At the time of its appearance on the market in early 2008, the graphics accelerator model GeForce 9600 from NVidia belonged to the middle class solutions and allowed solving most of the tasks. Moreover, the use of the most advanced technological process significantly reduced its energy consumption. Well, the cost of such adapters was quite affordable and allowed them to be used as part of computing systems average level.
Accelerator niche
At the beginning of 2008, NVidia's graphics accelerators were distributed as follows:
The 8600 GT belonged to the entry-class solutions. Very modest specifications and very low clock speeds provided the minimum acceptable performance level. Moreover, the cost of such video cards ranged from $ 100 to $ 120.
The middle class solutions included 8800GT, 8800GTS and GeForce 9600 with a GT prefix. These adapters had fairly similar characteristics and cost, but the use of improved production technology and increased clock frequencies allowed the solution in question to outperform its competitors without any problems.
The flagship accelerator was the 8800 Ultra. The solutions of the middle class could not make it worthy of competition, but its cost was significantly higher.
Equipment
In this case, NVidia included the following in the package:
Graphics adapter.
Warranty card.
The CD on which the entire necessary software and electronic documentation.
User guide.
DVI TO HDMI adapter.
A special adapter for organizing power supply of the accelerator through an additional 6-pin connector.

Chip specifications
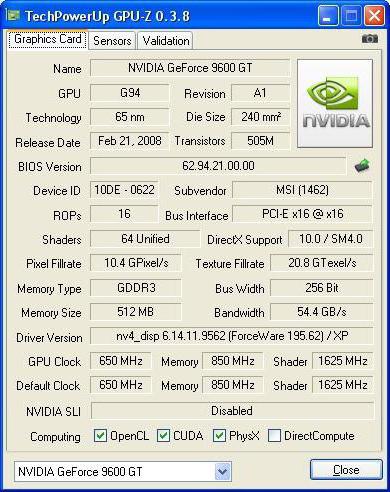
G94 is the codename for the graphics chip that underlies the GeForce 9600. Its specifications indicate that it included 505 million transistor components. The clock frequency of this semiconductor element was 650 MHz, and it was manufactured according to the standards of the 65-nm process technology. Its predecessors, the 8XXX series, in turn, were produced at 80 nm and had the worst characteristics in terms of energy efficiency. The number of shader processing units was 64, and their frequency in the nominal mode was equal to 1625 MHz. There were only 16 rasterization modules included in the adapter, and the number of TMUs for each pipeline was 32.
Memory
The only type of memory in conjunction with which the graphics accelerator in question could work is GDDR3. The nominal effective frequency of the microcircuits was equal to 1800 MHz. The video buffer size could be 512 MB or 1 GB. Width of the connection bus random access memory to the GPU was 256 bits. All of the above made it possible to obtain throughput at the level of 57.6 GB / s.
Communications
GeForce 9600 adapter plugs into an expansion slot PCI Express performed by 16X. In the basic version, such an adapter should be equipped with two digital DVI ports. But also some manufacturers could complement them with analog VGA or digital HDMI. Therefore, the equipment in terms of ports depends on specific model, and this nuance must be taken into account before buying.
Energy consumption. Temperature regime
Application advanced technology production of the semiconductor base of the processor allowed to significantly reduce the level of power consumption. The NVidia GeForce 9600 GT video card has a thermal package of 95 W. Of course, this number does not fit into the recommended 75 W, sufficient for the video subsystem to operate without additional power supply, but for graphics solutions of this class, such a power supply is typical. The maximum temperature for this product is set by the manufacturer at 105 0 C. normal operation this value does not exceed 60 0 С, in the overclocking mode and when solving the most demanding tasks it can rise to 75 0 С.

Tests. Comparison with analogues
The video card GeForce 9600 is a mid-range solution, and it is most rational to compare it with similar solutions. Since direct competitors from AMD were produced according to an outdated technical process at that time, it is impractical to compare them with 9600 GT for the reason that with comparable speed, their power consumption will be much higher. From the list of NVidia this adapter can only be compared with the 8800 GTS and 8800 GT. The test bench was based on the P35 system logic set, the RAM was of the DDR2 standard with a frequency of 800 MHz, and its volume was 2 GB (2 modules of 1 GB each for the RAM controller to function in dual-channel mode, due to this, a performance increase of about 10-15%). In the synthetic 3DMark06 test, the adapters scored the following conditional points in the 1600x1200 mode:
Most likely at the time of the this test the full optimization of the drivers was not carried out, and the indicators of the later video card were slightly underestimated because of this. On the other hand, the difference is not that big between them. The balance of power in Gears Of War is changing dramatically. In this case, we get this number of fps at 1280x1024:
The difference, of course, of one frame per second is not that big, but it still makes the more recent accelerator the leader in this test. Previous results indicate that the 9600 GT hides a slightly modified 8800 GT, which is made using a new process technology. The difference between these video cards is minimal. Moreover, in some cases, a representative of an earlier generation bypasses its updated modification.

The cost
At the very beginning of sales, NVidia GeForce 9600 could be purchased at a price of $ 150-170. Given the positioning and technical specifications, this approach to pricing was justified. Now such an accelerator can be purchased at prices ranging from 1,500 (used solutions) to 3,000 (brand new accelerators) rubles. Buying such an adapter for a new PC is now impractical. The new integrated video accelerators offer the same level of performance and there is no need to purchase them separately. But for repairing an old PC, such an accelerator can still be bought.
Dominance in the segment of high-performance solutions is good, but the majority of video cards are sold in another segment, which is called "mass". It is commonly said that this niche covers a range of offerings from $ 149 to $ 249 and should provide the buyer with something alternative, not the most productive, but providing acceptable speed in all modern games at an affordable price. Not so long ago, video cards based on the GeForce 8600GTS felt good enough in this niche, perhaps not as fast as we wanted, being only a small part of the flagship GeForce 8800GTX, but in many ways surpassing the offerings from AMD in the face of ATI Radeon HD2600XT. But after the competitor released new accelerators radeon series HD3800 and the gradual decline in prices for them, the alignment of forces changed and it was necessary to look for a way out, i.e. create equal or superior offers.
|
NVIDIA GeForce 8800 GS 384Mb |
NVIDIA GeForce 9600 GT 512Mb |
NVIDIA GeForce 8800 GT 512Mb |
ATI Radeon HD 3870 512Mb |
ATI Radeon HD 3850 256Mb |
|
|
Transistors, mln. |
|||||
|
Technological process, nm |
|||||
|
Core frequency, MHz |
|||||
|
Stream Processors |
|||||
|
Shader unit frequency, MHz |
|||||
|
Texture Mapping Units (TMU) and / or Texture Filtering (TF) |
|||||
|
Raster Operator units (ROP) |
|||||
|
Memory frequency (type), MHz |
|||||
|
Memory bus, bit |
|||||
|
Memory bandwidth, GB / s |
|||||
|
Interface |
PCIe ver 2.0 x16 |
PCIe ver 2.0 x16 |
PCIe ver 2.0 x16 |
PCIe ver 2.0 x16 |
PCIe ver 2.0 x16 |
|
Multi GPU support |
|||||
|
HDCP support |
|||||
|
Power consumption, (up to) W |
|||||
The first step towards regaining leadership in the mass segment was the release of the GeForce 8800GS, the performance of which we examined quite recently. But this GPU has only become a good competitor, both in cost and in features, to the Radeon HD3850. It turned out to be difficult for him to compete with the Radeon HD3870 due to noticeable architectural cuts, such as a decrease in the number of execution units, and most importantly, the amount of video memory and the width of the access bus. And with the help of the GeForce 8800GT, it turned out to be difficult to compete with the Radeon HD3870 - the 512 MB version is, of course, more productive, but noticeably more expensive, and the 256 MB version does not have enough video memory in heavy tasks and it loses in them. This state of affairs was the reason for the release of a new graphics processor, which should become a more profitable option both in terms of price and performance.
What is so revolutionary about the G94-300 (D9P by new system that this GPU is the firstborn of NVIDIA's new 9-series GPUs? Let's start with the fact that further "processing" of the G92 chip has lost its meaning - disabling an even larger number of execution units will make it even slower at the same cost of production, and returning the deactivated units to work will return the performance of the GeForce 8800 GT to the chip at, again, its rather high cost ... In such a situation, there is only one way out - to make a new chip, which initially has a smaller number of elements and, accordingly, a smaller die area, which will reduce the cost and power consumption, and will create the basis for further improving the architecture and increasing operating frequencies. And everything would be fine, even there is a “niche of names” for it, you can use an unoccupied GeForce 8700, but then one problem appears - the new chip is designed as a competitor to the Radeon HD3870, i.e. it should be faster than GeForce 8800GS. And this leads to a conflict of models in the series. There is only one way out - GeForce 9 Series.
Thus, GeForce appeared not so much thanks to some revolutionary architectural innovations, but more as a forced marketing step, which provides an opportunity for all future innovations to give logical names, in accordance with the level of performance. Therefore, architecturally, the GeForce 9600 GT is more reminiscent of the mainstream of the previous generation GeForce 8600GTS, for which the number of execution units has been doubled than the cut-down GeForce 8800GT.
G94 diagram (GeForce 9600 Series), iXBT.com
On the other hand, it is not only the increase in the number of execution units that distinguishes the GeForce 9 series from the 8 series. So, in comparison with the GeForce 8600, first of all, the manufacturing process has been changed - now it is 65 nm. In addition, a 256-bit memory bus has finally appeared in mainstream video cards, which, together with 512 MB of video memory, will be very useful when launching modern games. But there are changes in comparison with GeForce 8800GT / GS (NVIDIA G92):
In the block of raster operations ( ROP) improved color information compression technology, which has now become 15% more efficient... This to some extent makes the new architecture more productive, although quite a bit - according to various estimates, no more than 5% equal frequencies under equal conditions. In fact, this is the only noticeable architectural change related to performance improvements in GPU nodes.
Added "native" support the latest interface for connecting monitors DisplayPort... Now this output can be implemented without any additional transmitters, but due to the still rare prevalence of this interface, most video cards will be equipped with the usual Dual-Link DVI-I, and DisplayPort can be obtained using an adapter.
When several GeForce accelerators are combined into an SLI configuration, new motherboards with NVIDA chipsets will have support technology HybridPower, which will allow you to manage the power consumption of the entire video system, up to the complete shutdown of unused video cards.
By the release of GeForce, changes were made to the work PureVideo HD, but they are not hardware, but are driver modifications ForceWare 174.xx, therefore, will be supported by other chips (G84 / G92). Introduced: dual-stream decoding, which can be useful when watching some Blu-Ray discs; dynamic change contrast and color saturation; the ability without disabling hardware acceleration of video viewing in windowed mode of the Aero interface under Windows Vista.
GV-NX96T512H
The first video card on GeForce, which came to us for testing, was an offer from model number GV-NX96T512H. This video card does not differ from the reference in anything except stickers, which makes it very good option to get acquainted with the novelty.

Let's start with brief description video cards:
| Model | GV-NX96T512H |
| Graphics core | NVIDIA GeForce 9600 GT (G94-300) |
| Conveyor | 64 unified |
| Supported APIs | DirectX 10.0 OpenGL 2.0 |
| Core (shader domain) frequency, MHz | 650 (1625) |
| Amount (type) of memory, MB | 512 (GDDR3) |
| Real (effective) memory frequency, MHz | 900 (1800 DDR) |
| Memory bus | 256 bit |
| Tire standard | PCI Express 2.0 X16 |
| Maximum resolution | Up to 2560 × 1600 (Dual-link DVI) or 1920 × 1200 (Single-link DVI) Up to 2048 × 1536 (VGA) |
| Outputs | 2x DVI-I (VGA only via adapter) TV-Out (HDTV, S-Video and Composite) |
| HDCP support HD video decoding |
there is H.264, VC-1, MPEG2 and WMV9 |
| Drivers | The latest drivers can be downloaded from: - site of the video card manufacturer; - GPU manufacturer's website. |
| Products webpage | http://www.gigabyte.com.tw/ |


The GV-NX96T512H graphics card arrives in a medium-sized double cardboard box. The design of the packaging is made in the corporate style and is quite informative, although without specifying many exact characteristics (although this defect is compensated for in the user manual).

The delivery set, one might say, includes only the most necessary things:
- Power adapter from peripheral connectors to 6-pin PCI Express;
- 2 adapters from VGA to DVI;
- Combined Component S-Video and HDTV-Out;
- User manual for quick installation video cards, plus an illustrated poster;
- CD-ROM with drivers and utilities.

The user manual turned out to be quite informative, albeit somewhat generalized. It specifies the minimum system requirements (from 128 MB of RAM and a 450 W power supply), the purpose of the outputs of the video card and TV adapter, as well as explanations on the process of installing a video card in the case and settings software... Interestingly, for the SLI configuration, the manufacturer suggests using a 1000W power supply.

As noted above, the video card has a completely reference design, which is easily determined by appearance cooling system that covers the entire front part.

Only the 6-pin connector is visible from under the cooler cover additional foodparallel to the plane of the PCB. But, since the dimensions of the card are not very large, such an arrangement of the connector will not cause problems, even in rather compact cases.

![]()
The printed circuit board itself is completely filled with elements, i.e. it implements all the functions and nodes that were originally laid down. At the same time, we draw your attention to the fact that PCB does not imply installation hDMI outputs or DisplayPort, although the latter is one of key features series.

But through adapters, the new interfaces should work, since there is an SPDIF input at the top of the card, which is designed to add multi-channel audio processed sound card, to the video data.

It remains only to sound the standard set of interface connectors: two DVI, converted to VGA, HDMI and DisplayPort using adapters, and one universal TV output, converted through an adapter to S-Video and HDTV component-wise.
![]()
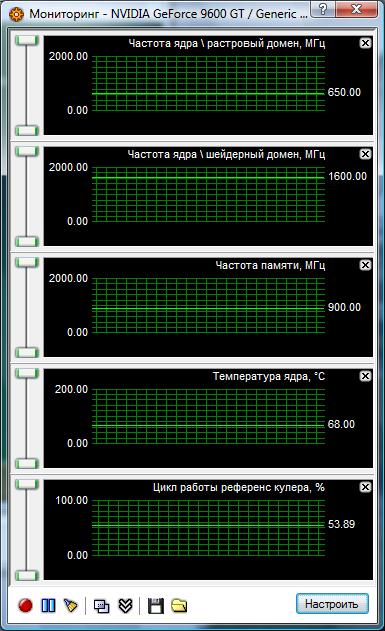
Now let's talk about the "stock" cooling system. Its positive properties are sufficient efficiency with a low noise level and relative compactness, since it only takes up one slot. This combination of properties is achieved due to the use of three flattened copper heat pipes for fast energy dissipation, and an aluminum radiator that is blown by a turbine for heat dissipation. Through the holes behind the turbine, air enters the printed circuit board... But there is a drawback in this design - the heated air remains in the case, and is blown out under the video card and is very likely to be re-captured for cooling. Therefore, even at nominal frequencies, the GPU warmed up to 68 ° C, but the turbine was only spinning up by 54%, and the cooler continued to run quietly.

The graphics processor NVIDIA GeForce 9600 GT (G94-300 or D9P) has a die that is not covered by a heat-distributing cover and rotated 45 ° relative to the substrate, which is made to simplify wiring. In its arsenal, this GPU has 64 unified processors, 32 texture units and 16 ROPs. The GeForce works at 650/1625 MHz for the raster and shader units, respectively. A 256-bit bus is used to exchange data with video memory.

The video memory itself is filled with eight GDDR3 Samsung K4J52324QE-BJ1A chips, which have a response time of 1.0 ns and are designed to operate at an effective frequency of 2000 MHz DDR, but work on the video card a little slower, at the recommended frequency of 1800 MHz. Thus, there is hope, with the help of overclocking, to run them at the nominal frequency, and if you are lucky, even faster.
Testing
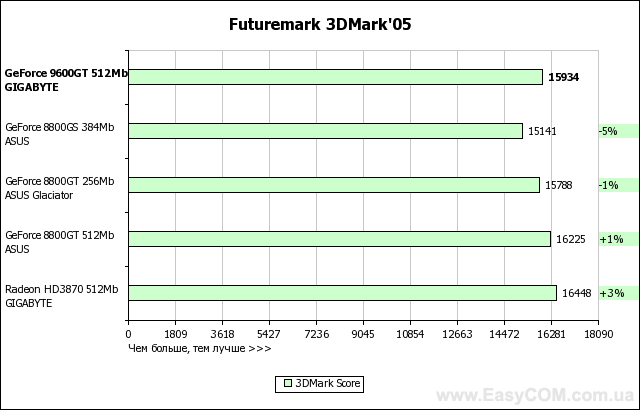
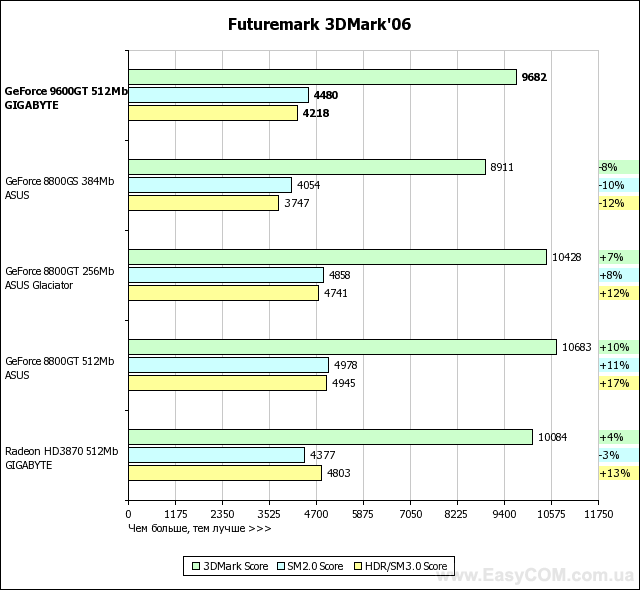
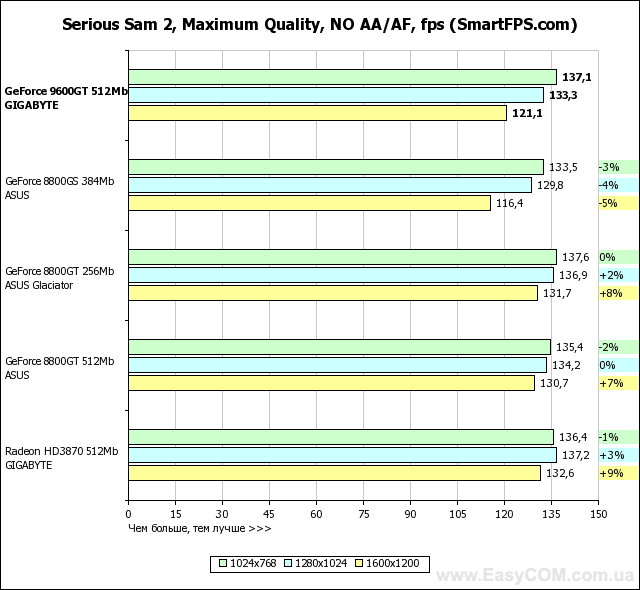
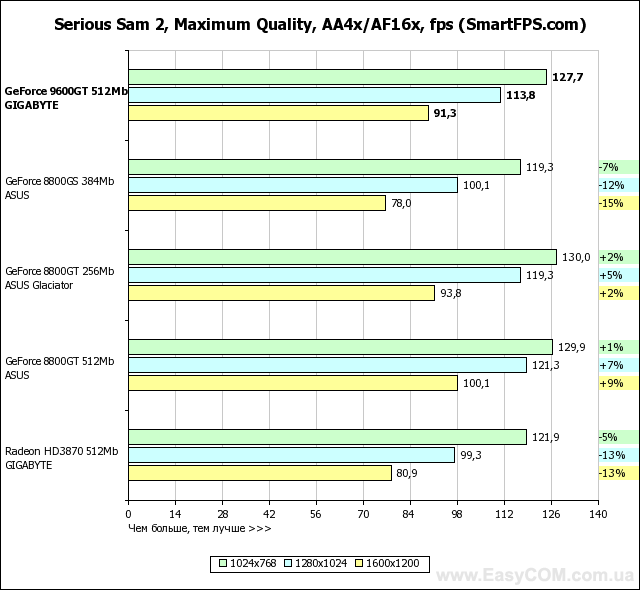
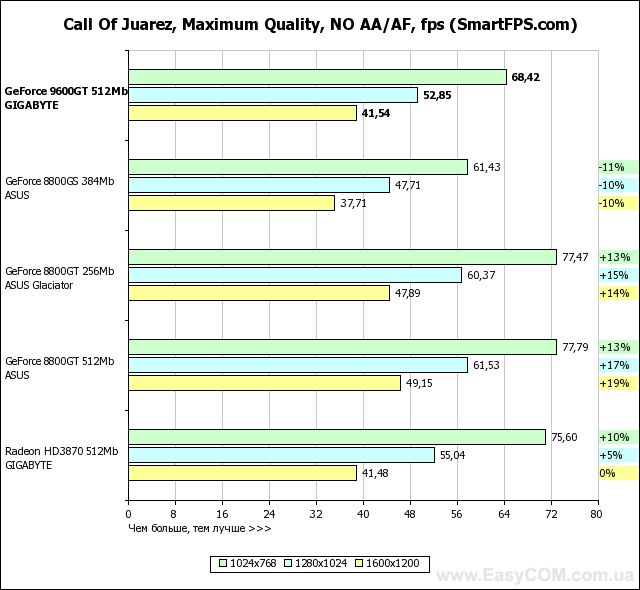
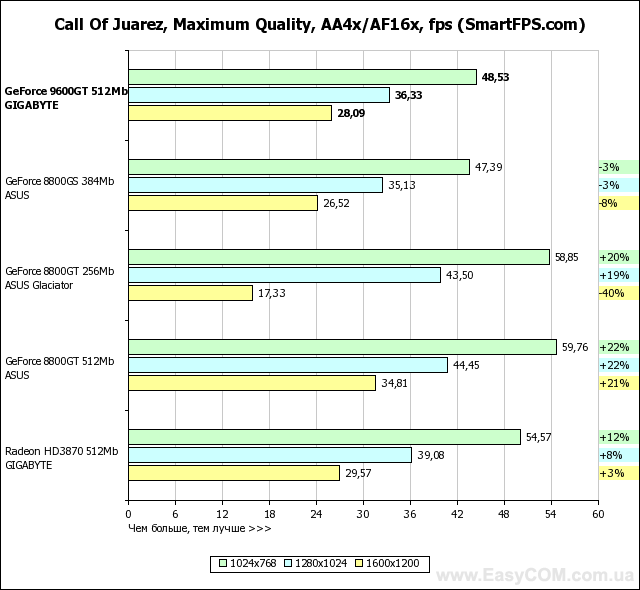
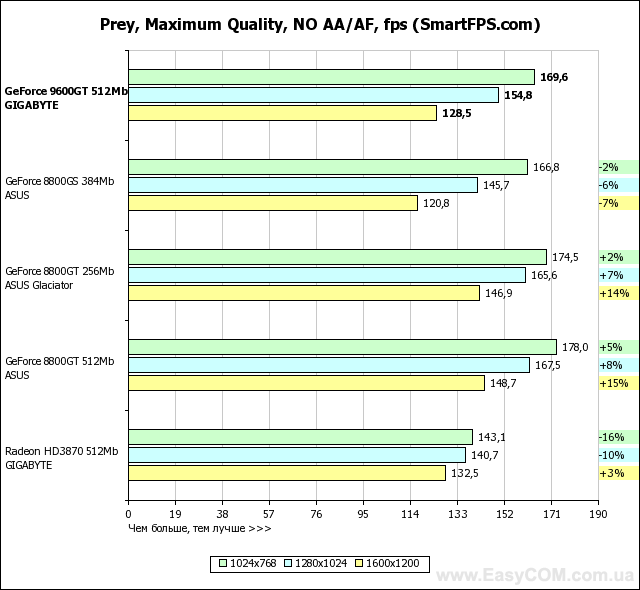
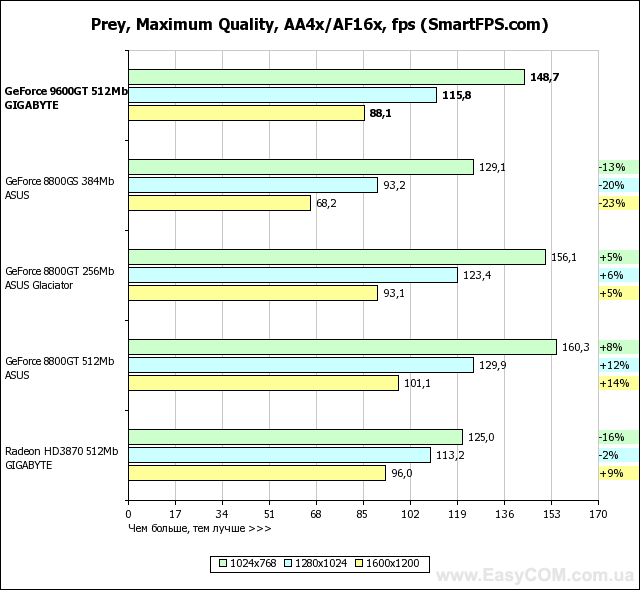
In terms of performance, solutions based on an NVIDIA GeForce graphics processor fully justify both their recommended price and positioning, in most tasks reaching the level of the Radeon HD3870, and in some places even surpassing. At the same time, the heavily "cut" G92 represented by the GeForce 8800GS, despite the larger number of pipelines, is defeated. And even the 256 MB version of the GeForce 8800GT turns out to be slower in applications that are very demanding on the amount of video memory. Considering the level of performance achieved by a well-balanced architecture, GeForce graphics cards have every chance of becoming successful hits, especially when the price of them drops to the level suggested by the developer.
Overclocking
The latest version of RivaTuner works great with GeForce and makes it easy to overclock them. We managed to overclock this graphics processor up to 780/1950 MHz in the raster and shader domains, respectively, and the video memory was able to significantly exceed the nominal value and worked stably at 2240 MHz. Thus, overclocking for GPU was 20%, and for video memory - 24.4%.
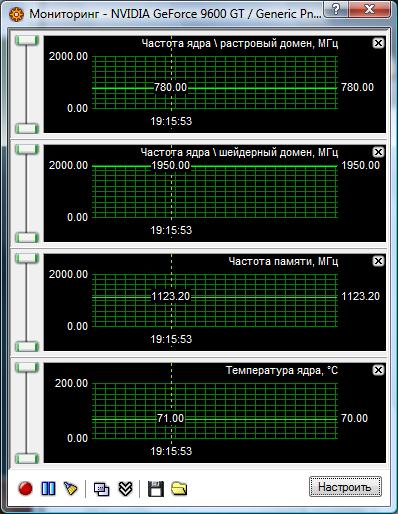
With such acceleration of the GPU and video memory, you can count on a noticeable increase in performance:
|
Test package |
Standard frequencies |
Overclocked graphics card |
Increase in productivity,% |
|
| Futuremark 3DMark'05 | ||||
|
Futuremark 3DMark'06 |
3DMark Score | |||
| SM2.0 Score | ||||
| HDR / SM3.0 Score | ||||
|
Serious Sam 2, Maximum Quality, NO AA / AF, fps |
1024 × 768 | |||
| 1280 × 1024 | ||||
| 1600 × 1200 | ||||
|
Serious Sam 2, Maximum Quality, AA4x / AF16x, fps |
1024 × 768 | |||
| 1280 × 1024 | ||||
| 1600 × 1200 | ||||
|
Call Of Juarez, Maximum Quality, NO AA / AF, fps |
1024 × 768 | |||
| 1280 × 1024 | ||||
| 1600 × 1200 | ||||
|
Call Of Juarez, Maximum Quality, AA4x / AF16x, fps |
1024 × 768 | |||
| 1280 × 1024 | ||||
| 1600 × 1200 | ||||
|
Prey, Maximum Quality, NO AA / AF, fps |
1024 × 768 | |||
| 1280 × 1024 | ||||
| 1600 × 1200 | ||||
|
Prey, Maximum Quality, AA4x / AF16x, fps |
1024 × 768 | |||
| 1280 × 1024 | ||||
| 1600 × 1200 | ||||
|
Crysis, Maximum Quality, NO AA / AF, fps |
1024 × 768 | |||
| 1280 × 1024 | ||||
| 1600 × 1200 | ||||
|
Crysis, Maximum Quality, AA4x / AF16x, fps |
1024 × 768 | |||
| 1280 × 1024 | ||||
| 1600 × 1200 | ||||
We think that additional "free" 10-20% of performance will always be a pleasant bonus and will never be superfluous, so we wish you to get the same overclocking result or even better.
Outcome
Well, the new series of NVIDIA GeForce GPUs brings us new "standard" specifications for a mainstream accelerator. Now 512 MB of video memory and a 256-bit bus of access to it become an integral part of video cards in the midle-end segment. At the same time, the GeForce has more execution units that operate at a higher frequency, which provides a noticeable increase in performance, raising it to a level sufficient for modern games. Although, on the other hand, there is nothing revolutionary in the architecture of this GPU, even DirectX 10.1 support is not implemented.
GeForce 9600 - a video card of the middle price segment from the Californian by Nvidia... In this article, we will analyze all the pros and cons of this chip, find out if its cost is justified, and also conduct some tests that will help determine the performance and stability of the chipset.
How did the card come about?
In 2008, AMD presented the 3800 series, which occupied the niche of middle-end video cards. For a low cost, the customer received excellent performance. AMD had no competitor in this category. Nvidia is thinking about creating a mid-range graphics card with good performance in order to take a share of the market from a competitive company.
An attempt to drive the weakened flagship 8800 GT by reducing the video memory failed. The prime cost of such boards is quite high, which in the end gave too little profit from one video card.
The company's engineers decided to create a perfect new platform G94, on which the GeForce 9600 was created. Let's see if the company's decision was justified, or did Nvidia deceive themselves, as in the case of the "lightweight" 8800? First, let's take a look at the characteristics.
GeForce 9600: specifications
The basis for the video card is the new G94 architecture, which is a direct heir to the 8800 series platform. In terms of architecture, this chipset stands between the middle 8600 and the older 8800. The number of stream processors is twice as much as in the first, but less than in the second.
The new technology made it possible to keep the bus width at 256 bits and thus keep the performance on good level... In terms of characteristics, the video card is barely inferior to the flagship. Its bandwidth has been increased by 15% compared to the previous generation. Simplification of the architecture made it possible to save on the production of the video card.

GeForce 9600 supports all known interfaces that were relevant at the time of the board's release. DirectX9 and DirectX10 are also present. The card connects to motherboard through an absolutely standard PCI Express 16 slot. The amount of built-in memory is 512 MB. 9600 is updated to this day, and the videocard supports the most latest versions, which is a big plus for the owners of these boards.
Video card package
The standard version of the chipset includes a very common set of everything you need. In addition to the board itself, the box contains adapters for various interfaces, a CD with drivers, instructions and warranty card on GeForce 9600 GT. Reviews of the video card are very positive. For modest money, no one demanded a rich set for this "hardware".
Appearance
For its cost, the video card equipment looks quite rich. The small board is cooled in the form of a single cooler and heatsink. From above, all this is covered with a plastic case. Looks expensive and stylish. One question remains: how will the GeForce 9600 actually behave?

Testing and results
To conduct tests in the 3DMark application and the games that were relevant at that time, a test bench was assembled with a special configuration. The basis was taken from MSI, which will withstand the most severe stress during testing. Processor from intel (Core 2 Duo dual-core with a frequency of 2.9 GHz for each core) was also not chosen by chance for testing the GeForce 9600 GT. Reviews show that video cards from Nvidia reveal their potential 100% precisely with intel processors, not AMD. The power supply in the computer is set at 750 W.
Competitors
Let's compare our subject with two competitive video cards from AMD. These are the HD 3850 and 3870. Both boards are priced under $ 200. All 3 video cards are built on approximately the same architecture, each of them is 512 MB.
The first test was the 3DMArk application. In it, the tested video card is slightly inferior to the competitor HD 3870, but remains on par with the 3850 video card. Then there are tests in games relevant in 2008 - Prey, Crysis, Company of Heroes and the classic Serious Sam 2. 
The first two games are a real challenge for most graphics cards. Surprisingly, Prey behaved very cheerfully on all the video cards we are testing. FPS did not fall at the highest settings and less than 150-160 frames per second.
Crysis is a stretch, but still does not slow down. All video cards produce stable 30 frames per second, which is quite enough for a comfortable game. However, this will require slightly lower settings or lower resolution. The AMD video card (HD 3870) performs slightly better - at about 5-10 frames per second.
The next test is Company of Heroes. Quite a demanding game that requires a lot of computer hardware resources. Video cards can handle it only at medium settings. On the maximum graphics, the program produces unplayable 15-20 frames per second. 
Let's move on to Serious Sam 2. Strange as it may seem, in this game the GeForce 9600 outperforms its competitors from AMD by about 20-25 frames per second. However, all representatives issue more than 100 FPS, so the difference does not matter. Recall that all tests were carried out on operating system Windows Vista specifically to support DirectX10 interface. If you use a video card on DirectX9, the results will be even better and higher. All the same, this middle-class video card is not suitable for full disclosure of DirectX10 capabilities in the top-end games.
Verdict
The GeForce 9600 GT video card is an excellent option for those who want to try all the charms of DirectX10 on their hardware without paying a lot of money for top chipsets. For ordinary users who did not chase better performance, this option was inferior to competitors from AMD. Their graphics cards were $ 20-30 cheaper, but delivered exactly the same performance as the 9600 GT. Nvidia engineers have developed this video card only for monetary gain, not for development lineup... This can be seen in outdated technologies and cut parameters to reduce prices and artificially conquer the middle segment.
On February 21, 208, the Canadian company officially introduced the 9600 GT video card. It was intended to send 8600 GTS to its "well-deserved rest" in the middle-end-segment in the price category up to 0. The new G94 core differs from its elder "brother" G92 only in quantitative characteristics, and functional purpose and the principle of operation of the executive blocks remained without any significant changes. From the point of view of quantitative characteristics, the 9600 GT has 64 universal processors in its stock, which is twice as many as in the "old" 8600 GTS, and half as many as in the GeForce 8800 GTS (G92) or GeForce 8800 GTX. This time, let's hope that there will not be such a colossal performance gap compared to the older solutions, as it was between the 8800 and 8600.
So, the newly made core of the G94 consists of 505 million transistors (for comparison: the G86 had 210 million, the G92 had 754 million, and the G80 had 681 million). It operates at a nominal frequency of 650 MHz for the NVIDIA GeForce 9600 GTS. The GPU uses the unified shader architecture that has proven itself in the G80 / 84/92 chips. The idea behind the unification of GPU functional units is as follows: earlier they were divided into vertex and shader units, and now universal units are able to process any kind of instructions without significant performance losses. This will allow you to dynamically change the performance of the kernel by reallocating resources for the required task at the moment. As a result, we get a full chip load, and as a result, performance increases.
In the case of the G94, we see an elementary reduction - 4 shader units, each of which contains 16 stream processors (Streaming Processors) and 8 texture units (TMU). In total, we get 64 stream processors and 32 texture units. All G94 processors, as in previous chips, work with higher GPUs clock frequencies... In particular, for the 9600 GT it equals 1650 MHz. Finally, let's note the blocks of writing to the frame buffer (ROP), of which there are 4 in this case (in the diagram there are blue blocks next to the L2 cache). In the work and the concept of building stream processors (SP) NVIDIA has not made any amendments since the days of the G84 chips.
For every four stream processors, there are two TA texture addressing modules and two TF texture filtering modules. Therefore, now each texture unit, due to the increase in the number of calculated texture addresses, will be able to process twice as many samples as, for example, in the G80. Each shader unit has its own L1 cache. It can store not only textures, but also due to the unification of the blocks themselves, various kinds of data. All stream processors (SPs) on which the G94 architecture is based are scalar. Why not vector? The reason lies in the fact that, based on the research of shader programs by NVIDIA developers, it was found that the vector architecture is quite uneconomical uses computing resources when complex instructions are being processed - for example, scalar and vector simultaneously (generally speaking, scalar calculations on vector processors are performed very inefficiently ). In light of the emerging recent times the trend towards more and more transition from vector computing to scalar strategy NVIDIA developers, perhaps, becomes clear. Well, what to do with vector program code? Everything is very simple: they are converted to scalar operations directly by the G94 chip itself. As already mentioned, the GeForce 9600 has 4 units for recording into the frame buffer (ROP). They have not undergone any changes relative to the G92 architecture and support the following anti-aliasing methods: multisampling, supersampling and adaptive anti-aliasing.
NVIDIA GeForce 9600 GT specifications
| Name | GeForce 9600 GT |
| Core | G94 (D9P) |
| Process technology (μm) | 0.065 |
| Transistors (million) | 505 |
| Core frequency | 650 |
| Memory frequency (DDR) | 900 |
| Bus and memory type | GDDR3 256-bit |
| Memory bandwidth (GB / s) | 57.60 |
| Unified shader units | 64 |
| Unified Shader Unit Frequency | 1625 |
| TMU to conveyor | 32 |
| ROP | 16 |
| Shaders model | 4.0 |
| Fill Rate (Mpix / s) | 10400 |
| Fill Rate (Mtex / s) | 20800 |
| DirectX | 10.0 |
| Memory size | 512/1024 |
| Interface | PCI-E 2.0 |
The ninth generation of Nvidia graphics cards was born in early 2008. The center of attention will be the mid-price chipset - GeForce 9600 GT. Characteristics, test results, general impression of the stability of work - you can find all this below. As a result, you will be able to decide on the choice of a budget video card.
History of appearance
In 2008, when AMD was busy releasing budget graphics cards, Nvidia had only copies of the top-end version. Thus, they have deprived themselves of the largest segment of consumers. The question arose about creating a competitor for the Radeon 3800 Series. First of all, we tried to occupy this niche with the help of a weaker version of the top geForce video cards 8800. has been reduced to a ridiculous 256 MB. And the board was released for sale. However, this modification of the video card did not gain popularity among PC users.
The sales profit was negligible. This is because the cost of such a top-end chip is high enough to cut its performance and sell it at a low price. As a result, the ninth series came to the fore. Initially, production was planned to start no earlier than a year later. In particular, this applies to the first GT. The performance of the video card is at an average level: between 8600 and 8800 GTS. From the AMD lineup, the 3800 series became a competitor.

The motto to boost 9600 GT sales is: good performance for little money. From the review, you will find out whether the statement has been confirmed or not regarding the Nvidia 9600 GT graphics card, whose specifications are impressive. This graphics chip became the real founder of a whole generation of new chipsets, which brought even more popularity to the company and significantly expanded the customer base both among buyers of high-end hardware and in the middle price segment.
Nvidia 9600 GT Specifications
So, let's figure out what this video card is. It is based on the 8800 GTS chipset. Only trimmed down in parameters. Since the 8800 GTS was just an intermediate development, the technology was used later in the 9800. The card is based on the G94 chipset, the same as in the 8800 series. You may ask: why, then, is it much cheaper and what does the manufacturer save on? The answer is quite simple. The 9600 GT has cut the number of streaming processes in half compared to the older model. This made it possible to significantly reduce the price. But the performance gain was achieved due to the use of the same buses with a width of 256 bits. This allowed us to reach higher rates of processor frequency and shader processing.

According to the manufacturer, the 9600 GT graphics card, the characteristics of which are cut down, are more productive than the 8800 series by as much as 15%. What a breakthrough in technology! A little later, we will determine on practical tests: is it true or not. Also, the video card is equipped with 512 MB of internal memory, support for SLI mode (simultaneous connection to the system of up to three identical video cards operating in parallel). It has a DirectX 10 interface and all the necessary connectors for connecting monitors, displaying images on a TV, and so on.
External video card review
The board has become somewhat smaller than its predecessor, mainly due to simplified technology. This allows it to be installed in fairly tight budget cases. After all, 9600 GT (middle-end characteristics) must correspond to its class, whatever one may say. There are many holes throughout the board that are designed to improve heat dissipation. From above it is closed with a plastic case with a heatsink and one cooler. This is enough to maintain a consistently low temperature even at high loads.
Test results
To conduct tests in games, the following stand was installed. Processor from Intel - Core 2 Duo, dual-core with a frequency of 3 Hz for each core. In addition, 4 GB of RAM were available, hDD 750GB and 500W Acbel PSU. The tests were carried out in those games that were relevant at the time of the release of the 9600 GT video card. The characteristics of the bench computer also correspond to that time.

The indicators in the games Crysis, Call of Duty 4, Bioshock, Lost Planet are taken as a basis. All of them were launched with DirectX 10 support and at maximum settings at Full-HD resolution. The first game (Crysis) behaved very badly - only 10 frames per second. Affected by the budget model of the video card. In Call of Duty 4 and Bioshock, the game produces a stable 40 frames per second at maximum settings. This is already good for the middle price segment of video chips. Lost Planet was comfortable to play on medium or low settings with the maximum screen resolution.
Power consumption and overclocking
Let's move on to power consumption. Nvidia engineers have managed to reduce power consumption by as much as 15%. The creators show in every way that they belong to the middle class nvidia graphics cards 9600 GT: specifications, power consumption, performance are at a good level for their price. The creators of the video card have not forgotten about those who like to experiment with their hardware. We decided not to touch the overclocking capabilities. Therefore, at their own peril and risk, owners can try to create a real monster and conqueror of modern games from a board with an average performance.