In Windows 8 (as in previous versions Windows), if you successfully connect to a wireless Wi-Fi network, the system automatically creates a separate Wi-Fi network profile for this connection. This profile contains all the information necessary to establish a wireless connection: the network name (SSID), the authentication method, the network password (password key) and other information. In the future, if this Wi-Fi network is in sight, this profile is used to automatically connect to it.
In Windows 7, there was a special control panel element that allows you to manage the profiles of wireless networks (Manage Wireless Network): delete profiles, change their settings or priority. In Windows 8, for some reason Microsoft decided to remove this functionality, so in Windows 8 you can manage Wi-Fi network profiles using third-party tools (these are not our methods!), Or using the command line.
So, wireless networks in Windows 8 can be controlled from the command line, the netsh command will help us.
A list of wireless network profiles can be displayed using the command:
netsh wlan show profiles
The command returns a list of saved profiles wireless Wi-Fi networks. In this example, there is one Wi-Fi network profile named michael.
View saved passwords for Wi-Fi networks in Windows 8
It's no secret that the system preserves the network key (the password for network connections) for the convenience of the user.
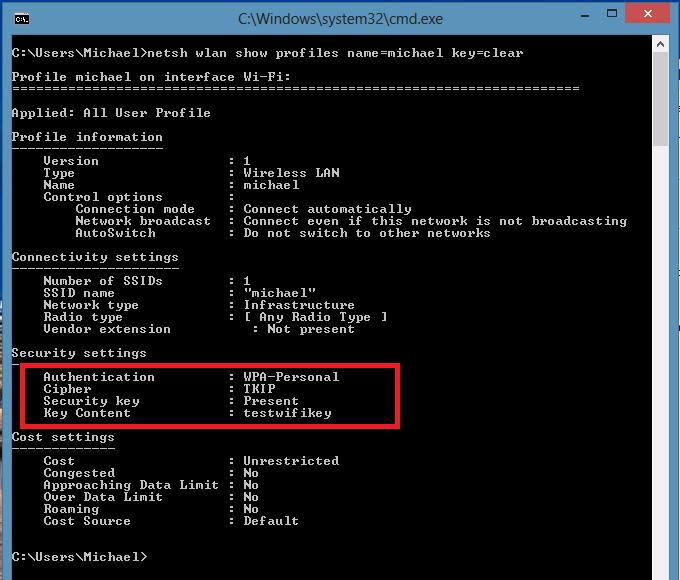
To view the saved password for accessing the Wi-Fi network (WPA, WEP, etc.), you can directly from the command line with the command netsh, specifying the desired profile:
netsh wlan show profiles name = michael key = clear
The password (key) of the Wi-Fi network can be seen in the Security settings -\u003e Key Content section. In this case, the password for connecting to Wi-Fi point access: testwifikey.
Deleting a Wi-Fi connection profile in Windows 8
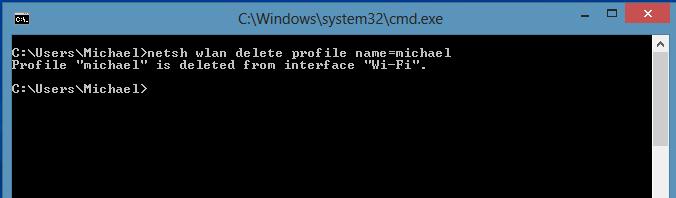
To delete the saved wireless profile in Windows 8, use the command:
netsh wlan delete profile name =
This command will delete all saved profiles for all WLAN interfaces.
If you need to delete the wi-fi network profile for a specific WLAN interface, use the following command:
netsh wlan delete profile name = interface =
Note. The wireless profiles in Windows 8 are stored as XML files in the C: \\ ProgramData \\ Microsoft \\ Wlansvc \\ Profiles \\ Interfaces \\ (GUID_interface) \\ (GUID_Profile) .xml directory
Each Wi-Fi adapter has its own GUID interface (GUID_interface), and all saved profiles for this interface are stored in the xml file with (GUID_Profile) as a name. To delete information about a specific wireless profile, it is enough to delete the corresponding xml file.
How in Windows 8 to connect to a wireless network through the command line
You can connect to a wireless network through the command line in Windows 8 if the system already has the required profile. To connect, use the command:
netsh wlan connect name =
In case if you need to connect from the command line to the network stored in the profile (how to get the list of all profiles in the system described above) with the name wlr3S3 $$, run the following command:
netsh wlan connect name = "wlrЗ1З $"
It is also possible to specify a specific interface with which to install Wi-Fi connection. In this case, the command will look like this:
netsh wlan connectmso-ansi-language: EN-US "lang =" EN-US "\u003e 1З $" interface = "Wireless Network Connection 2"
Disconnecting from WiFi network
To disconnect from the wireless network, use the command:
netsh wlan disconnect
Or specify a specific interface:
netsh wlan disconnect interface = "Wireless Network Connection 2"
How to change the priority of wireless networks in Windows 8
If there are several Wi-Fi networks in the coverage area, the priority of wireless connections is determined as follows: the last connection becomes the highest priority if the "connect automatically" item is active. If this network is unavailable, Windows 8 tries to connect to the Wi-Fi network, which was the priority last time and if the connection is successful, the priority of this network is increased.
Note. In Windows 8, if there are multiple network connections, the system tries to connect first by Ethernet, if it is not possible - it tries to connect Wi-Fi connection, and if both of these options are not available, Windows 8 will connect to the mobile network.
The current priority for wireless networks can be displayed using an already familiar command:
netsh wlan show profiles
The higher the profile is in the list, the higher the priority of this connection. To change the priority of one of the Wi-Fi networks, use the command:
netsh wlan set profileorder name = "wlrЗ1З $" interface = "Wireless Network Connection 2" priority = 1
This command raises to the maximum (1) priority of the wireless network wlrS1S $$ for the Wireless Network Connection 2 interface.
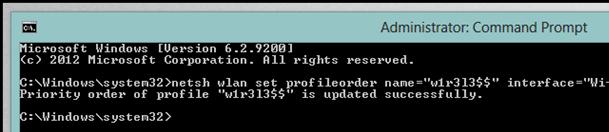
And if you again display a list of all network profiles, you will see that the priority of the network wlrS1S $$ was increased (in the list it stands above all).

Transferring Wi-Fi network profiles between computers running Windows 8
To transfer an existing Wi-Fi profile from one computer to another, you need to export it to an XML file, and then upload it to another computer.
And again we are helped by the utility netsh, which allows you to export and import the settings of wireless networks (profiles) into an XML file:
Unload wi-Fi settings Profile:
netsh wlan export profile name = "wlrЗ1З $" folder = c: \\ wifi
As a result, an xml file should appear in the c: \\ wifi directory, which must be copied to another computer and imported by the command:
netsh wlan add profile filename = "c: \\ wifi \\ WiFi_profile_name.xml"
With the help of these commands, you can also implement backup all Wi-Fi profiles on your computer.
Restricting access to Wi-Fi networks
Restrict access to Wi-Fi networks can be through Windows group policies. An example of implementing such a restriction is described in the article: Blocking wireless networks in Windows 7.
Windows 8-based access point
From a Windows 8-based computer Wi-fi adapter Using the same netsh command, you can organize an access point. The procedure is described here: How to create a point wi-Fi access on Windows 8.
Hello everyone, today I will tell you how to remove wifi network in Windows 10, Windows 8.1 and 7. For what it may be necessary, for a number of reasons, first a bunch of garbage connections that you no longer need, in the second for security reasons. Below, we will analyze everything in more detail, so that even the most novice user can understand this without spending a lot of time on it.
Earlier I told and this article complements it in terms of understanding what and where is located. Just an example of what this good should be cleaned, suppose you came to a crowded place, saw the left free WiFi. Connected to it, even put up a daw, to be connected by a machine, and then, after discovering that you are being broken and trying to hack you or you are catching a virus, it does not matter. You naturally turn off immediately, delete viruses and all that and calmly forget about this case, time passes and you again get to this place, and since you have a tail from this connection, it will connect again without you, which is not good, for this and it is worth all to delete. There are at least two built-in methods without third-party programs, which will remove the network wifi in Windows 10 and other editions.
how to remove a wifi connection via the graphical interface
Delete wifi network in Windows 7
This method is most suitable for beginners who do not like the command line and are used to graphical interface. Find the network icon in the lower right corner and click on it with the right mouse click, where you next select Network Management Center and sharing.
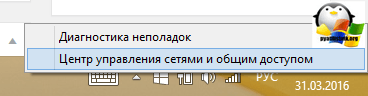
You will open the Network and Sharing Center, where you will next go to Manage wireless networks.
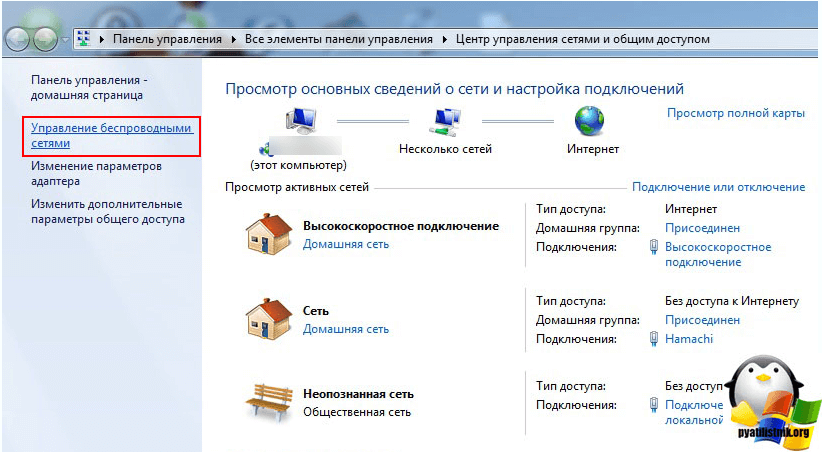
Or in Wireless Network Management, you can immediately get through the WIFI icon, through a left click on it, I specifically showed you both ways so that you know that there are several ways.

As a result, you will see a window of profiles of wireless networks, which you can delete by right-clicking on them. These profiles of wireless networks store the SSID in it, this is the name of the Wifi network and their passwords are also called authentication keys.

Delete the wifi network in Windows 8.1
In Windows 8.1, there is no snap-in Management of wireless networks and the term delete is already replaced by forget, apparently the difficulty of localization. Why there is no standard and convenient window Management of wireless networks, everything is simple in Windows 8.1 came the first test interface METRO for mobile devices and even then Microsoft dreamed of shoveling the interface closer to mobile version and gradually began to do this by transferring some things into the metro interface in Windowx 10, they did it even more proficiently, but not today. The Eight still still remembers the profiles of wireless networks along with SSID and passwords.
And so that in Windows 8 to remove the wireless network, open a window with a list of available by clicking on the WiFi icon in the lower right corner and you will open a sidebar in which you must select the desired network and click on it with the right click, from the context menu, click Forgot this network. Now this is called forgetting, in the place of the usual to remove us, well, God be with them.

In this case, you are behind, only the available networks, but you can look at the list of saved wireless network profiles like this. Press the WIN + I key combination and you will see the All parameters panel, in more detail about the combination, read the hot keys of Windows 8.1. We press change the parameters of the computer.

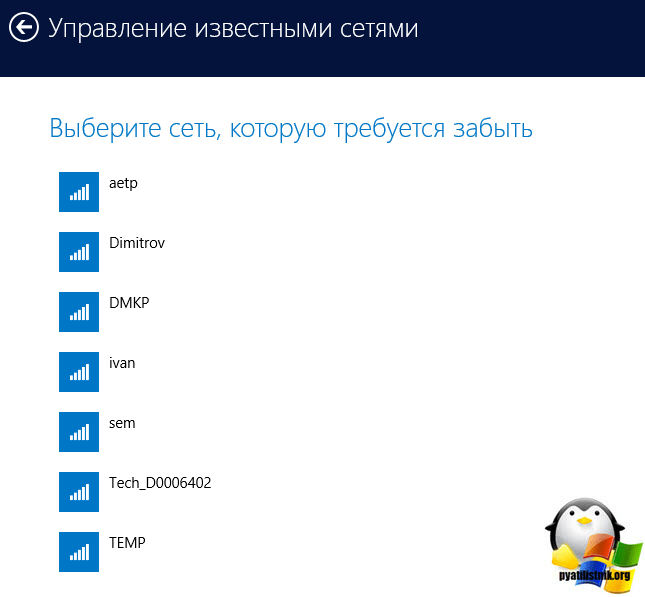
Now, to remove the wireless network, select the network item, click on the Wi-Fi point on the Manage Known Networks

In the Manage Known Networks window, you will find all the Wi-Fi networks known to you
January 30, 2016
How so? How could you forget the password from your own wi-fi ?! Well, nothing happens. I'll help you learn forgotten password from your wireless network, the more it will not be difficult even for a novice user. I hope you managed to connect at least one device to the Wi-fi before you forget the password. If not, it does not matter either. Then the second method from the article will help you (find the forgotten wi-fi password with the help of the router). Or the third - remember the password using the program WirelessKeyView.
How to learn a forgotten wi-fi password from a computer
We go to the computer from which we have already connected to the desired wireless network, to the "Network and Sharing Center". To do this, right-click the wireless network icon in the tray and select "Network and Sharing Center".
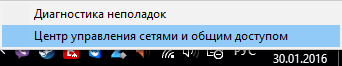
In the next window, select "Manage wireless networks"

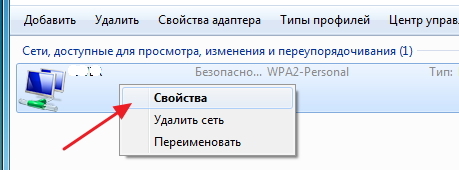
Go to the "Security" tab and tick the "Display input characters" checkbox. In the "Security Key" column, you will see your wi-fi password.

And what if the item "Manage wireless networks" is missing?
If you do not have the "Manage wireless networks" item (for example, in Windows 10) - it does not matter.
Similarly, go to the "Network and Sharing Center".

Click on your wireless network connection, then "Wireless Network Properties", then the "Security" tab. Check the box "Display input characters". In the "Security Key" column, you will see your Wi-fi password.
![]()
Attention! To use this method, you must be connected to the correct wireless network.
If you do not have a device with which you have already connected to the desired wireless network, the following method will help you.
Find the Wi-fi password from the router settings
So, we connect the computer with a cable to the router. Enter the address of the router in the address bar. Most often this is 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1. You can find out the exact address and password for logging into the router's web panel on the label below or on the back of the router (you do not have to use a computer - you can also go to the interface of the router from your smartphone or tablet)
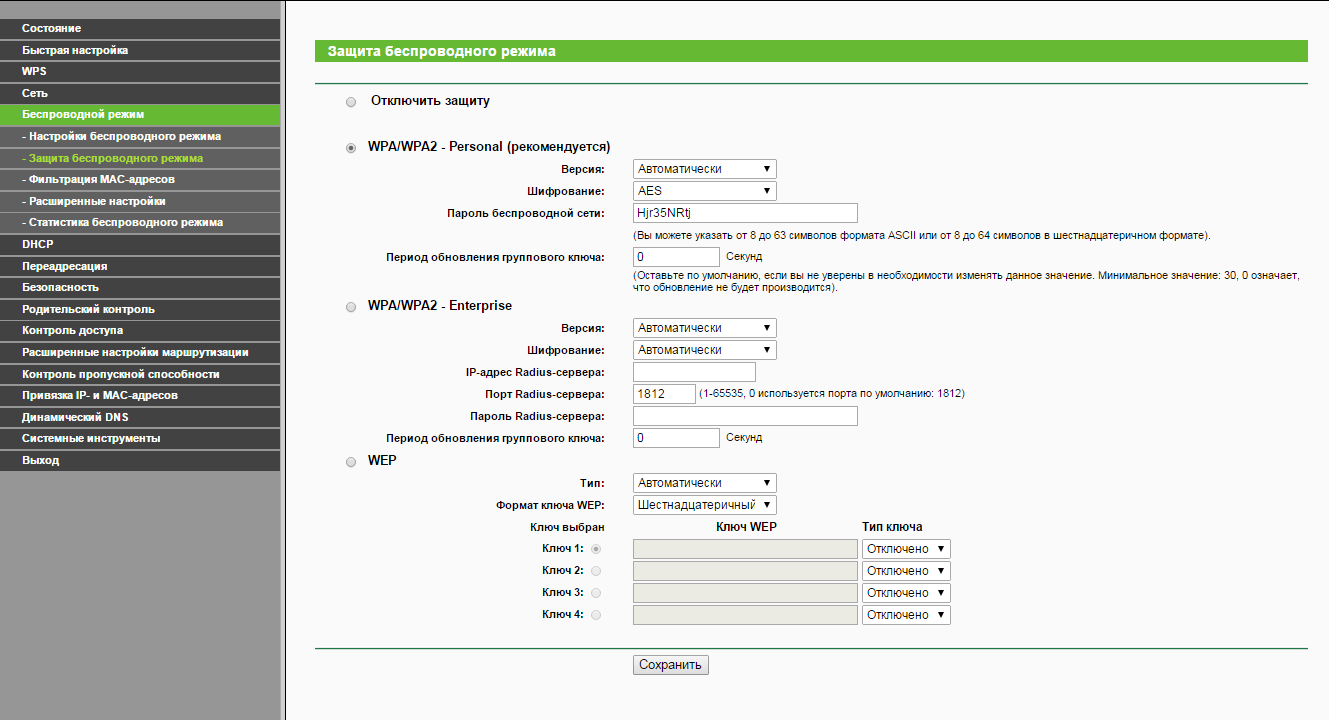
The web panels of the routers differ, but in general the wireless settings are similar. For example, the example of a router TP-Link TL-WR841N / ND.
Select "Wireless mode" - "Wireless security" - "Wireless network password". In this box, you will see your password in clear text.
If not one of the proposed methods did not suit you, then there is one "magic" program that will definitely help you.
Find out the Wi-fi password with WirelessKeyView
The program, through which you can see ALL the passwords stored on the device under Windows management, is called. The program weighs less than 100 kb, does not require installation and works on almost any modern Windows. I personally tested it on Windows 10, 8.1, 7 and XP.
- Download WirelessKeyView from the official site
- Extract files from the archive, run WirelessKeyView.exe
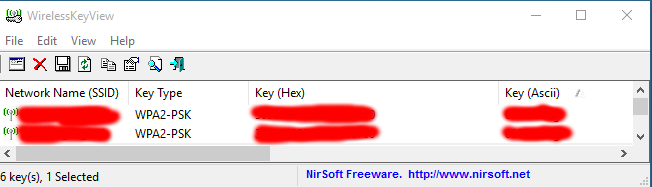
- And we see all the passwords from all the networks stored on the computer (the password from wi-fi will be in the Key column (Ascii)). You can save the necessary passwords in a text file.
As you can see, the method is incredibly simple =)
I hope my article helped you find out your forgotten password from Wi-fi. Write it down and do not forget.
This documentation has been moved to the archive and is not supported.
Cable: Connecting to wireless networks in Windows 7
There are several ways to connect to wireless networks in Windows 7, and each has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Cableman
Now wireless communication is used everywhere. The ability to connect to the network and the Internet everywhere and everywhere has become vital. Windows 7 provides a simplified user interface for working with wireless local networks standard IEEE 802.11.
In Windows 7, there are many ways to create and configure a wireless network connection, which are called wireless network profiles:
- The network connection icon in the notification area is the primary way to connect users to available wireless networks.
- The "Set up a connection or network" dialog box is a way of manually creating user profiles of a wireless network.
- The Manage Wireless Networks dialog box is another way to manually configure wireless networks and specify their exact settings.
- Group Policy - Network administrators can use Group Policy settings in an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) environment to centrally configure and automatically deploy wireless network settings to computers, members of a domain. (See the article under the heading "Cableman" for April 2007)
- Command line - Network administrators can use the netsh wlan context of the Netsh.exe utility to manually configure wireless networks and their settings. There are Netsh commands for exporting existing wireless network profiles to an XML file and then importing the wireless network profile from this file to another computer. (See the section.)
The following sections detail how to connect to a wireless network using the network connection icon in the notification area and the "Configure a connection or network" dialog box in Windows 7, how to manage wireless networks, and how to connect to non-broadcast wireless networks.
Using the network connection icon in the notification area
To connect to an available wireless network, click the network connections icon in the desktop notification area. In the opened panel, a list of detected wireless networks will be presented, and on computers, members of the domain, the names of the wireless networks configured by the Group Policy tool ( fig. 1)
Fig. 1 List available networks
From this panel, you can connect to a wireless network from the list by double-clicking, or by selecting a network, and then clicking the Connect icon, or by right-clicking the network name and selecting context menu Connect.
To view information about wireless networks in the list, hover over the network name. You will see the name of the wireless network, the signal strength, the type of security, the type of connection (802.11b / g / n) and the network ID (SSID). The status of the connected network and its properties or network that is configured through Group Policy can be seen by selecting the command to display the properties of the wireless network in the context menu fig. 2).
To update the list of wireless networks, click the up or down arrow in the upper-right corner of the panel. To disconnect from the wireless network, right-click the network icon and select "Disconnect".
Fig. 2 The Wireless Network Connection Status dialog box.
Dial-up dialog box "Configure a connection or network"
Open this dialog box in Windows 7 ( fig. 3) can be done by selecting the "Set Up a New Connection or Network" link in the "Network and Sharing Center" window.
Fig. 3 Dialog box for setting up a connection or network.
To manually create a wireless network profile, select "Manually connect to a wireless network", and then click "Next". You should see what is shown on the figure 4.
Fig. 4 The page for entering information about the wireless network being added.
Enter information about the wireless network to add:
Network name - enter the name of the wireless network;
Security type - Select the method used to authenticate the wireless network connection from the following options:
- No authentication (Open) (No authentication (Open)) - an open authentication system without encryption;
- WEP is an open authentication system using the Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) protocol;
- WPA2 - personal access via Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2) with a shared key (also known as a passphrase);
- WPA - personal access via Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) with a shared key;
- WPA2 - Enterprise access using WPA2 with IEEE 802.1X authentication;
- WPA - Enterprise access using WPA with IEEE 802.1X authentication;
- 802.1x - IEEE 802.1X authentication with WEP (also known as dynamic WEP).
The choice depends on the capabilities of the wireless network adapter known to Windows. If any authentication type does not appear in the list, you need to check whether the wireless adapter supports this type and whether the latest version of the driver is compatible with Windows 7.
Authentication using a shared key is not listed. Microsoft strongly discourages its use because it provides a low level of security for the wireless network. To configure authentication using a shared key, in this panel, select "Unauthenticated" (Open), and then select "Shared" on the "Security" tab in the wireless network properties (as described later in this section). article).
Encryption type - select the method used to encrypt the data when transmitting over the wireless network. The choice depends on the selected security type.
- If you select the "No authentication" type of security, nothing will be selected;
- when WEP security type is selected, the WEP encryption type will be selected;
- if you select the 802.1x security type, the WEP encryption type will be selected;
- if you select the security type "WPA2-personal", "WPA2-Enterprise", "WPA-personal" or "WPA-enterprise", you can choose the type of encryption - AES or TKIP.
As before, the list of encryption options depends on the capabilities of the wireless network adapter, registered in Windows.
- Security Key - Enter the WEP key (if the WEP security type is selected), the WPA shared key (if the security type is "WPA-personal") or the WPA2 shared key (if the security type is "WPA2-personal"). For security types WPA2-Enterprise, WPA-Enterprise, and 802.1x, Windows 7 automatically detects the security key when performing 802.1X authentication.
- Hide characters - specify whether you want to view the values of the entered security key.
- Start this connection automatically-Specify whether Windows 7 will automatically connect to this wireless network. If you deselect this option, you must manually connect to the wireless network from the list of available networks displayed by clicking the network notification area icon.
- Connect, even if the network does not broadcast (determine if Windows should try to connect, even if the wireless network does not report its name. This will cause Windows to send a trial request frame to discover the wireless network. These test requests can be used by attackers to determine the name of a non-broadcast network. For more information about the privacy issues of the non-broadcast network, see the article.
Fig. 5 Successfully added page.
You can select "Change connection settings" to access the wireless properties page, as described later in this article, or click the "Close" button.
Dialog box for managing wireless networks
Get access to the dialog box "Managing wireless networks" can be accessed through the corresponding link in the "Network and Sharing Center" window ( fig. 6th).
Fig. 6th Dialog box for managing wireless networks.
Note: If the "Network and Sharing Center" does not have the link "Manage wireless networks", click the "Change adapter settings" link and make sure that the laptop or laptop has a wireless network adapter, it is in the " Network connections»(Network Connections) as wireless connection and switched on. If the wireless network adapter appears in the "Network Connections" folder, make sure that you have installed latest version driver that supports Windows 7.
In the Manage Wireless Networks dialog box, you can add a new wireless network, remove the wireless network, access the properties of the wireless network adapter, and select the type of profile for the new wireless networks (applies to all users or the current user).
To manually add a wireless network, click the Add button to open the Wireless Network Connection Wizard, which will help create a profile for a regular wireless network or computer-to-computer network fig. 7th).
Fig. 7th The page for selecting the option of adding a network.
To create a normal wireless network profile, select Manually create a network profile. To create a wireless computer-to-computer network profile, select Create an ad hoc network.
To view or change the properties of a wireless network in the list, double-click its name in the Manage wireless networks dialog box. Windows 7 displays the dialog box shown on the fig. 8.
Fig. 8 The wireless network properties window.
On the Connection tab, you can see the name of the wireless network, SSID, network type (access point or computer-to-computer network), and availability. You can also configure the following properties:
- Connect automatically when the network is in range (Connect automatically when the network is in range)
- Connect to a more suitable network if available - determines whether Windows 7 will automatically disconnect from this wireless network if a more suitable network is available within reach.
- Connect, even if the network does not broadcast its name (SSID) (Connect even if the network is not broadcasting its name (SSID))
Clicking on the link "Copy this network profile to a USB flash drive" will open the Network Settings Copy Wizard, which will write the profile to the media. After that, you can use this device to automate the configuration of the wireless profile on other computers. On Ha fig.9 the Security tab is displayed.
Fig. 9 The Security tab of the Wireless Properties dialog box.
On the Security tab, you can specify the following types of security:
- Without authentication (Open) (No authentication (Open)).
- Shared or Shared key authentication (The "Security" tab is the only place where you can configure a shared key, because its use is highly discouraged.)
- WPA2 is personal.
- WPA is personal.
- WPA2-enterprise.
- WPA is an enterprise.
- The standard is 802.1x.
Depending on the type of security selected, you can either configure the network security key, or you can set and configure how the network is authenticated. If you select "WPA Enterprise", "WPA2 Enterprise" or "802.1x" as the security type, you must perform the following setting (as shown in the previous figure):
- Choose the Choose a network authentication method? Select Select Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) as the authentication method for the network and click the Settings button to configure the EAP type.
- Remember my credentials for this connection every time I log on (indicates my credentials for this connection each time I'm logged on) - indicates that when the user logs out, his credentials are not deleted from the registry. If you uncheck the box, the next time you log in, the user will be prompted for credentials (user name and password).
If you set the security type to be "WPA-personal" or "WPA2-personal", or security without Authentication (Open) or shared authentication with WEP encryption, you must configure the network security key, as shown in fig. 10.
Fig. 10 An example of setting a network security key.
If you choose the security type "WPA-Enterprise", "WPA2-Enterprise" or "WPA2-personal", you can also configure additional parameters. On Ha fig. eleven The "Advanced settings" dialog box for the security type "WPA2-Enterprise" is displayed.
Fig. eleven The tab for configuring 802.1X.
On the "802.1X settings" tab, you can specify the authentication mode ("user or computer", "computer", "user" or "anonymous user"), save a set of credentials for user authentication, and delete credentials all users.
Single Sign-On (SSO) allows you to configure 802.1X authentication when a user logs on and integrates the user logon and 802.1X user verification data in the Windows logon window. For more information on SSO parameters, see the article published in the "Cableman" column in April 2007. fig. 12 A tab for configuring 802.11 is shown.
Fig. 12 The 802.11 configuration tab.
In the "Quick Move" section, you can configure the Pairwise Master Key (PKM) caching parameters and pre-authentication. For more information about the quick navigation settings, see the article published in the "Cableman" column in April 2007.
Note: if you select the security type "WPA-Enterprise" in the dialog box additional parameters 802.11 there is no "Settings" tab.
The Enable Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) compatibility for this network check box allows you to specify whether to perform AES encryption in the FIPS 140-2 authentication mode. The FIPS 140-2 standard is a state standard of computer security in the US, which defines the requirements for the development and implementation of cryptographic modules. Windows 7 is FIPS 140-2 certified. When the FIPS 140-2 verification mode is enabled, Windows 7 performs AES encryption programmatically, rather than relying on the wireless network adapter. This flag appears only when you select the authentication method "WPA2-Enterprise" or "WPA2-personal" in the "Security" tab.
Non-broadcast wireless networks
Non-broadcast wireless networks do not transmit their network name, or SSID. You can configure the non-broadcast wireless network access point to send a signal frame with SSID equal to NULL to send. Non-broadcast wireless networks are also called hidden wireless networks.
In Windows 7, wireless networks can be configured as broadcast or non-broadcast. A computer running Windows 7 will try to connect to the wireless network in the order of the list of preferred networks, regardless of which of the two types they are related to. In addition, non-broadcast networks are displayed last in the list of available networks under the name "Other Networks" (Other Network). On fig. 13 an example is given.
Fig. 13 Non-broadcast wireless network.
When you connect to such a network, Windows 7 prompts you to enter the name of the wireless network (SSID). On fig. 14 an example is given.
Fig. 14. Enter the name of the non-broadcast wireless network.
Joseph Davies - leading technical writer in a group of technical writers on the topic windows Networks in Microsoft. He is the author and co-author of several books published by Microsoft Press, including "Windows Server 2008 Networking and Network Access Protection (NAP)", "Understanding IPv6, Second Edition" and "Windows Server 2008 TCP / IP Protocols and Services" ..
- Webpage
- To go to the articles list of the "Cableman" rubric, click.
You can access the "Manage wireless networks" dialog box by clicking the appropriate link in the "Network and Sharing Center" window (Figure 6).
Fig. 6 Dialog box for managing wireless networks.
Note: If the "Network and Sharing Center" does not have the link "Manage wireless networks", click the "Change adapter settings" link and make sure that the laptop or laptop has a wireless network adapter, it is in the "Network Connections" folder as a wireless connection and switched on. If the wireless network adapter appears in the Network Connections folder, make sure that you installed the latest version of the driver that supports Windows 7.
In the Manage Wireless Networks dialog box, you can add a new wireless network, remove the wireless network, access the properties of the wireless network adapter, and select the type of profile for the new wireless networks (applies to all users or the current user).
To manually add a wireless network, click the Add button. A wizard for connecting to a wireless network will open, which will help create a profile of a regular wireless network or computer-to-computer network. Fig. 7).

Fig. 7 The page for selecting the option of adding a network.
To create a normal wireless network profile, select Manually create a network profile. To create a wireless computer-to-computer network profile, select Create an ad hoc network.
To view or change the properties of a wireless network in the list, double-click its name in the Manage wireless networks dialog box. Windows 7 displays the dialog box shown in Fig. 8.
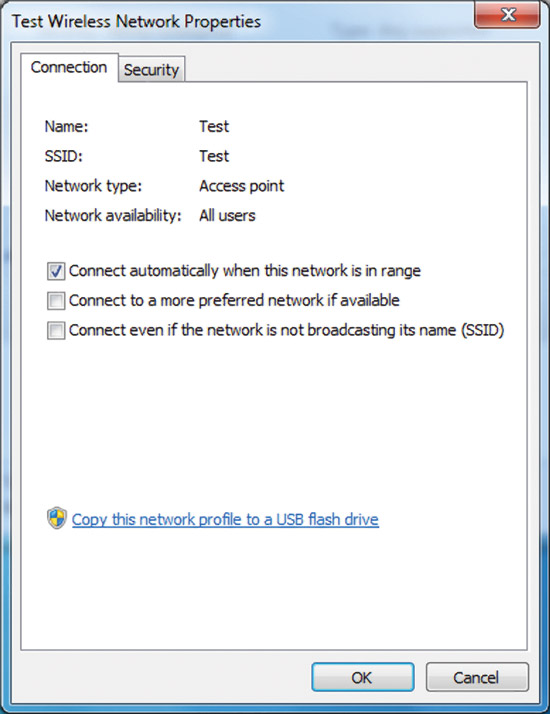
Fig. 8 Wireless Network Properties Window.
On the Connection tab, you can see the name of the wireless network, SSID, network type (access point or computer-to-computer network), and availability. You can also configure the following properties:
- Connect automatically when the network is in range (Connect automatically when the network is in range);
- Connect to a more suitable network if available - determines whether Windows 7 will automatically disconnect from this wireless network if a more suitable network is available within reach;
- Connect, even if the network does not broadcast its name (SSID) (Connect even if the network is not broadcasting its name (SSID)).
Clicking on the link "Copy this network profile to a USB flash drive" will open the Network Settings Copy Wizard, which will write the profile to the media. After that, you can use this device to automate the configuration of the wireless profile on other computers. The Figure 9 shows the Security tab.
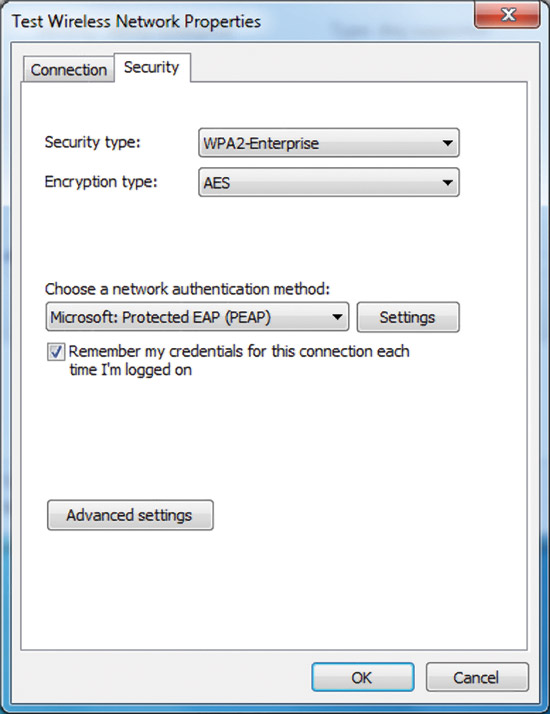
Fig. 9 The Security tab of the Wireless Network Properties dialog box.
On the Security tab, you can specify the following types of security:
- Without authentication (Open) (No authentication (Open));
- Shared or Shared key authentication (the "Security" tab is the only place where you can configure a shared key, because its use is highly discouraged);
- WPA2-personal;
- WPA- personal;
- WPA2-enterprise;
- WPA-enterprise;
- The standard is 802.1x.
Depending on the type of security selected, you can either configure the network security key, or you can set and configure how the network is authenticated. If you select "WPA Enterprise", "WPA2 Enterprise" or "802.1x" as the protection type, you need to perform the following configuration (as shown in the previous figure):
- Choose the Choose a network authentication method? Select Select Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) as the authentication method for the network and click the Settings button to configure the EAP type;
- Remember my credentials for this connection every time I log on (indicates my credentials for this connection each time I'm logged on) - indicates that when the user logs out, his credentials are not deleted from the registry. If you uncheck the box, the next time you log in, the user will be prompted for credentials (user name and password).
If you set the security type to be "WPA-personal" or "WPA2-personal", or security without authentication (Open) or shared authentication with WEP encryption, you must configure the network security key, as shown in Fig. 10.

Fig. 10 Example of setting a network security key.
If you choose the security type "WPA-Enterprise", "WPA2-Enterprise" or "WPA2-personal", you can also configure additional parameters. In Fig. Figure 11 shows the Advanced settings dialog box for the security type WPA2-Enterprise.

Fig. 11 The tab for configuring 802.1X.
On the "802.1X settings" tab, you can specify the authentication mode ("user or computer", "computer", "user" or "anonymous user"), save a set of credentials for user authentication, and delete credentials all users.
Single Sign-On (SSO) allows you to configure 802.1X authentication when a user logs on and integrates the user logon and 802.1X user verification data in the Windows logon window. For more information about SSO settings, see the Wireless Group Policy Settings for Windows Vista, published in the section "Cableman" in April 2007. Fig. Figure 12 shows the tab for configuring 802.11.
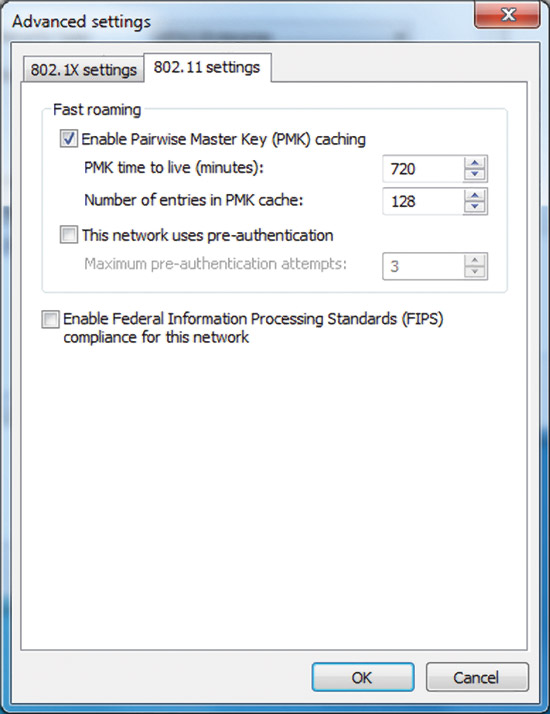
Fig. 12 The 802.11 Settings Tab.
In the "Quick Move" section, you can configure the Pairwise Master Key (PKM) caching parameters and pre-authentication. For more information about the quick navigation settings, see the article "Wireless Communication Group Policy settings in Windows Vista," under the "Cableman" rubric in April 2007.
Note: when you select the security type "WPA-Enterprise" in the Advanced 802.11 Options dialog box, there is no "Settings" tab.
The Enable Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) compatibility for this network check box allows you to specify whether to perform AES encryption in the FIPS 140-2 authentication mode. The FIPS 140-2 standard is a state standard of computer security in the US, which defines the requirements for the development and implementation of cryptographic modules. Windows 7 is FIPS 140-2 certified. When the FIPS 140-2 verification mode is enabled, Windows 7 performs AES encryption programmatically, rather than relying on the wireless network adapter. This flag appears only when you select the authentication method "WPA2-Enterprise" or "WPA2-personal" in the "Security" tab.
Non-broadcast wireless networks
Non-broadcast wireless networks do not transmit their network name, or SSID. You can configure the non-broadcast wireless network access point to send a signal frame with SSID equal to NULL to send. Non-broadcast wireless networks are also called hidden wireless networks.
In Windows 7, wireless networks can be configured as broadcast or non-broadcast. A computer running Windows 7 will try to connect to the wireless network in the order of the list of preferred networks, regardless of which of the two types they are related to. In addition, non-broadcast networks are displayed last in the list of available networks under the name "Other Networks" (Other Network). In Fig. 13 shows an example.
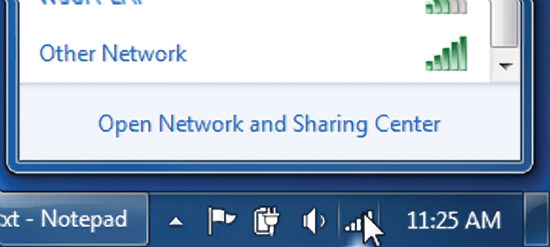
Fig. 13 Non-broadcast wireless network.
When you connect to such a network, Windows 7 prompts you to enter the name of the wireless network (SSID). In Fig. 14 shows an example.

Fig. 14. Enter the name of the non-broadcast wireless network.
Joseph Davies (Joseph Davies) is a leading technical writer in the team of technical writers on Windows networking in Microsoft. He is the author and co-author of several books published by Microsoft Press, including "Windows Server 2008 Networking and Network Access Protection (NAP)", "Understanding IPv6, Second Edition" and "Windows Server 2008 TCP / IP Protocols and Services" .