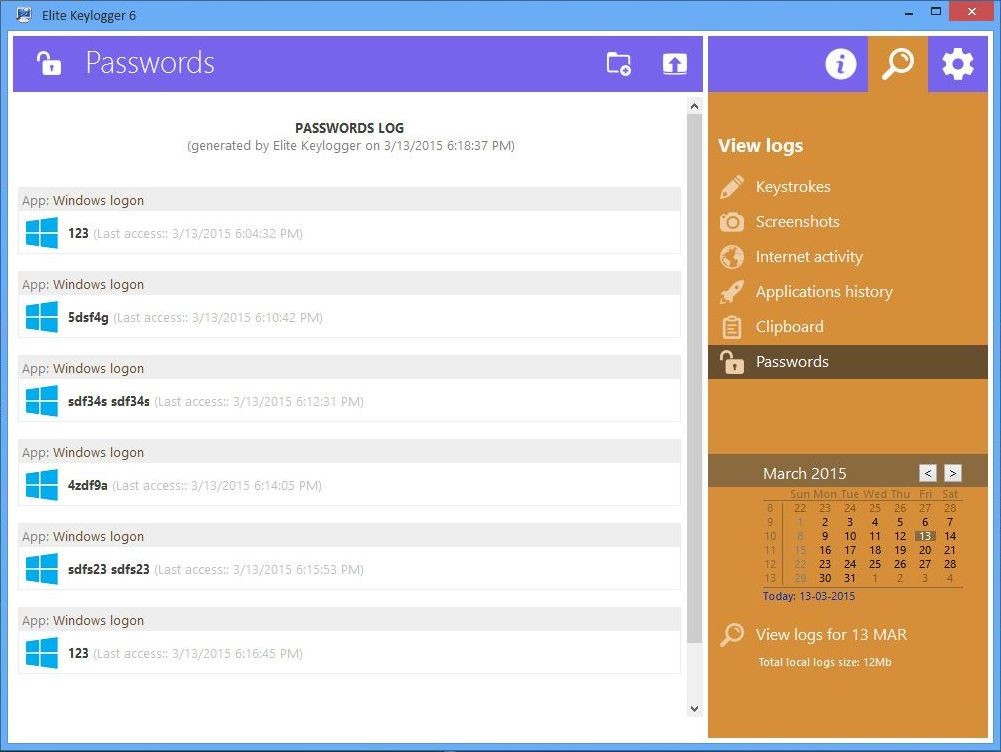
Currently, there are countless types of malware. Experts in the field of antivirus software are well aware that solutions based only on virus signature databases cannot be effective against certain types of threats. Many viruses are able to adapt, resize, file names, processes and services.
If it is impossible to detect the potential danger of the file by external signs, you can determine its malicious nature by its behavior. It is the behavioral analysis that is involved in the Host Intrusion Prevention System (HIPS).
HIPS is a specialized software that monitors files, processes, and services in search of suspicious activity. In other words, HIPS proactive protection is used to block malicious programs by the criterion of dangerous code execution. The use of technology allows you to maintain optimal system security without the need for database updates.
HIPS and firewalls (firewalls) are closely related components. If the firewall controls incoming and outgoing traffic based on sets of rules, then HIPS controls the start and operation of processes based on the changes made to the computer according to the control rules.
HIPS modules protect your computer from known and unknown types of threats. When suspicious actions are performed by a malicious program or an attacker, HIPS blocks this activity, notifies the user and offers further solutions. What kind of changes does HIPS pay attention to?
Here is a rough list of actions that HIPS is closely monitoring first and foremost:
Manage other installed programs. For example, sending emails using a standard email client or launching certain pages in the default browser;
Attempt to make changes to certain registry entries so that the program starts when certain events occur;
Completion of other programs. For example, disabling an anti-virus scanner;
Installing devices and drivers that run before other programs;
Inter-processor memory access that allows malicious code to be injected into a trusted program
What to expect from a successful HIPS?
HIPS must have sufficient authority to terminate malware activity. If a user confirmation is required to stop the operation of a dangerous program, the efficiency of the system is low. An intrusion prevention system must have a specific set of rules that the user can apply. Operations for creating new rules should be available (although there should be certain exceptions). A user working with HIPS must clearly understand the consequences of their changes. Otherwise, software and system conflicts may occur. Additional information on the operation of the intrusion prevention system can be found on specialized forums or in the antivirus help file.
HIPS usually works when the process starts. She interrupts the actions during their execution. However, there are HIPS products with preliminary detection, when the potential danger of the executable file is determined even before its immediate launch.
Are there any risks?
The risks associated with HIPS are false positives and incorrect user decisions. The system is responsible for certain changes made by other programs. For example, HIPS always tracks the registry path. HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \\ Software \\ Microsoft \\ Windows \\ CurrentVersion \\ Runresponsible for startup programs at system startup.
Obviously, many safe programs use this registry entry to start automatically. When changes are made in this key, the HIPS will ask the user about the next action: enable or disable the changes. Very often, users simply click enable, without delving into the information, especially if they are installing new software at that moment.
Some HIPS inform about similar solutions of other users, however, with a small number of them they are irrelevant and can mislead the user. It is hoped that most users have made the right choice before you. The system works great in identifying potential hazards and displaying an alarm message. Further, even if HIPS correctly identified the threat, the user can perform the wrong action and thereby infect the PC.
Conclusion: HIPS is an important element of layered protection. It is also recommended to use other protection modules with the system. For optimal and efficient HIPS operation, the user must have certain knowledge and qualifications.
Based on materials from the Malwarebytes Unpacked blog
Found a typo? Highlight and press Ctrl + Enter
Currently, the protection provided by the firewall and anti-virus is already ineffective against network attacks and imalvari. IDS / IPS class solutions that can detect and block both known and still unknown threats come first.
INFO
- About Mod_Security and GreenSQL-FW read the article “The Last Frontier,”] [_ 12_2010.
- How to teach iptables to “look” inside the package, read the article “Fire Shield”,] [_ 12_2010.
IDS / IPS Technologies
To make a choice between IDS or IPS, you should understand their principles of operation and purpose. So, the task of IDS (Intrusion Detection System) is to detect and register attacks, and also to alert when a certain rule is triggered. Depending on the type, IDS can detect various types of network attacks, detect attempts of unauthorized access or privilege escalation, the appearance of malware, track the opening of a new port, etc. The distinction is made between a firewall that controls only session parameters (IP, port number and communication state), IDS “looks” inside the packet (OSI seventh level), analyzing the transmitted data. There are several types of intrusion detection systems. APIDS (Application protocol-based IDS) are very popular, which monitor a limited list of application protocols for specific attacks. Typical representatives of this class are PHPIDS, which analyzes requests to PHP applications, Mod_Security, which protects the web server (Apache), and GreenSQL-FW, which blocks dangerous SQL commands (see the article “The Last Frontier” in] [_ 12_2010).
Network NIDS (Network Intrusion Detection System) are more versatile, which is achieved thanks to DPI technology (Deep Packet Inspection, deep packet inspection). They control an ambiguously specific application, all traffic passing through, starting at the scan level.
For some packet filters, the opportunity to “look inside” to block danger is also realized. An example is the OpenDPI and Fwsnort projects. The latter is a program for converting the Snort signature database to equivalent blocking rules for iptables. But initially, the firewall is sharpened for other tasks, and the DPI technology is “expensive” for the engine, so the functions for processing additional data are limited by blocking or marking strictly defined protocols. IDS just alerts all suspicious activity. To block an attacking host, the administrator will reconfigure the firewall while viewing statistics. Naturally, there is no speech here in any real-time response. That is why IPS (Intrusion Prevention System, an attack prevention system) is more interesting today. They are based onIDS and can independently rebuild the packet filter or interrupt the session by sending TCP RST. Depending on the operating principle, IPS can be installed “on the fly” or use traffic mirroring (SPAN) received from several sensors. For example, the break is set by Hogwash Light BR, which operates at the OSI level two. Such a system may not have IP addresses, which means it remains invisible to the cracker.
In ordinary life, the door is not only locked, but additionally protected, leaving a guard near it, because only in this case you can be sure of safety. VIT as such a security is hosted IPS (see "New Defensive Line" in] [_ 08_2009), which protect the local system of viruses, rootkits and hacking. They are often confused with antiviruses that have a proactive defense module. But HIPS, as a rule, do not use signatures, which means that they do not require constant updating of databases. They control much more system parameters: processes, the integrity of the system files and registry, log entries and much more.
To fully control the situation, it is necessary to control and compare events both at the network level and at the host level. For this purpose, hybrid IDS were created that collect data from various sources (such systems are often referred to as SIM - Security Information Management). Among the OpenSource projects, the Prelude Hybrid IDS is interesting, collecting data from almost all OpenSource IDS / IPS and understanding the format of the logs of various applications (support for this system was suspended several years ago, but you can still find bundled packages in Linux and * BSD repositories).
In the variety of proposed solutions, even pros can get confused. Today we will meet the most prominent representatives of IDS / IPS systems.
Joint Threat Control
The modern Internet carries a huge number of threats, so highly specialized systems are no longer relevant. You must use a comprehensive multifunctional solution that includes all protection components: firewall, IDS / IPS, antivirus, proxy server, content filter and anti-spam filter. These devices are called UTM (Unified Threat Management). Examples of UTM include Trend Micro Deep Security, Kerio Control, Sonicwall Network Security, FortiGate Network Security Platforms and Appliances or specialized Linux distributions such as Untangle Gateway, IPCop Firewall, pfSense (read their overview in the article “Network Controllers”,] [_01_2010).
Suricata
The beta version of this IDS / IPS was presented to the public in January 2010 after three years of development. One of the main goals of the project is to create and run completely new attack detection technologies. Suricata is backed by OISF, which enjoys the support of serious partners, including the guys from the US Department of Homeland Security. Actual today is the release at number 1.1, released in November 2011. The project code is distributed under the GPLv2 license, but financial partners have access to the non-GPL version of the engine, which they can use in their products. To achieve the maximum result, a community is involved in the work, which allows to achieve a very high pace of development. For example, compared to the previous version 1.0, the code size in 1.1 increased by 70%. Some modern IDSs with a long history, including Snort, are not very efficient at using multiprocessor / multicore systems, which leads to problems when processing large amounts of data. Suricata is initially multithreaded. Tests show that it is six times faster than Snort (on a system with 24 CPUs and 128 GB of RAM). When assembling with the ‘—enable-cuda’ parameter, the possibility of hardware acceleration on the GPU side appears. Initially, IPv6 is supported (in Snort it is activated by the ‘—enable-ipv6’ key), standard interfaces are used to intercept traffic: LibPcap, NFQueue, IPFRing, IPFW. In general, the modular layout allows you to quickly connect the desired element for capturing, decoding, analyzing or processing packets. Blocking is done using the standard OS packet filter (in Linux, to activate IPS mode, you need to install the netlink-queue and libnfnetlink libraries). The engine automatically detects and parses the protocols (IP, TCP, UDP, ICMP, HTTP, TLS, FTP, SMB, SMTP and SCTP), so the rules do not need to bind to the port number (as Snort does), just set the action for the desired protocol . Ivan Ristic, the author of Mod_security, created a special HTP library used in Suricata to analyze HTTP traffic. Developers primarily seek to achieve accuracy of detection and increase the speed of checking rules.

The output is unified, so you can use standard utilities to analyze them. Actually, all the backends, interfaces, and analyzers written for Snort (Barnyard, Snortsnarf, Sguil, etc.) work without modification using Suricata. This is also a big plus. HTTP exchanges are logged in detail in the standard Apache file format.
The basis of the detection mechanism in Suricata is rules. Here, the developers didn’t invent anything yet, they allowed to connect the rouletsets created for other projects: Sourcefire VRT (can be updated via Oinkmaster), and Emerging Threats Pro. In the first releases, support was only partial, the engine did not recognize and some rules were loaded, but now this problem has been solved. A proprietary rules format has been implemented that resembles snortovskiy. A rule consists of three components: an action (pass, drop, reject or alert), a header (IP / port of the destination source) and a description (what to look for). In the settings, variables are used (flowint mechanism), allowing, for example, to create counters. At the same time, the information of the stream can be saved for later use. This approach, used to track password guessing attempts, is more effective than the method used in Snort, which operates with a threshold value. It is planned to create an IP Reputation mechanism (like Cisco SensorBase, see the article “Touch Cisco” in] [_ 07_2011).
Summarizing, I note that Suricata is a faster engine than Snort, a fully compatible snapshot-corrected backend capable of checking large network streams. The only drawback of the project is the scarce documentation, although an experienced administrator does not have to figure out anything with the settings. Installation packages have already appeared in the distribution repositories; clear instructions on self-assembly of sources are available on the project’s frontend. There is a gambling distribution called Smooth-sec built on the base of Suricata.

Samhain
Launched under the OpenSource license, Samhain is a hosted IDS that protects a single computer. He uses several analysis methods to fully cover all the events occurring in the system:
- creation of important files at the first start of the signature database; its comparison with the “live” system;
- monitoring and analysis of journal entries;
- input / output control in the system;
- monitoring connections with open network ports;
- file control with installed SUID of spark processes.

The program can be launched in invisible mode (the kernel module is activated) when kernel processes cannot be detected in memory. Samhain also supports monitoring of several nodes running different OSs, recording all events at a water point. At the same time, agents installed on remote nodes send all the collected information (TCP, AES, signature) to the encrypted channel server (yule), which stores it in the database (MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle). In addition, the server is responsible for checking the status of client systems, distributing updates of icon-configuration files. Several options have been implemented for notifications and sending collected information: e-mail (mail is signed to avoid falsification), syslog, log file (signed), Nagios, console etc. You can manage it using several administrators with clearly defined roles.
The package is available in the repositories of almost all Linux distributions, download the project there is a description of how to install Samhain under Windows.
StoneGate Intrusion Prevention System
This solution was developed by a Finnish company that creates enterprise-class products in the field of network security. We have implemented all the required functions: IPS, protection against DDoS and 0day attacks, web filtering, support for encrypted traffic, etc. Using StoneGate IPS, you can block a virus, spyware, certain applications (P2P, IM, etc.). For web filtering, a constantly updated database of sites is used, divided into several categories. Particular attention is paid to protecting the evacuation of AET (Advanced Evasion Techniques) security systems. Transparent Access Control technology allows you to break the corporate network into several virtual segments without changing the actual topology and establish individual security policies for each of them. Traffic validation policies are configured using templates that contain generic rules. These policies are created offline. The administrator checks the created policies and downloads their remote IPS hosts. Similar events in StoneGate IPS are handled by the principle used in SIM / SIEM systems, which greatly simplifies the analysis. Multiple devices can easily be combined in a cluster and integrated with other StoneSoft solutions - StoneGate Firewall / VPN and StoneGate SSL VPN. Management is provided by a single management console (StoneGate Management Center), which consists of three components: Management Server, Log Server and Management Client. The console allows you to not only configure IPS and create new rules and policies, but also monitor and view the logs. It is written in Java, so versions for Windows and Linux are available.

StoneGate IPS is delivered both as a hardware complex and as a VMware image. The latter is intended for installation on proprietary equipment or virtual infrastructure. By the way, in the presence of the creators of many such solutions, the development company allows you to download a test version of the image.
IBM Security Network Intrusion Prevention System
The attack prevention system developed by IBM uses a patented protocol analysis technology that provides proactive protection, including 0day threats. Like all products in the IBM Security series, its basis is the protocol analysis module - PAM (Protocol Analysis Module), which combines the traditional signature method of attack detection (Proventia OpenSignature) and behavioral analyzer. At the same time, PAM distinguishes between 218 application-level protocols (attacks via VoIP, RPC, HTTP, etc.) and data formats such as DOC, XLS, PDF, ANI, JPG, in order to predict where the malicious code can be embedded. More than 3000 algorithms are used for traffic analysis, 200 of them “catch” DoS. Firewall features allow access only to specific IP and IP ports, eliminating the need for an additional device. Virtual Patch technology blocks viruses at the distribution stage and protects computers before installing an update that addresses critical vulnerabilities. If necessary, the administrator himself can create and use a signature. The application control module allows you to manage P2P, IM, ActiveX-elements, VPN tools, etc., and if necessary, block them. A DLP module has been implemented that monitors attempts to transmit confidential information and move data to a secure network, which allows you to assess risks and block a leak. By default, eight types of data are recognized (credit card numbers, phone numbers ...), the administrator sets the rest of the organization-specific information independently using regular expressions. Currently, most of the vulnerabilities are in web applications, therefore, the IBM product includes a special Web Application Security module that protects systems of common types of attacks: SQL injection, LDAP injection, XSS, JSON hijacking, PHP file-includers, CSRF um . d.

There are several options for detecting an attack — blocking the host, sending a warning, recording attack traffic (file with tcpdump compatible), quarantining the host, and performing some other user-defined actions. Policies are written down to every port, IP address or VLAN zone. High Availability mode ensures that if one of the several IPS devices available on the network fails, traffic will go through the other and established connections will not be interrupted. All subsystems inside the hardware - RAID, power supply, cooling fan - are duplicated. The settings made using the web console are as simple as possible (training courses last only one day). If you have multiple devices, you usually purchase IBM Security SiteProtector, which provides centralized management, log analysis and reports.
McAfee Network Security Platform 7
IntruShield IPS, manufactured by McAfee, has always been one of the most popular IPS solutions. It is now based on the McAfee Network Security Platform 7 (NSP). In addition to the full functionality of the classic NIPS, the new product received tools for analyzing packets transmitted by the internal corporate network, which helps to detect malicious traffic initiated by infected computers. McAfee uses Global Threat Intelligence technology, which collects information from hundreds of thousands of sensors installed around the world, and evaluates the reputation of all passing unique files, IP and URL addresses and protocols. Due to this, the NSP can detect botnet traffic, detect 0day threats and DDoS attacks, an attack with a wide coverage allows reducing the probability of false positives.
Every IDS / IPS can work among virtual machines, because all the exchange takes place inside the interface. But NSP has no problems with this; it can analyze traffic between VMs, as well as between VMs and the physical host. To monitor the nodes, the agent module of the company Reflex Systems is used, which collects information from the graphics in VM and transfers it to the physical environment for analysis.
The engine distinguishes over 1100 applications running at the seventh level of OSI. It views traffic using a content analysis engine and provides simple management tools.
In addition to NIPS, McAfee also launches its IPS host Hostrusion Prevention for Desktop, which provides comprehensive protection for PCs using threat detection methods such as analyzing behavior of signatures, monitoring the status of connections using a firewall, and assessing reputation to block attacks.
Where to deploy IDS / IPS?
To maximize the use of IDS / IPS, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- The system needs to be deployed on the side of the protected network or subnet, and usually with an off-network screen (it makes no sense to control traffic that will be blocked) - this way we will reduce the load. In some cases, the sensors are installed inside the segment.
- Before activating the IPS function, you should run the system for a while in non-blocking IDS mode. In the future, you will need to periodically adjust the rules.
- Most IPS settings are set up with typical networks. In certain cases, they may turn out to be ineffective, so it is necessary to specify the IP of internal subnets and the applications (ports) used. This will help the piece of iron to better understand what it is dealing with.
- If the IPS-system is installed “out of tune”, it is necessary to control its operability, otherwise the device’s output can easily paralyze the entire network.
Conclusion
Winners will not be determined. The choice in each particular case depends on the budget, the network topology, the required protection functions, the administrator’s desire to tinker with the settings and, of course, the risks. Commercial solutions are supported and provided with certificates, which allows them to be used in organizations involved in the processing of personal data. Snort distributed under the OpenSource license is well-documented, has a sufficiently large database and a good track record to be in demand by the admins. Compatible snapshot Suricata may well protect the network with a lot of traffic and, most importantly, absolutely free.
Modern electronic devices are almost universal. So, for example, a smartphone perfectly copes not only with calls (their reception and completion), but also with the ability to surf the Internet, listen to music, watch videos or read books. A tablet is also suitable for these tasks. The screen is one of the most important parts of electronics, especially if it is a touch screen and serves not only to display files, but also to control it. Let's get acquainted with the characteristics of displays and the technologies by which they are created. We will pay special attention to what an IPS screen is, what kind of technology it is, and what are its advantages.
How the LCD screen works
First of all, we will figure out how the modern equipment is equipped with which. Firstly, it is an active matrix. It consists of microfilm transistors. Thanks to them, an image is formed. Secondly, it is a layer of liquid crystals. They are equipped with light filters and create R-, G-, B-subpixels. Thirdly, it is a screen backlight system that allows you to make the image visible. It can be fluorescent or LED.
Features of IPS technology
Strictly speaking, the IPS matrix is \u200b\u200ba type of TFT technology by which LCD screens are created. TFT is often understood to mean TN-TFT monitors. Based on this, we can compare them. To get acquainted with the subtleties of the choice of electronics, we will understand what IPS screen technology is, what this concept means. The main thing that distinguishes these displays from the TN-TFT is the location of the liquid crystal pixels. In the second case, they are arranged in a spiral, are at an angle of ninety degrees horizontally between the two plates. In the first (which we are most interested in) the matrix consists of thin-film transistors. Moreover, the crystals are located along the plane of the screen parallel to each other. Without voltage coming to them, they do not turn. At TFT, each transistor controls one point on the screen.

The difference between IPS and TN-TFT
Let's take a closer look at IPS, what it is. Monitors created using this technology have a lot of advantages. First of all, this is an excellent color rendering. The whole range of shades is bright, realistic. Thanks to the wide viewing angle, the image does not fade, no matter where you look at it. The monitors have a higher, sharper contrast due to the fact that the black color is transmitted simply perfectly. We can note the following disadvantages that the IPS screen type has. What is, first of all, a large energy consumption, a significant drawback. In addition, devices equipped with such screens are expensive, since their production is very expensive. Accordingly, TN-TFT have diametrically opposite characteristics. They have a smaller viewing angle, when you change the point of view, the image is distorted. It is not very convenient to use them in the sun. The picture is getting dark, glare interfere. However, such displays have a quick response, consume less energy and are affordable. Therefore, such monitors are installed in budget electronics models. Thus, we can conclude in what cases the IPS screen is suitable, that this is a great thing for movie, photo and video lovers. However, due to their less responsiveness, they are not recommended to fans of dynamic computer games.

Developments by leading companies
IPS technology itself was created by the Japanese company Hitachi in conjunction with NEC. New in it was the arrangement of liquid crystal crystals: not in a spiral (as in TN-TFT), but in parallel to each other and along the screen. As a result, such a monitor transmits colors brighter and more saturated. The image is visible even in the open sun. The viewing angle of the IPS-matrix is \u200b\u200bone hundred seventy-eight degrees. You can watch the screen from any point: bottom, top, right, left. The picture remains clear. Apple is launching the popular IPS tablets with the IPS Retina matrix. One inch uses an increased pixel density. As a result, the image on the display comes out without grain, the colors are transmitted smoothly. According to the developers, the human eye does not notice microparticles if the pixels are more than 300 ppi. Now devices with IPS displays are becoming more affordable, they are beginning to be supplied with low-cost electronics models. New varieties of matrices are created. For example, MVA / PVA. They have a fast response, wide viewing angle and excellent color reproduction.

Devices with multi-touch screen
Recently, electronic devices with touch control have gained great popularity. And these are not only smartphones. Produce laptops, tablets, which have an IPS touch screen, which is used to manage files, images. Such devices are indispensable for working with video, photos. Depending on the compact and full-format devices. multitouch is able to recognize ten touches at the same time, that is, on such a monitor you can work with two hands at once. Small mobile devices, such as smartphones or tablets with a diagonal of seven inches, recognize five touches. This is quite enough if your smartphone has a small IPS screen. That it is very convenient, appreciated by many buyers of compact devices.
Dmitry Volkov
Head of IT Incident Investigation, Group-IB
The current development of IPS
Network Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) can be both an effective tool for people involved in security, and an expensive piece of iron dusting around. To IPS-system does not become a disappointment, it must at least meet the following requirements that must be considered when choosing it.
The system should:
- have a wide range of models that satisfy the requirements of both small regional offices and the main enterprise with multi-gigabit networks;
- to support not only signature analysis, but also anomalous protocol analysis, and, of course, behavioral analysis;
- give a clear picture of the network and devices connected to it;
- provide work in IDS mode, conduct behavioral analysis, have tools for conducting investigations;
- have centralized management of installed IPS / IDS systems;
- have good analysis tools to effectively improve security policies.

IDS / IPS systems are most often connected where critical resources exist. But besides the fact that it is necessary to block attacks on these resources, you should constantly monitor them, namely: know which of these resources are vulnerable, how their behavior on the network changes. Therefore, additional functionality must be added to IDS / IPS systems, which allows them to protect the required resources more reliably, while reducing the cost of ownership. So, protection can be carried out in three phases - IPS, Adaptive IPS, Enterprise Threat Management. The functionality of each subsequent phase includes all the functions from the previous phase and is expanded by newer ones.

Phase 1. You can control and / or block attacks using thousands of vulnerabilities, that is, these are standard IPS sensors and their control centers.
Phase 2. There is an opportunity to study the network, prioritize events and automate IPS settings.
Phase 3. Full possible functionality to protect the corporate network before, during and after the attack.
ETM is the first embodiment of the awareness that, while protecting information resources, it is necessary to work smarter and not harder. From a technological point of view, ETM is a combination of four threat and vulnerability management technologies combined into a single solution that is centrally managed. As a result, this solution provides more features than each product individually. As shown in fig. 3, ETM consists of an intrusion prevention system (IPS), behavioral network analysis (NBA), network access control (NAC), vulnerability analysis (VA), data exchange subsystem and centralized management.
Comparison of IPS manufacturers
In fig. Figure 4 shows which of the manufacturers of IPS-systems is in the lead. But, not being attached to Gartner, let's look at what functionality each manufacturer has.
As you can see, some lack such important functions as investigation at the batch level, as well as viewing and creating rules. Without such capabilities, it is sometimes completely incomprehensible why the system issues warnings, and it takes a long time to find out the reason for these warnings.

The lack of a mechanism for creating compliance policies also imposes certain restrictions. For example, in an external audit it is useful to demonstrate how the provisions of your policies are actually implemented. Further comments are unnecessary, since the true state of things will become clear only after a real implementation in the industrial environment.
It must be remembered that ensuring network security is a complex task, and disparate solutions do not always ensure integrity of perception and lead to additional costs.
Short review
Cisco systems
Reliable solutions have excellent support, but are difficult to configure, signature analysis gives a lot of false positives, the management interface with a large number of events does not adequately disassemble the recorded events. For full operation, additional investment is required in the Cisco Security Monitoring, Analysis and Response System (CS-MARS).
Tippingpoint
 The systems of this manufacturer are convenient to configure and install. They have a good control interface, but can only connect to the gap, that is, without passive detection. They do not allow expanding the functionality and are simply an IDS / IPS system.
The systems of this manufacturer are convenient to configure and install. They have a good control interface, but can only connect to the gap, that is, without passive detection. They do not allow expanding the functionality and are simply an IDS / IPS system.
At a conference, a TippingPoint spokesman said in a speech that their equipment could be installed and forgotten - and that’s their protection strategy.
Maybe someone shares it, but it's hard for me to agree with her. Any security measure should be controlled, otherwise you will never get the proper return from it. For example, if someone stubbornly tries to hack your affiliate portal and failed to do it the first two times thanks to the IPS system, then the third time he will succeed, and without monitoring the IPS system you will not know this and prevent subsequent attempts you will not succeed.
Juniper NetworksNo matter what the analysts of Gartner or other publications write, it is difficult to say something good about their products. The system is terribly complicated to set up. The NSM management console is very limited. The results are displayed in such a way that it seems that the developers tried to make it looked at it as little as possible and hoped that the attacks really were repelled.
Sourcefire
Perhaps the best system. Everything is convenient. The functionality is incredibly wide. In addition, the system already has built-in capabilities for detailed data collection about attacking and attacking nodes, and not just IP and MAC addresses, which greatly reduces the analysis and analysis of events. This information also includes connection history, open and then
closed ports, types of the transmitted address, user names, if, for example, the transfer was via FTP or e-mail, and, of course, the e-mail address itself. In large networks, it can become an indispensable means of protection. They have been releasing their solutions since 2001, but have recently entered the Russian market.
Conclusion
You should not introduce a number of new products that solve only one problem. Static security cannot protect a dynamic environment. It is necessary to save the time of your employees and their efforts. Let them work better and not harder. Reduce the cost of maintaining a heterogeneous environment. Reduce the time spent analyzing data from multiple consoles and reports. Spend money wisely until security systems cost you more than the risks you are protecting yourself from.
Intrusion Detection is software or hardware for detecting attacks and malicious activities. They help networks and computer systems give them the proper rebuff. To achieve this, IDS collects information from multiple system or network sources. The IDS then analyzes it for attacks. This article will attempt to answer the question: "IDS - what is it and what is it for?"
What are intrusion detection systems (IDS) for?
Information systems and networks are constantly subjected to cyber attacks. Firewalls and antiviruses are clearly not enough to repel all these attacks, since they are only able to protect the “front door” of computer systems and networks. Various teenagers, imagining themselves to be hackers, are constantly scouring the Internet in search of gaps in security systems.
Thanks to the World Wide Web, they have at their disposal a lot of completely free malicious software - all sorts of slammers, blindpers, and similar malicious programs. The services of professional crackers are used by competing companies to neutralize each other. So systems that detect intrusion detection systems are a must. Not surprisingly, every day they are increasingly used.

IDS Elements
IDS elements include:
- detector subsystem, the purpose of which is the accumulation of network or computer system events;
- an analysis subsystem that detects cyber attacks and dubious activity;
- storage for the accumulation of information about events, as well as the results of the analysis of cyber attacks and unauthorized actions;
- a management console with which you can set IDS parameters, monitor the status of the network (or computer system), have access to information about attacks and illegal actions detected by the analysis subsystem.
By the way, many may ask: "How is IDS translated?" The translation from English sounds like "a system that catches on hot uninvited guests."
The main tasks that intrusion detection systems solve
An intrusion detection system has two main tasks: analysis and an adequate response based on the results of this analysis. To perform these tasks, the IDS system performs the following actions:
- monitors and analyzes user activity;
- audits the configuration of the system and its weaknesses;
- checks the integrity of critical system files as well as data files;
- conducts a statistical analysis of system states, based on a comparison with those states that occurred during already known attacks;
- audits the operating system.
What an intrusion detection system can provide and what it cannot do

With its help, you can achieve the following:
- improve integrity parameters;
- to trace the user's activity from the moment of his entry into the system until the moment of harming her or performing any unauthorized actions;
- recognize and notify about data changes or deletions;
- automate Internet monitoring tasks in order to search for the latest attacks;
- identify errors in the system configuration;
- detect the beginning of the attack and notify about it.
IDS cannot do this:
- make up for flaws in network protocols;
- play a compensatory role in the case of weak identification and authentication mechanisms in the networks or computer systems that it monitors;
- it should also be noted that IDS does not always cope with problems associated with packet-level attacks.
IPS (intrusion prevention system) - continued IDS

IPS stands for Intrusion Prevention. These are extended, more functional versions of IDS. IPS IDS systems are reactive (as opposed to conventional). This means that they can not only detect, record and notify about an attack, but also perform protective functions. These features include dropping connections and blocking incoming traffic packets. Another hallmark of IPS is that they operate online and can automatically block attacks.
IDS subtypes for monitoring method

NIDS (that is, IDSs that monitor the entire network) are analyzing the traffic of the entire subnet and are managed centrally. By correctly positioning several NIDS, monitoring a fairly large network can be achieved.
They work in unintelligible mode (that is, they check all incoming packets, but do not selectively do this), comparing subnet traffic with known attacks from their library. When an attack is identified or unauthorized activity is detected, an alarm is sent to the administrator. However, it should be noted that in a large network with high traffic, NIDS sometimes do not cope with the verification of all information packets. Therefore, there is a possibility that during the “rush hour” they will not be able to recognize the attack.
NIDS (network-based IDS) are those systems that are easy to integrate into new network topologies, since they do not have a special effect on their functioning, being passive. They only record, record and notify, in contrast to the reactive type of IPS systems discussed above. However, it should also be said about network-based IDS that these are systems that cannot analyze encrypted information. This is a significant drawback, because of the increasingly widespread adoption of virtual private networks (VPNs), encrypted information is increasingly being used by cybercriminals for attacks.
Also, NIDS cannot determine what happened as a result of the attack, whether it caused harm or not. All that they can do is fix its beginning. Therefore, the administrator is forced to independently recheck each attack case to make sure that the attackers have achieved their goal. Another major issue is that NIDS has difficulty capturing attacks with fragmented packets. They are especially dangerous because they can interfere with the normal operation of NIDS. What this can mean for the entire network or computer system does not need to be explained.
HIDS (host intrusion detection system)
HIDS (IDS monitoring host) only serve a specific computer. This, of course, provides much higher efficiency. HIDS analyzes two types of information: system logs and the results of an audit of the operating system. They take a snapshot of the system files and compare it with an earlier snapshot. If files critical to the system have been modified or deleted, then an alarm is sent to the administrator.
A significant advantage of HIDS is the ability to perform its work in a situation where network traffic is encrypted. This is possible due to the fact that host-based information sources can be created before data can be encrypted, or after decryption on the destination host.
The disadvantages of this system include the possibility of blocking it or even banning it using certain types of DoS attacks. The problem here is that the sensors and some HIDS analysis tools are located on the host that is being attacked, that is, they are also attacked. The fact that HIDS use the resources of the hosts whose work they monitor is also difficult to call a plus, since this naturally reduces their performance.
IDS subtypes for attack detection methods

The anomaly method, the signature analysis method, and the policy method - these are the subspecies for attack detection methods that the IDS system has.
Signature Analysis Method
In this case, the data packets are checked for attack signatures. An attack signature is an event matching one of the patterns describing a known attack. This method is quite effective, because when it is used, reports of false attacks are quite rare.
Anomaly Method
With its help, illegal actions are detected on the network and on the hosts. Based on the history of the normal operation of the host and the network, special profiles are created with data about this. Then special detectors come into play that analyze events. Using various algorithms, they analyze these events, comparing them with the “norm” in profiles. The lack of the need to accumulate a huge number of attack signatures is a definite plus of this method. However, a considerable amount of false signals about attacks during atypical, but quite legitimate events on the network is its undoubted minus.
Policy Method
Another attack detection method is the policy method. Its essence is to create network security rules, which, for example, may indicate the principle of interaction between networks and the protocols used for this. This method is promising, but the difficulty lies in the rather complicated process of creating a policy base.
ID Systems Provides Reliable Protection for Your Networks and Computer Systems

Today, ID Systems Group of Companies is one of the market leaders in the field of creating security systems for computer networks. It will provide you with reliable protection against cyber villains. With ID Systems protection systems you can not worry about the data that is important to you. Thanks to this, you can enjoy life more, because you will have less anxiety in your soul.
ID Systems - Employee Reviews
A great team, and most importantly, of course, is the right attitude of the company management to its employees. Everyone (even the fledgling newcomers) has the opportunity for professional growth. True, for this, of course, you need to prove yourself, and then everything will work out.
The team has a healthy atmosphere. Beginners will always be taught everything and everyone will be shown. No unhealthy competition is felt. Employees who have been with the company for many years are happy to share all the technical details. They kindly, even without a trace of indulgence, answer the most stupid questions of inexperienced workers. In general, working with ID Systems has some pleasant emotions.
The attitude of management is pleasantly pleasing. It is also encouraging that here, obviously, they know how to work with staff, because the team is really highly professional picked up. The opinion of employees is almost unambiguous: they feel at home at work.