Good afternoon friends! I am very pleased to welcome you to our training Internet portal http: // site. We continue the conversation about setting up home network. The topic is extensive, but interesting and very important.
Today we will be engaged in a network of educational programs or network settings. In order to be able to configure the home network, you need to get a minimum of ideas about how the local computer network works.
The "Network Connections" page appears. This page lists all of your network adapters. If your device has more than one adapter, this page additional adapters. The "Properties" dialog for the network adapter appears. This dialog box contains seven tabs that allow you to configure the adapter.
Antivirus, firewall, third-party programs and drivers
To view the settings for a specific property, select the property name from the drop-down list. This parameter is usually used with peer-to-peer networks, but you can use it even if your network has dedicated servers.
- Developments.
- List of recent events that have been registered for the device.
- Power management.
- Allows you to configure the power management settings for the device.
- He must always be present.
We will talk about the terminology of local networks, the configuration of network adapters, and also consider in detail the connection of two or more computers to the network.

choice network connection
Let's look at the network connection settings:
1. For Windows XP: Go to the "Start" menu -\u003e "Control Panel" -\u003e "Network Connections". If there is a network card on the computer, the network connection icon appears in the window that appears. Click on it with the right mouse button, and in the opened menu select "Properties".
Installing the Network Card Driver
A list of available protocols appears. For security reasons, you must do everything possible to remove any clients, protocols or services that you do not need. Without installing the driver, your network card will not work. You need to check the status of the driver to make sure that it works well after installing the driver, look at this if you do not know how to do it.
You must configure the network card so that this computer can communicate normally with other computers or network devices. Note. Note that widows will see a connection to local Area Networks as the access type, if you connected the computer to the router using a network cable.
2. For Windows 7: Go to the "Start" -\u003e "Control Panel" -\u003e "Network and Internet" -\u003e in the first paragraph "Network Management Center and sharing select the sub-item "View network status and tasks" -\u003e click on the link "Local Area Connection" and then on the "Properties" button.

Internet Protocol version 4 is a protocol that allows your computer to talk to other computers on your network. The physical process of transition from the old to the virtual can sometimes be a difficult task for the administrator, since the conditions and functions of the virtual sphere sometimes differ from what was learned earlier.
First, take the second and read the following questions. Have any of these questions called you? Such features include creating team projects, saving work items, or merging code changes. In some cases, these functions can never end, and you may receive an error message that contains the phrase "The main connection was closed." Configuring network switches and network adapters for your computers can affect the network bandwidth.
In the appeared window in the list, select "Internet Protocol (TCP / IP) (version 4, if specified)" and click on the "Properties" button.
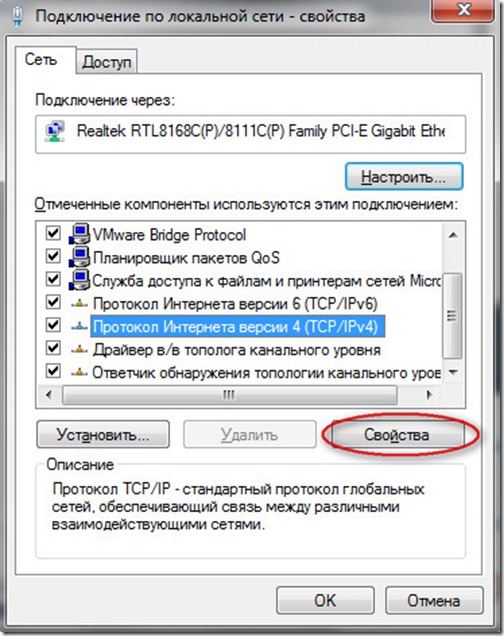
A window will open, in which the main ones will be displayed.
network adapter settings
- a kind of formal designation of your computer in the global or local information space. Most likely, the network we create will work on the TCP / IP protocol (data transfer protocol / Internet protocol).
Windows Network Settings
For example, auto-save mode or auto-negotiation can be enabled, and information can be transmitted in full-duplex mode or half-duplex mode. For more information about how full-duplex differs from half-duplex mode, contact your network administrator. To perform these procedures, you must be a member of the Administrators security group on the local computer.
- The "Local Area Connection Status" dialog box appears.
- The Network Connection Properties dialog box appears for the network adapter.
The protocol is a set of standard algorithms and rules, according to which the data is exchanged in the network.
In accordance with the operation of the TCP / IP protocol, each network device is assigned a unique IP address. It consists of 32 bits (or 4 bytes), which are written as four decimal numbers in the range 0-255, separated by dots, for example: 192.168.0.10.
The adapter properties dialog box appears. It is necessary for interconnection and for Internet access. Provides automatic diagnostics for diagnosing and troubleshooting network problems. Network Explorer. . Before discussing how these network tools are used, we must first look at the functions on which these tools rely.
- Network discovery.
- Controls the ability to view other computers and devices.
- Reports changes to the network connection and configuration.
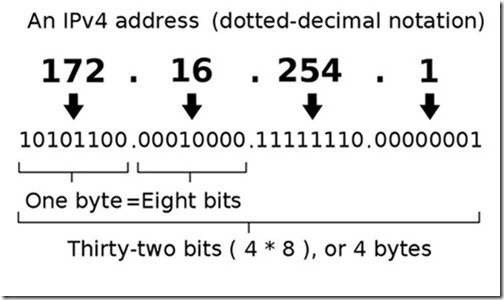
Note that the addresses 0.0.0.0, 127.0.0.1 and addresses ending in 0 and 255 are reserved for service purposes and you can not assign them to network devices.
When configuring the connection to the Internet, pay attention to the IP address input field: if your ISP specified an IP address, enter it in the appropriate field; if it was not provided to you, simply select the "Obtain an IP address automatically.
- Opening of network computers and devices.
- Opening the computer by other users.
Designed to designate a network in which computers are connected to a corporate domain to which they are connected to a private network. Designed to designate a network in which computers are configured as members of a homegroup or workgroup and are not directly connected to a publicly available public Internet network. Designed to refer to a guest network in a public place, such as a cafe or airport, and not for an internal network. Domain network. . In domains, you can enable detection on domain controllers to view member computers.
2. Subnet mask. As a rule, a large network is divided into subnets, each of which is assigned its own unique address, as a separate computer. The full IP address, which we discussed above, contains information about both the address of a specific node and the address of the subnet.
To select these sections from the same IP address, you need to know the subnet mask. It also consists of 32 bits and takes the value 0 or 1. If you overlay the subnet mask with an IP address, then the digits that appear under the units will mean the subnet address, and under the zeros the address of the specific node. The subnet mask is also written as an IP address, four digits separated by periods, for example: 255.255.255.0.
On member computers, you can enable discovery to view other member computers. Homegroups have special sharing options that are not available in workgroups. Correction of the network category. Since the computer saves the settings separately for each network category, you can use different blocks and allow settings for each network category. If the computer has multiple network adapters, the adapters can be connected to different networks and therefore different network categories can be assigned.
Selecting a network connection
You can also manage these settings. Regardless of whether automatic and automatic network access control was detected manually, the "On" state means the following.
- The computer can detect other computers and devices on the network.
- Other computers on the network can detect the computer.
For reference, computers can be connected to the network without the help of a router, only if they are on the same subnet (or have the same subnet address). If the subnet addresses differ at least by one, then the information between them will not be transmitted.
3. Types of IP addresses and the default gateway. As you already know, the number of unique IP-addresses on the Internet is limited, and the number of computers that want to access the world wide web is growing every day. It was decided to divide the addresses into private and public addresses.
- The computer can not detect other computers and devices on the network.
- Other computers on the network can not detect the computer.
- Public IP addresses can be connected to the Internet directly. They are visible to every computer on the Internet. To get a public IP-address, you need to pay money. Pleasure is not cheap. As a rule, such addresses are distributed to providers and dedicated servers, sometimes to customers.
- Private IP addresses are addresses that are not visible from the Internet. They are assigned to computers located in subnets connected to the Internet through a router. A router is a device that connects two subnets: local and global (Internet), and therefore has at least two network ports (IP addresses): public (for Internet connection) and private (for operation inside the local network). Because subnets do not interact with each other, then the same addresses can be repeated many times in different subnets.
To create a home network, it's best to use private IP addresses. A common option is to use an address of type 192.168.x.x, where x is a number from 0 to 254.
Typically, you do not want to enable network discovery and file sharing on public networks, as this can open a computer for attack. Otherwise, if the computer is connected to an unidentified private network, select the option to create the network on the private network.
View and manage network settings using the Network and Sharing Center. The Access type field indicates whether the computer is connected to its current network, such as "No Internet access" or "Internet access". The "Connections" field indicates the name of the connection to the local network, which is used to connect to the current network. Often the fastest solution to this mixed state problem is to disable and enable the network adapter. Often the quickest solution to this mixed state problem is to disable the network adapter that is not connected to the corporate network.
 4. DNS-server. We looked at what an IP address is. But everyone probably will agree that it is difficult to remember so many figures. What is easier to remember 94.100.191.204 or mail.ru? Of course, it is easier to remember the alphabetic address of the site (domain name). To replace IP-addresses with understandable nominal values, special servers - DNS-servers are invented. If the IP address changes, then the DNS server is immediately notified of this, and for you the access to the site remains for the same domain name.
4. DNS-server. We looked at what an IP address is. But everyone probably will agree that it is difficult to remember so many figures. What is easier to remember 94.100.191.204 or mail.ru? Of course, it is easier to remember the alphabetic address of the site (domain name). To replace IP-addresses with understandable nominal values, special servers - DNS-servers are invented. If the IP address changes, then the DNS server is immediately notified of this, and for you the access to the site remains for the same domain name.
Connect wirelessly to an access point
You can aggregate throughput using network adapters. You can configure up to 32 network adapters to work together. Enter 0 in the subnet mask field. When the access point is in the factory default settings, it will broadcast two wireless networks with open protection. Connect to any of these names wireless network is required to access the web interface and configure the access point.
Each of the blue bars is a network. This is from the top down. 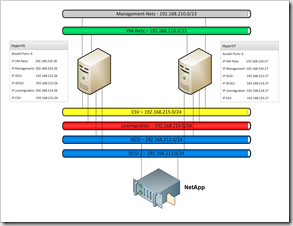
In total, five private networks are involved. It can be routed and interact with the Internet through a firewall. All the other four networks between hosts and storage are shared, since they are not routed. In this article, we will discuss the binding and setting of adapter priorities in more detail. Ideally, one or two adapters are required. You can then split the clustered connection and the redirected access to each other.
To configure Internet access, you must specify the IP address of the DNS server (usually it is issued by the provider or it is automatically assigned). If you do not do this (or the DNS server stops working), you will have to specify their IP addresses to access the sites.
home network "for two"
If you need to quickly connect two computers to a network (for example, to transfer information, create backup or just to play), then it's not necessary to buy a router or switch. We'll consider two connection options:
However, our configuration shown is a good compromise and is also created in our laboratory. But now to the real configuration. It is important to install the latest network card drivers. If you are now opening a network configuration, you first turn on and deactivate all network cards, except for the management interface. Then think about how network adapters are best distributed, so redundancy is also guaranteed.
Retrieving IP parameters
Then all this looks like the screenshot on the right. Again, all that is written does not apply to the control network. Now uncheck "Allow sharing of this network adapter for the management system". To continue to configure the network for the cluster, we need to configure the cluster. They are automatically created subnets. Until now, we have reached the point where our networks have a logical meaning for us. Now we also need to tell the cluster which adapter to use for which function. This occurs at several configuration points, which we now enter for each of the networks.

I will not consider setting up wireless access in this article. In this version, we will stop later, when considering the settings of the routers.
Selecting the type of cable connection, you can go to the settings of network adapters.
First, make sure that the computers are in the same workgroup, in the same range of addresses, and with different network names. We look, how it is done:
This adapter has two functions: cluster sharing and shared cluster volumes. As mentioned above, we would put these functions on separate network cards, if more were available. Here you can select the network that will be used to communicate the cluster. Then right-click and select Properties.
The screenshot shows the links network card and the cluster settings for this network interface on the right. Each network interface in the cluster is assigned a metric. This metric is defined by the cluster using network properties. If you want to determine which card is there, you must change the automatically assigned metrics. Then we leave the metrics of the individual interfaces with a command.
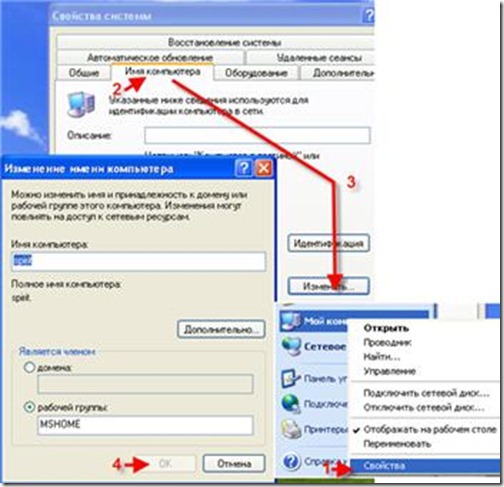
Next, you must set up IP addresses and a subnet mask (the subnet mask is automatically substituted with the IP address specified) to each computer. How to choose IP-addresses, we considered above. We are watching how to configure the IP address:
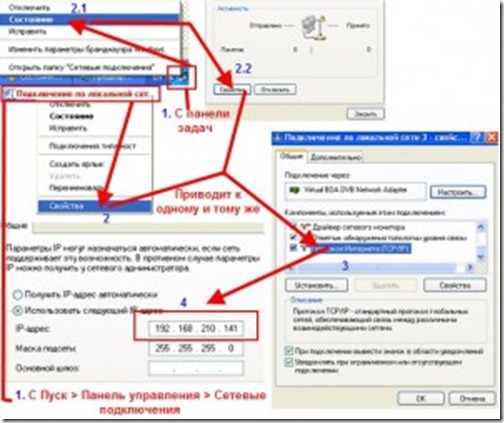
If you connect several computers to the network using a switch (network switch), then repeat the above settings on each computer on the network.
troubleshoot network problems
1. The first thing to look for when troubleshooting a network is whether the network connection is established. Those. Is there a physical connection between the computers (are network cables connected to network adapters and network devices such as a router, are the wireless adapter Wi-Fi, for example on laptops it is disabled by a special shortcut key). It is also necessary to determine the serviceability of the network adapter. As a rule, sometimes it's enough to see if the yellow-orange diodes of the network connector blink when the cable is connected.
2. It is necessary to verify that IP addresses do not repeat in this subnet. All computers must have different addresses so that there are no conflicts in the data exchange.
3. Verify that the subnet address is correct. Those. you must verify that the subnet mask on all network adapters is set to the same.
4. Make sure that the same group is specified in the computer properties (we discussed this earlier).
5. If a particular site has become unavailable, this does not mean that the network has disappeared, perhaps a DNS server has failed. Check other sites. To control the operation of the DNS server, enter 94.100.191.204 in the address bar of the browser instead of mail.ru. If the site boots, then the DNS is faulty.
The order of the network card configuration depends on its model and configuration. Most modern network cards support the Plug-And-Play standard, and the operating system automatically detects these devices after installing them and turning on the power of the computer: the user only needs to specify in the appropriate window from where the system should copy the appropriate drivers. Older network adapters (mostly connected to the ISA bus) are not automatically detected in Windows and require manual configuration. In some cases, on the card of the network adapter itself there is a set of jumpers or switches, through which you can set the mode of its adjustment. Carefully read the technical documentation of your network card before proceeding with its configuration.
Plug-And-Play Network Adapters
Almost all modern network adapters support the plug-and-play standard, which allows the operating system to automatically configure devices connected to the computer. After installing such network cards, turning on the power of the computer and boot Windows, on the screen, as a rule, the message "found a new device" with a suggestion to specify the source for copying the drivers, which are usually delivered on a floppy disk with the network card. In some cases, this may not even be required: in particular, the operating system Microsoft Windows XP independently identifies and configures network adapters that are compatible with the NE 2000 model, using standard Microsoft drivers for this.
After installing the drivers and rebooting the computer, the network adapter is actually ready for use. However, in some cases, the automatic configuration of Plug-And-Play adapters does not work correctly, and as a result, there are hardware conflicts between the network card and other hardware. Typically, these situations are caused by the fact that several different devices start using the same resources, such as interrupt request (IRQ, Interrupt Request), addresses of direct memory access (DMA) channels or I / O (I / O Range). You can solve this problem in one of the ways listed below.
- 1. While the computer is restarting, sign in bIOS settings, go to the PCI or ISA bus configuration section to change the hardware interrupts assigned to the various slots of these buses, and release one of the interrupts for the corresponding bus, which will be automatically assigned to the network adapter afterwards. For example, if you know that your network adapter connected to the PCI slot,
requires interrupt 20, assign IRQ = 20 for one of the PCI bus slots. If this did not work, you can proceed as shown in the next paragraph. - 2. By moving the appropriate jumper or switch on the network adapter card or using the network adapter configurator, turn off the Plug-and-Play mode for the network card. Then it can be configured as a hardware-configurable or software-configurable device.
Program-configurable network adapters
Software configuration LAN adapters are usually network cards of old models, for which special software is included in the package. Many of these programs only work with operating system MS-DOS and therefore they are often run with errors on Windows 2000 / XP platforms that do not fully support this system. The principle of the program configuration utilities network adapters is as follows. The program-configurable network card contains a special chip of reprogrammable permanent EPROM memory, which stores information about the current settings of the device and the resources used by it. When the utility is started, the internal configuration of the card is tested and the data recorded in EPROM is read, after which the user is offered to change them. Sometimes the program requires manually specifying the type of network connector available in the adapter: BNC, RJ-45 (UNC), Attachment Unit Interface (AUI), or COMBO for the combined interface card. Before exiting the program, all settings must be stored in the EPROM.
Often, in addition to the actual configuration functions, these utilities offer to test the network adapter, and similar tests can be divided into internal (internal or self test) and external (external) tests. In the first case, the program tests the network card for errors in the registers of its built-in memory, in the second it sends information packets to the local network and analyzes the received responses. It is often possible to run the test on two different machines at the same time, specifying one of them in the program settings as a server (server computer), and the second as a client (client computer), and thus check the performance of a particular section of the local network. However, one should take into account the fact that many tests automatically finish their work when the interval of waiting is exceeded in one minute. This means that if during the specified time you do not manage to get to another computer and run a similar utility on it, the test will report the presence of a failure in the network.
If you bought a used network card without an appropriate configuration utility, or you lost a floppy disk with software, you can use a similar program from another network adapter that has exactly the same type of chipset (controller chips). Also, the network card configuration utility can be downloaded for free from the Internet by searching it on the device manufacturer's website or in the driver collections for various PC hardware.
Hardware-configurable network adapters
Some network adapters of old, or rather, very old models allow you to configure addresses and interrupts of the device using the jumpers located directly on the board, or, as they are also called, "jam-feathers". Each of the jumpers can be in one of two stable states: On or En (Enable) - the jumper is on (Figure 4.9, a), or Off - the jumper is off (Figure 4.9, b). The jumpers are rearranged with tweezers on the network card previously removed from the computer. In the switched-off position, the jumper is freely left on one of the contacts - in order to avoid accidentally losing it. The correct jumper position should be indicated in the documentation for the network card, or printed with paint on the adapter itself.
Sometimes jumpers are three- and four-position. This means that the switching unit contains several contacts, one of which must be marked with the number 1, the other contact numbers are counted from it in order. In this case, to change the adapter settings, you must set the jumper to the appropriate position. For example, if the required configuration is achieved by setting the jumper to the position 2-3, then such activation of the "jumper" is shown in Fig. 4.9 (c), position 3-4 is shown in Fig. 4.9 (d). Sometimes the network adapter configuration is performed by a combination of several jumpers.
Fig. 4.9. Configuring a Hardware-Configurable Network Adapter
How to find a free interrupt?
In case you are a "happy" owner of an outdated network card that does not support the mode automatic settings, you have to look for free resources manually in order to configure the adapter to use them. This problem is easiest to solve in the operating systems of the Microsoft Windows NT / 2000 / XP family, where the user has a special utility WinMsd, designed to determine the free and used resources of the computer. In order to call this program for execution, it is necessary to execute a sequence of commands Start\u003e Run and by typing the wi nmsd command in the appeared window Run the program, press the Enter key (Figure 4.10).
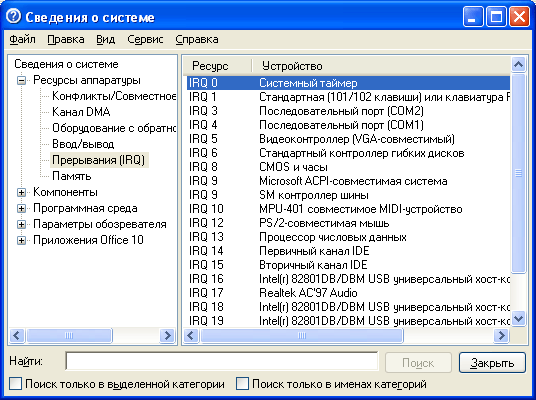
Fig. 4.10. WinMsd utility interface for MS Windows XP
While viewing the list of resources of the computer displayed in the left window of the program, you can select the required component by clicking the mouse, while the right window displays a list of acceptable values. For example, by selecting Interrupts (IRQ), you will see a list of free and occupied hardware interrupts by clicking on the I / O point, you will get information on I / O ranges for various devices by accessing the DMA channel item, you can view information about the equipment used Your computer addresses the channels of direct memory access.
In Microsoft Windows 9x / ME with the definition of free addresses and interrupts, the situation is somewhat more complicated, because the OS of this family does not have a separate utility that allows you to monitor the resources of the computer. In order to get the list of used addresses and interrupts in Windows 9x / ME, you need to open the Control Panel window, double-click the System icon, in the System Properties window go to the Devices tab, right-click on the Computer device and select in the appeared menu item Properties. A special window will appear on the screen containing a list of all the hardware resources of your PC (Figure 4.11).
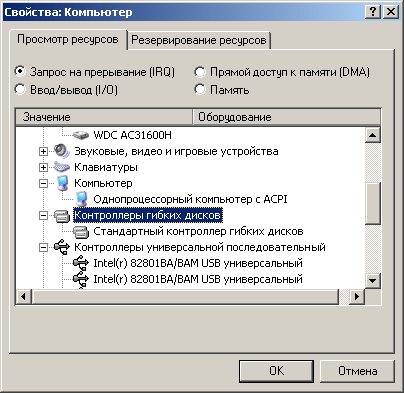
Fig. 4.11. Monitoring hardware resources in Windows 9x / ME operating systems
By setting the switch at the top of this window to one of the possible positions, you can monitor various hardware configuration resources of the computer: system interrupts (IRQ switch position), input / output ranges (I / O switch position (1/0 )), direct memory access channels (DMA switch position), or RAM resources used by various devices (the Memory switch position). Here you can reserve any of the resources for its subsequent use by your network adapter: for this go to the Resource reservation tab, select the switch to the position corresponding to the resource that you want to reserve, click on the Add button and select a free resource from the offered list .
A separate program for viewing the hardware resources of the computer is also included in the delivery package of the MS-DOS / Windows operating system Zx. This utility is called msd.exe, and it is stored, as a rule, in system folder DOS. You can run it from command line: if during the download process the program causes the computer to hang, try calling it on the command msd.exe / i. After its launch, the program msd shows a list of the characteristics of the computer, which it can determine: the type of processor, the version of the operating system, the amount of available memory, the model of the video adapter, etc. To view the list of free and busy interrupts, select IRQ Status from the program menu or simply press the Q key.
If you select a free interrupt and its corresponding I / O range in the list that appears on the screen, you can configure your network adapter to use these parameters.
Problems connecting network uSB adapters
Sometimes it happens that the network adapter connected to the USB port of the computer is not determined by the operating system and, accordingly, can not work correctly. In this situation, you can advise you to do the following.
1. Right-click the My Computer icon on the desktop and select context menu item Properties. In Windows 9x / ME, go to the Devices tab, in the OS Network cable Windows NT / 2000 / XP, start Device Manager by going to the Hardware tab and clicking the Device Manager button. 2. Locate the USB bus controller in the hardware list:
- if the USB bus controller is not listed, install and configure it using the Hardware Configuration Wizard;
- if the USB bus controller is present in the list but is working with errors or causes a conflict with other devices, install the appropriate drivers for it, which are usually included in the package software motherboard, or try to remove the device from the list and configure it again using the Hardware Configuration Wizard;
- if the USB bus controller is present in the list, configured correctly and does not cause conflicts with other devices, check the pin of the cord by which the adapter is attached to the USB port and reinstall the network adapter drivers. In some cases, it makes sense to try to forcefully detect the network adapter using the Hardware Configuration Wizard.