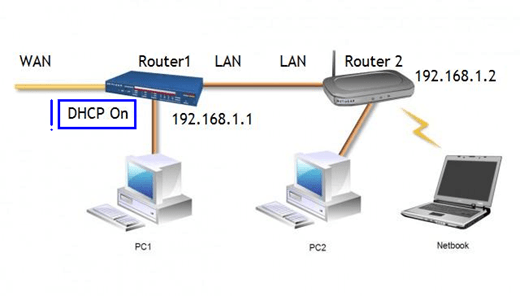
Nowadays, each user is faced with the question of setting up a network in the Windows 7 operating system. If you are a home user, someday you will be faced with the task of setting up an Internet connection, synchronizing with the XBOX game console, and if you have several pieces of computer equipment at home, then in any case, you will have to configure a wired or wireless network, and one computer will have to distribute the Internet to all the others. In the event that you are working as a system administrator in a small office, you will need to configure a network with static or dynamic addresses. Unfortunately, many users usually try to configure a local network without the skills to work with network technologies, and therefore carry out the configuration at random, because of which they have many problems during subsequent work. This series of articles focuses on a variety of local network configuration methods, terminology, and Internet connectivity.
Often, setting up a local network in Windows Vista, Windows 7, and Windows Server 2008/2008 R2 operating systems starts with such an area for configuring network properties as a component. Using this network configuration tool, you can select a network location, view a network map, configure network discovery, file and printer sharing, and configure and view the status of your current network connections. In this article, you will learn about managing this component.
Opening the Network and Sharing Center component
In order to use the functionality of the network configuration tool, you must first open it. To open a window, do one of the following:
The following illustration shows the window Network and Sharing Center:
Fig. 1. “Network and Sharing Center”
Network Location Concept
Before you start working with this component, you should understand such a thing as network location. This parameter is set for computers at the first connection to the network and during the connection, the firewall and security settings are automatically configured for the type of network to which you are connecting. Unlike the Windows Vista operating system, where the most strict firewall profile for network hosting is used for all network connections, the Windows 7 operating system supports several active profiles, which makes it possible to use several network adapters connected to different networks most securely. There are four types of network locations:
home network. This network location is designed to use the computer at home or in networks where users know each other very well. Such computers can create and join home groups. For home networks, network discovery is automatically turned on.
Enterprise network. This network location is used in a small office network (SOHO). Network discovery is also enabled for this network location, but you cannot create or join a computer to a homegroup.
Community network. This network location is for computer use in public places such as cafes or airports. This is the most stringent placement, which by default disables the ability to join the homegroup and network discovery.
Domain network. If the computer is joined to an Active Directory domain, the type of network location will be automatically assigned to the existing network "Domain". The domain type of network location is similar to the production network, except that in the domain the configuration of the Windows firewall, network discovery, and network card is determined by Group Policy.
The network locations available for selection by the user can be seen in the following illustration:
Fig. 2. Choosing a network location
Network map
A network map is a graphical representation of the location of computers and devices, which allows you to see all the devices on your local network, as well as a diagram of their connection to each other. In the window Network and Sharing Center only the local part of the network card is displayed, the layout of which depends on the available network connections. The computer on which the map is created is displayed in the upper left corner. Other subnet computers are displayed on the left. Infrastructure devices such as switches, hubs, and gateways to other networks are displayed on the right. You can see an example of a network map in the following illustration:
Fig. 3. Example network map
Two components are responsible for the operation of a network card in operating systems:
Link Layer Topology Discover Mapper - LLTD Mapper - a component that requests devices on the network to include them in the card;
LLTD Response Device (Link Layer Topology Discover Responder - LLTD Responder) is the component that is responsible for the LLTD Mapper component requests.
By default, a network map can only be viewed for locations. "Home network" or "Enterprise Network". When trying to view a network card for locations "Domain Network" or "Public network" You will see the following message:
Fig. 4. Attempting to view a network map for the location of a domain network
In order to enable network mapping in a domain network, you need to perform the following actions on the domain controller:
Fig. 5. Change Group Policy to enable network mapping
Fig. 6. Network map for the location of the domain network
- Open snap "Group Policy Management";
- Select a group policy object (for example, Default Domain Policy, the scope is the entire domain), which will be distributed to the computer located in the domain network, right-click on it and select the command from the context menu "Change";
- In a snap Group Policy Management Editor expand node Computer Configuration / Policies / Administrative Templates / Network / Link Topology Discovery (Link Layer) and select a policy “Enables the I / O Display Driver (LLTDIO)”;
- In the properties of the policy setting, select the switch on the option Enable and check the box "Allow operation for domain";
- Repeat for the policy setting. “Enable Responder Driver (RSPNDR)”;
- Update the policy settings on the client machine using the command gpupdate / force / boot;
- Update the network map. The result is shown in the following illustration:
Network connections
After installing the driver for each network adapter, the Windows operating system attempts to automatically configure network connections on the local computer. All available network connections are displayed in a window. "Network connections". A network connection is a set of data necessary to connect a computer to the Internet, a local network, or any other computer.
Open window "Network connections" You can use any of the following methods:
Window "Network connections" displayed in the following illustration:
Fig. 7. Window "Network Connections"
When choosing any network connection, you can perform the following actions with it:
In the dialog box that opens Windows Network Diagnostics follow the steps in the wizard to troubleshoot.
The check boxes next to the components indicate that these components are tied to the connection. The network connection properties dialog box is displayed below:

Fig. 11. Network Connection Properties Dialog Box

Conclusion
This article briefly describes the components of the configuration tool for the network properties of Windows operating systems - Network and Sharing Center. The concepts of network location, network cards, with which the local part of the network card is displayed, the layout of which depends on the available network connections, are considered. You also familiarized yourself with the network connection window, which allows you to configure network connections on the local computer. In the next article, you will learn how to configure clients, services, and network connection protocols using the graphical user interface.
The behavior of the phone in roaming sometimes seems not quite clear and predictable, for example, in terms of network selection.
Let's try to understand from a technical point of view in some issues:
- What is the phone guided by when choosing a network in roaming?
- How do blacklists of networks work?
- Is it possible to influence the choice of network in roaming?
- What is roaming management?
- When and why you can be in roaming without even leaving Russia?
First of all, the following applies not only to phones, but to all GSM-UMTS-LTE mobile terminals - tablets, modems, routers, and so on. To understand the process, it is important that each base station has a transceiver that constantly transmits radio signals containing “system information”. System information is grouped into system messages (in the GSM network) or system blocks (in UMTS and LTE networks) that carry the information necessary for mobile stations in order to navigate in the environment and make decisions to perform certain actions when gaining access to services and work in a mobile network.
In particular, system information contains the following parameters:
- Country and network code (MCC and MNC - Mobile Country Code and Mobile Network Code), which determine the ownership of a particular base station transceiver in a particular operator’s network.
- The levels of the received signal at which access to a particular BS is allowed.
- The output power levels that mobile phones can use at the beginning of a communication session.
- Location Area Code (LAC) - identifier of the zone (group of base stations) within the network, which are allocated for registering the location of mobile devices and distributing signal traffic.
- Cell ID - identifier of a specific radio transmitter serving the sector (“cell”).
- In relation to packet information transfer, identifiers are transmitted:
- Routing Area ID - service area identifier in the packet information network.
- Tracking Area ID (TAC) is a unique analogue of LAC and RAC for LTE network.
Turn on the phone and ...
So, having flown to another country, we turn on the phone to get access to mobile services.After you turn on, you need to complete a number of tasks to access your mobile phone services. To speed up access to services, some tasks are performed in parallel, but there are several key procedures that must be performed.
And which networks work in the district?
Obviously, to access the telephone services, it is necessary to establish a communication channel with one of the base stations. To do this, the phone must search for base station signals for all supported radio access technologies and in all supported frequency ranges. It is clear that this task is quite lengthy, which may not cause the most pleasant emotions for the user, especially for models with the greatest capabilities for supported radio access technologies and frequency ranges. Therefore, standards allow manufacturers to optimize this process.As a result of the search, the telephone for each supported radio access technology should make a list of detected BS signals, from the signals of which it selects the information necessary for deciding on further actions when choosing a network:
- Network Code (MCC + MNC).
- LAC, CellID.
- Received signal strength in order to select the communication channel with the best conditions
- Information about restrictions on access to the cell imposed by the operator, etc.
Golden Key to network services
In order to provide access to mobile communication services, the operator needs to make sure that these services can be provided to the subscriber - he has a subscription to these services. The key to accessing services is a (U) SIM card. Therefore, immediately after turning on the power of the mobile terminal and establishing the operating voltages for its nodes, the procedure for initializing the (U) SIM card begins, during which the phone searches for files and tries to read from them the information necessary for deciding on the choice of network and subsequent registration in the selected network.6F7B - EF fplmn (Forbidden PLMN) - a list of "forbidden" networks
This is a small file for recording MCC + MNC codes for four networks organized in a “queue” (FIFO). When making a (U) SIM card, this file has no entries (FF value is written in all fields). When the phone receives a refusal with the reason code # 11 PLMN not allowed when trying to register on a “foreign” network, the MCC + MNC code of this network is written to this file. Then, when choosing a network for automatic registration, the terminal no longer attempts to automatically register in networks whose codes are currently in this file.If the user manually selects the network whose code is contained in this file, the phone will try to register on this network, despite the fact that the network code is in the “forbidden” list.
If the registration is successful, the phone will remove the code for this network from the list of “forbidden” (fill the space with the value FF). If manual registration is denied, then everything will remain unchanged.
6F30 - EF plmnsel (PLMN selector)
This is one of the oldest files that affect the choice of network in roaming. It contains network codes (at least 8 MCC + MNC codes) in the priority order of their choice in roaming. This list can be created both by the user through the telephone interface and by the operator, moreover, not only in the manufacture of (U) SIM-cards, but also subsequently, downloading information “by air”.In the course of further development of standards and technologies, several more files appeared in which the influence of the user and operator were already separated, but information about the radio access technologies available in each network was added to the files.
6F60, 6F61, 6F62
6F60 - EF plmnwact (User controlled HPLMN Selector with Access Technology)6F61 - EF oplmnwact (Operator controlled PLMN Selector with Access Technology)
6F62 - EF hplmnwact (HPLMN Selector with Access Technology)
These three files have the same structure. They can contain a list of codes (MCC + MNC) for at least 8 networks, but with additional information about the radio access technologies supported by each of the networks (GSM, GSM-Compact, UTRAN, E-UTRAN, cdma2000 HRPD, cdma20001xRTT).
The 6F60 file can be populated by the user, usually via the telephone interface, if the telephone manufacturer provides such an interface.
The contents of file 6F61 are controlled by the operator that issued the (U) SIM card, both when ordering a batch of (U) SIM cards, and subsequently when it can change the list by transferring the new contents of the file “over the air”.
6F31 - EF hpplmn (Higher Priority PLMN Search Period)
This is a short file containing a number that determines the length of the interval after which the phone should try to search for a network with a high priority (home, etc.).So what does the phone choose?
So, there comes a time when the switched-on phone after initializing the (U) SIM card, finished reading the files necessary for making a decision on choosing a network, and as a result of the search, it found signals from the base stations of mobile networks and collected the system information transmitted by them. How is the decision to automatically select a network made?3GPP-ETSI TS 23.122 automatically instructs the phone to select the network (PLMN) with the highest priority from those networks that are available and not prohibited. The phone checks the “forbidden” networks in the 6F7B file - EF fplmn (Forbidden PLMN).
- Home network (HPLMN - Home Public Mobile Network), or its equivalent, with the highest priority.
- Each of the networks and its supported radio access technologies in order of priority from the 6F60 file is EF plmnwact (User controlled HPLMN Selector with Access Technology).
- Each of the networks and its supported radio access technologies in order of priority from the 6F61 file is EF oplmnwact (Operator controlled PLMN Selector with Access Technology). If the SIM card installed in the phone does not contain files containing information about the radio access technologies supported in the listed networks, then the phone should use the list of networks from the 6F30 file - EF plmnsel (PLMN selector), and all supported radio access technologies.
- A randomly selected network and radio access technology from those whose signals are received with high quality.
- Other networks and radio access technologies in decreasing order of signal quality.
Which mode of network selection, automatic or manual, is better to use in international roaming?
First of all, it should be remembered that the phone will start working in the network selection mode (automatic or manual) in which it was at the time the power was turned off. It seems like a trifle, but if you immediately automatically plug the phone into your pocket immediately after turning it on, and at home, for some reason, select the network manually (after all, other networks still wouldn’t let you in!), Then when roaming the phone will not automatically select the network, and the subscriber can remain unconnected for an indefinite time!In addition, you need to understand that when using the phone while roaming in the manual network selection mode and subsequently there are chances to remain without communication, if you find yourself in places where the coverage of the selected operator disappears - the phone will wait for the owner’s decision to choose a network from others available in this place. Therefore, it is useful to either select one of the local networks in manual mode and wait for successful registration, or put the phone in the automatic network selection mode and make sure that it is registered in one of the local networks.
How can an operator influence the automatic selection of roaming networks by the telephone
The recommendations of the operator who issued the (U) SIM card are written to a file 6F61 - EF oplmnwact (Operator controlled PLMN Selector with Access Technology) and / or 6F30 - EF plmnsel (PLMN selector).Many operators are part of groups of companies providing mobile services in several countries. Naturally, in such cases, operators are interested in subscribers receiving roaming services in partner networks. And the point here is often not so much in the desire to receive additional income from higher prices, but in the desire to leave income within the group of companies. Therefore, many operators are implementing roaming management systems (Steering of Roaming). Many, probably, turning on the phone upon arrival in the country, found a welcome text message from the operator, which contained practical recommendations on the use of voicemail, etc.
It appears because at the moment of registration in roaming the “home” operator receives a request from the “business” network for information that is necessary to provide services to the subscriber, which means that the “home” operator finds out which country the subscriber is in. Having this information, it is possible to send a special format “SMS-ku” to the subscriber’s phone, which will not be displayed to the user, but will be “downloaded” by the phone to the (U) SIM card, where it will update the contents of the desired file. Using this mechanism, the operator tells the phone priorities when automatically selecting networks in roaming.
How a user can influence the automatic selection of roaming networks by his phone
Since it has already been noted that in international roaming, in order not to be left without a connection, it is better to use automatic network selection, but you do not want to rely on the operator completely, the question arises of how a subscriber can influence the choice of network in automatic mode.First of all, it is useful to familiarize yourself in advance with the list of operators providing services in the visited country (or countries) and the tariffs for their services. Based on this information, you can create your own list of priorities for choosing networks in the host country. In the phone’s menu in the settings section, you need to find the network settings and a list of priority networks. Since this interface is not regulated by standards, the name and location of this menu item may be different in different models, and in some models this item may be completely absent! If the item is found, then the list of networks that may be present there should be edited in accordance with the selected preferences.
Why in the list of networks to select preferred only 2G or 3G networks are indicated
Do not be embarrassed if only one radio access technology is indicated in the list for a particular network, although it is known that the operator uses several technologies - GSM, UMTS, LTE. After the phone detects the desired network and gets access to it, it will be able to learn about the network support and other technologies from the system information transmitted by the BS, then to select the one that is optimal from the point of view of radio conditions.It is also worth noting that manual tuning of the list of priorities for choosing networks is best done already in the country, after the operator could correct the list of preferences as you see fit. Or, at a minimum, verify that a prioritization of priorities has not changed. This is especially true when both the operator and the user use the same 6F30 file, EF plmnsel (PLMN selector), to manage priorities.
Should I buy a SIM-card of a local operator on vacation?
Everyone can decide this issue based on their interests, needs and preferences. Recently, Russian operators have significantly reduced prices for roaming services, or began to offer special options or packages that optimize communication costs in roaming. Of course, if you intend to communicate a lot with the owners of local numbers, then using a local operator’s SIM can be really more profitable. However, it may turn out to be inaccessible for incoming calls from the homeland - after all, not everyone knows the phone number assigned to the local SIM card, and forcing people to make international calls is not always convenient. In general, everyone solves this issue individually, based on specific conditions.Emergency Firewall Roaming (AMR)
This concept appeared several years ago, and even now it is not very well known to a wide audience.The fact is that the Russian regulatory framework does not allow the provision of roaming services to subscribers of another operator that has licenses in the same territory (republic, territory, region). That is why files with lists of “forbidden” networks (6F7B) in (U) SIM-cards of Russian users usually contain codes of all “alien” networks working where the subscribers live. After all, operators put BS at different points, and you can almost always find a place (elevator, basement, the middle of a large reinforced concrete building, etc.), where the phone will lose its home network for a while, and at the same time it will find another operator’s network. For the first time in this situation, the phone will try to access the services in the network of this operator. Due to the prohibition of roaming, the phone usually receives a denial of services with reason code # 11 PLMN not allowed, and the code of this network is entered in the list of “prohibited” in the (U) SIM card to prevent repeated attempts of automatic registration in a “foreign” network.
But in cases of natural disasters (for example, a recent flood on), serious accidents in the networks of operators (for example, when a meteorite fell in the Chelyabinsk region), a very large number of citizens are left without communication. They cannot call for help, for example, a doctor, tell relatives about their whereabouts or find out about their condition. In cases of such serious disasters, it is customary to help the victims "all over the world." It is for such cases, at the initiative of the regulator (the Ministry of Communications) or at the request of the injured operator, the inclusion of Emergency Network Roaming in the territory covered by an emergency may be allowed. In this case, subscribers get the opportunity to use the services of any of the operators whose network is available at a particular time. Unlike emergency calls (to number 112), with the AMP turned on, you can call not only the Ministry of Emergencies, but also contact relatives and friends by their usual phone numbers - mobile or wire, if they work, of course.
In such difficult situations, it is important for subscribers not to be confused and to know what needs to be done to use the networks of other operators in an emergency, because without special actions on the part of the user, their phones will not be registered in the networks of other operators in order to become available for incoming calls.
If the phone has lost contact with the network of the “home” operator due to a failure of the network equipment, the phone will automatically find the signal of one of the base stations of the other operator that has remained operational, and will be in the Limited Service state, waiting for the owner’s command to make an emergency call ( 112). In this case, you can simply try to call the desired number. If AMR is enabled, then the “alien” network should provide a connection.
If the phone continues to receive signals from the base stations of the “home” network, but the network does not allow you to make calls, you need to manually search for available networks and select one of the “foreign” networks detected by the phone. If the “alien” network provides access, then AMR is on, and such a subscriber will be able to make outgoing calls and receive incoming calls. If the network denies access, then you should try to repeat the manual selection of other networks detected by the phone until registration in one of the networks occurs. If none of the “foreign” networks has completed the registration, this means that the AMR is not turned on in this place, and in the “foreign” networks you can use only the “Emergency Call” service.