When opening, deleting, or otherwise manipulating files and folders, you may encounter a file access error. I will talk about how to deal with this and why it happens.
1. How to get full access to files and folders
First, an instruction on how to get full access to folders and files. The next chapter will be an explanation for the curious.
Open the folder where the problem file or folder is located. To get full access to their content, you need to configure file access:
1. Right-click on a locked file (or folder) without access - Properties -select the tab Safety:
2. Push the button Additionally -select the tab Owner:
3. Push the button Edit and select your username (in my case it is Dima, you will have something else), also put a daw on Replace owner of subcontainers and objects:
4. If a window appears with the text “You do not have permission to read the contents of the folder. Do you want to replace the permissions for this folder so that you have full access rights? " Yes:
5. After changing the owner of the folder, a window will appear with the text “You have just become the owner of this object. You must close and reopen the properties window for this object to see or change the permissions. " Push OK, then press again OK (in the window Additional security options).
6. In the window Properties – Safety press again Additionally, only now we are looking at the first tab of the window that opens - Permissions.Gotta push a button Change permissions:
7. Click the button Add to:
(If you are working with properties folders, not a file, check the box next to Replace all child object permissions with inherited permissions from this object.)
8. In the "Select: users or groups" window that opens, you will need to enter your username (you can see it in the "Start" menu - the name will be the very top line), click Check namesthen OK:
If you need a folder (or file) to open without restrictions by absolutely all users, i.e. not only yours, then press again Add to and enter the name " Everything"Without quotation marks (" All "in English windows versions), then press Check names and OK.
9. In the tab Permissions in turn, double-click on the lines with usernames and check the box " Full access»:
This will automatically check the boxes below.
10. Then press OK, in the next window answer the warning Yes, again OKto close all windows.
Done! Full access to files and folders received! You can safely open them, change and perform other actions with them.
Conclusion: you need to take two steps: become the "owner" of a file or folder (item 3), then assign yourself access rights (item 6). Many instructions on how to get full access to files and folders mention only the first step, forgetting about the second. This is not entirely correct, because the security settings of the file / folder may be different, you need to bring them to normal view, not just become the "owner".
2. Why do we need permissions to files and folders
The mechanism of access control to files and folders is necessary for many reasons. For instance:
1. Restriction of access to information by different users.
If on one computer or in common network several (more than one) users work, it is logical to restrict access to information - some users have access to all information (most often they are administrators), others - only theirs own files and folders (regular users).
For example, at home, you can restrict the rights of one user so as to protect important files and folders from deletion (so that a child cannot unknowingly delete important documents), while from another ( parent profile) you could do whatever you wanted.
In the first chapter I showed how allow access to certain users. The same can be done limit access - the steps are the same, only in paragraph 9 other checkboxes must be checked.
2. Security of the operating system.
In Windows XP, everything is arranged rather primitively - users with administrator rights can change (and delete) any folders and files on the hard disk, including system ones, i.e. owned by Windows. In fact, any program running in the admin user profile could do with the content hard disk anything... For example, delete the boot.ini file, which will cause Windows to stop loading.
Under the rights limited user, where, thanks to the security settings, it was impossible to delete important system files, few people sat, preferring the administrator account... Thus, an account with administrator rights in Windows XP creates the most favorable environment for viruses.
IN Windows Vista, in Windows 7 and Windows 8 "User Account Control" (UAC for short) works: when working in an administrator account, programs launched by the user work with limited rights. That is, delete or change the system files of the program can not... Programs are able to gain more complete access by requesting it from the user using the UAC window, which I already mentioned:
If the file permissions are configured correctly and UAC is enabled, viruses running in the Vista / 7/8 administrator account cannot seriously harm the system without the permission of the person sitting at the computer.
UAC useless in cases:
1. If a user is sitting at the computer, thoughtlessly pressing the "Yes" and "OK" buttons
2. If you run programs "as administrator" (right-click on the program shortcut - Run as administrator).
3. UAC is disabled.
4. For system files and folders on the hard drive are allowed full access to all users.
Programs running in a restricted account windows user Vista / 7/8 ("Normal access" type) cannot bring up the UAC window and work with administrator rights, which is quite logical.
I will repeat once again: when there is no way to elevate your rights to administrator rights, you cannot harm the operating system files protected by restricting access rights.
3. Reasons and solutions for problems with access to files
The problem is that you are trying to access files and folders created under a different account. There are two solutions: either allow all users access, or allow only those who need it by listing them. Both solutions are easily implemented using the instructions above. The only difference is that you will enter in paragraph 8 - the word "All" or listing users.
By the way, you can allow access to all, but deny access to one (several) users, while the deny setting will be a priority for the listed users.
There are many reasons for problems with accessing files. Most often they appear if you have several accounts, several operating systems or computers - all accounts are different, when creating files and folders, the rights are also assigned different.
4. What can not be done with the rights of files and folders
Attention
Do not under any circumstances assign full access to files and folders on the entire hard disk with the installed operating system!
There is a myth that operating system does not consider the user to be the owner of his files, so you must assign permissions to all files on the disk. This is not true and you cannot change the rights of all files! The system, which was not "poked", did not assign access rights manually, is able to correctly assign the necessary rights!
Use my instructions only in case of real problems, not to prevent contrived ones.
Let me explain: by allowing access to system files, Windows will still work, but any virus or incorrectly working program can do very bad things. You hardly need problems.
The folders “C: \\ Windows”, “C: \\ Program files”, “C: \\ Program files (x86)”, “C: \\ Users”, “C: \\ System Volume Information"," C: \\ ProgramData "," C: \\ Recovery "and many others. They cannot be changed, except for cases when it is necessary to perform any manipulations with the files (for example, to change windows theme), and you need to return the settings back.
Attention
Do not change the security settings "just like that", making the system defenseless against viruses and crashes! After windows installations access rights to system folders are configured correctly, do not need to change them!
Advice: if the program works correctly only if it is run "as administrator", giving errors during normal startup, try assigning full rights to change the folder with it in "C: \\ Program files" or "C: \\ Program files (x86)" (not the Program files folder itself, but the folder with the right program inside it!).
Very often it helps to run old games on Windows Vista / 7/8, which store settings files, save files inside their folder. Being launched without permission to modify their own files, such games at best cannot save game progress, at worst they close or do not start at all. It's the same with old programs.
5. Conclusions
1. Assigning access rights is relatively easy.
2. Access rights cannot be changed without a justified purpose.
3. Changed the permissions of system files - change them back. To change rights systemic folders and files to the old ones, you can use this instruction (the method for Windows Vista should also work for Windows 7, Windows 8).
4. Changing security settings is a delicate matter and the author of the article is not responsible for your actions.

If in Windows 8 or Windows 8.1 you try to open, move or edit a system file, you will most likely get an error indicating that you do not have access rights. Moreover, this error occurs even if you are working with administrator rights. And why do you need to intervene in the system and change something there? There can be many reasons for this. Let's say you need to manually edit a log or image, or replace a file for some bold experiment. So, you cannot do this, even if you have administrator rights.
The reason is that in Windows 8 there are even more rights high level access, so to speak root rights... They belong to the system itself. To get them you need to change a few simple settings... There are two options - changing access rights manually and using special utility TakeOwnershipEx... First, consider the first method. Let's say you want to get full permissions on the system file twinui.dll. Right-click on it and select Properties from the context menu.
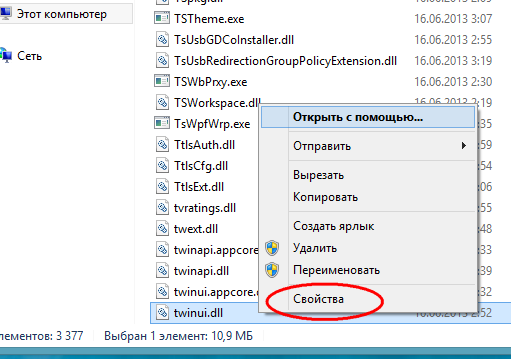
In the properties window, switch to the "Security" tab and click "Advanced".
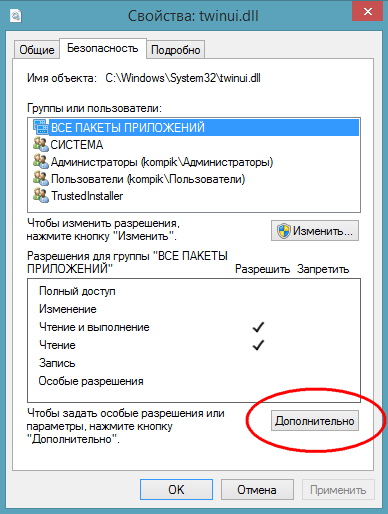
This will open a window additional parameters security.
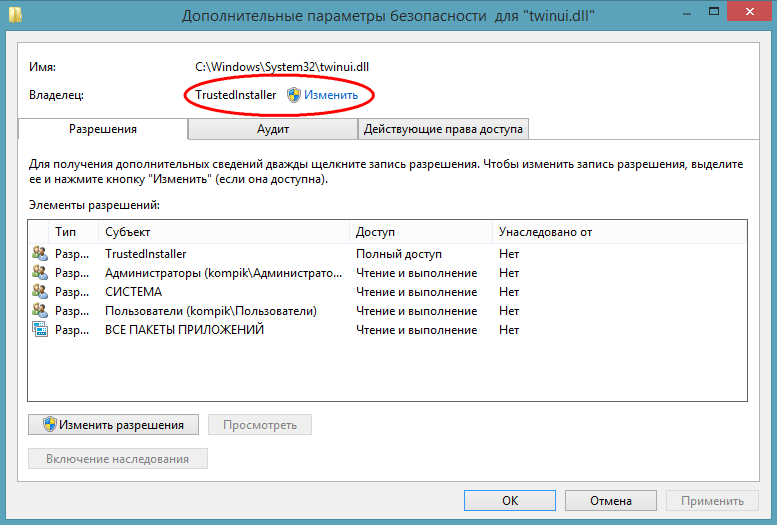
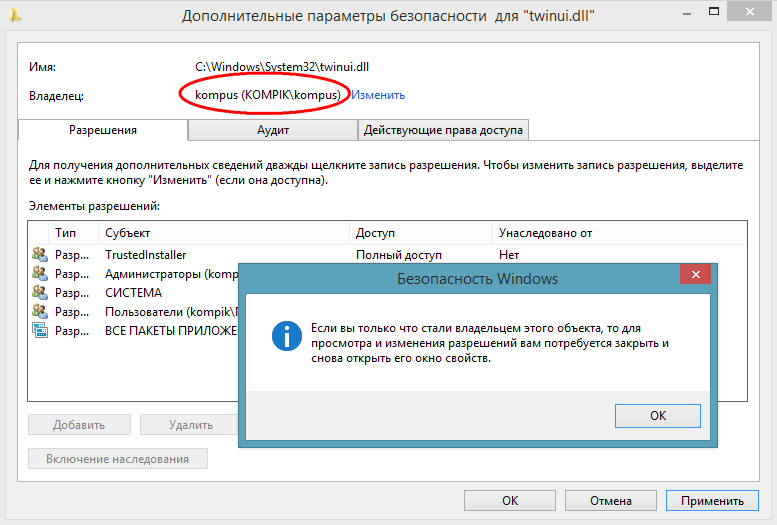
At the top of the window, you can see the file name and path, as well as the name of its true owner. By default it is TrustedInstaller, for some types of files it can be SYSTEM... This is exactly what you need to change. Click "Change", in the window that opens, enter your username and by clicking the "Check names" button, make sure the specified name is correct. If specified correctly, the computer name will be appended to it. Click OK and save the editing result.
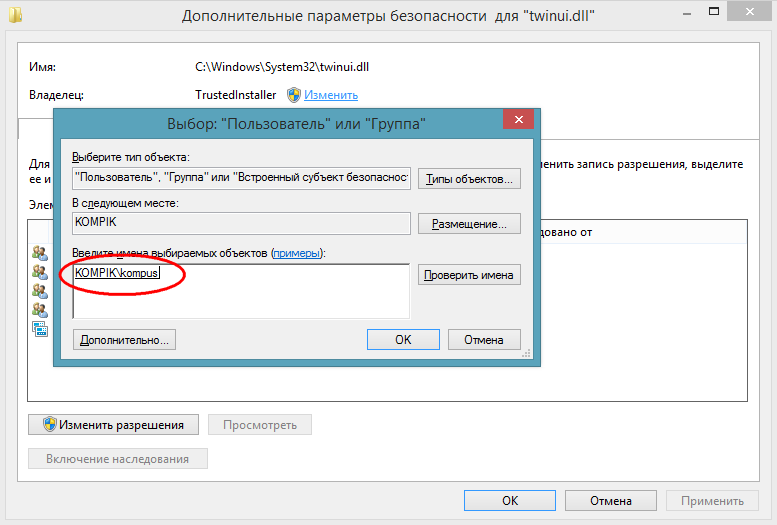
Now we return to the properties window of twinui.dll, click the "Change" button,
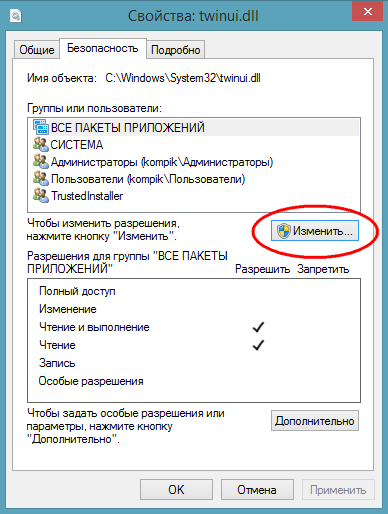
in the list, select the username that we assigned instead TrustedInstaller, set the checkboxes in the checkboxes and save the result.
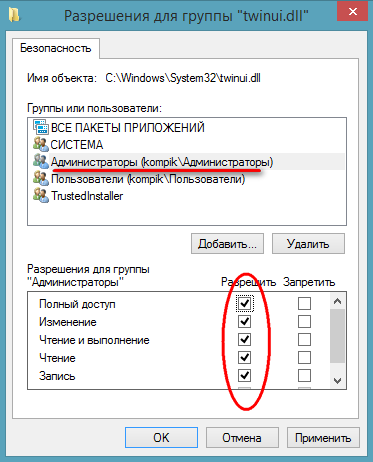
Congratulations, you are now the rightful owner of this property. In much the same way, you can set permissions on directories.
Everything that we have done manually up to this point can be done using the utility TakeOwnershipEx... This very simple and easy-to-use application does all the above operations, only much faster. In the utility window, click the "Get access rights" button and specify the path to the folder or file that you want to "unlock".

The utility remembers all changes, so it will not be difficult to restore access rights, especially since for this in TakeOwnershipEx there is a corresponding option.

By the way, during installation, the program is built into Explorer, which makes working with it even more convenient and quick.
Compared to the first method, the use of the utility has certain limitations. So, you will not be able to set the rights to directories recursively, that is, when setting the rights to a folder, subfolders and the files they contain not processed ... In conclusion, I would like to draw your attention to the following. It is not recommended to change access permissions to system files and directories unnecessarily, as this weakens the protection of Windows and makes it vulnerable to malware attacks ... If possible, after editing one or another system object, the access rights to it must be returned to their default values.
Previous / Next
Surely many Windows 7 users have faced the problem that sometimes when performing some actions with files and folders, the system not only asks for confirmation at the level of administrator rights, but also issues a message stating that there is no access to target folder Windows 7. How to fix this situation will now be considered. But first, a little theory.
Windows 7 target folder cannot be accessed. Why?
The thing is that the developers of the seventh version of the system, as well as all subsequent modifications, tried to protect it from accidental intervention of inexperienced users by creating for this a super-administrator account, on whose behalf all permissions for conducting critical operations for the system are executed.
That is why sometimes a message may appear stating that the user does not have access to the target folder of Windows 7 when copying, moving, deleting or trying to change some important system components. Many such constant restrictions, frankly, irritate in earnest. However, they can be bypassed, and quite simply. But more on that later.
Problems copying or moving files
Usually, if user actions are not related to system components, but, for example, with installing programs, copying and moving some objects, usually a confirmation request is simply issued.
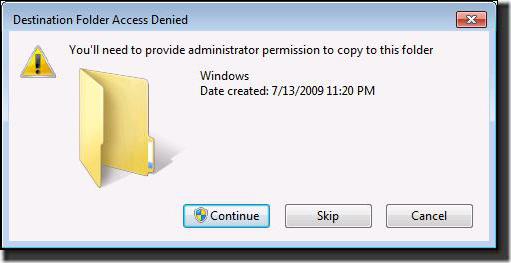
You just need to agree and the process will be completed without problems. The situation looks much worse when attempts are made to access or perform some actions with system files and folders. This is where a notification appears that the user does not have access to the target Windows 7 folder. In the simplest case, this is an attempt to copy an object to or from the system partition. To remedy the situation, it is logical to assume two solutions: disable the "account" of the superadmin and grant yourself absolutely all access rights or change system components.
Windows 7 target folder cannot be accessed: what to do?
For the first case, the technique looks quite simple, but first you still have to use administrator rights.
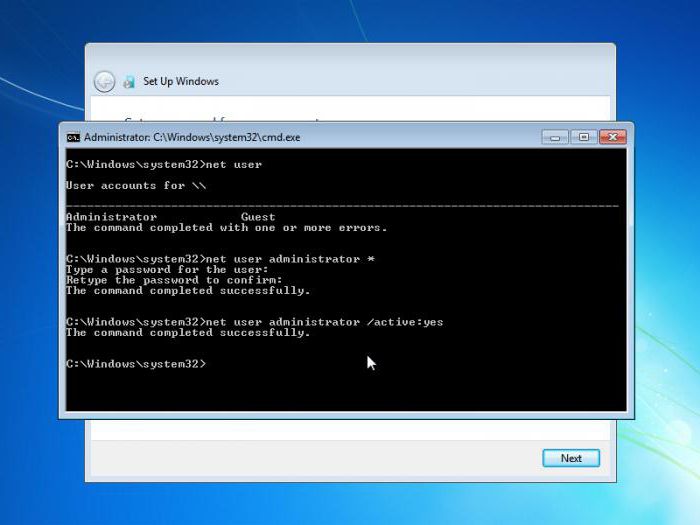
They are needed to launch the command console, which is invoked through cmd in the Run menu. Here you need to register a single line: net user Administrator / active: yes (if the action is performed in the English version of Windows, instead of the Russian word, you should use its corresponding analogue - Administrator), and then press the Enter key.
The second technique will take a little more time, but it gives a complete guarantee that the message that the user, whether he is at least three times an administrator, does not have access to the target folder of Windows 7, will not appear again. True, this applies exclusively to single selected objects with which it is supposed to perform some action.
Here you need to use the context menu, invoked by right-clicking on a directory or file, in which you first select the property line, and then use the security tab, where you need to select a group or user for which you are supposed to set extended privileges. Below there is a button for additional settings, after clicking on which a new window appears.
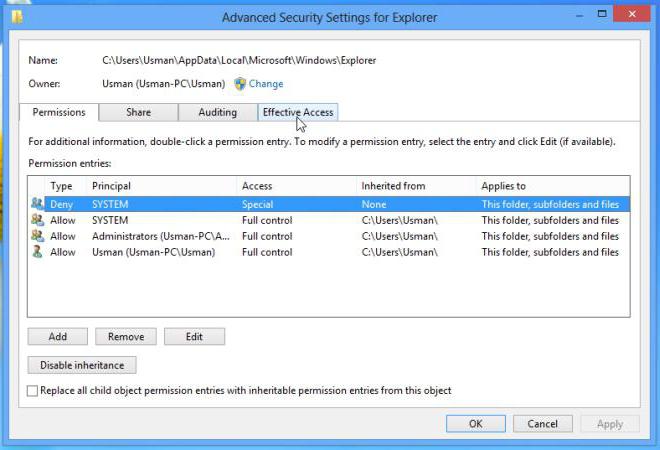
In it, you need to use the permissions tab (it is the first), in the type column look at all the lines in which the ban is set, and then click the button for changing permissions. In a new window, find a similar line and press the button again, as in the previous case. After that, we simply change the type of permission by setting the checkbox opposite the full access line.

If you return to the first menu, you will see that the checkboxes are automatically put in the permission column in front of all types of operations.
Now, when working with the selected object, the message that the user does not have access to the target Windows 7 folder will no longer appear. But note that this only applies to the selected object. If rights are required for another directory, the above operations will have to be performed again. By the way, this method also works in case of denial of access to removable devices, only in this case you need to use the properties menu of the device itself.
Access problems on local networks
But that's not all. Problems can arise with LANs. Sometimes the system also reports that the user (or a group of users) does not have access to the target folder; it can simply have such settings when some restrictions are set not only on general access to directories on network terminals, but also to their detection on the network.
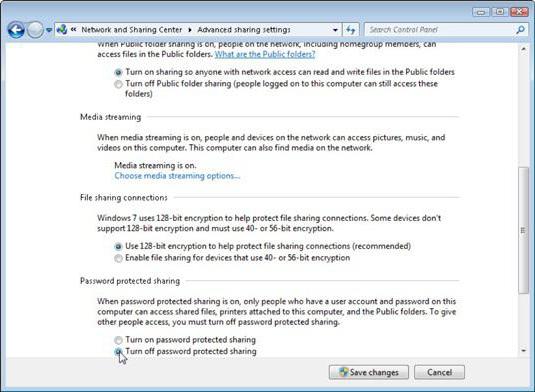
First, you need to check the additional network settings and set the enable options there for all parameters except password access... Thus, the visibility of computers on the network and everything that is on them is established.
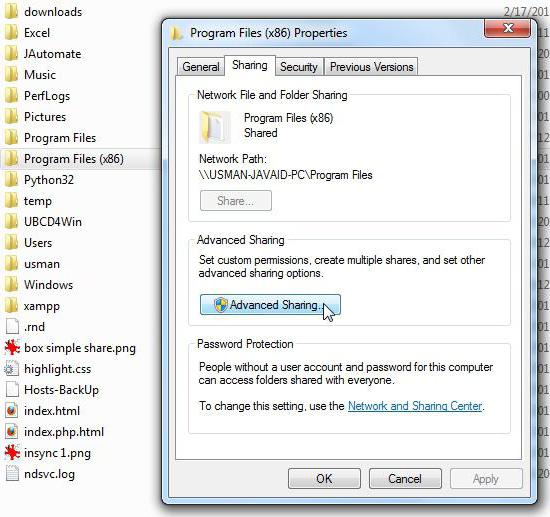
Next, you should select a specific folder and just open it to public access through the corresponding line in the right-click menu. In addition, in the settings, you can specify a group of users or specifically selected users for which these parameters will be applied.
Instead of a total
As you can see, getting rid of a constantly pop-up message in different situations can be quite simple. Which method should you use? It all depends on the specific case. However, the first two techniques for home terminal users work flawlessly. For enterprise networks, you may need to refer to system administrator... In particular, this concerns the setting network parameters... But the user can enable general access to a separate directory himself (this does not require the administrator's permission).
How to get full access to system files and folders without much manipulation and with a minimum of wasted time. We advise you to use exactly the methods that are described in that article. This article is for those who want to do it themselves. However, the second part of it will be useful to everyone who, after replacing system files, wants to return them to default access, i.e. the way it was in Windows originally.
So, to the point!
Part one. Changing the owner of files and getting access to them
This method will probably take the longest. Well, let's get started.
1. The first step is to go to the folder where the file or directory we need is located. For this example, we will use the explorer.exe file located in C: \\ Windows \\
2. Select explorer.exe, using context menu (right mouse button) go to "Properties" -\u003e then go to the "Security" tab -\u003e and click the "Advanced" button.
3. Now go to the "Owner" tab and click "Change".
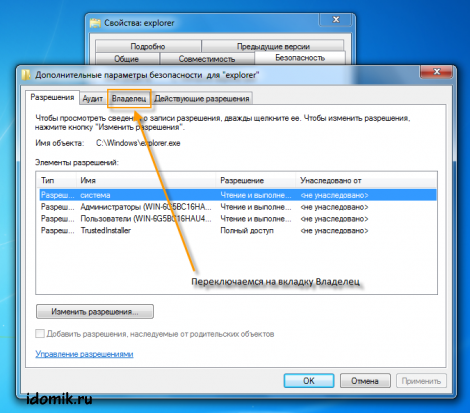
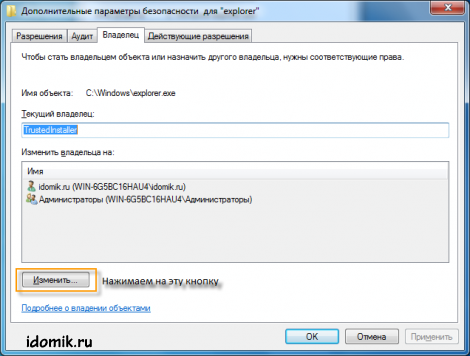
4. From the list, select a group of administrators or yourself (your account) as the owner, click "Apply", then "OK", then "OK" again.

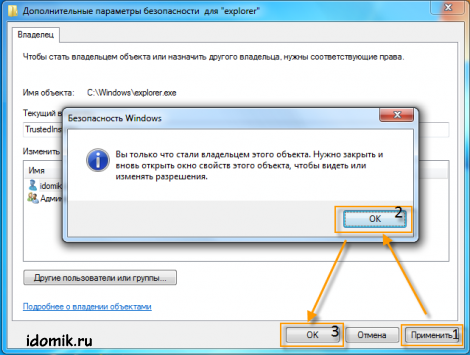
5. Never close any windows., and click everywhere "Apply" or "OK" for the changes to take effect.
6. Re-select explorer.exe, using the context menu (right mouse button) go to "Properties" -\u003e then go to the "Security" tab -\u003e
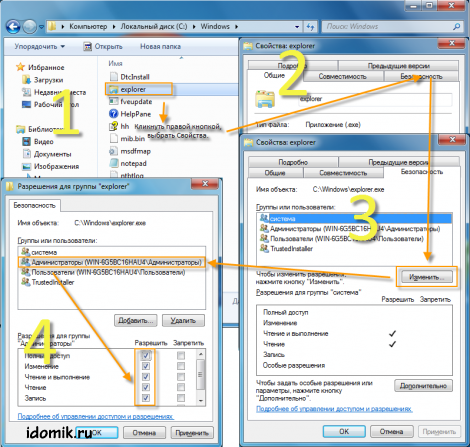
2. Select the group in which the user is located (the group of administrators) from the list and give it full control (check the box next to "Full access"). Click on "Apply", then "Yes" and "OK" again.

3. After all these manipulations, you can go to the file properties again and check whether it worked or not. If it works, your result should be the same as in the picture below.
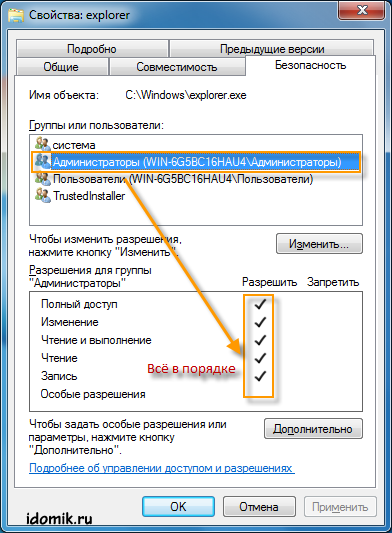
That's it, we became the owner and got full access to the explorer.exe file. Now you can rename it, delete it, in general, do whatever you want with it.
Attention! To replace explorer.exe (and any other system file) with a new file, be sure to rename it first, otherwise nothing will work. Rename better to explorer.exe .backup, so you will always know that this is a copy of the original explorer.exe (or any other system file) and in which case you will return it back without any problems.
Part two. Restore default access
So, after changing the system files, you decided to return them to default access. Basically, the owner of the system files and full access over them has trustedInstaller user... It is to this user that we will return full access. Let's start.

1. The first step is to go to the folder where the file or directory we need is located. In this example we are using the explorer.exe file located in C: \\ Windows \\
2. Select explorer.exe, using the context menu (right mouse button) go to "Properties" -\u003e then go to the "Security" tab -\u003e and click the "Change" button.
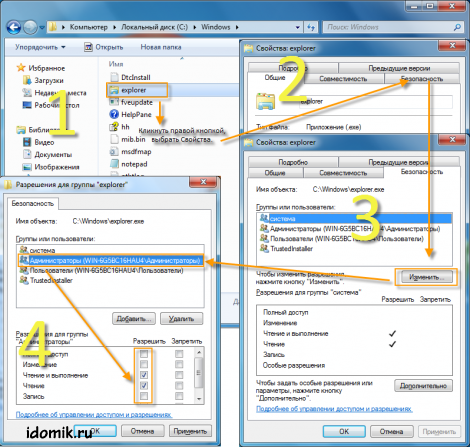
3. Select the administrator group from the list and uncheck the boxes: "Full access", "Change", "Record". Click on "Apply", then "Yes" and "OK".

4. After all these manipulations, you can go again to the file properties and check whether it worked or not. If it works, everything should be as in the picture below.

5. We changed the access of the "Administrators" group to what it was originally. It remains to change the owner of the file to TrustedInstaller. Select explorer.exe again, using the context menu (right mouse button) go to "Properties" -\u003e then go to the "Security" tab -\u003e and click the "Advanced" button.