We often talk a lot about information security. We argue on the theme of protection from viruses, trojans. Consider a different software and compare it with each other. We use keyloggers, network screens, we use cryptography and various password systems. But information, no matter how we defend it in such ways, sometimes still seeps into the wrong hands. One way to obtain confidential (and secret) information is to restore it from the formatted disks on which this information was previously located.
Many people know that neither reformatting nor formatting of disks does not provide a full-fledged removal of information stored on such media. If you understand the process of reformatting, it turns out that this process destroys the references to the partitions in the disk partition table without affecting the data itself. You can find many programs (once very useful program was Tiramisu), which will help restore seemingly completely lost data, including after accidental reformatting of the disk.
Not completely destroys the data and formatting of storage media, including low-level data. Yes, with normal programs after such a procedure, you may not be able to restore the information, but there are other, non-software methods. For example, the use of technology of magnetic microscopy. For a long time? Expensive? Certainly. But the information sometimes costs much more time spent on its restoration. (This method can be used even for discs whose plates have been mechanically exposed.)
Therefore, in cases where information should by no means fall into the wrong hands, information carriers must be subjected to a procedure of irreversible deletion and destruction of data. This procedure is called cleaning discs. It is believed that after cleaning, carriers can no longer represent any interest, and even advanced technical means can not remove any information from them. In many countries, special standards have been adopted that define algorithms for cleaning carriers. Here is an excerpt from the documentation for the program, which will be discussed below.
- US DoD 5220.22-M is the standard of the US Department of Defense;
- uS naval standards NAVSO P-5239-26:
- NAVSO P-5239-26 for RLL-encoded devices;
- NAVSO P-5239-26 for MFM-encoded devices;
- british standard HMG Infosec No.5;
- german standard VSItR;
- australian ASCI 33;
- russian GOST R 50739-95;
- the Peter Gutmann algorithm;
- bruce Schneier's algorithm;
- algorithm of Paragon:
- each sector is overwritten with an absolutely random 512-bit string, new for each sector, using CSPRNG (cryptographically safe generator random numbers);
- each clean sector is overwritten by its binary addition;
- each sector is rewritten with a 512-bit string (CSPRNG), again completely random, different from that used in the first pass, and new for each sector;
- each cleaned sector is filled with a value of 0xAA. Upon completion of the operation, the resultant data area is checked.
I will not give more detailed description algorithms, users of the program Paragon Disk Wiper will find in its documentation additional information. Almost all of the above algorithms are implemented in the program, and there is also the possibility to define your own mashing algorithm. The choice of algorithm depends on the version of the program. There are two of them - personal and professional. In the personalized algorithm is implemented Paragon, in the professional - ten different algorithms. This is the main difference between the versions.
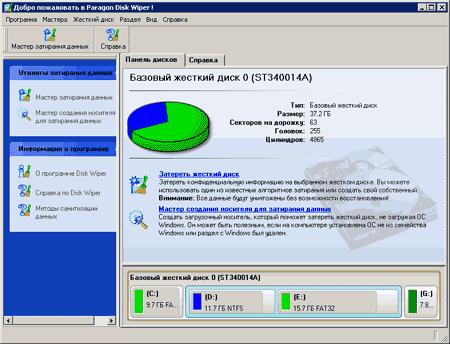
The main features of the program are disk wiping, for which you can use the basic version of the program or specially created with its help bootable media (CD-ROM, floppy disks) for DOS-mode, as well as basic functions for initializing, partitioning and formatting disks. The program can work under any versions of Windows and supports all file systems. Cleaning can be used for both hard drives and floppy disks, as well as for flash drives.
The program is operated through its main window. Its main field is intended for displaying information about physical and logical disks connected to your computer. Their list is located at the bottom of the main window. In the top line - physical disks, in the bottom - their division into logical ones. Both formatted and unformatted partitions are displayed. If you select a physical or logical drive, information about it will be displayed at the top of the main window.
For physical disk in the header of the window its type is displayed, and as information - the size, number of heads, cylinders and sectors. For logical drives the amount of information displayed is larger. Data about the file system, the number of boot sectors, the version of the file system, the size of the disk, the occupied and free space are displayed. Additional information is whether logical disk active and visible.
You can clean up both the physical disk and the logical partition. To facilitate the work in the program, special wizards are implemented, which step by step guide the user through all the stages of preparation for the task.

Consider the process of preparing to clean the disk (partition). In the first step you can choose the cleaning option - either wipe the section completely, or clear only free place. The second option, perhaps, will be in demand more often - without removing all information, you can destroy all the deleted information without the possibility of its recovery. To test the work, I would suggest first to use this option. The next step is to make a choice of the algorithm that will be used for cleaning. The default algorithm can be defined in the program settings. Then it will be proposed as the main one.
In the personal version, only two options are available - either use the Paragon algorithm, or define your own cleaning algorithm. Having chosen the standard algorithm, you will be taken to a page where detailed information about the principle of its operation will be displayed and a possibility of its some modification will be given, in particular, you will be able to completely or partially turn off the verification of the performed operation. For test runs this can be played, but in real conditions it is better to use the full capabilities of the chosen algorithm. On the same page, the estimated time of the operation is determined and displayed.
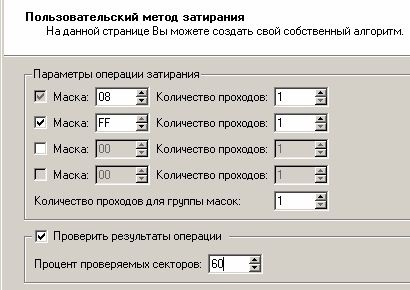
If you select the option of assigning your own algorithm, a window will open in which you will have to enter your own characteristics. The user can define up to four masks of data mashing, the number of passes for each mask and for a group of masks. To define a mashing mask, the user will need to specify a two-digit number in hexadecimal form (the default value is "00"). In addition to masks and the number of passes, it is possible to check the operation of the algorithm for the presence of the remaining data as a percentage of the total number of sectors scanned.
By selecting or assigning an algorithm, you can start the work, but the wizard will again ask for your confirmation - do you really want to complete the task. Who knows, maybe, at the last moment, you will remember that among the information being cleared, there remains what must be left. Then you have the last opportunity to refuse stripping and again to check whether it is possible to perform the operation.
The wipe wizard can be started different ways: through the context menu of the logical or physical disk, through the main window with information about the selected disk (partition), through the main menu or through the toolbar. The only difference is that when you start the wizard from the main menu in the first step, you will need to select the disk with which you are going to work, and when working through the context menu - it is not necessary.
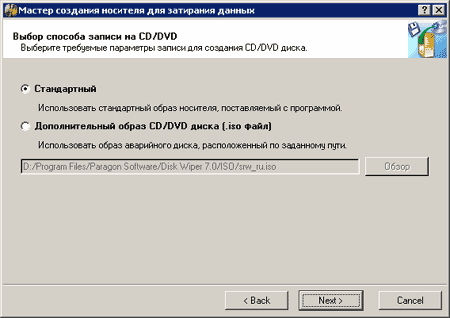
In the event that you need to destroy the data of the boot partition or destroy the data on a disk from which the operating system does not already boot, you can use another option of the program - downloading it from the the boot disk or a floppy disk. To do this, you need to first create such a disk. For this purpose, you can use the wizard to create media for overwriting data. It prompts you to select the media-CD or floppy disk, and then either use the standard image of the disk or floppy that comes with the program, or use your existing rescue disk image. If there was any information on the disk, it will be destroyed beforehand (of course, this only applies to CD / RW disks) and floppy disks.
Now a little bit about working with disk partitions. As already noted, the program features the ability to create, delete, format logical partitions, assign and delete letters of sections, check the surface. But there are some limitations when creating partitions. In particular, the current version of the program can not create new partitions on dynamic disks. Only supported hard disks, using the DOS-scheme of partitioning the disk (in Windows 2000 and XP such disks are called the main disks). Accordingly, the restrictions imposed by the DOS-scheme also apply.
Setting up partitions is done using graphical interface, in which the program initially offers some agreed parameters. Often these values suit the user, but you can change any available values. After the partition is created, it is formatted. The program offers a choice of different options: file systems FAT16 / FAT32, NTFS and HPFS, ReiserFS and Linux Swap v. 2. You can then assign the drive to the drive. Similarly, you can perform the reverse operations - delete the letter ("unmount" the disk), delete the partition. These actions are performed both from context menu disk, and from the submenu "Section" of the main menu of the program. Another option is to view the sectors of the partition or disk.
In conclusion, I would like to note the high-quality interface of the program - it is pleasant and convenient to work with. Perhaps, only one remark. The help about the program is opened in the same field of the window, where information about disks and partitions is also displayed, therefore it will not be possible to simultaneously read help and perform operations. But the need for this exists only at the initial stage of familiarization, then you will not need a certificate.
Many users, rummaging through the numerous menus and settings of the application CCleaner, suddenly come across the section "Erasing discs". Quite naturally the question arises: obliterating cDs with CCleaner what is it? Moreover, there is very little that can be understood from the menu items themselves. So…
Erasing CCleaner Drives - What Is It?
This mysterious function is located on the "Tools" tab, in the "Erase Disk" item. The tip at the top of the window gives a meager and little informative message: "Reliably mashing all the contents or free space on the disks." In fact, this very useful function, which is surely useful to those who want remote information to be really deleted from hard drive computer.
The thing is that an erased file, even if it passed the Recycle Bin or was removed from it, remains some time still written on the hard drive. Just the user sees this place as free. However, with the help of special utilities you can "pull out" and restore the erased files. But this can only be done until the moment when no new information is written over the deleted file. In this case, no utilities will help. CCleaner also allows you to repeatedly re-erase a deleted file, that no recovery utility will get to it.
How to use Erase CDs
The following options are available in the drop-down menu:
- only free space. The visible free space is erased. Wherein visible files will not be affected. However, earlier deleted files rubbed clean;
- the whole disk. In this case, absolutely all files on the selected disk are deleted. But do not confuse this function with the formatting of the disk.
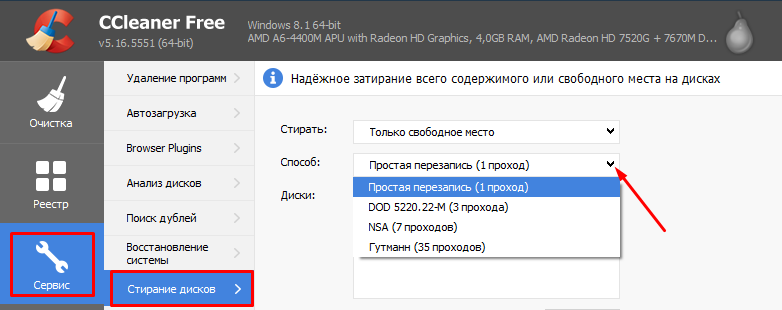
Ways of erasing:
- simple dubbing in one pass. For most cases this is quite enough;
- DOD 5220.22-M - three-time erasure is proposed for greater reliability;
- NSA - mashing in seven passes;
- finally, the most reliable - Gutmann - in 35 passes.
It is also suggested that you select the disc that you want to erase. At the same time, although the erasure process does not take much system resources, depending on the method chosen, the computer's power and disk capacity may take quite a long time. And now, knowing about erasing the CCleaner discs - what is it for the function, you can use it at your discretion and not be afraid for the secrecy of your data deleted from the computer.
To prepare the surface of concrete for further use, treatment with special trowels is necessary. Rubbing in cement hardener also does not do without special equipment. When leveling, the trowel disks will allow you to get rid of unevenness, curvature and sagging of different sizes. The choice of these discs will depend on the type of troweling equipment, as well as the scope of the tools. The market presents components of different diameters (610-1200 millimeters).
Under the trowels are meant the details of the machines intended for smoothing the unevennesses on the concrete. Instruments are produced in the form of plates, which are installed on two-or one-rotor technology. They are necessary for rough grouting in concrete or when working with industrial cement floors. In addition, various modifications of the tools allow for finishing the concrete. All discs manufactured by leading manufacturers are capable of withstanding heavy loads.
Typically, specialists first smooth out the irregularities and rips that formed after the application of the vibrating device, with the help of disks, after which special blades or knives are used. They will help to give the concrete smoothness and shine. Among the advantages of components, experts mention their durability: can handle up to 1500 square meters of surfaces. To extend the life of the disk, there are special fuses on the disk. However, manufacturers do not equip them with all models. For additional smoothing, use blades. Such tools are divided by diameter, as well as by the number of fasteners.
Dimensions of the trowel
Accessories are selected depending on the type of equipment. Their dimensions are 300-1800 millimeters. In addition, the disks are either completely flat, or slightly convex.
Examples of manufacturers and characteristics

Conclusion
When carrying out various construction works: pouring screeds, cement floor and road surfaces it is necessary to use the trowel special equipment. With the help of such devices it is possible to achieve an ideally smooth surface.