\u003e Work with information retrieval systems ( general information, order of work, saving and editing the information found)
Information retrieval system - a set of information retrieval rules for translating from a natural language to information retrieval and reverse translation, as well as a matching criterion designed to carry out information retrieval. In number component parts a specific information retrieval system (IPS), in addition to the information retrieval language, translation rules and compliance criteria, also includes means for its technical implementation, an array of texts (documents) in which information search, and people directly involved in this search.
Information search is the process of finding in a certain set of texts (documents) all those that are dedicated to the topic (subject) indicated in the request or contain facts and information that the consumer needs. IP is carried out by means of an information retrieval system and is carried out manually or using means of mechanization or automation. An indispensable participant in the IP is a person. Depending on the nature of the information contained in the issued information - search engine (IPS) texts, IP can be documentary, including bibliographic, and factual. IP must be distinguished from the logical processing of information, without which it is impossible to directly give a person answers to the questions asked. When IPs are found - and can be found - such and only such facts or information that were entered into the IPS. Before entering a text (document) into the IPS, its main semantic content (topic or subject) is determined, which is then translated and recorded in one of the information retrieval languages. This entry is called a text search image. The same thing happens when the recorded facts, information are introduced into the IPS in a certain way. The received request is also translated into the information retrieval language, forming a search order. Since search images of texts and search instructions are written in the same language, expressions in which allow only one interpretation, it is possible to compare them formally, without delving into the meaning. For this, certain rules (matching criteria) are set, which establish to what extent the formal match of the search image with the search prescription should be considered as responding to an information request and to be issued.
The technical efficiency of IP is characterized by two relative indicators - the accuracy coefficient (the ratio of the number of texts responding to the information request to the total number of texts in this issue) and the completeness coefficient (the ratio of the number of texts responding to the information request, to the total number of such texts contained in this IPS). The required values \u200b\u200bof these indicators depend on the specifics of information needs. For example, when searching for patent descriptions for the purpose of examining a patent application for novelty, 100% completeness of issuance is required; when searching for an ordinary researcher or engineer, accuracy of about 80% is considered very good, completeness is about 50%.
Figure 1 - The search process
IP can be of two types - selective (or targeted) dissemination of information and retrospective search. In the selective dissemination of information, IP is carried out at the constant request of a certain number of consumers (subscribers), is carried out periodically (usually once a week or two weeks) and is performed only in an array of texts received by the IPS for this period of time.
An effective feedback is established between the IPS and consumers (subscribers) (the subscriber informs to what extent this text corresponds to the request and whether he needs a copy of the full text, the degree to which this text corresponds to his information needs), which allows us to clarify the needs of subscribers and respond to change these needs and optimize system performance.
In a retrospective search, the IPS searches for texts containing the required information in the entire accumulated array of texts for one-time requests.
The architecture of modern WWW information retrieval systems.
Consider a typical scheme of such a system. In various publications devoted to specific systems, schemes are given that differ from each other only in the application of specific software solutions, but not the principle of organizing the various components of the system. Therefore, we consider this scheme in the presented example:
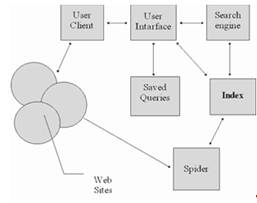
Figure 2 - Structure of the IPS for the Internet
On this diagram are indicated:
client is a program for viewing a specific information resource. Currently, the most popular multiprotocol programs like Netscape Navigator. This program provides viewing of World Wide Web, Gopher, Wais documents, FTP archives, mailing lists and Usenet newsgroups. In turn all of these informational resources are the subject of a search for information retrieval system.
user interface - the user interface is not just a viewer. In the case of the information retrieval system, this phrase also means the way the user communicates with the search engine of the system, i.e. with a system for generating queries and viewing search results. Viewing search results and network information resources are completely different things, which we will dwell on a little later.
search engine - a search engine is used to translate a user’s request, which is prepared in the information retrieval language (IPN), into a formal query of the system, search for links to the Web’s information resources and return the results of this search to the user.
index database - an index is the main data array of an information retrieval system. It serves to search for the address of an information resource. The architecture of the index is designed so that the search occurs as quickly as possible and at the same time, it would be possible to assess the value of each of the found information resources of the network.
queries - the user's queries are stored in his personal database. Debugging each request takes a lot of time, and therefore it is extremely important to store requests for which the system gives good answers.
index robot - an indexing robot is used to scan the Internet and keep the index database up to date. This program is the main source of information on the status of network information resources.
www sites is the entire Internet. And more precisely, these are the information resources that are provided for viewing by viewing programs.
Search engines usually consist of three components:
1. an agent (spider or crawler) that moves around the Web and collects information;
2. a database that contains all the information collected by spiders;
3. A search engine that people use as an interface to interact with the database.
Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation.
Adygea State University
Course.
On the topic "Automated information retrieval systems."
Performed
group student
Checked
Introduction ……………………………………………………………………… 3
1. Information Systems ……………………………………… .4
The concept information systems………………………………………4
The structure of information systems ……………………………………… 4
Classification of information systems …………………………… ..6
2. Information retrieval systems ………………………… 7
Historical prerequisites for the development of search engines …………… 7
The concept of search engines …………………………………………… ..... 9
Features of search engines …………………………………………… 10
· network structure ………………………………………………… .... 11
· the structure of the search engines ……………………… ..... 13
3. Characteristics of search engines …………………………… 17
4. problems and opportunities of search engines ………………… 24
Conclusion ……………………………………………………………………… .25
References …………………………………………………………… ... 26
INTRODUCTION
The current stage of development of civilization is characterized by the transition of the most developed part of humanity from industrial society to informational. One of the most striking phenomena of this process is the emergence and development of a global information computer network.
In this course work are considered theoretical basis information retrieval, classification and varieties of information retrieval systems. Presented material on currently used information - search directory full-text and hypertext search engines.
With the advent of the Internet, the search problem became more relevant. Internet - Worldwide computer network, which is a single information environment and allows you to receive information at any time. But on the other hand, a lot of useful information is stored on the Internet, but it takes a lot of time to find it. This problem gave rise to search engines. In this course work will be considered search engines on the Internet.
INFORMATION SYSTEMS
The concept of information systems
Information system is understood as an organized set of software, hardware and other auxiliary tools, technological processes and functionally defined groups of workers providing the collection, presentation and accumulation of information resources in a specific subject area, the search and delivery of information necessary to meet the information needs of users. Information systems are the main means, tools for solving problems information support various activities and the fastest growing industry in the information technology industry.
Information system structure
The information system can be divided into three subsystems:
1. The organizational and technological subsystem for collecting information provides an information system and includes a set of sources of information, the organizational and technological chain of selecting information for accumulation in the system. Without the proper organized subsystem of information collection, the effective organization of the functioning of the entire information system as a whole is impossible.
2. The subsystem for the provision and processing of information is the core of the information system and is a reflection of the presentation by the developers and subscribers of the system of the structure and picture of the subject area, information about which should be reflected in the information system. The subsystem for the presentation and processing of information is one of the most complex components in the development of an information system.
3. Regulatory - functional subsystem the issuance of information determines the users, or otherwise the subscribers of the system, implements the target aspect of the appointment and execution of tasks of the information system.
The basis of all search engines is databases - a collection of data organized according to the limit rules, providing general principles for the description, storage and manipulation of data, regardless of application programs.
The following elements of the functioning of information systems can be distinguished:
* Information gathering - a process of collecting and displaying information organized in a special order:
receiving the information
information relevance assessment
the procedure for selecting and recording information.
* Acquisition - the process of adding information from many parts into a single whole and bringing it to the user.
* Search and delivery of information - the establishment of a special technological order to meet the information needs of subscribers of the information system in management activities and technological processes.
* Maintaining the integrity and preservation of information - the review, revision and screening of information that is no longer relevant is an integral function information units. The safety of information is carried out using regulatory and instructive documents.
Classification of Information Systems
By the nature of the provision logical organization The stored information is divided into factual, documentary and geographic information.
Factographic data are accumulated and stored as multiple instances of one or more types. structural elements. Each of these instances of structural elements, or some combination of them, reflects information on an event or event. The structure of each type of information object consists of a finite set of details reflecting the main aspects and characteristics of information for objects of this subject area.
In documentary, a single element of information is a document that is not divided into smaller elements, and information that is entered as a rule is not structured, or structured in a limited way. For the input document, some formalized positions can be established - the date of manufacture, artist, subject. Some types of documentary information systems ensure the establishment of a logical relationship of input documents - subordination of semantic content.
In geographic information data are organized in the form of separate information objects tied to a common electronic topographic basis. Geographic information systems are used for information support in those subject areas, the structure of information objects and processes in which there is a geographical component.
Another criterion for the classification of search engines are functions or tasks to be solved.
Inquiries are the most common type of functions of information systems, and is to provide subscribers of the system with the possibility of obtaining installation data for certain classes of objects.
Search engines are the most common class of information systems. In general, a view can be considered as a kind of information space defined in terms of an information - logical description of a subject area.
Settlement consists in processing the information in the system according to certain calculation algorithms for various purposes.
The technological functions of information systems are to automate the entire technological cycle or its individual components, production or organizational structure.
INFORMATION SEARCH SYSTEMS
Historical background to the development of search engines.
Let us turn to the history of the emergence of the Internet, which was created in connection with the need to share information resources distributed between various computer systems. Most of the early applications, including FTP and email, were developed exclusively for exchanging data between Internet host computers.
Other applications, such as Telnet, were created so that the user can access not only information, but also the working resources of the remote system. With the development of the Internet (an increase in users and host computers), previous methods of exchanging data have ceased to meet the increased needs of users. There was a need to develop new ways to search for network resources and access to them, which would allow the use of information regardless of its format and location.
To meet these needs, the Archie search engine was first created, solving problem localization of resources on the FTP server, and the Gopher system, which simplifies access to various network resources. Then network information wWW systems and WAIS, which offer completely new methods of obtaining information. The principles of operation of these systems make it easy to navigate a huge amount of information resources without the need to provide mechanisms for the operation of the Internet itself. This approach allows us to speak not only about resources interconnected computer systems, but about the special information spaces of the network.
System Archie is a complex software toolsworking with special databases. These databases contain constantly updated information about files that can be accessed through the FTP service. Using the services of the Archie system, you can search for a file by its name template. In this case, the user will receive a list of files with an exact indication of where they are stored on the network, as well as information about the type, creation time and file size. Access to the Archie information retrieval system can be carried out in various ways, from requests by e-mail and using the Telnet service to the use of graphical Archie clients.
System Gopher was developed to simplify the process of localizing Internet FTP resources and to more conveniently present information about the contents of files stored on FTP servers. The Gopher system provides an opportunity in a convenient form (in the form of a menu) to present users about the available files and their contents. Gopher server menus may contain links to other Gopher and FTP servers. Thus, the user gets the opportunity to "travel" on the Internet, not paying attention to the location of the resources of interest to him, and gain access to these resources.
System Veronica used to search for information in the Gopher space by the headings of menu items. After entering the keyword, the Veronica system finds out whether it appears in the menu on any Gopher server, and as a search result displays a list of headers of menu items containing the keyword. Since Veronica is not a standalone system search program, but is closely connected with the Gopher system, it has the same drawback as the Gopher system: it is far from always possible to say in the heading what a particular information resource is. The advantages of the system is that there is no need to find out where the information is located, just select the desired entry from the list.
The concept of information search engines.
Automated search system is a system consisting of personnel and a set of automation tools for its activities, which implements information technology for performing established functions.
The experience and practice of creating systems in various fields of activity allows us to give a broader and universal definition that more fully reflects all aspects of their essence.
In the future, an information system is understood as an organized set of software, hardware and other auxiliary tools, technological processes and functionally defined groups of workers providing for the collection, presentation and accumulation of information resources in a specific subject area, the search and delivery of information necessary to satisfy the information needs of the established contingent of users - subscribers of the system.
Features of search engines.
In the work, the search process is presented in four stages: wording (occurs before the start of the search); action (beginning search); overview of the results (the result that the user sees after the search); and improvement (after reviewing the results and before returning to the search with a different formulation of the same need). A more convenient nonlinear information retrieval scheme consists of the following steps:
1. Fixing information needs in a natural language;
2. Choice search services networks and formalization of recording information needs in specific information retrieval languages \u200b\u200b(IPN);
3. Fulfillment of created requests;
4. Pre-processing of received lists of links to documents;
5. Appeal to the selected addresses for the documents sought;
6. Preview the contents of the documents found;
7. Saving relevant documents for further study;
8. Extracting links from relevant documents to expand the request;
9. Studying the entire array of saved documents;
10. If the information need is not completely satisfied, then return to the first stage.
The search process has an extremely deep didactic aspect - it has been established that the use of interactive information systems leads to the formation of ordinary users of a style of information retrieval activity, which is usually characteristic of the most prominent scientists.
In most cases, the information need arises after studying any new informationreceived by the user. Often there is a situation when the user already has some array of documents on the desired topic. It is proposed to use these documents for automated compilation. search query via specialized system document management (COD) (the system is under development).
The system should index all user documents. During the indexing process, all words contained in documents are divided into the following semantic classes: stop words; the most frequent words of everyday (spoken) language; general cultural terminology; general scientific terminology; domain terms known to the system; unknown words. The partition is based on the appropriate dictionaries, which should be an integral part system. Unknown words will be attributed primarily to many special words in the subject area. Newly formed terms and words containing errors will also get there.
Based on the index, a vector representation of documents is constructed, after which the COURT hierarchically clusters many documents, resulting in a breakdown of this set into thematic groups. During the dialogue with the user, one or more of the most relevant document clusters is selected and the characteristics of the search process are set.
The search query should be based on the centroid vector of the selected cluster. The optimal request size is from 8-12 to 25-30 terms. The last preparatory operation carried out by the COURT is to record a request for an IPN.
Network structure.
As you know, the easiest way to expand the information search on the Internet is used in metasearch systems and consists in increasing the number of primary IPS used. This mechanism should be implemented in any developed system. The task of distributing search engine resources across various IPS of the global network should be solved adaptively, based on the percentage of links recognized as relevant during previous search sessions.
The second block of the automated search system sends the created request and sorts and selects the received links, after which it contacts the selected addresses and receives from the network a certain set of documents that also contain hyperlinks.
The study shows that the widespread opinion that the content of the global network is chaotic and that there is no structure of connections is a fallacy. The presence of the so-called “communities” is revealed - well-connected groups of sites containing materials of similar topics. The “central” pages are highlighted - containing large lists of links and the pages to which many links lead - the "authoritative" pages. Thus, the aim of the 8th stage of the search is to identify such groups and identify among their members the most “authoritative” ones. As shown in, the algorithm for solving this problem is quite simple.
Processing search results.
After receiving as a result of a search on the network a certain set of documents, among them it is necessary to highlight the most relevant. The presence of “communities” does not facilitate this task. The following several classes of the most common situations can be distinguished.
1. The lack of the required information in the network segment being studied. A similar situation is described in. In this case, we should move on to another segment, i.e., usually explore resources created in other languages.
2. The found “communities” do not contain information on the required topic, but mainly on others that are close to the desired one.
3. Too many informational resources detected.
In the last two cases, it is necessary to automatically search through all the documents found and determine the degree of proximity to the original request. More than 20 metric proximity measures suitable for comparing documents in a vector representation are considered in the paper. The optimal solution to the ranking problem is achieved by applying a system based on an agent-based approach.
In many cases of searching in a new area, when the general level of the user is not high enough, it is desirable to filter the information displayed by the style of the text so that the initial familiarization with the material occurs using popular and popular science texts.
To reduce the volume of the materials under consideration, it is also necessary to filter the search results by type of sources. So it is obvious that documents located on scientific sites, on commercial, or on media servers will vary significantly in nature.
The structure of the search engines.
The search pointer works in three stages, of which the first two are preparatory and invisible to the user. The search index first collects information from World Wide Web . For this use special programs, similar browsers. They are able to copy the specified Web page to the search engine server, browse it, find all the hyperlinks that have resources on it, find the hyperlinks in them again, etc. Such programs are called worms, spiders, caterpillars, crawlers, spiders and other similar names. "Each search index uses for this purpose its own unique program, which it often develops itself. Many modern search engines were born from experimental projects related to the development and implementation of automatic programs that monitor the network. Theoretically, with a successful login spider it is able to comb through the entire Web space in one dive, but it takes a lot of time, and it still needs to periodically return to previously visited resources in order to monitor the changes taking place there and identify “dead” links, that is, those that have lost relevance.
After copying the searched Web resources to the search engine server, the second stage of work begins - indexing. During indexing, special databases are created with the help of which it is possible to establish where and when a particular word was found on the Internet. Consider an indexed database a kind of dictionary. It is necessary so that the search engine can very quickly respond to user requests. Modern systems are able to give answers in fractions of a second, but if you do not prepare the indexes in advance, then the processing of one request will continue for hours.
At the third stage, the client’s request is processed and the search results are returned to him in the form of a list of hyperlinks. Suppose a client wants to know where on the Internet there are Web pages that mention the famous Dutch mechanic, optician and mathematician Christian Huygens. He enters the word Huygens into the dial field. keywords and presses the button. Find Based on its index databases, the search engine in a split second searches for suitable Web resources and forms a page of search results, on which recommendations are presented in the form of hyperlinks. Further, the client can use these links to go to the resources of interest to him.
All this looks quite simple, but in fact there are problems. Main problem modern internet linked to the abundance of web pages. It is enough to enter such a simple word in the search field as, for example, football, and the Russian search engine will give out several thousand links, grouping them in 10-20 pieces on the displayed page.
A few thousand - this is not so much, because a foreign search engine in a similar situation would give hundreds of thousands of links. Try to find the right one among them! However, for the average consumer it’s all the same, they will give him a thousand search results or a million. As a rule, customers look at no more than 50 links that are the first, and what’s going on next, few people worry. However, customers are very, very concerned about the quality the very first links. Customers do not like when in the top ten there are links that have lost relevance, they are annoyed when there are links to neighboring files of the same server in a row. The worst option is when there are several links in a row leading to the same resource, but located on different servers.
The client has the right to expect that the most useful links will be the first. This is where the problem arises. A person easily distinguishes a useful resource from a useless one, but how to explain this to the program ?! Therefore, the best search engines show miracles of artificial intelligence in an attempt to sort the links found by the quality of their resources. And they must do it quickly - the client does not like to wait.
Strictly speaking, all search engines draw source information from the same Web space, so their source databases can be relatively similar. And only at the third stage, when issuing search results, each search engine begins to show its best (or worst) individual features. The operation of sorting the results called ranking. The system assigns a rating to each found Web page, which should reflect the quality of the material. But quality is a subjective concept, and a program needs objective criteria that can be expressed with numbers suitable for comparison.
High rankings are given to Web pages for which the keyword used in the request is included in the title. The rating level increases if this word appears several times on a Web page, but not too often. Favorably affects entry ranking the right word in the first 5-6 paragraphs of the text - they are considered the most important when indexing. For this reason, experienced Webmasters avoid giving tables at the top of their pages. For a search engine, each cell in the table looks like a paragraph, and therefore the informative body text is moved far back (although this is not noticeable on the screen) and ceases to play a decisive role for the search engine.
It is very good if the keywords used in the query are included in the alternative text accompanying the illustrations. For a search engine, this is a sure sign that this page exactly matches the query. Another sign of the quality of a web page is the fact that there are links to it from some other web page. The more of them, the better. So this web page is popular and has a high citation index. The most advanced search engines monitor the citation level of their registered Web pages and take it into account when ranking.
Web page creators are always interested in having more people see them, so they specially prepare the pages so that search engines give them a high rating. The good, competent work of a Web master can significantly increase the attendance of a Web page, but there are also such "masters" who try to trick search engines and give their Web pages a significance that they actually do not have. They repeatedly repeat some words or groups of words on a Web page, and in order to prevent them from catching the eye of the reader, they either make them exceptionally small print, or apply a text color matching the background color. For such "tricks," the search engine can punish a Web page by assigning it a negative penalty.
In recent years, the practice of commercial rating has developed. Technically, they are equipped with the most modern facilities, corresponding to the level of 2000, and the total size of the Runet (the Russian Internet sector) today is approximately the same as the western sector in 1994-1995. Therefore, today in Russia there are no special problems with the search for information and in the near future they are not expected. And in the western sector, search problems are very big, and different search engines try to overcome them in different ways. About how this happens, we will tell.
Of the search indexes in Russia today there are three “whales” (there are smaller systems, but we will not dwell on them). These are “Rambler” (www.rambler. Ru), “Yandex” (www.yandex. Ru) and “Aport2000” (www.aport. Ru).
Historically, the most popular search engine is Rambler. She started working earlier than others and for a long time was the leader in terms of search index and quality of search services. Alas, today these achievements are in the past. Despite the fact that the size of the search index "Rambler" is approximately equal to 12 million Web pages, it has not really been updated for a long time and gives outdated results. Today, Rambler is a popular portal, the best classification and rating system in Russia (what we will describe below), plus an advertising platform. Traditionally, this system holds the first place in Russia in terms of attendance and has good advertising revenue. But funds, as we show below, are not invested in the development of search tools.
The largest index lies at the heart of the Yandex system — about 27 million Web pages, but it's not just about the size. This is not just a pointer to resources, but a pointer to the most relevant resources. In terms of relevance, Yandex today is the undisputed leader (Fig. 7.3).
The Aport system wins in the third stage: at the time of presenting information to the client. She does not strive to create the largest index by automatic means, but instead widely uses information from the @Rus catalog, which is manually processed. Therefore, the system does not produce as many results as its closest competitors, but these results, as a rule, are accurate and clearly presented.
Characteristics of search engines.
Starting a search for something on the Internet and having a minimum of information, as well as trying to save time, to get the most general information access to the following database is possible.
Database: The subject leads to internetworking resources built by librarians.
Search: Searches may be limited to the name of the resource, a description of it, or with the specified subject headings.
Results: Results are shown in alphabetical order by resource names.
Address: http://sunsite.berkeley.edu/InternetInd ex /
Yahoo! - The most famous search engine. Its sites are divided into categories and keywords. It contains useful information on his home page. Can connect to other search engines
Databases: it manages a search service for Internet resources, news, maps, advertising information, sports information, business, phone numbers, personal WWW pages, and email addresses (a separate database).
Search: All Yahoo pages offer not only a simple search box, but also options for this search, as well as a Usenet or Email address search. Search may be limited to indicating a certain period of time. Boolean operators (and, or) and sequential search are also supported. Note: if the search in Yahoo! if it doesn’t lead to a positive result, the search process automatically switches to Alta Vista, which continues the search, and in case of positive results, automatically returns the information found to Yahoo !.
If Yahoo! cannot establish a connection fast enough with Alta Vista, then in this case Yahoo! will provide a link page with a set of search tools. After one of these links is selected, the keywords are transferred to the search engine of your choice.
A tool to facilitate the search is the presence of “tip search” (TS) - search using a “hint”: Yahoo! It is a subordinate directory, which means that the system does not have as many pages as search engines, however, setting the most common keywords will allow you to find the necessary topic on the page high level (the first page that appears before the user when visiting the site) for the organization or company.
Results: Links are displayed in accordance with the order of the words given by the search sequence along with their descriptive text and subordinate hierarchy.
Address: http://www.yahoo.com/
Upgrade Frequency: Daily

Alta Vista supports keyword searches and uses artificial intelligence techniques to determine the language of a particular page. Users can customize the search options and choose the type of search - complex or simplified, and also use different ways providing information. Unlike machines that index only keywords, it indexes the entire text, which allows full search. However, because of this, the user can simply drown in information.
Databases: Worldwide WWW pages and Usenet News (news).
Search: Offers a simple (simple (S)) search or (much more advanced (MMS)), i.e. more advanced way. S - the search should mainly be used for common issues, MMS - Search uses specific search syntax. To facilitate the procedure there is a hint (Simple Search Help). MMS - search using boolean, i.e. using key unions, using (and, or, not - (and, or, not)) and simple adjacency (near - (near)) allows you to use several words, alternating words, phrase as key for search.
TS - search: By entering a key of the type: "Your Phrase" as the first search direction, which will limit the number of WWW documents found with headings of the "Your Phrase" type.
Results: Offers three choices of results (but two give the same result):
1) "Standard" - the results obtained by the machine in the form of a list of paragraphs, summarized by it, with the presence of a URL address, file size and last date modernization. Results are returned as ten points on the screen,
2) "Compact" ("Compact") place each item on the same line with the last date of modernization of the file cabinet,
3) “Detailed”, which is the same as “Standard”.
Address: http://altavista.digital.com
Frequency of modernization: Constantly WWW-robot.
Excite uses search technology IntelligentConceptExtraction, which allows you to make queries on the sample. This is the most popular search engine in America. For each page found, it evaluates the degree of compliance with the request.
Databases: WWW-pages around the world, news, maps, "yellow pages", free software, basic quotes, television programs, weather, E-mail addresses, airline flights.
Search: Offers only S - search, which supports some MMS search options.
TS - search: use plus (+) to determine that all documents have the given word, or use minus (-) to clarify that none of the documents has this word. Perhaps also support byoolean operators.
You can use the "AND", "OR" and "AND NOT" (AND, OR, and. AND NOT) operators and parentheses to group. For example: (digital or virtual or electronic) AND library.
(digital or virtual or electronic) AND library.
Results: Results are shown with the title of the document, relevance rank as a percentage, URL, summary software document, and the option to restore "More Like This", which allows you to use the document as your question.
Address: http://www.excite.com/
Upgrade Frequency: Continuously - WWW-robot.
![]()
It uses multiprocessing parallel processing of 10. million pages daily to search the Internet. The useful side of Hot Bot is the restriction on the type of pages by means of button selection.
Database: Worldwide WWW pages.
Search: Offers S - search and Expert (E) - search, supports boolean operators (AND and OR), phrase search, and choice of "person" or "URL". E-search also supports setting date, location (country, etc.)
TS - search: uses double quotation marks (for example, "phrase words").
Results: Results are shown with the title of the document, relevance rank in percentage, URL, document size.
Address: http://www.hotbot.com/
Frequency of modernization: Constantly WWW-robot ("Slurp").

Infoseek is the most popular search engine in the computer industry. In May 1996, it was recognized as the most reliable machine providing information. The attractiveness of the machine is that after filtering out the information, you can check the information found again.
Databases: Worldwide WWW pages, news, stores quotes, maps, yellow pages ("yellow pages"), e-mail addresses, etc.
Search: it offers only a simple S - search, but search keywords can be limited to specific fields (such as within the document headers), search using capabilities either with the exception of a specific word (this word is preceded by a minus "-") or with the inclusion of the desired word ( this word is preceded by "+"). For additional information regarding the choice of search used. Infoseek Help
Results: Includes the title of the document, file size, URL, a brief summary extracted from the document, and the percentage of relevance.
Address: http://www.infoseek.com/
Frequency Upgrade: Continuously WWW-robot.
Additional information: in case of a large amount of information, see http://info.infoseek.com/.

Lycos is one of the first search engines. The machine is convenient for working with search and for simultaneously viewing sites. When outputting information shows short review, and found addresses.
Databases: Worldwide WWW pages, sounds, pictures, "top 5% sites"
Search: offers S - search and client (Custom (C)) search. C-search supports the boolean operators AND and OR (AND and OR), as well as some other assignments.
Results: results are listed in an ordered list; Information includes document address (URL), name, file size, and excerpts from the file.
Address: http://www.lycos.com/
Frequency of modernization: constantly WWW-robot.
PROBLEMS AND OPPORTUNITIES OF SEARCH SYSTEMS.
The work of many search engines is considered quite successful. However, all modern search engines suffer from some serious flaws:
1. Keyword search gives too many links and many of them are useless.
2. A huge number of search engines with different user interfaces raises the problem of cognitive overload.
3. Database indexing methods are generally not related to information content.
5. machines are not yet perfect enough to understand natural language
at recent times intellectual assistance needs are growing rapidly. This led to the emergence of intelligent agents.
Typically, intelligent agents are the main part of a search engine using artificial intelligence to search. The user teaches the agent, and then he goes online to search.
Intelligent agents execute instructions on behalf of the user, have some independence. After the search, they notify the user of the results. Agents learn from their activities.
Intelligence - Learning Based feedback by examples of errors and by means of interaction with other agents.
Ease of use - you can train an agent using natural language.
Individual approach - adaptation to user preferences.
Integration - lifelong learning the application of already existing knowledge to new situations.
Autonomy - a sense of the environment, and analysis of conclusions.
CONCLUSION
The search engines I reviewed are far from perfect. It is believed that an ideal search engine should meet the following requirements:
1. ease of use
2. A clearly organized and updated index.
3. quick database search and quick response.
4. reliability and accuracy of search results.
The scale of information resources and their number is constantly expanding. It becomes clear that the database is not perfect. Intelligent agents - a new direction underlying the new generation of search engines that can filter information and get more accurate results. The Internet continues to evolve with relentless intensity, essentially erasing the restriction on the distribution and receipt of information in the world. However, it is not very easy to find the necessary document in this information ocean. It should also be borne in mind that new networks appear along with long-running servers in the network.
The information systems in which the storage and processing of information is carried out using computer technology are called automated, various types of activities and the most rapidly developing industry in the information technology industry.
Bibliography.
1. E.A. Jakubaitis "Computer Science-Electronics-Networks". M., "Finance and Statistics", 1989.
2.. A. V. Gavrilov " Local networks Computer ", Moscow," Mir "Publishing House, 1990.
3. N.A. Gaydamakin "Automated information systems, databases and data banks", M .: "Helios", 2002.
Excerpt from work
INTRODUCTION
The modern stage in the development of civilization is characterized by the transition of the most developed part of humanity from an industrial society to an information society. One of the most striking phenomena of this process is the emergence and development of a global information computer network.
The problem of searching and collecting information is one of the most important problems of information retrieval systems. Of course, one cannot compare in this respect, say, the Middle Ages, when the search for information was a problem because this information was scarce, and efforts were required only to find at least something on a more or less significant issue of interest. So, at first there was an opportunity to go to the library and, spending time there on choosing the right book from the catalog, find the necessary information. But catalogs do not completely solve the problems of information retrieval even within the framework of one library, since relatively little information is included in the catalog entry: title, author, place of publication. The problem of finding information acquired a new character in the 20th century, with the beginning of the development of the century of information technology. Now it consists not in the fact that there is little information and therefore it is difficult to find, but in the fact that it is now becoming more and more on the contrary, and from this finding the answer to the question of interest can also be quite a difficult task. The problem of finding information is much more complicated when using virtual sources. It uses the technology of online directories, as a result of which the user has the ability to search directories of several libraries at once, which, in fact, complicates the task even more, but, on the other hand, increases the chances of solving it.
1. INFORMATION AND SEARCH SYSTEMS
An information system is understood as an organized set of software, hardware and other auxiliary tools, technological processes and functionally defined groups of workers providing for the collection, presentation and accumulation of information resources in a specific subject area, the search and delivery of information necessary to meet the information needs of users. Information systems are the main means, tools for solving the problems of information support of various types of activities and the most rapidly developing industry in the information technology industry.
An information retrieval system is a system that provides the search and selection of necessary data in a special database with descriptions of information sources (index) based on the information retrieval language and relevant search rules.
Currently, two fundamentally different information retrieval systems (IPS) can be used to search for information in an ever-expanding information space: information retrieval systems for the global network and reference legal systems (SPS). Both systems develop and operate independently of each other. The joint use of these systems allows you to quickly and efficiently solve the problem of finding information when solving a wide range of engineering problems.
The main task of any IPS is to search for information relevant to the information needs of the user. It is very important as a result of the search that you don’t lose anything, that is, find all the documents related to the request and not find anything superfluous. Therefore, a qualitative characteristic of the search procedure is introduced - relevance.
1.1 Information retrieval language and information retrieval dictionary
When they talk about the information retrieval system, it is implied that it uses an index. The index allows you to search for documents relating to a "subject". To compile a subject index, the content of the document is analyzed and the “subject” or “subjects” defined in the document are determined. Then the names of these items are translated into the information retrieval language (IPN). Thus, we get the search image of the document (AML). Indexing (creating search images) all information resources, we get what is called an index (index database) - the main dataset of IPS.
Since the search process consists in comparing the user's request with the available data, the received request should also be translated into IPN. After comparing the query translated into IPJ and the search images of documents, the user receives a list of links to documents that correspond, in the opinion of the system, to his request.
The search does not take place according to the text of the documents, but according to their search images compiled on the IPN. Therefore, IPA is the main part of the information retrieval system, on which the quality of the system primarily depends. The information retrieval language includes:
1. Glossary of indexed terms - many indexing terms.
2. Code Dictionary - many code terms.
3. Vocabulary of inputs - many input terms.
4. Aids indexing language - means used in conjunction with indexing terms to expand or narrow certain concepts.
5. Rules for using the indexing language.
Typical circuit IPS using subject indexing is shown in Fig. 1.1.
Figure 1.1 - Typical scheme of IPS
To increase the efficiency of the search, the dictionary used by the system should be controlled, that is, it should be organized in such a way that the completeness and accuracy of the search is optimal. Obviously, the organization of the dictionary depends on many factors - the subject area in which the IPS will be used, the nature of the interests of users, the degree of their preparation, etc.
In general, the search procedure is iterative, that is, the query correction is followed by the search results, the search for this query, etc. Schematically, such a procedure is shown in Fig. 1.2.
Figure 1.2 - Search procedure
The request is corrected based on the number of documents received and their relevance, and can be performed by both the user and the information retrieval system itself.
1. 2 Information system subsystems
The information system can be divided into three subsystems:
1. Organizational and technological subsystem for collecting information provides an information system and includes a set of sources of information, organizational and technological chain of selection of information for accumulation in the system. Without the proper organized subsystem of information collection, the effective organization of the functioning of the entire information system as a whole is impossible.
2. The subsystem for the provision and processing of information is the core of the information system and is a reflection of the presentation by the developers and subscribers of the system of the structure and picture of the subject area, information about which should be reflected in the information system. The subsystem for the presentation and processing of information is one of the most complex components in the development of an information system.
3. The normative - functional subsystem for the issuance of information defines users, or otherwise subscribers of the system, implements the target aspect of the purpose and performance of tasks of the information system.
2. FUNCTIONS OF INFORMATION AND SEARCH SYSTEMS
The basis of all search engines is databases - a collection of data organized according to the limit rules, providing general principles for the description, storage and manipulation of data, regardless of application programs.
The following elements of the functioning of information systems can be distinguished:
Information collection is a specially organized process for collecting and displaying information:
Receiving the information;
Assessment of the relevance of information;
The procedure for selecting and fixing information.
Acquisition is the process of adding information from many parts into a single whole and bringing it to the user.
Search and delivery of information - the establishment of a special technological order to satisfy the information needs of subscribers of the information system in management activities and technological processes.
Maintaining the integrity and preservation of information - review, revision and screening of information that has lost its relevance are an integral function of information departments. The safety of information is carried out using regulatory and instructive documents.
By the nature of the provision of the logical organization of stored information, information systems are divided into factographic, documentary and geographic information systems.
Factographic information systems accumulate and store data in the form of multiple instances of one or more types of structural elements. Each of these instances of structural elements, or some combination of them, reflects information on an event or event. The structure of each type of information object consists of a finite set of details reflecting the main aspects and characteristics of information for objects of this subject area.
In documentary information systems, a single element of information is a document that is not divided into smaller elements and information, as a rule, is not structured, or is structured in a limited form. For the input document, some formalized positions can be established - the date of manufacture, artist, subject. Some types of documentary information systems ensure the establishment of a logical relationship of input documents - subordination of semantic content.
In geographic information systems, data is organized in the form of separate information objects tied to a common electronic topographic basis. Geographic information systems are used for information support in those subject areas, the structure of information objects and processes in which there is a geographical component.
Another criterion for the classification of search engines are functions or tasks to be solved. On this basis, reference, search and settlement systems are distinguished.
Inquiries are the most common type of functions of information systems, and is to provide subscribers of the system with the possibility of obtaining installation data for certain classes of objects.
Search engines are the most common class of information systems. In general, a view can be considered as a kind of information space defined in terms of an information - logical description of a subject area.
Settlement consists in processing the information in the system according to certain calculation algorithms for various purposes.
The technological functions of information systems are to automate the entire technological cycle or its individual components, production or organizational structure.
Thus, the main functions of the IPS include:
- storage of large volumes of information;
— quick search required information;
- adding, deleting and changing stored information;
- information output in a form convenient for the person.
Distinguish: - automated (coputerised);
- bibliographic (reference);
- dialogue (online);
- documentary and factographic information retrieval systems.
Information retrieval systems have recently begun to grow rapidly, new systems appear, they are widely advertised and sold. This is due to the significantly increased need of society for effective work with legal and regulatory-technical information and the use of computer information retrieval systems. The widespread use of search engines was a genuine breakthrough in the field of informatization in Russia and made it possible for technical specialists of enterprises to have free access to legal and regulatory documents.
The quality of decisions made by a specialist depends on the amount of information processed. In modern conditions, it is impossible to do without a powerful and convenient tool that helps in the search and processing of information. The effective use of search engines depends on how much the technical specialist knows the specifics, capabilities and scope of these new information systems.
Creature modern systems Information storage is carried out in two main ways: using hierarchical and hypertext models. The hierarchical model uses multi-level rubrication in the classification of information. To search for a document, use it. short descriptioncompiled by entering information into the system. The modern hypertext model allows the use of links to other documents in electronic documents.
Operating experience various systems processing and retrieval of information based on such models indicates that they are not without drawbacks. Both systems require significant material costs for the development and formation, and therefore, are limited in the amount of stored information. The formation of categories and links is carried out by specialists, and their understanding of information and the presentation of the user may vary.
3. OVERVIEW OF MODERN INFORMATION AND SEARCH SYSTEMS
Making informed decisions in the field of both economics and politics is impossible without having sufficient legal information. This need is especially acute during the period of reforming the economic and political structure. The task of satisfying the need for the timely provision of the necessary amount of legal information is solved by various media.
In this area, both traditional media and reference legal systems (CPS) compete. A truly effective PCA can only be created using modern information technology. ATP created in this way is called computer.
A computer reference and legal system is a software package that includes an array of legal information and tools for working with it. These tools can allow you to search for documents, form collections of documents, print documents or their fragments. The advantages of computer ATP are obvious. This is the availability of information, and the convenience of working with it. The problem inherent in such systems - lack of efficiency - can be solved using the global Internet.
In the market of legal reference systems in Russia, a large number of firms operate both developing their own software systems and serving existing ones. The best known are the following products of such firms (filed by Consultant Plus JSC):
“Consultant Plus” (JSC “Consultant Plus”);
GARANT (NPP Garant-Service);
"Code" (Center for Computer Development).
Systems created by state-owned enterprises to meet the legal information needs of government departments:
“Etalon” (NTSPI under the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation);
"System" (STC "System" at FAPSI).
Also on russian market systems such as:
USIS (Intaleks company);
"Referent" (CJSC "Referent-Service");
“Legal World” (Publishing House “Case and Law”);
“Your Right” and “Legal Advisor” (company “Information Systems and Technologies”);
"Legislation of Russia" (Association for the Development of Banking Technologies) and some others.
Different products can vary significantly not only in tasks solved with their help, but also in quality.
The quality of ATP depends both on the quality of the information provided and on the quality of the tools used to work with it. Application of the most recent computer technology It will not help if the PCA does not contain full legal information or if the information is updated with insufficient frequency. Conversely, an ATP containing even the most complete and quickly updated information will not be effective enough if high-quality tools for processing this information are not provided. Thus, the main parameters to determine the quality of the content of the information base are:
completeness of information;
accuracy of information;
efficiency of updating information.
Parameters characterizing the quality of the software shell:
search capabilities of the system;
means of updating information;
additional service functions.
Consider the basic help systems.
3.1 Reference legal system "Consultant Plus"
The Consultant Plus reference and legal system was created by Consultant Plus JSC and has been distributed since 1992. The system is well known and, as of the beginning of 2005, occupies one of the leading positions in Russia. The network of the Consultant Plus company unites more than 300 regional information centers that supply ATP, service and transmit information to users. The reference legal system "Consultant Plus" contains the most different types legal information: from regulations, materials of judicial practice, comments, bills, financial consultations, reflection schemes of operations in accounting to reporting forms and highly specialized documents, the documents are contained in a single informational consultant Plus. Since documents of each type have their own specific features, they are included in the relevant sections of the information array: legislation, judicial practice, financial advice, legislative comments, document forms, bills, international legal acts, legal acts on healthcare.
To search for documents in the ATP “Consultant Plus”, you can use several tools, the main one being a search card.
A search card is a table with a number of search fields. For each search field, a dictionary is provided in the system that is automatically filled in and adjusted as documents arrive in the information base (IS). When each document is entered into the system, its details are entered into the corresponding dictionary.
In ATP “Consultant Plus” it is possible to transfer the found document or its part to text editor Word to insert quotes into your own material.
The Consultant Plus program has a Legal Navigator. It is an alphabetical subject index consisting of key concepts. Close key concepts are grouped. This two-tier structure makes it easier to select key concepts when you specify them for document searches.
All databases of the ATP “Consultant Plus” are interconnected via hypertext links that allow you to instantly switch, for example, from the text of the consultation to the text of the normative document to which the author of the answer refers by pressing a key. The most important thing that gives hypertext to users is the ability to follow the author’s reasoning without additional efforts, quickly reviewing the normative acts during the course of reading the consultation that he uses to argue his position on a particular issue.
3.2 Reference legal system "Guarantor"
The Garant reference legal system has been distributed since 1990 and is deservedly very popular among a large number of users in the ATP market. It was developed and distributed by the computer company-developer of reference legal systems - Scientific-Production Enterprise (NPP) "Garant-Service".
The company actively cooperates with the Legal Department of the State Duma and a number of other state institutions and organizations. It has a high-tech and high-tech production with a large staff in Moscow and a wide network of representative offices in Russia and abroad.
The “Guarantor” system is a reference system that provides search and work with various legal documents. The system includes regulatory documents, comments and clarifications, judicial and arbitration practice, as well as explanatory dictionaries.
The system has a periodic update mechanism infobasesTherefore, you will always be up to date with the latest changes in legislation.
The “Garant” system has a whole group of small and large information and legal blocks from which the user can choose what he needs by type of activity and compose an individual set in which the document will be searched through.
The Garant-Maximum package includes all federal blocks and one regional legislative block. This kit includes documents on all sections of the law: criminal, administrative and international law, as well as judicial and arbitration practice and much more.
Some special information blocks have no analogues in other ATP to date. These include “Legislation in the Schemes”, “Draft Laws”, “Comments on the Legislation”, “Russian Legislation in English”.
Quite often, a situation arises when, when accessing a particular ATP, the user knows only the problem in question, and there is no information about the formal details of the document. In such cases, without a powerful search system for a situation, it is almost impossible to find the right rule of law. In SPS "Garant" this problem is solved by a two-level dictionary of keywords ("Encyclopedia of situations").
3. 3 Codex Legal Information Systems
The developer of the Codex Information and Legal System (IPS) is the Center for Computer Development State Enterprise (GP TsKR, St. Petersburg), which was established in early 1991.
Sales of the first version of the system containing regulatory acts of St. Petersburg and Russia began in May 1992.
IPS “Codex” refers to software products made at a good professional level, with positive characteristics in all basic parameters (completeness, efficiency, legal processing, etc.).
Codex information products include: professional legal systems, judicial and arbitration practice systems, specialized reference systems, electronic legal directories.
Regardless of the number of connected infobases, work is carried out in a single information space connected by hyperlinks.
A single line of software products includes a number of developments, including the Codex-Master software package, which is a set of tools for creating and managing full-text information retrieval systems of various directions.
The principle of openness of the Codex information system allowed using the Codex-Master complex to create new projects, while significantly expanding the range of Codex information products, for example: Auditor Assistant, Housing and Communal Services of Russia, Industrial Safety , which is extremely important in our era of technological disasters.
An important area of \u200b\u200bactivity of the Codex Consortium is the provision of access to legal information via the Internet, providing both commercial and free access to the legal resources of the Codex system.
3. 4 Systems of the Referent series
guarantor information search system
CJSC “Referent-Service” at the end of 1995 registered the integrated information system (IIS) “Referent”, the distribution of which began in 1996. By this time, ATP “Consultant Plus”, “Garant” and “Codex” were already well-known market leaders , and the "Referent-Service" had the opportunity to take into account all the best that was achieved by these companies.
Systems of the "Referent" family consist of a shell and information modules. Currently, the Referent-2000 shell is the most popular. It allows you to simultaneously work with local databases and Internet servers of legal information, as well as create your own database inside the shell with a powerful editor and administration tools.
Reference legal systems of the “Referent” family have a convenient user-friendly interface and implement all the basic functions of traditional legal bases for searching documents, as well as for working with a list and text of documents.
The "Referent" interface is as close as possible to Windows, so the user does not need to spend a lot of time developing the program. The "Referent" supports the Drag and Drop function, which allows you to move information around the screen with the mouse when generating a query to search for documents. The search itself can be performed simultaneously in the combined modules, and a number of documents contain built-in color graphic objects, for example, the coat of arms of Russia or Moscow.
The built-in document editor allows not only editing texts, but also creating a document map, making comments, as well as inserting graphic images, including animated (moving) ones, and arranging hypertext links.
Another feature of the Referent shell is the ability to create and maintain your own database of documents containing up to 200 documents, including graphics and video. This feature is especially interesting for companies with a small workflow and number. Large firms are offered a document storage system with a volume of up to 65,000 documents.
CONCLUSION
The easiest way to get information in the ever-expanding information space of the Internet is to use various search engines. The main function of such a machine is to automatically browse network nodes and collect necessary information. The collected information is indexed, that is, it is built in a certain order and classified according to a certain criterion. In the future, this information is used to service customer requests.
Specialized catalogs or directories are created for individual industries and topics, news, cities, addresses email etc.
When servicing a user, two main approaches are implemented: searching for information either by moving through the tree of the hierarchical catalog, or by forming a search query within the framework of a search language supported by the system.
For a user of modern Internet, the main problem is organization effective search information. The difficulties associated with solving this problem, obviously, will increase over time, since every four months the amount of information in the network doubles.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Alekseev E. G., Bogatyrev S. D. Informatics. Multimedia electronic textbook.
2. Ashmanov I. S. Website promotion in search engines / I. S. Ashmanov. - M.: "Williams", 2007. - 304 p.
3. Ivasenko A. G. Information Technology in economics and management: tutorial / A.G. I Vasenko, A. Yu. Gridasov, V.A. Pavlenko.- 2nd ed., Erased. - M.: KNORUS, 2007.- 160s.
4. Computer science. Basic course: textbook / ed. S.V.Simonovich. - SPb .: “Peter”, 2007.- 110 p.
5. Kadeev D. N. Information technology and electronic communications / D. N. Kadeev.- M .: "Electro", 2005.- 250 p.
6. Kolisnichenko D. N. Search engines and website promotion on the Internet / D. N. Kolisnichenko. - M .: "Dialectics", 2007. - 272 p.
7. Lande D.V. Search for knowledge on the Internet / D.V. Lande. - M .: "Dialectics", 2005. - 272 p.
8. Manning K. Introduction to the information search / K. Manning. - M .: "Williams", 2011.- 200 p.
9. Mikheeva E. V. Information technology in professional activities: a training manual .- M: TK VELBI, Prospect Publishing House, 2007.- 448с.
10. Organization of work with documents: Textbook / Ed. prof. V.A. Kudryaeva. - 2nd ed., Rev. and additional.- M .: INFRA-M, 2001.- 592s.
11. Sakharova E. V. Informatics. Guidelines / E.V. Sakharova.- Stavropol: STIS, 2006.- 200 p.
12. Chursin N. A. Popular informatics / N. A. Chursin.- M .: "Williams", 2007.- 300 p.