Hello friends! The other day, once again, I stumbled upon an error when running some system services. Why am I saying that again? The fact is that I meet with her already not for the first time, but somehow to describe the ways through which I successfully coped with error 5, I could not get at all.
So we meet several possible solutions that can help you in case of problems with the launch of services, namely " Errors 5. Access denied". In general, first I will describe the very essence of the error about which I say that you could determine the same problem in you or something quite different.
A file or folder can be encrypted
You must obtain a certificate from the person who created the file. In the Import or export certificates and private keys section.
A file or folder may be damaged
In the section "Damaged files: frequently asked questions". Your user profile may be corrupted. In the section "Restoring a corrupt user profile".You may not have the right to own a file or folder
After creating a user profile, you can copy existing user files to a new profile so you can access them. To own a file or folder, follow these steps: If you are prompted for an administrator password or confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation. If you want this person to own files and subfolders In this folder, select the "Replace owner on subcontainers and objects" check box. Click the name of the person to whom you want to submit the property. . To fix the problem automatically, click the link or the "Fix" button.
So, by opening the services menu and selecting the item I need, I get into their properties, where in the item about the method of starting the service I set the value to "Automatic", and also click on the "Start" button to start it immediately. But alas, instead of a successful start, a small window appears on the screen, with a rather strange message that the service could not be started because of "Error 5. Access is denied".
Check the registry permissions
If you decide to solve this problem yourself, go to the "Fix it for yourself" section. Open the folders that contain the files that you want to restore. For example, to restore files from the Documents folder, double-click Documents.
- This assistant can be one in English.
- Click "Start" and select "Computer".
- Double-click the Users folder.
- Double-click the user name.
This message surprised me that there was talk about a lack of rights, although I worked at the computer by logging in using the system administrator account, and as you know there are all possible rights to change the properties and settings of the operating system.
How to solve the problem with Error 5?
Solutions of this kind of problem, namely, corrections of the causes of the appearance of "error 5. Access is denied", when the services are started, there are quite a few, it all depends on the situation the user encountered. Further, as usual, I will not describe one hundred percent way that will help everyone, as there is none, but I'll write about how I got out of this situation with a positive result.
If the account specified for the user "Run as a user" is a member of the local group security group or the domain administrators group, it will not be displayed on the "Permissions" page. To view or edit permissions in the registry directories.
In the Registry Editor, go to the directory where you want to view or edit the permissions. After adding the account, select "Run as a user" and click "Advanced". In the "Advanced Security Settings" section, on the "Permissions" tab, select "Run as a user" and click "Change". In the "Permissions" section in the "Basic Permissions" section, make sure that the "Read" and "Special Permissions" options are selected. Make sure that it is not selected. To view or change special permissions, click Show Additional Permissions. In the "Additional permissions" section, make sure that the permissions that appear at the beginning of this section are selected. Verify that the application of these permissions only for objects or containers in this container is not selected. If you have installed new permissions, click OK in all windows to complete. If you saw the permissions, but did not edit anything, click Cancel to close all the windows. This article describes how to configure, view, change, or remove permissions for files and folders.
Some examples to fix error 5, I found on the net, to others I got myself. In general, let's see what helped in my practice to get rid of the problems with the launch of services, but you will try to do the same in yourself, perhaps one of the variants I proposed will work for you.
"Error 5. Access is denied" when starting system services, solutions
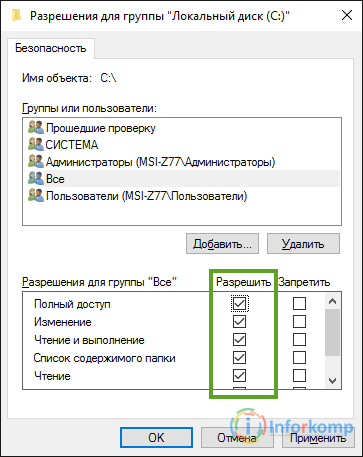
1. Open full access to drive "C". I do not know why, but I've come across computers where the security of the system disk has been set to read only and no more, and this parameter has been set for all accounts. But, as soon as I returned all the security checkmarks, error 5 disappeared forever, well, the service started its work without problems.
Permissions for files and folders include full control, change, read and execute, read and write. The "Configure, View, Change, or Delete Permissions for Files and Folders" section of this article. Configure, view, change or delete permissions on files and folders.
To configure, view, change, or delete permissions for files and folders. The "Troubleshooting" section of this article. Use one of the following steps: To configure permissions for a group or user that is not listed in the Groups or User Names list, click Add, type the name of the group or user for whom you want to configure permissions, and then click OK. To change or remove permissions for a group or an existing user, click the name of the group or user.
To return rights, you need to get into the properties window of the system drive "C" and go to the tab " Security". After missing the list of users and groups, go down to the buttons "Change" - "Add".
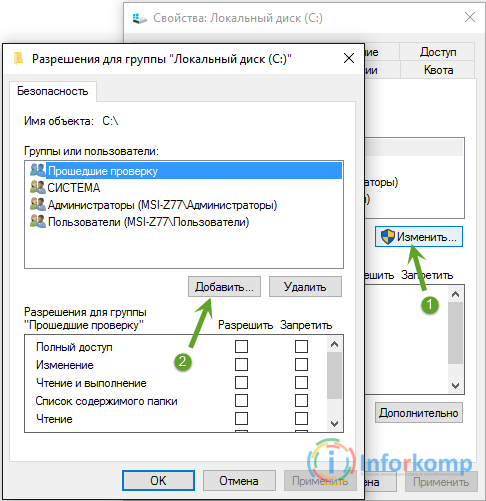
In the appeared area, with the hands on the keyboard we fill the word " All", Which means that we will establish the same access rights absolutely for all users of the system.
Perform one of the following actions. To enable or disable permission, select the Allow or Deny check box in the User Permissions or Group boxes, where the user or group is the user or group name. To delete a group or user from a group or user name, click Delete.
Important: If you do not join the domain and want to view the "Security" tab. Click the Start button, and then click Control Panel. Click "Appearance" and "Themes", and then "Folder Options." Click the "Preview" tab and uncheck the "Advanced settings" box.
![]()
If everything is so, then in the previous step you did not make mistakes, click on "OK".
For those who are still users of Windows XP, you should pay attention to the fact that by default you may not see the "Security" tab. In order to bring it back to its place, follow a few simple steps.
Notes. The All group does not include the anonymous logon permission. To change permissions, you must be the owner or owner, so you can change the permissions. Groups or users that are granted full access to a folder can delete files and subfolders from this folder, regardless of the permissions that protect files and subfolders. If the check boxes in the "User Group Permissions" field are shaded or if the "Delete" button is not available, the file or folder has permissions inherited from the parent folder.
When you add a new user or group, by default the user or group has Read and Run permissions, Show Folder Contents, and Read. How inheritance affects the permissions of files and folders. After setting permissions in the parent folder, the new files and subfolders created in the folder inherit these permissions. If you do not want the files and folders to inherit permissions, click "Only this folder" in the "Apply" box when you configure special permissions for the parent folder.
- Open any folder;
- From the top click on "Service";
- "Folder properties";
- "View";
- In the list of additional parameters, we remove the mark from using simplified public access.
After this, we perform the above described actions and of course we check whether you succeeded with this method to cope with the error5 or not.
If you want to prevent inheritance of rights for only certain files or subfolders, right-click the file or subfolder, click Properties, click the Security tab, click Advanced, and then click Advanced. click to remove the Inherit from parent objects associated with child objects check box. Include them together with the data specified here explicitly.
If the check boxes are unavailable, the file or folder has permissions inherited from the parent folder. There are three ways to make changes to inherited permissions. Make changes to the parent folder so that the file or folder inherits permissions. Click to select the opposite permissions to bypass the obsolete resolution. Clear the Inherit from parent objects associated with child objects check box. When you do this, you can make changes to permissions or delete a user or group from the permissions list.
2. Also, there is another way I got on the Microsoft support pages. Seeing this tip in the comments I decided to try it and the problem with error 5 when starting the service, I decided.
The first step is to open a command prompt on behalf of the administrator, if you are on this account, then you can not steal and just open cmd with "Run".
How to change the owner of a folder or file using the icacls command
However, the file or folder does not inherit permissions from the parent folder. When this happens, the inherited configuration of the parent folder closest to the object in the subtree takes precedence. When using the "Deny and Allow" options, pay attention to the following.
Inherited permissions are inherited only by child objects. You can determine what permissions a user or group has over the object if they see effective permissions. View effective file and folder permissions. To view the effective permissions of files and folders. Find the file or folder for which you want to view the current permissions. Right-click the file or folder, click Properties, and then click the Security tab. Click Advanced, and then click the Effective Permissions tab.
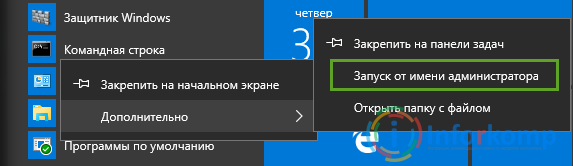
Now in the window that appears, write this: net localgroup Administrator / add networkservice (Important: if you have English. OS then instead of Admin. specify Administrator) and click on the "Enter" key.
Then we do it: net localgroup Administrators / add localservice . (Administrators)
Using the icacls command-line utility
In the "Name" field, enter the name of the user or group and click "OK". Enabled check boxes indicate effective user or group permissions for this file or folder. The following security key values are not used in the calculation: anonymous logon, authenticated users, lots, author group, owner-developer, dialing, corporate domain controllers, all, network, proxy, restriction, self-service, system and User of the terminal server.
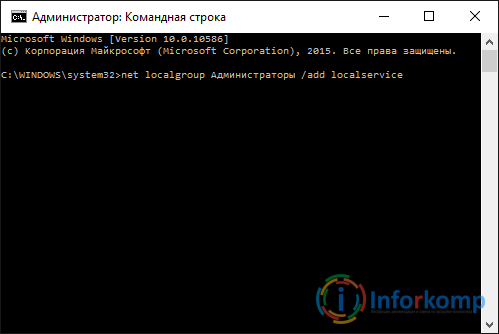
After completing the commands, close the command window and restart the computer.
If the commands were entered correctly and you were lucky, then error 5, which prevents the start of services, should disappear, and the services themselves will start without any denial of access messages.
An example of these values is an attempt to remotely access a file. The Effective Permissions tab displays information that is calculated from existing permission entries. Therefore, the information displayed on this page is read-only and does not allow you to change the permissions of the user by enabling or disabling permissions. Manage shared folders and files using computer management.
The computer management tool provides a convenient way to manage and view the security settings of files and folders. For more information about security and permissions, click Help on the computer's control panel. To start the computer management tool. Click "Start", "Control Panel", "Administration". Click on "Computer Management" and select "Shared Folders". Double-click Shared resources to view the list of public folders. Note that each shared volume on the computer appears with the dollar sign after the resource name.
3. We try to fix the error with denial of access when the services are started using the operating system registry.
But, before we rush to crash our registry, we need to first find out the name of the service that does not want to start. To do this, in the list of services, open the properties of the service we need and see the line " Service Name". Remembering it, we go directly to work with the registry.
These are hidden administrative shares that you can not change. Double-click the shared folder to view the security settings for this folder. If the Security tab is not available and you can not configure permissions for users and groups. Simple file sharing is enabled. To work around this behavior, disable the simplified exchange.
Special access permissions are a set of permissions that you can configure. This article describes how to configure, view, modify, or delete special permissions for files and folders. File and Folder Permissions Folder rights include full control, change, read and execute, view folder contents, read and write. Each of these permissions consists of a logical group of special permissions that are listed and defined in the following sections.
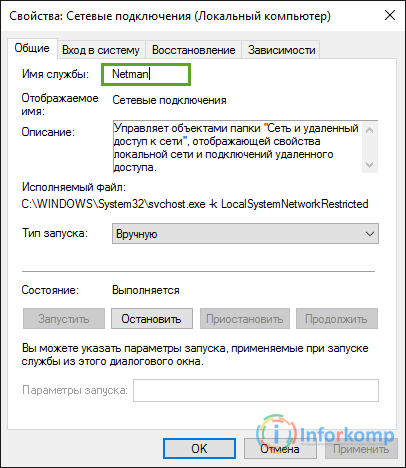
Registry Editor - run it using the "Run" window. If you do not understand what it is, then you.
You should open a large list of services located in alphabetical order. In order to understand what kind of service we need, I said to look at her name in the properties. So we are looking for a section with the appropriate name, right click call the menu of the section and select the line " Resolutions».
The section "Configuring, Viewing, Modifying or Deleting Specific Permissions for Files and Folders" in this article. Special permissions on files and folders. The following table describes the special permissions for files and folders. Groups or users who are granted full access to a folder can delete any file in this folder, regardless of the permissions that protect the file. NOTE. Although it seems that the contents of the Disk in the folder both Read and Execute have the same special permissions, these permissions are inherited in different ways.
Folder content is inherited by folders, but not by files, and appears only when viewing folder permissions. Reading and executing it inherits both files and folders and is always present when it sees the permissions of files or folders. Definition of special permissions.
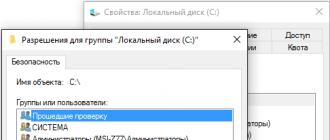
You should see the same security setting as I described in the first paragraph. In general, we look that in "Administrators" and "Users" groups we have full access.
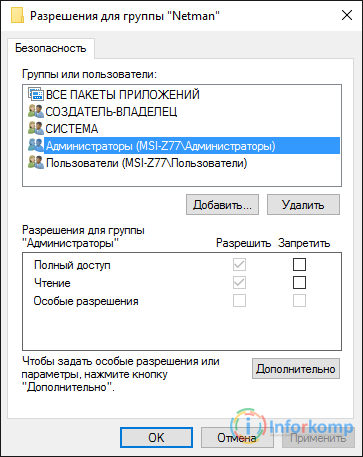
If they are not there at all, then we correct this matter, in the same way as I showed at the beginning of the article.
4. Consider one more thing, which is also related to access to the C drive, only this time not to all users, namely LOCAL SERVICE.
So, again we go into the security properties of the system disk. Next, after the list of users and groups, click on the "Add" button.
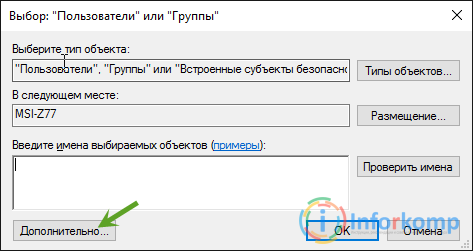
In the window that appears, click on "Search". As a result, a list should appear from which we need to select "" and click on the "OK" button.
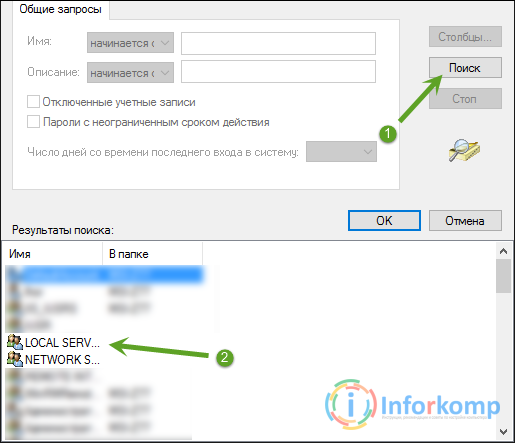
This group should be added to the user list, now for going down a bit lower to the "Permissions for LOCAL" window, we set all possible checkboxes and apply the changes.
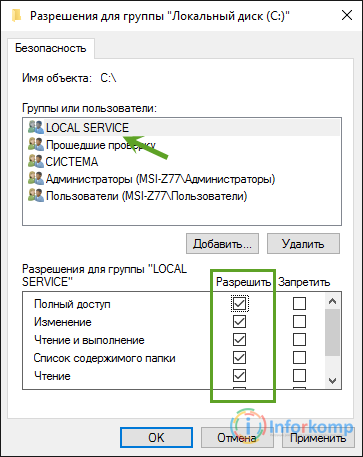
In theory, the service after that should start, well, error 5, completely disappeared.
5. Alternatively, you can also disable or delete your antivirus and try to start the service without it. The fact is that some anti-virus software besides the software installs additional services that could take away your rights to enable or disable some local services.
6. Well, one hundred percent option, of course, is, I know that not everyone will do it, but I can say with certainty that it will definitely help get rid of error 5 with the denial of access to the launch of the service, and, in addition, will save the computer from other various glitches and problems 🙂
On this I'll probably finish my article, but if you can help at least one of the above options, then do not forget to join us
If you receive messages indicating that you are denied access, "No access to the folder", "Request permission to change this folder" and the like, when trying to change, open or delete a folder or file in Windows, you should change the owner of the folder or file, which we'll talk about.
There are several ways to become the owner of a folder or a file, the main ones being the use of the command line and additional OS security settings. There are also third-party programs that allow you to change the owner of a folder in two clicks, one of whose representatives will also look. Everything described below is suitable for Windows 7, 8 and 8.1, as well as Windows 10.
Notes: in order to become an owner of an item using the methods below, you must have administrator rights on the computer. In addition, you should not change the owner for the entire system drive - this can lead to unstable operation of Windows.
Additional information: if you want to become the owner of a folder in order to delete it, otherwise it will not be deleted, and write Request permission from TrustedInstaller or from Administrators, use the following instruction (there is video in the same place):.
Using the takeown command to become the owner of the object
In order to change the ownership of a folder or file using the command line, there are two commands, the first one is takeown.
To use it, run a command prompt on behalf of the Administrator (in Windows 8 and Windows 10, you can do this from the menu that is called by the right click on the Start button, in Windows 7 - with the right-click on the command line in standard programs).
At the command line, depending on the owner of which object you need to become, enter one of the commands:
- takeown /F "full path to file" - become the owner of the specified file. To make all computer administrators owners, use the / A after the path to the file in the command.
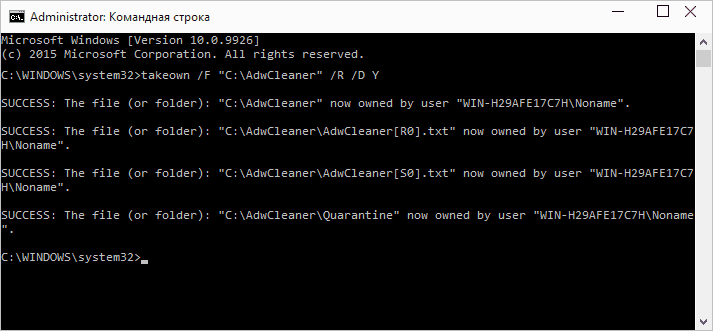
- takeown / F "path to a folder or disk" / R / D Y - become the owner of a folder or disk. The path to the drive is specified as D: (without a slash), the path to the folder is C: \\ Folder (also without a slash).
When executing these commands, you will receive a message stating that you have successfully become the owner of a particular file or individual files in the specified folder or disk (see screenshot).
How to change the owner of a folder or file using the icacls command
Another command that allows you to access the folder or files (change their owner) is icacls, which should also be used on the command line running as administrator.
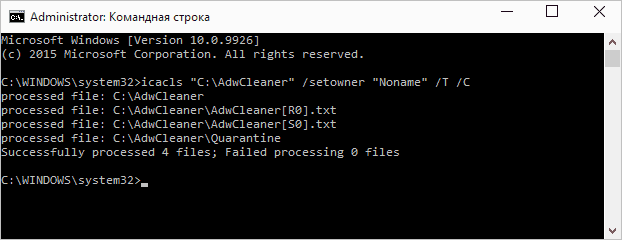
To install the owner, use the command in the following form (example on the screenshot):
Icacls "path to file or folder" /setowner "UserName" /T /C
The paths are indicated in the same way as the previous method. If you want to make the owners of all administrators, then instead of the user name, use Administrators (or, if it does not work, Administrators).
Additional information: In addition to becoming the owner of a folder or file, you may also need to obtain permissions to change, for this you can use the following command (gives the full rights to the user for the folder and the nested objects): ICACLS "% 1" / grant: r "username" :( OI) (CI) F
Accessing with security settings
The next way is to use only the mouse and the Windows interface, without going to the command line.
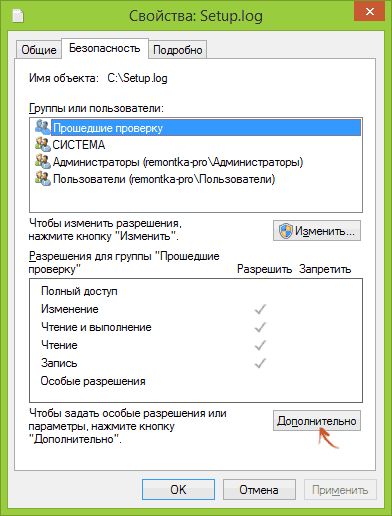
On this you become the owner of the specified Windows object and the message that there is no access to the folder or file, you should not be disturbed anymore.
Other ways to become owners of folders and files
There are other ways to solve the problem of "denied access" and quickly become the owner, for example, using third-party programs that embed the "Become an owner" item in the explorer context menu. One such program is TakeOwnershipPro, free and, as far as I can tell, without something potentially unwanted. A similar item can be added to the context menu by editing the Windows registry.
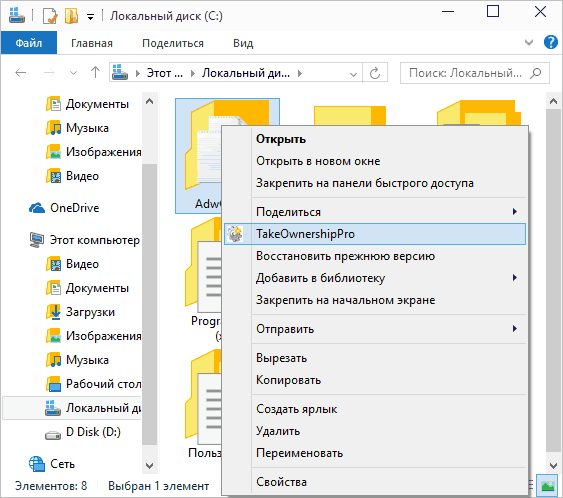
However, given that this task occurs relatively rarely, I do not recommend installing third-party software or making changes to the system: in my opinion, it is better to change the owner of an element by one of the ways "manually".