August 30 Readings: 17,125
NVIDIA continues its victorious march through the expanses of the desktop segment of graphics accelerators and unhurriedly answers AMD for the output of the RX 480. The third accelerator was named GeForce GTX 1060 and, perhaps, this model will be the most in demand in our market due to its price and performance. But let's not run ahead and tell everything in order.
Specification
- Manufacturer: NVIDIA;
- Model: GeForce GTX 1060;
- Graphics processor: GP106;
- Process technology: 16 nm;
- The frequency of the GPU: 1506 / turbo mode 1708 MHz;
- Number of shader processors: 1280;
- Video memory: 6 GB;
- Video memory type: GDDR5;
- The size of the video memory bus: 192 bits;
- Video memory frequency: 2000 MHz (8 GHz QDR);
- SLI support: no;
- HDCP support: yes (1080p);
- Ports: 3x DisplayPort, DVI-D, HDMI 2.0;
- Max. number of connected monitors: 4 (up to 3 for 3D Vision Surround);
- Connector supplementary feeding: 6-pin;
- Consumption level: 120 W;
- Length: 250 mm;
- Price: 19000 rub.
What's new?
According to the company NVIDIA new architecture is revolutionary, but is it really so? The most striking innovation in the case of PASCAL is the transition to a new 16 nm process technology. This allowed us to achieve a significant increase in the operating frequency of the GPU, which resulted in a noticeable increase in performance. Another important feature was the use of FinFET (Field Effect Transistor with Fin) - transistors, which resulted in a reduction in power consumption and efficiency. Despite this, the architecture of PASCAL is more like the evolution of Maxwell than something fundamentally new.
If we pay attention to the sphere of innovative technologies, it is important to note the availability of support for an advanced tool package Nvidia VRWorks, which is designed to provide the most complete immersion in the VR environment.

This will be achieved by combining various player sensations that will be provided with high-quality surround sound, a correct reaction of the environment to certain actions and a high-quality graphic component.
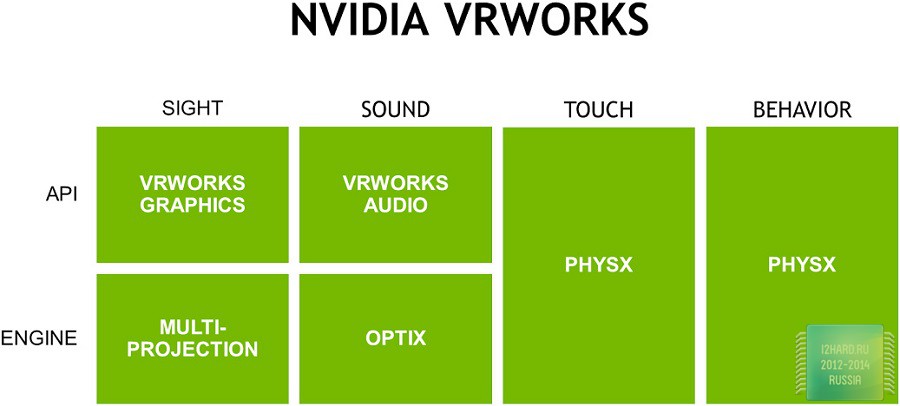
For fans of multi-monitor configurations and helmets of virtual reality, NVIDIA has prepared a one-time multiprojection technology Simultaneous Multi-Projection). In fact, this optimization is designed to perform simultaneous rendering of geometric data for several pre-prepared projections. What is it for? First, to eliminate various distortions when using curved monitors or configurations with multiple displays. Secondly, it allows you to increase the performance for similar scenarios using your system. Few of us had the opportunity to test in due time NVIDIA 3D Vision, but those who happened to have noticed a noticeable lack of performance, since the video card was under double load when drawing images for each eye. With the introduction of SMP, this problem is eliminated.

Also, we can not fail to mention two more interesting innovations, which are entitled as Ansel and Fast Sync.
Ansel - an invaluable tool for creating companion game content that will be useful to streamers and authors of various game blogs. During the game, you can press the pause and adjust the camera at any desired angle to create a screenshot. In addition, you will have a number of effects to improve the image, as well as the ability to take a picture with stunning clarity. In addition, it is possible to create 3D images, panoramic screenshots and 360 ° images. However, it should be noted that this will be available only in those games where appropriate support for this option will be introduced.

Fast Sync - this is a kind of addition to a function such as VSYNC. In general, the activation of this innovation will allow you to get rid of the delays that occur when you enable VSYNC. In addition, artifacts are removed in the form of a picture gap, which can be noticeable when the vertical synchronization is turned off. This scenario is only valid if the FPS exceeds the refresh rate threshold.
Positioning
First, let's define the typical portrait of the consumer. NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1060 has good performance and is aimed primarily at those who want to play comfortably on monitors with a resolution of Full HD (1920 × 1080). To get such a video card for playing on WQXGA (2560x1440) and especially 4k UHD (3840x2160), the occupation is far from the most reasonable. The popularization of this model is facilitated by a more affordable price tag, which fluctuates around 19 thousand rubles. We add here low requirements for the power supply unit and we have a new applicant for an optimal choice in the middle price segment. The only negative nuance in this case is the lack of the possibility of combining several video cards in SLI. This can be used by a competitor who offers the RX 480 with Crossfire support.
Packing and equipment
The video card arrived on the test without packaging. However, the box and bundle are no different from those considered earlier in the material on. In turn, I want to note that in versions from third-party brands the bundle can be supplemented with all possible adapters and accessories or bonus codes for actual game projects.
Appearance of the product
Externally, the video card does not look as impressive as the GTX 1080 or GTX 1070. Despite this, it is necessary to note the expressive outlines in the design and use of high-quality materials. To the advantages of Founders Edition is undoubtedly a compact size that guarantees compatibility with any standard components of computer assembly. The video card occupies exactly two slots, and its length does not exceed 25 cm.

The absence on the back of the metal plate spoils the final impression of the device, which is especially noticeable by the owners of the cases with a transparent side window. Also striking is the fact that the printed circuit board is noticeably shorter than the cooling system installed on it.
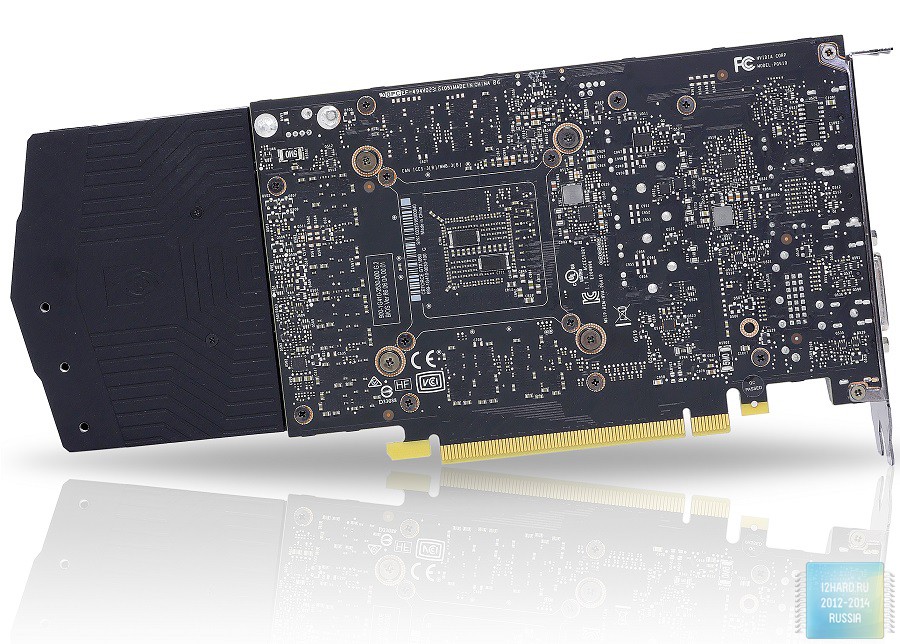
To connect additional power supply, the device is equipped with one 6-pin connector, which is located on the end closer to the end of the board. For good performance you will need a power supply unit with a power of 400 W or higher. A distinctive feature of the GTX 1060 from older brothers in the face of GTX 1070 and GTX 1080 is the lack of a connector for combining graphics cards in SLI. And this despite the fact that the nearest competitor from AMD this option is implemented.
It is interesting to observe how with the growth of performance, video cards become more and more economical in consumption and against this background there is no need for super-power power supplies. Also, there is no need to use cumbersome alternative cooling systems, but some manufacturers continue to install three fans and huge radiators even for economical solutions like the GTX 1060. The pleasant nuances include the green backlighting of the logo, which is regulated through the GeForce Experience application.

On the front part there is no any additional connectors, only the fins of the radiator are seen here. If you look closely, this angle causes persistent associations with the bumper and the hood of the car.

The interface panel is not remarkable and repeats the typical set of ports, which we have already met repeatedly on video cards of the past generation: 3x DisplayPort, DVI-D, HDMI 2.0.

Cooling system
The GeForce GTX 1060 Founders Edition cooling system is a turbine-type design. To remove heat from the GPU, a separate radiator with a copper base is used. Memory chips with power elements that contact a separate metal plate on which the fan is installed have not been ignored. The impeller of the fan is equipped with some optimizations, thanks to which it was possible to reduce the noise level without reducing the air flow. I also want to note the absence of "backplays", which slightly worsens the overall appearance.
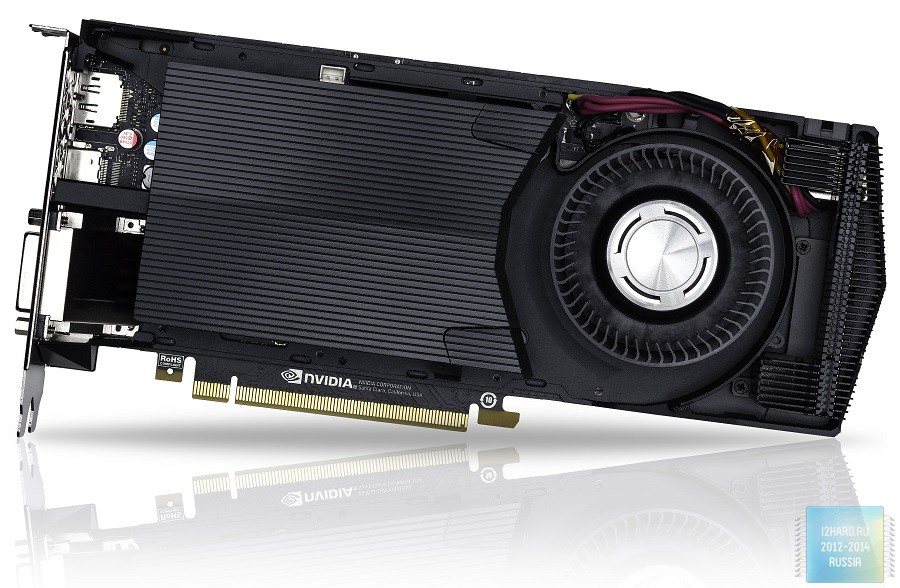

Most often, video cards with a reference cooling system are used where it is necessary to remove hot air outside the enclosure. This usually means operating the accelerator in compact assemblies, where the possibilities for installing additional fans are very limited.
Printed circuit board
Before us is a compact printed circuit board made in black with a classic arrangement of components. In the central part is a graphics chip around which the memory chips are soldered. The power subsystem is located on the left side.
Pay attention to the lack of a protective frame around the GPU. This means that you need to carefully remove or install the cooling system, so as not to accidentally damage the chip.
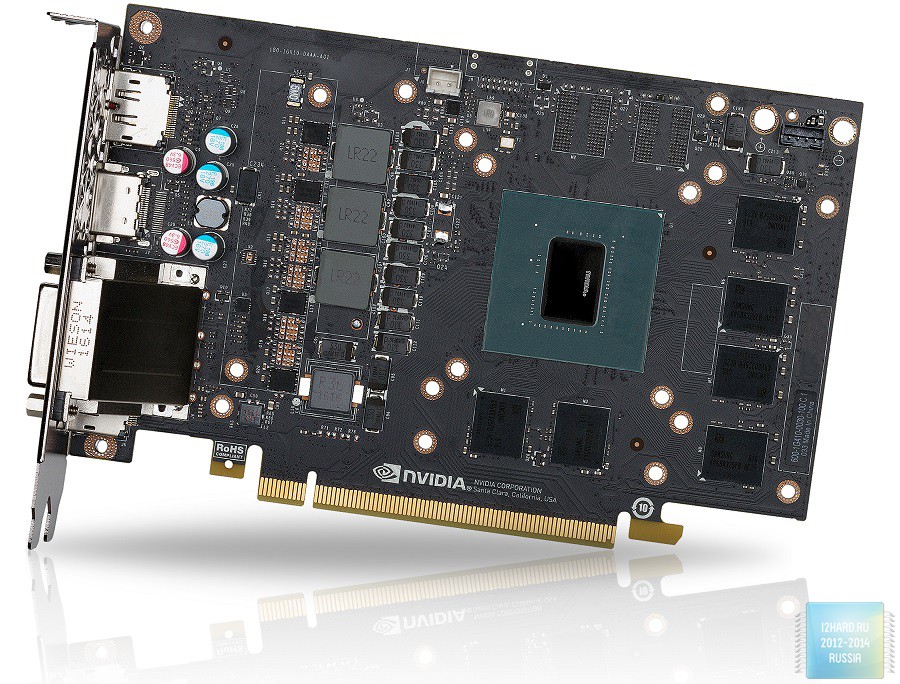

The total amount of memory is recruited by six chips with the marking K4G80325FB produced by Samsung. The power subsystem has 4 phases, three of which are allocated for the GPU and one for memory. The power management uses the uP9509P PWM controller uPI Semiconductor. Transistors use NTMFD4C85N from ON Semiconductor.
Testbed configuration
- Processor: Intel Core i7-6700K (4000 MHz);
- Motherboard: GIGABYTE GA-Z170X-Gaming 7;
- Cooler:;
- Thermal interface: Cryorig CP15;
- Memory: 4 x 4 GB DDR4 3400,;
- Video card: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1060;
- SSD Drive:;
- Fan rotation control: Schyte Kaze Q-12;
- Power Supply: ;
- Case: NZXT Switch 810;
- Monitor: SAMSUNG U32E850R;
- Operating system: Windows 10 64-bit.
- Drivers: GeForce 368.81.
Intel Core i7-6700K was used as the central processor, while the processor frequency was nominal. The role of the platform was performed by the GIGABYTE GA-Z170X-Gaming 7 motherboard. The value of FCLK was set manually and corresponded to 1000 MHz. The memory functioned at a frequency of 3400 MHz with an active XMP profile with 16-18-18-36 timings.

The considered instance is the reference one: the core and memory frequencies correspond to the standard values, and the reference CO is used for cooling. The thermal interface for the GPU corresponds to the factory default.
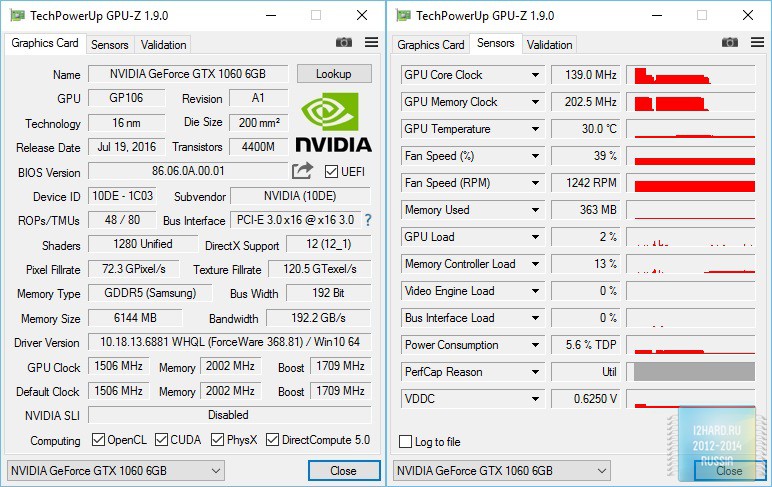
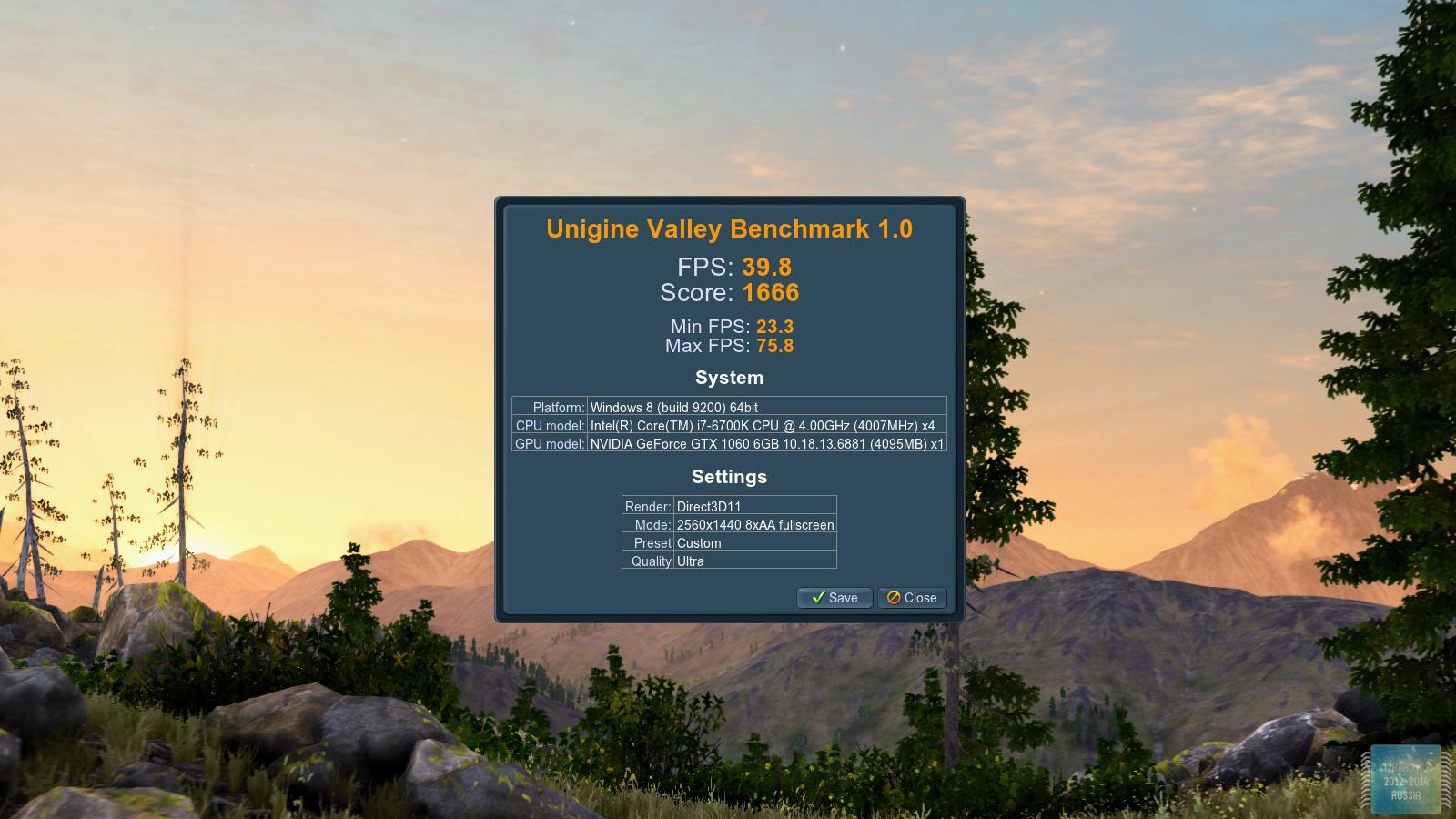
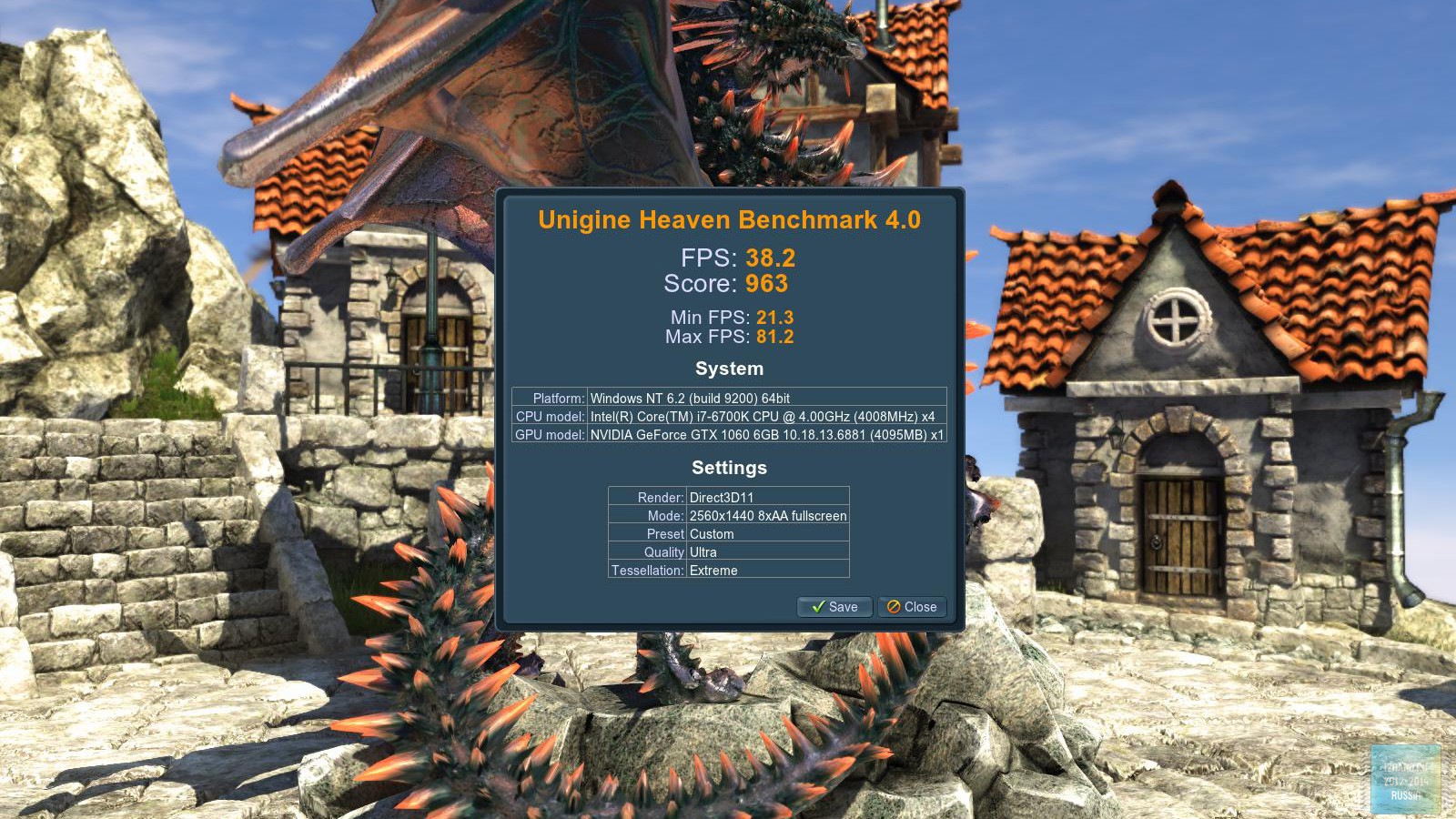
Synthetic tests
Benchmark, Heaven Benchmark and 3DMark13 tests were used to evaluate the performance in synthetics.







Game Tests
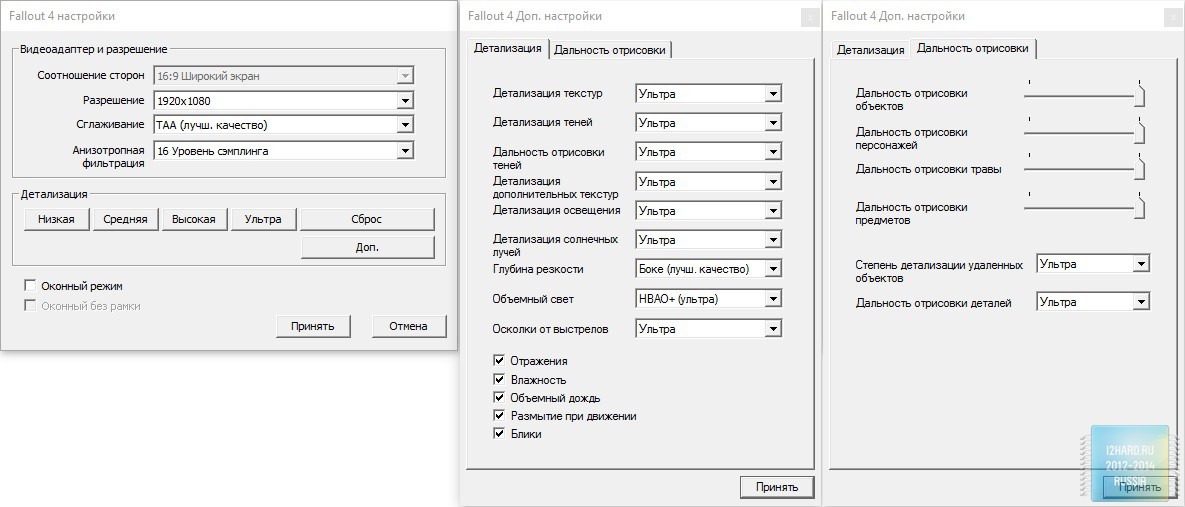
Let's move on to the gaming applications and focus on the testing methodology. The FPS was measured using the FRAPS utility. All games were tested in the three most current resolutions: 1920x1080, 2560x1440 and 3840x2160. The following parameters are manually disabled:
- VSync (vertical synchronization)
All other settings, including anti-aliasing, were set to the maximum possible. For clarity, each game is provided with screenshots from the graphics settings menu, only the resolution was changed, all other parameters remained unchanged.



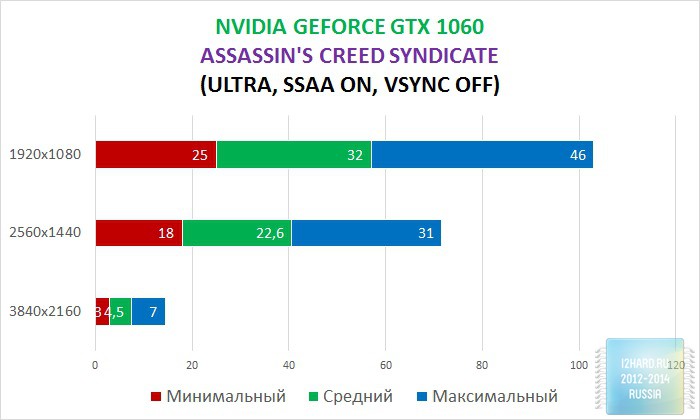

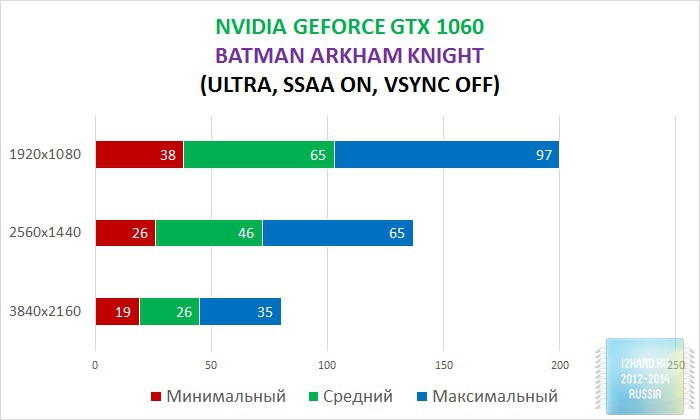

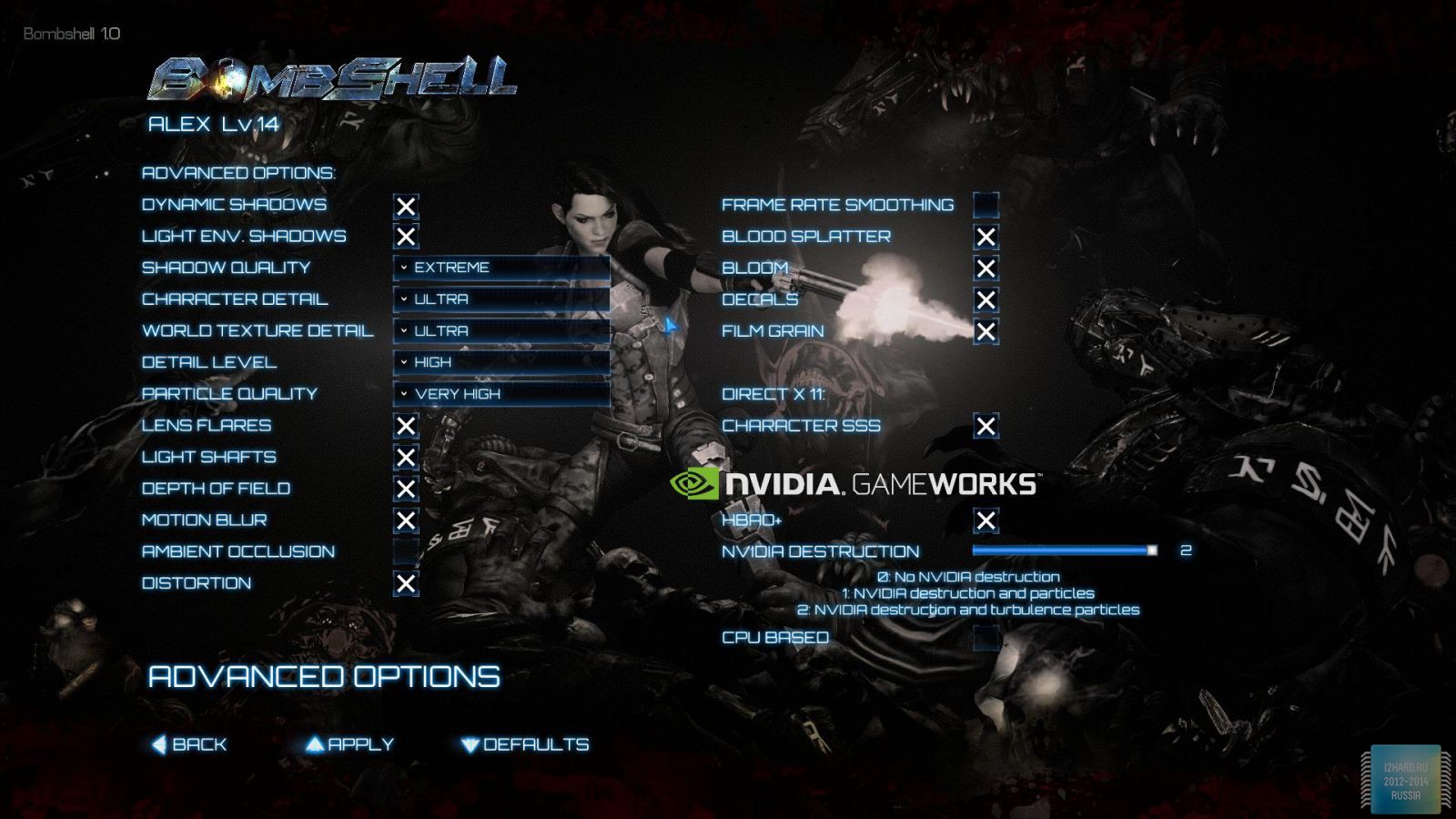





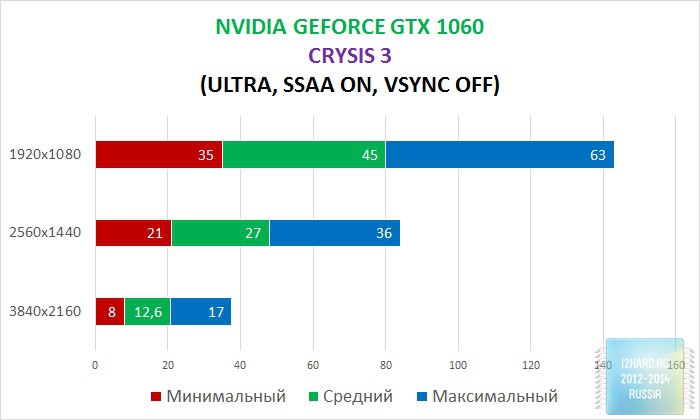




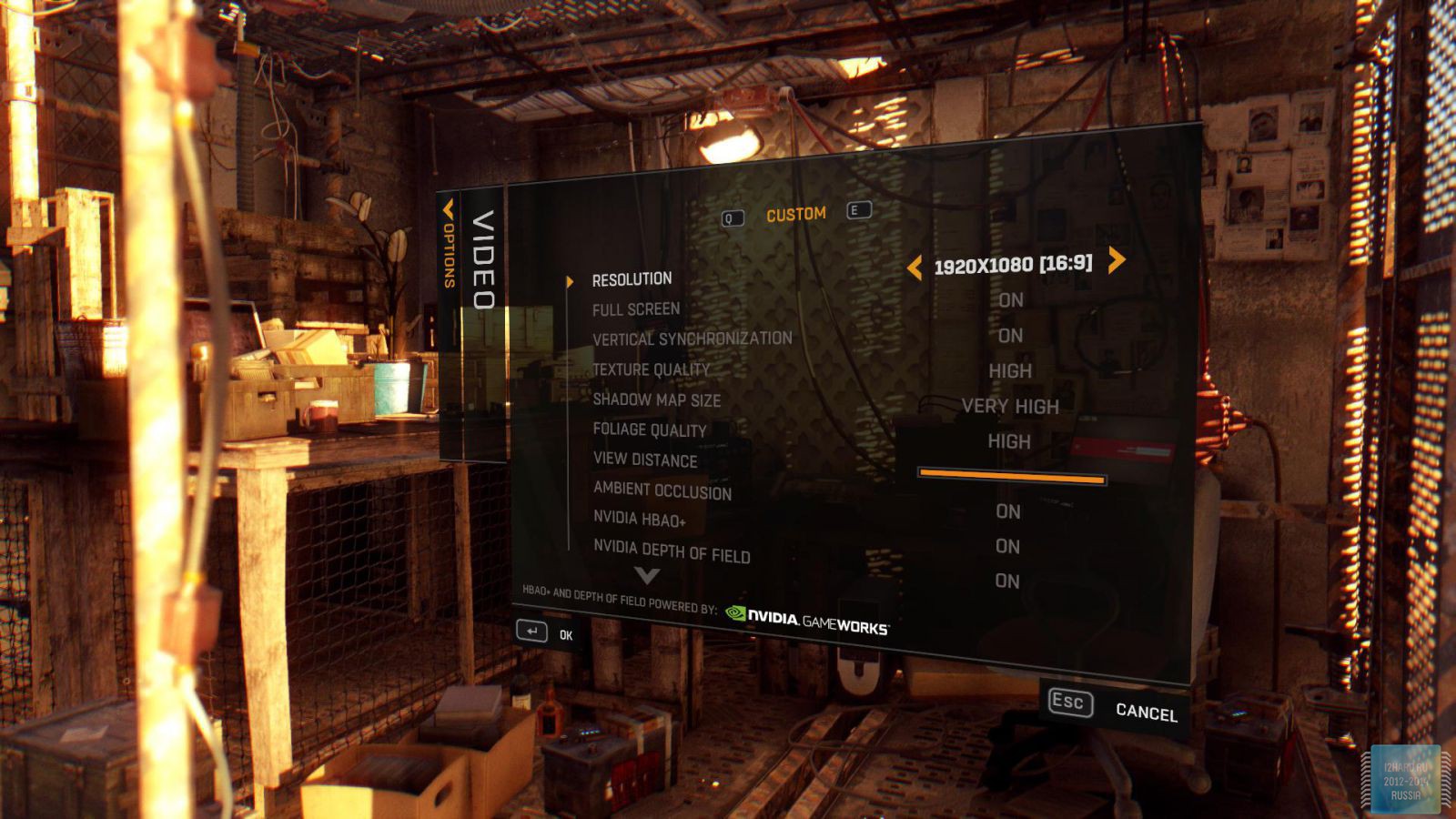
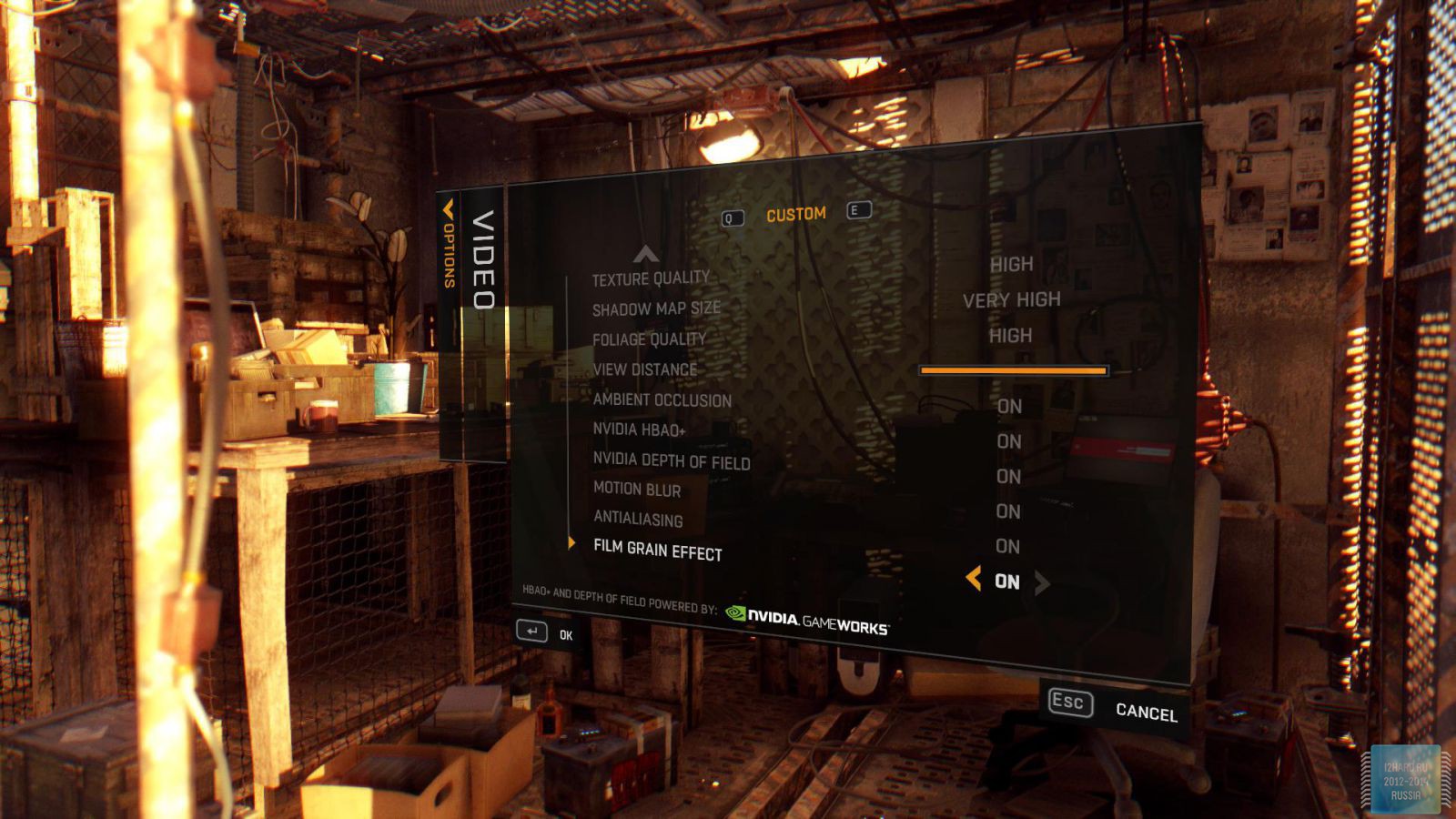
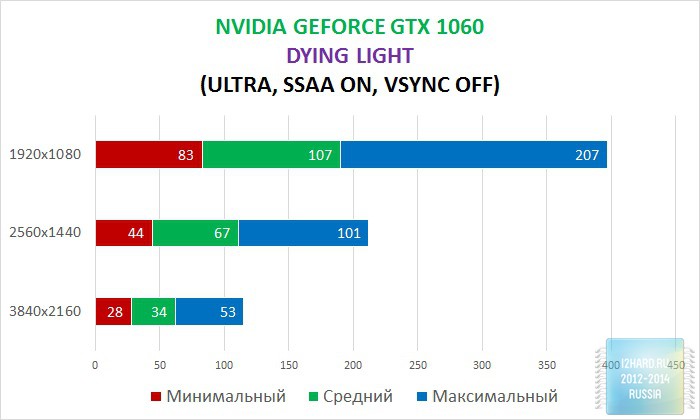

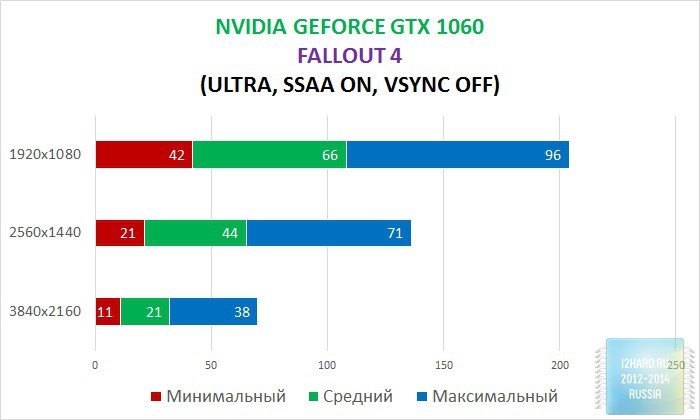


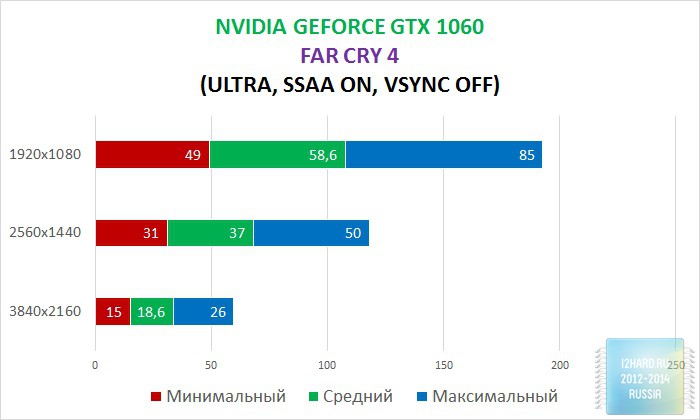

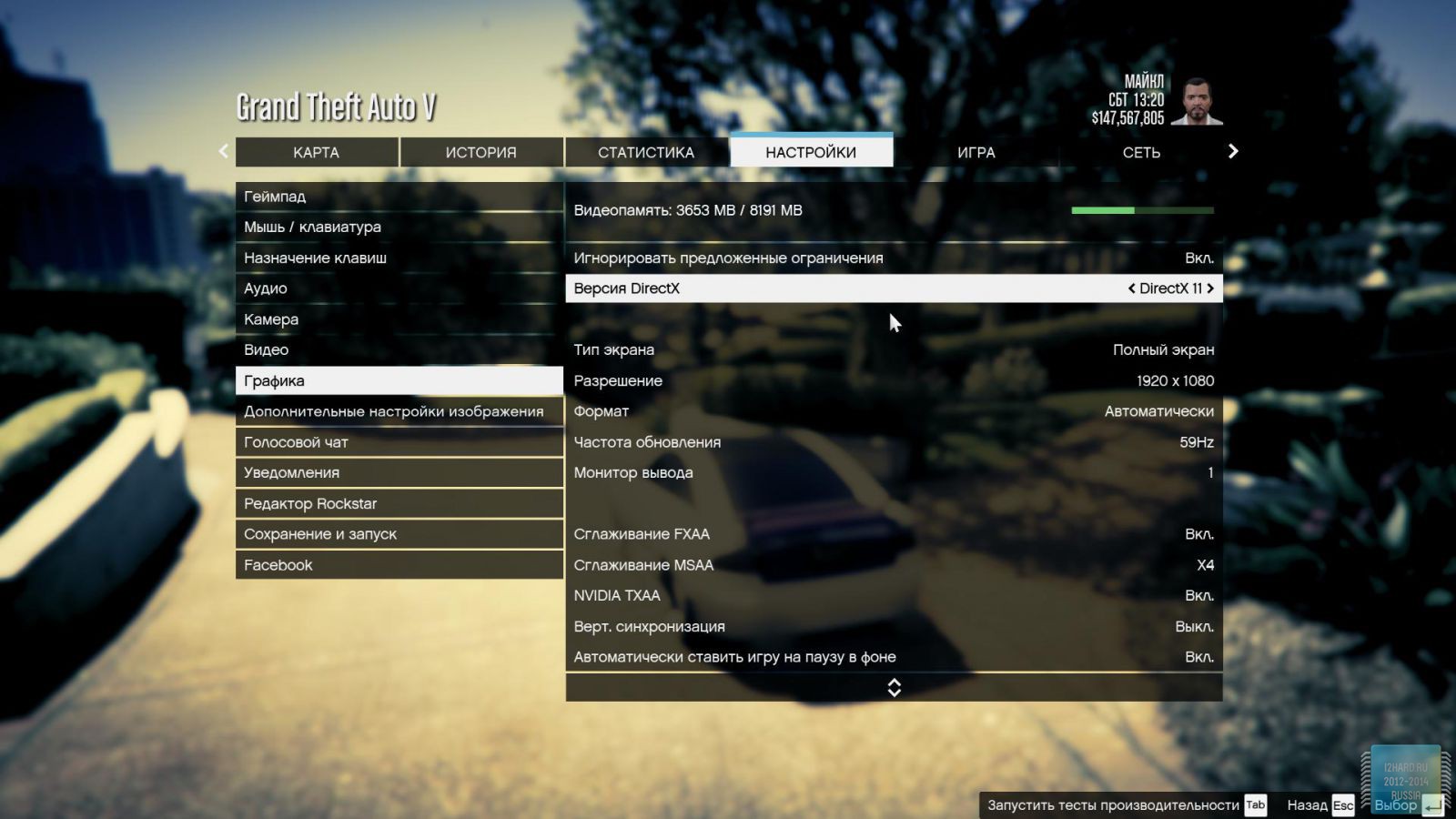
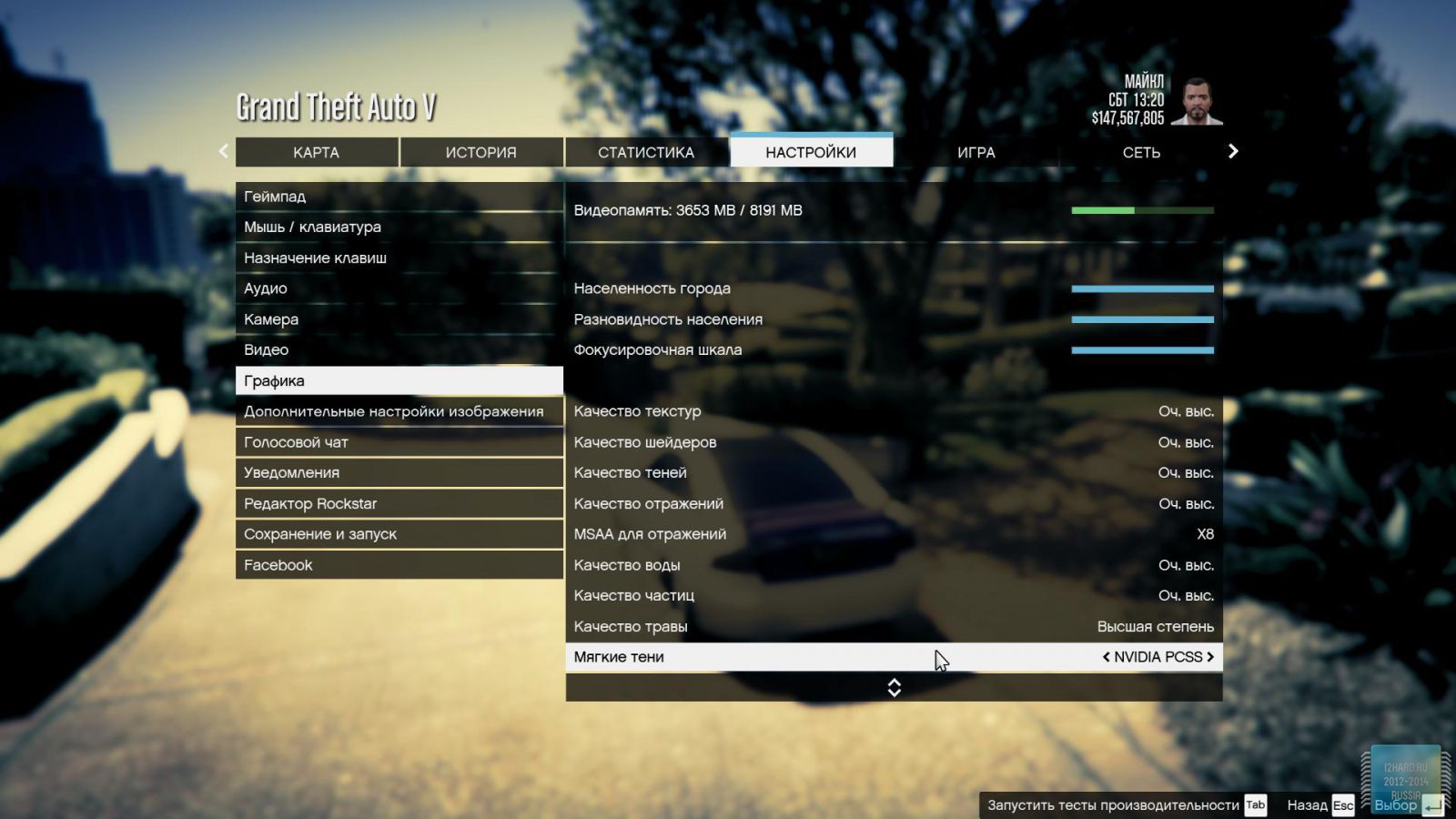

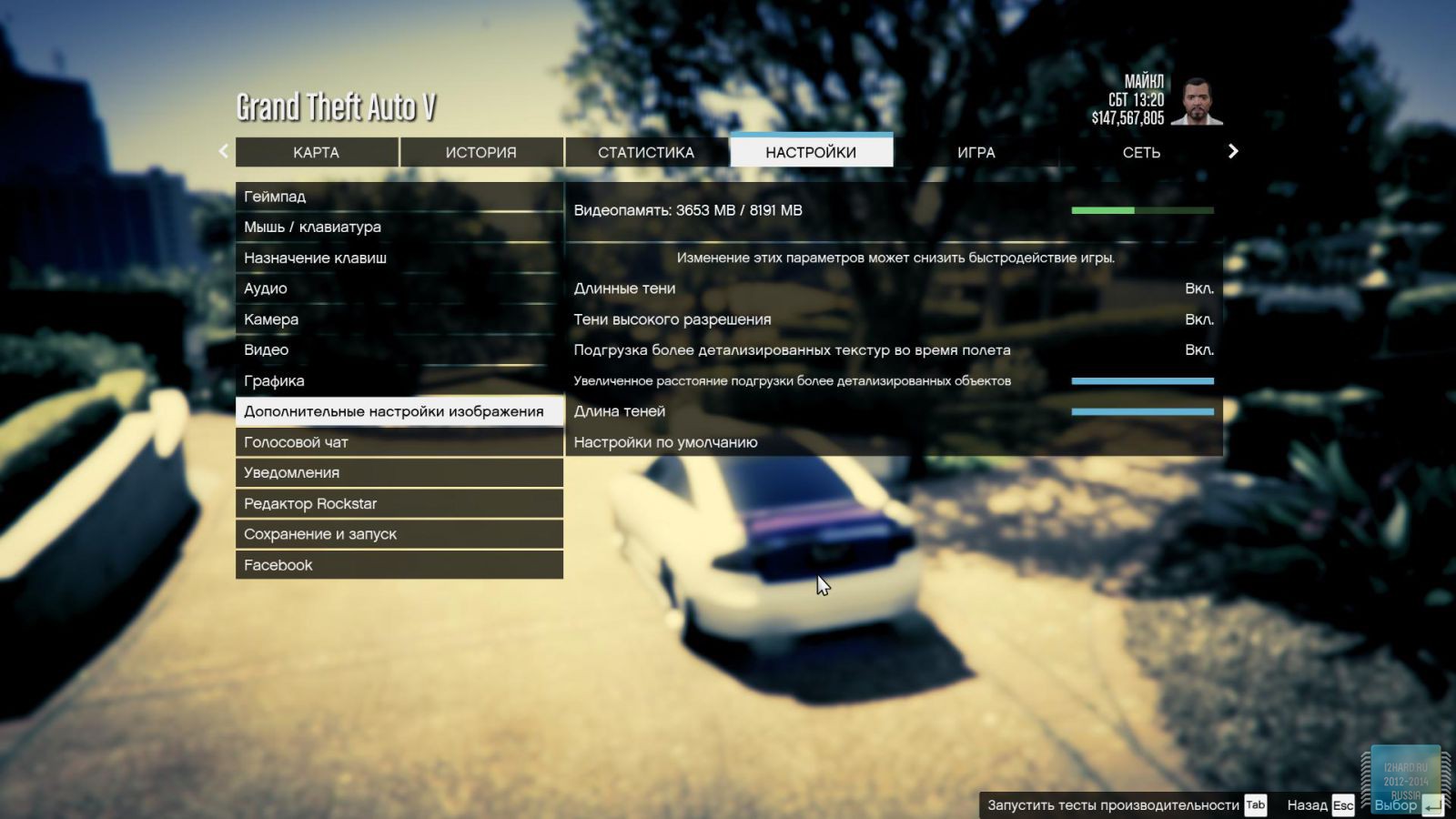
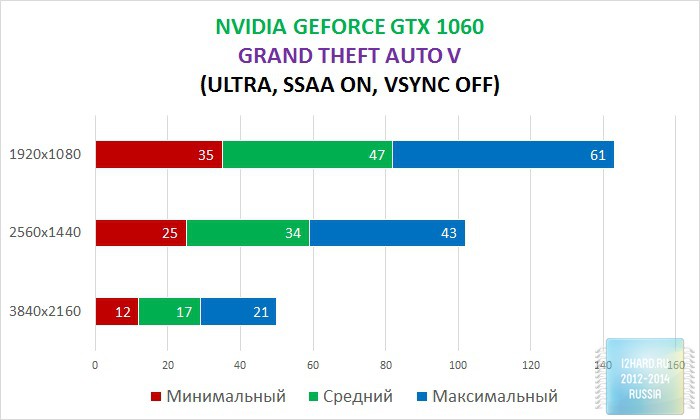


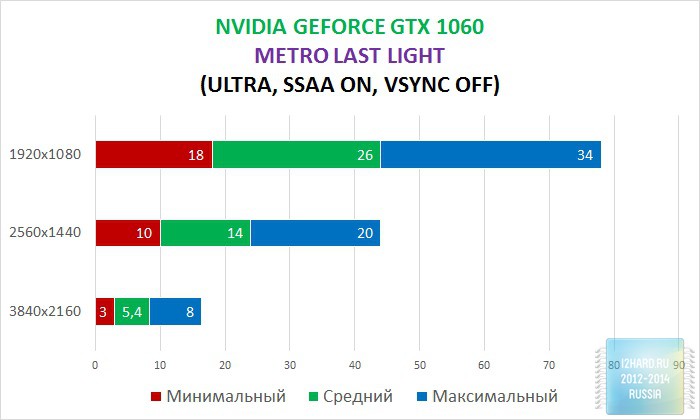


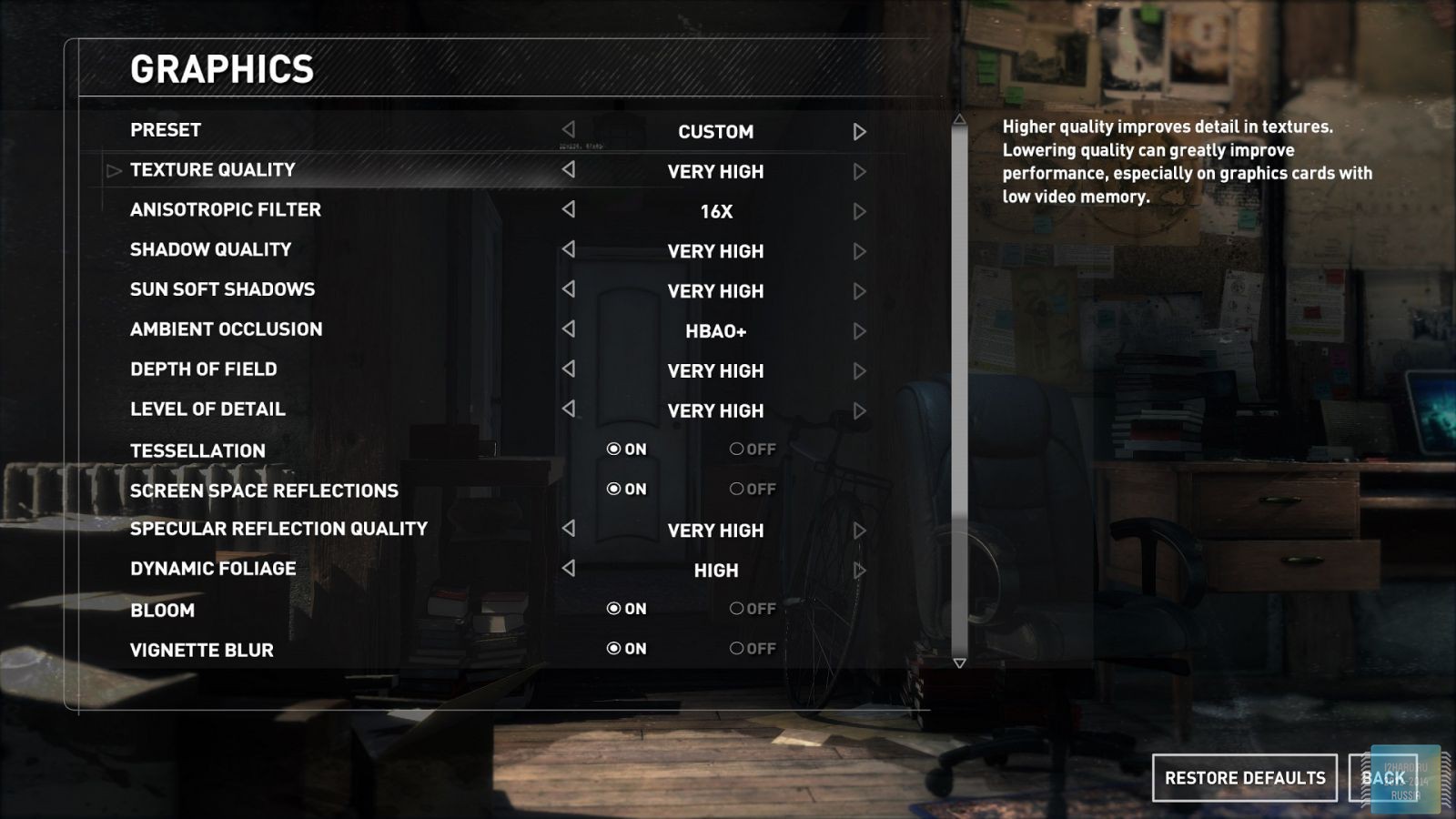
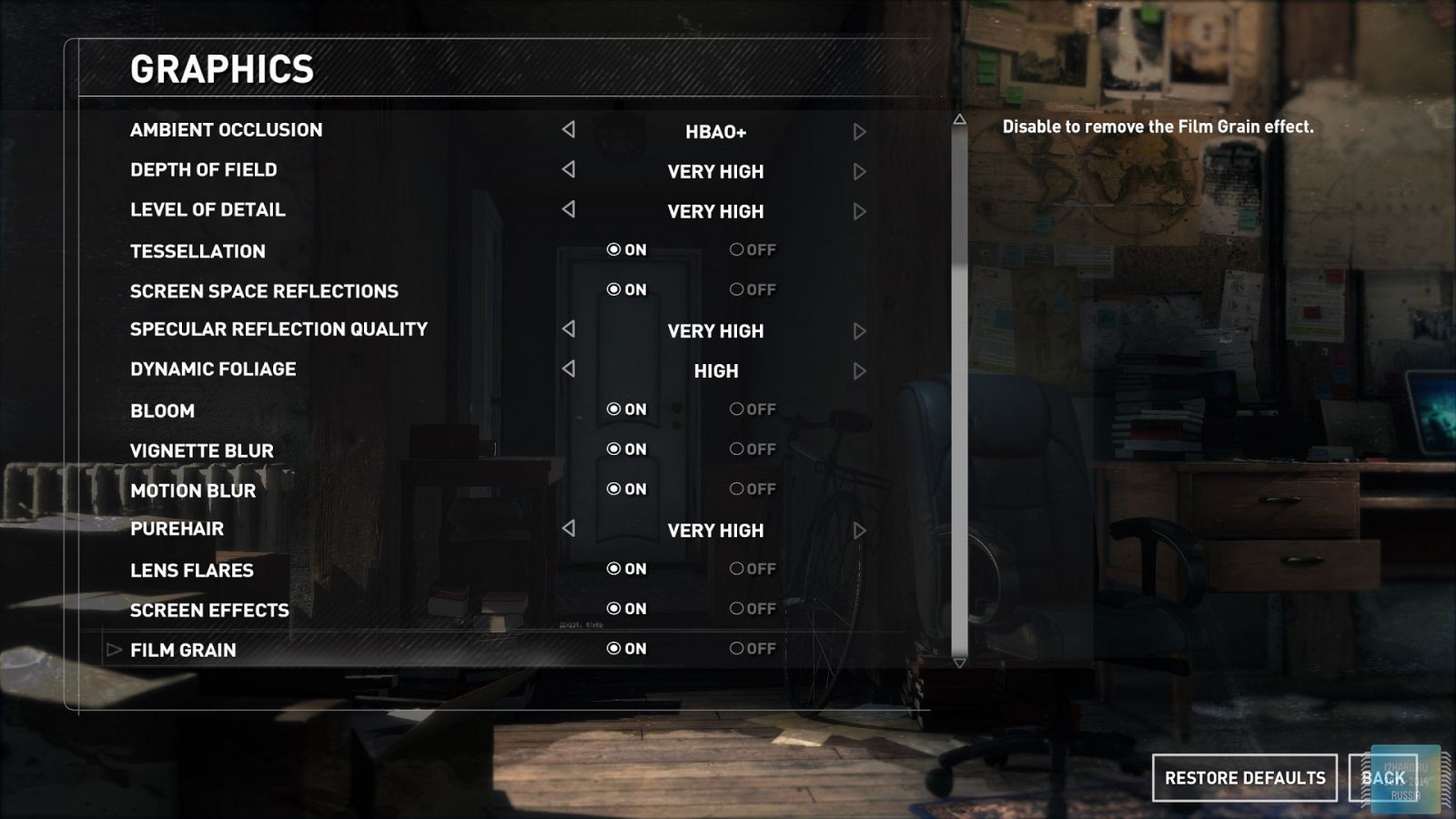


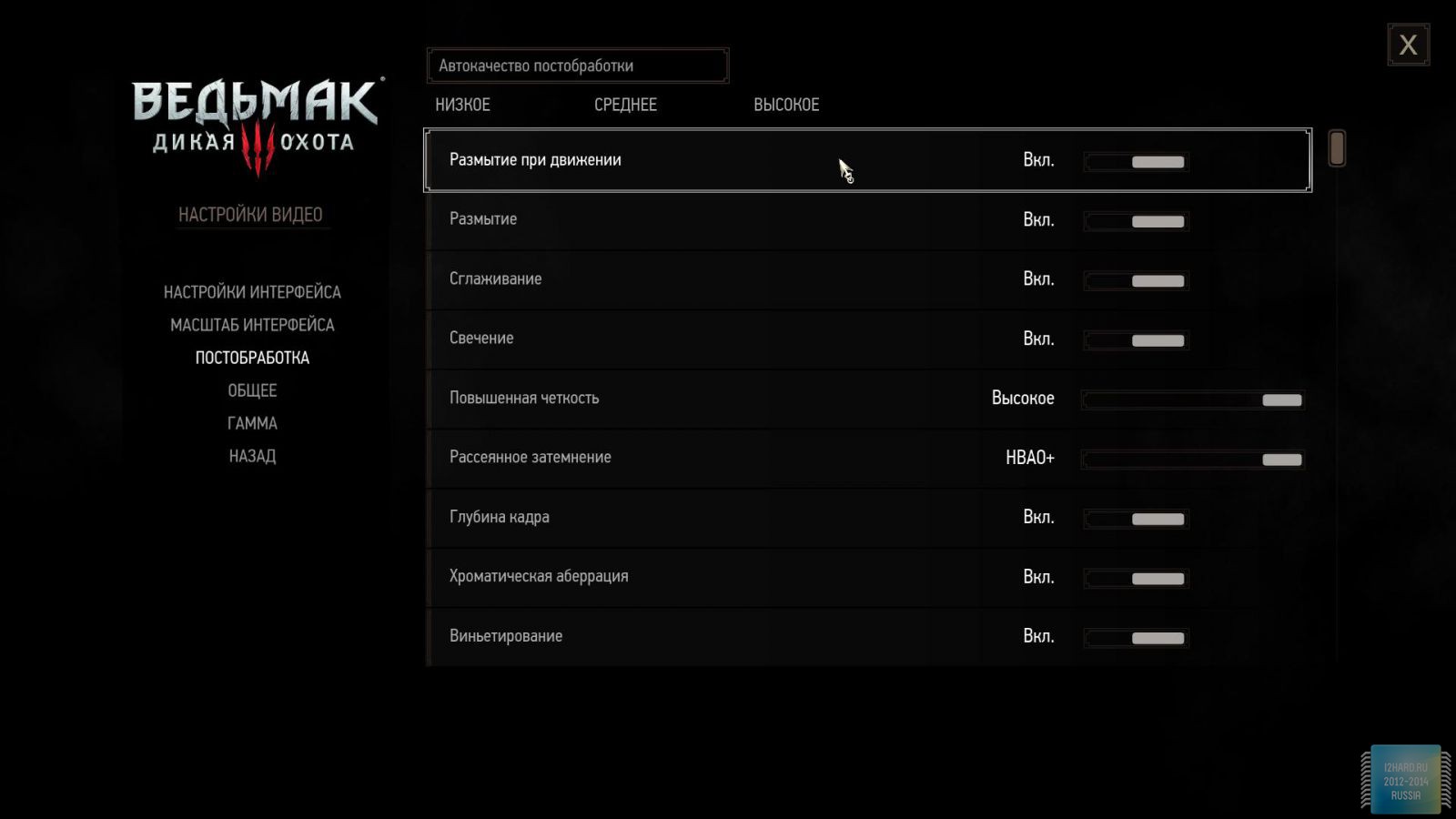
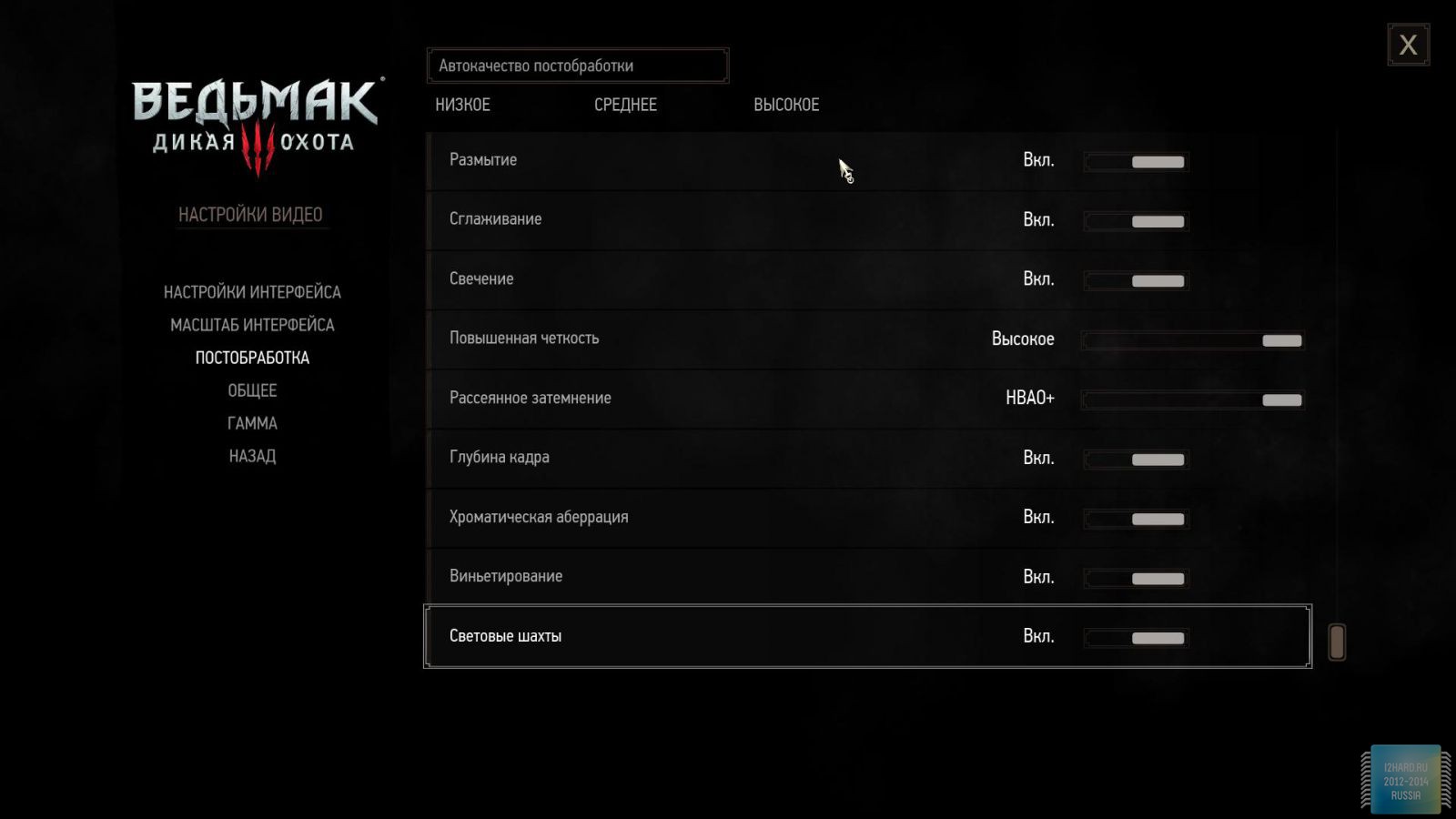
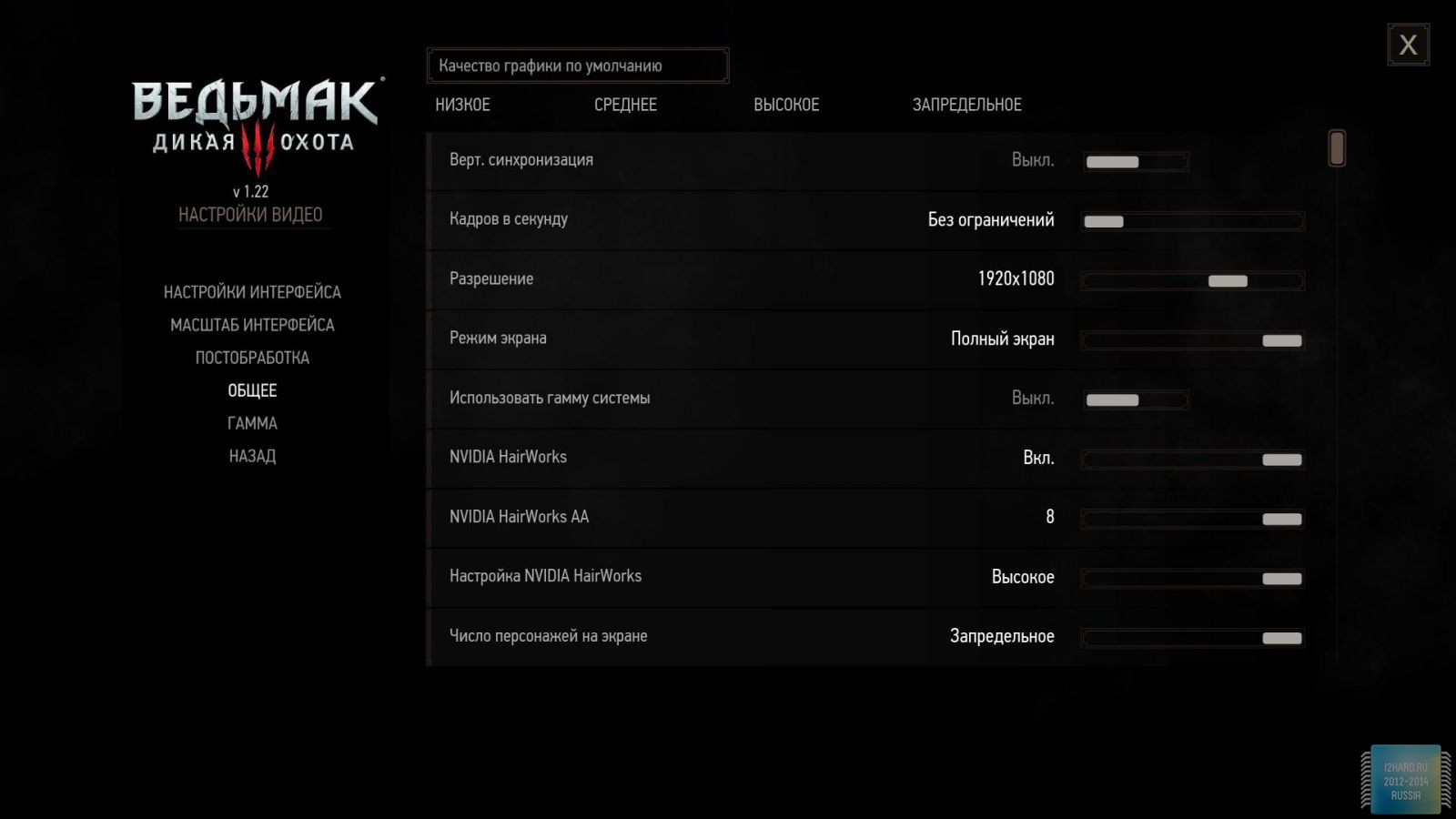
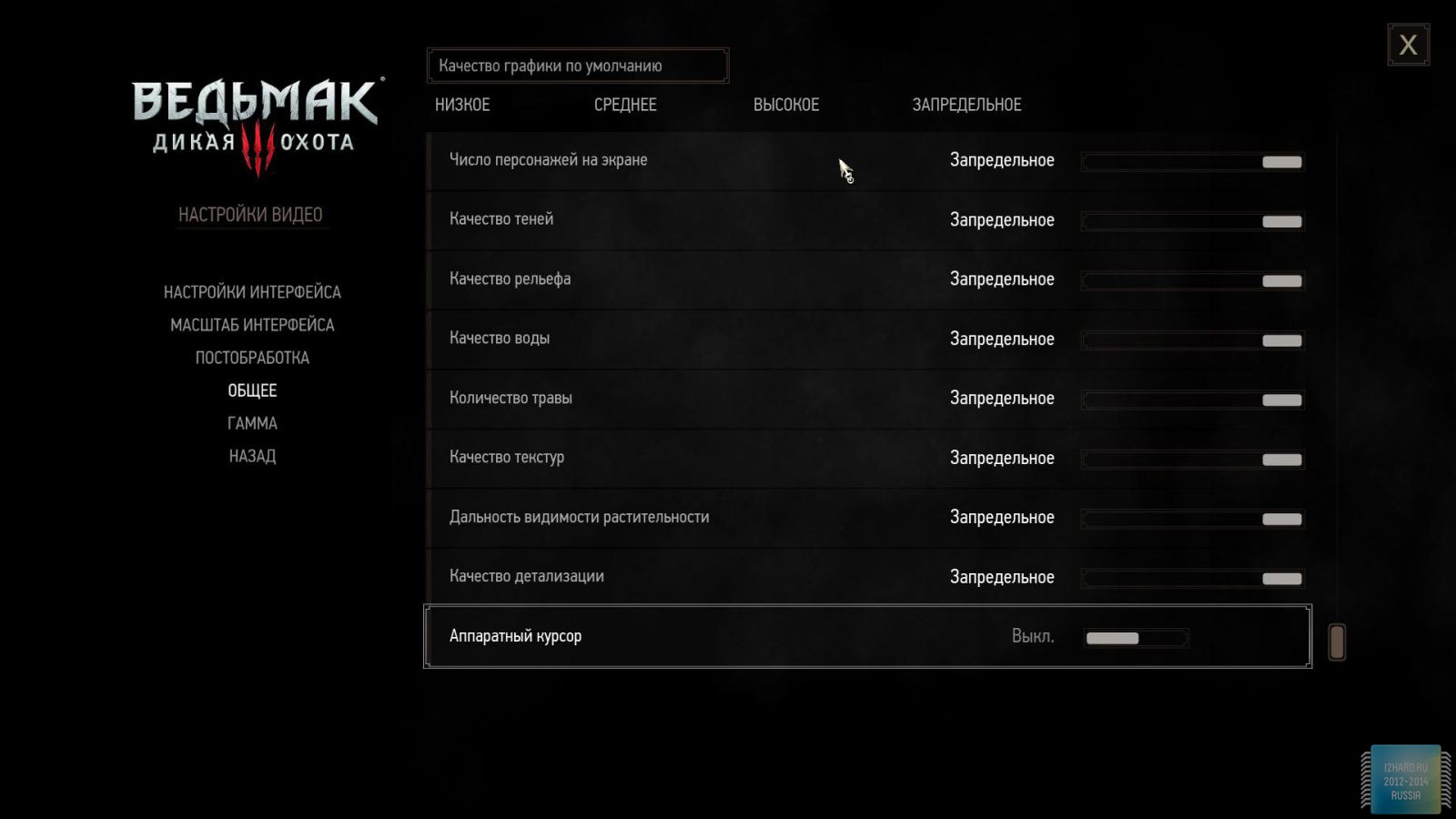


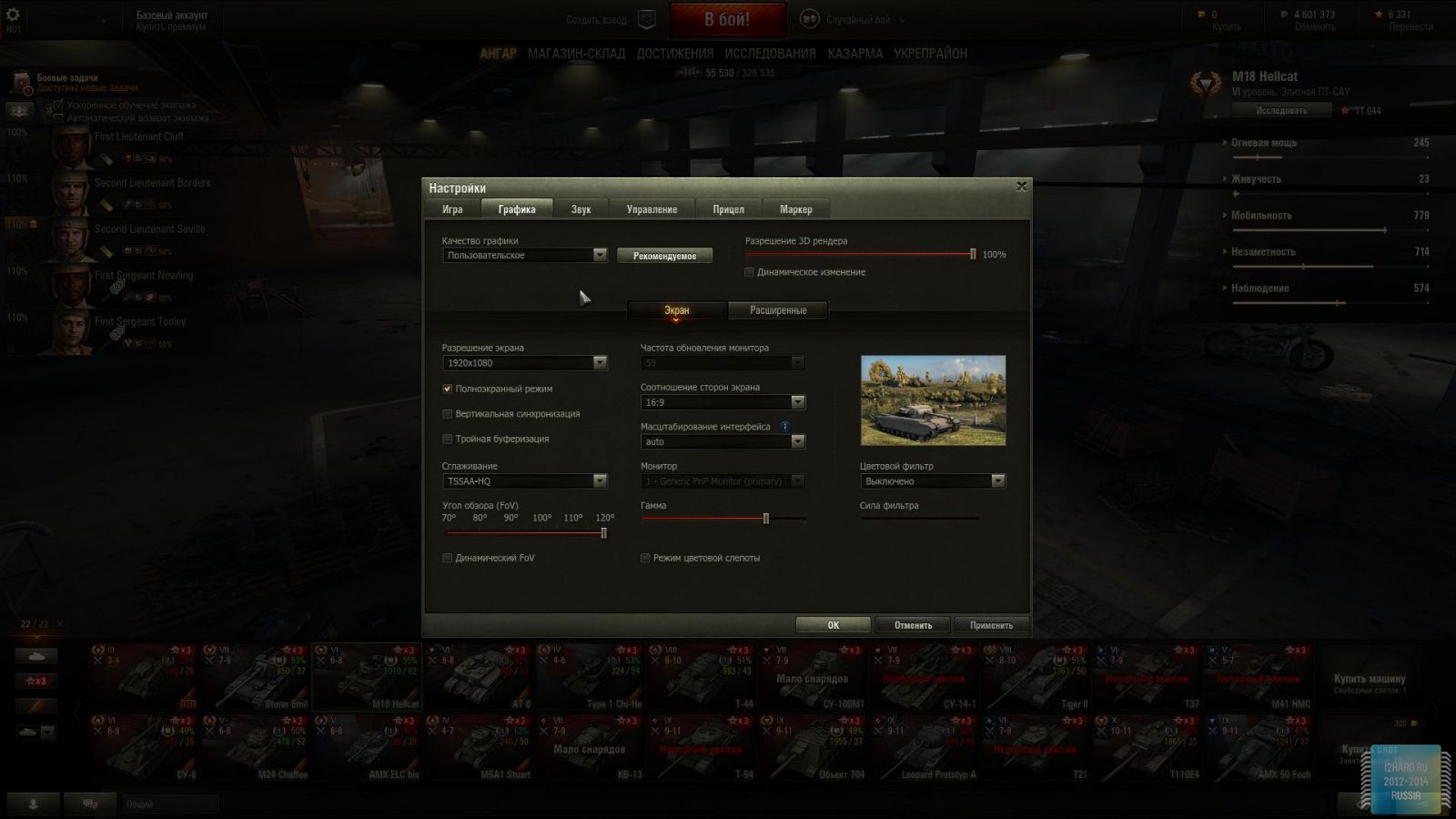

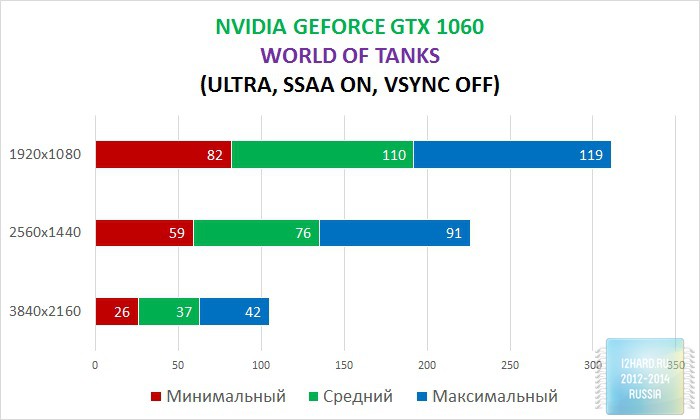
As a result of testing, it can be noted that the performance of the GTX 1060 is roughly on par with the GTX 980. This graphics card perfect for playing on a resolution of 1920x1080, even if the inclusion of such a resource-intensive option as anti-aliasing. The exception in our case is games such as Assassin's Creed Syndicate and Metro Last Light, it's recommended to disable this option.If you pay attention to the higher resolution of 2560x1440, then here you can expect a decent level of performance, but only when disabling anti-aliasing and parameters such as shadows, volumetric illumination, the range of objects drawing. For a new-fangled 4K video card is completely inappropriate and to a large extent this is facilitated by the lack of SLI support.
Temperature and acceleration
Testing took place in an open case at room temperature of 25 degrees. In idle mode, the frequency of the GPU and memory is reduced to 139/405 MHz, which directly affects energy efficiency and improves temperature performance. In the resting mode, the temperature dropped to 32 ° С, and under load it did not exceed 72 ° С. As for the noise level, then at low loads the video card works quietly enough and hardly anyone can not arrange on this parameter. Under load, noise also does not come out of the comfort zone. In general, due to the reduced power consumption and, as a result, reduced heating - the reference cooling system copes quite reliably with the heat removal.

Overclocking was carried out with the help of latest version utility EVGA PrecisionX 16.
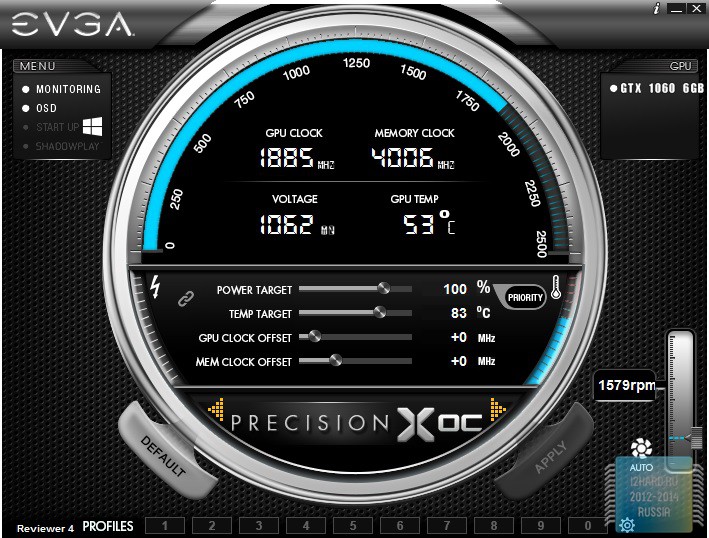
In addition to the standard menu with changing frequency and voltage parameters, three more modes are available in this utility:
- Basic - select a point on the chart with a certain voltage value and specify the required frequency level, while this line is linearly constructed this dependence.
- Linear - we build on two points, which makes it possible to set the initial and final values, which affects the steepness of the line.
- Manual - we manually set each frequency point for the corresponding value of the supply voltage.
![]()
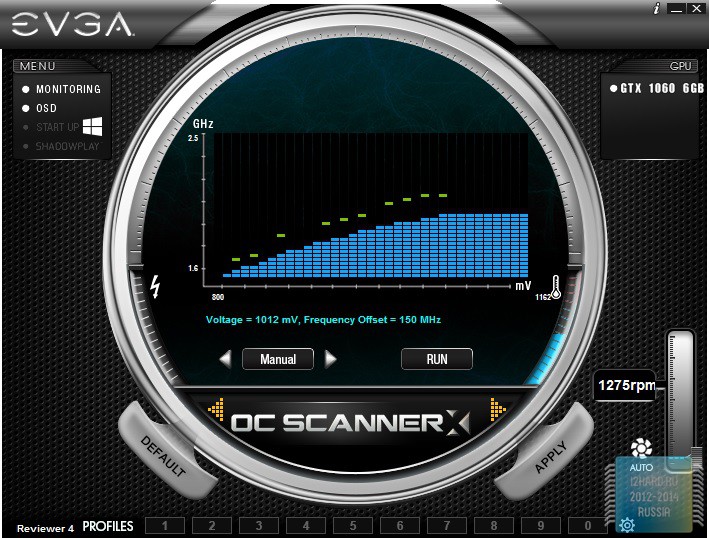
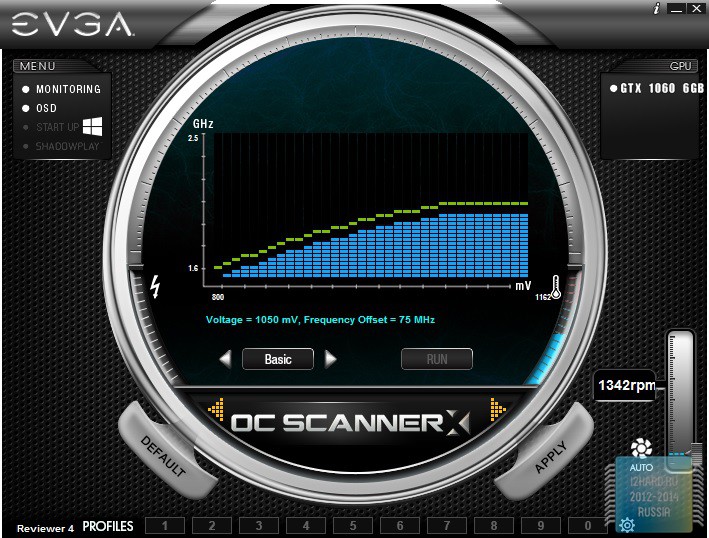
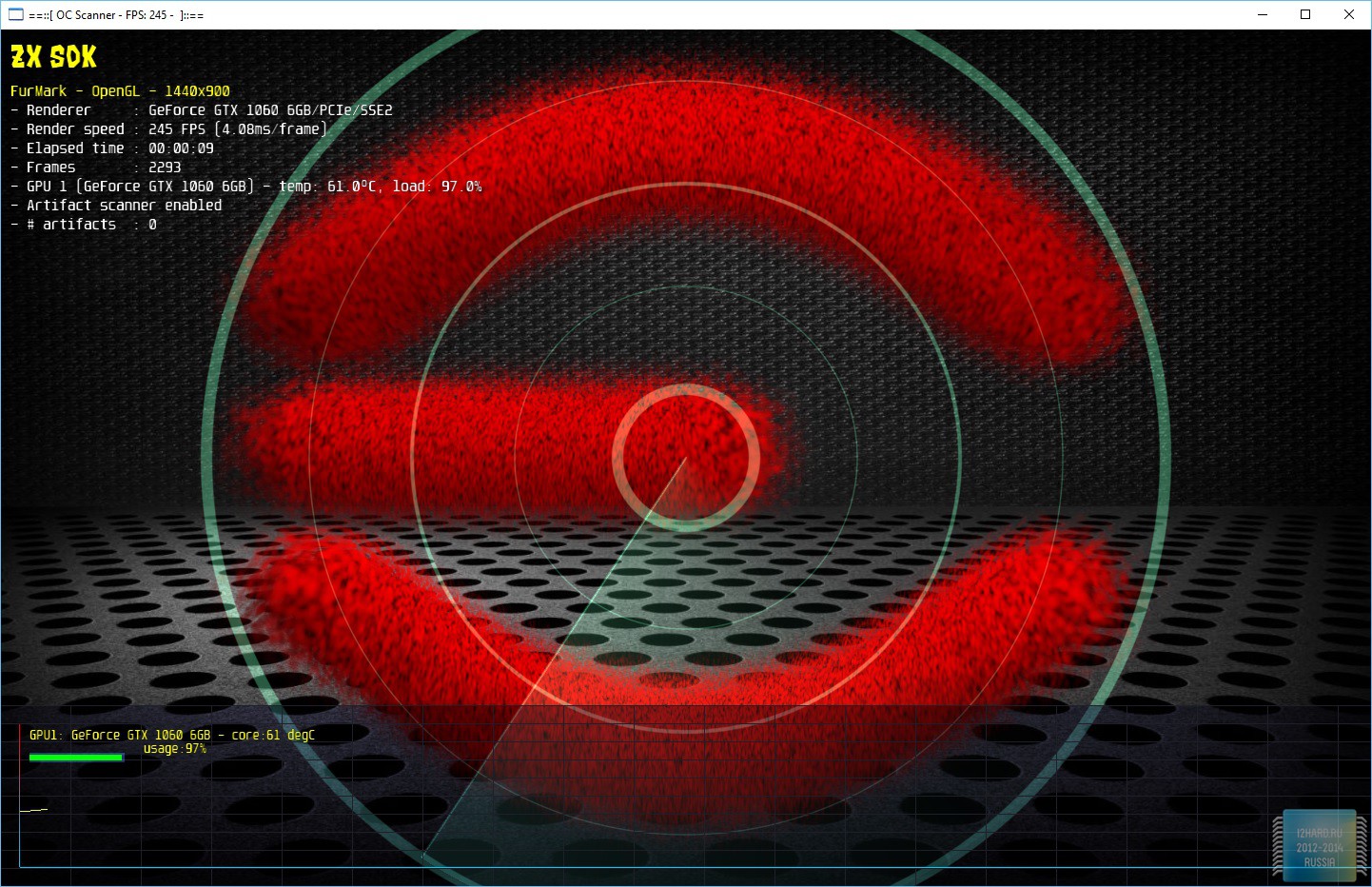
In order to check the stability of the installed parameters, it is recommended to use the built-in OS scanner, which verifies the stability of the video card, depending on the frequency and the level of the supply voltage. As a result, you can save the profile, where all the points on the graph will be marked.
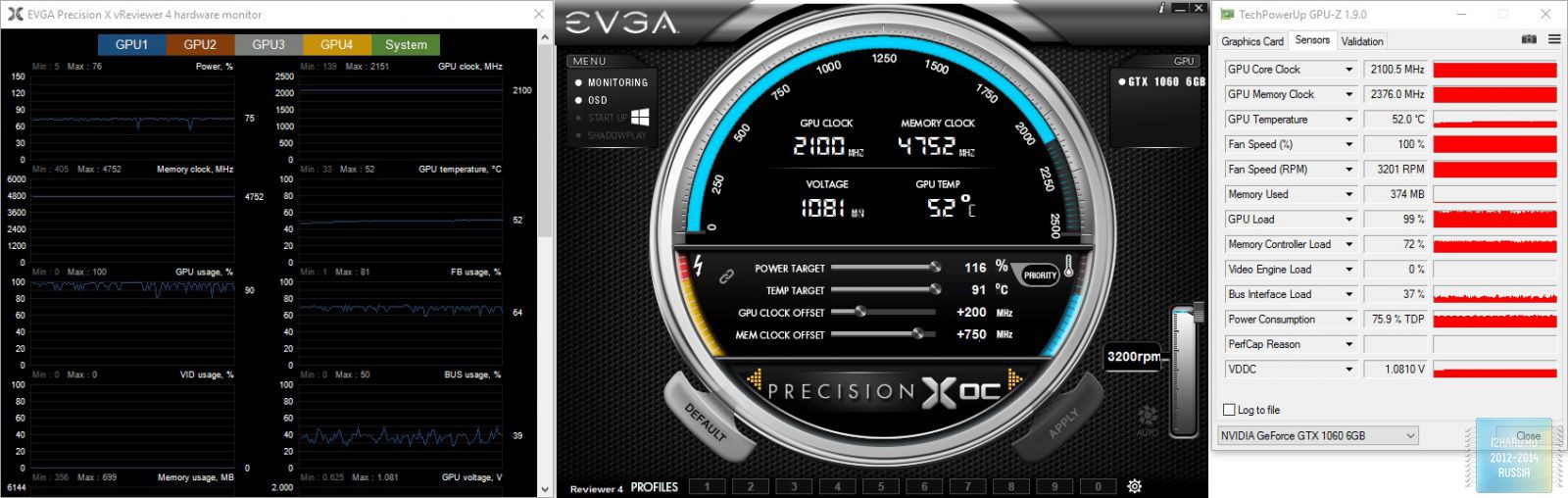
Overclocking result:
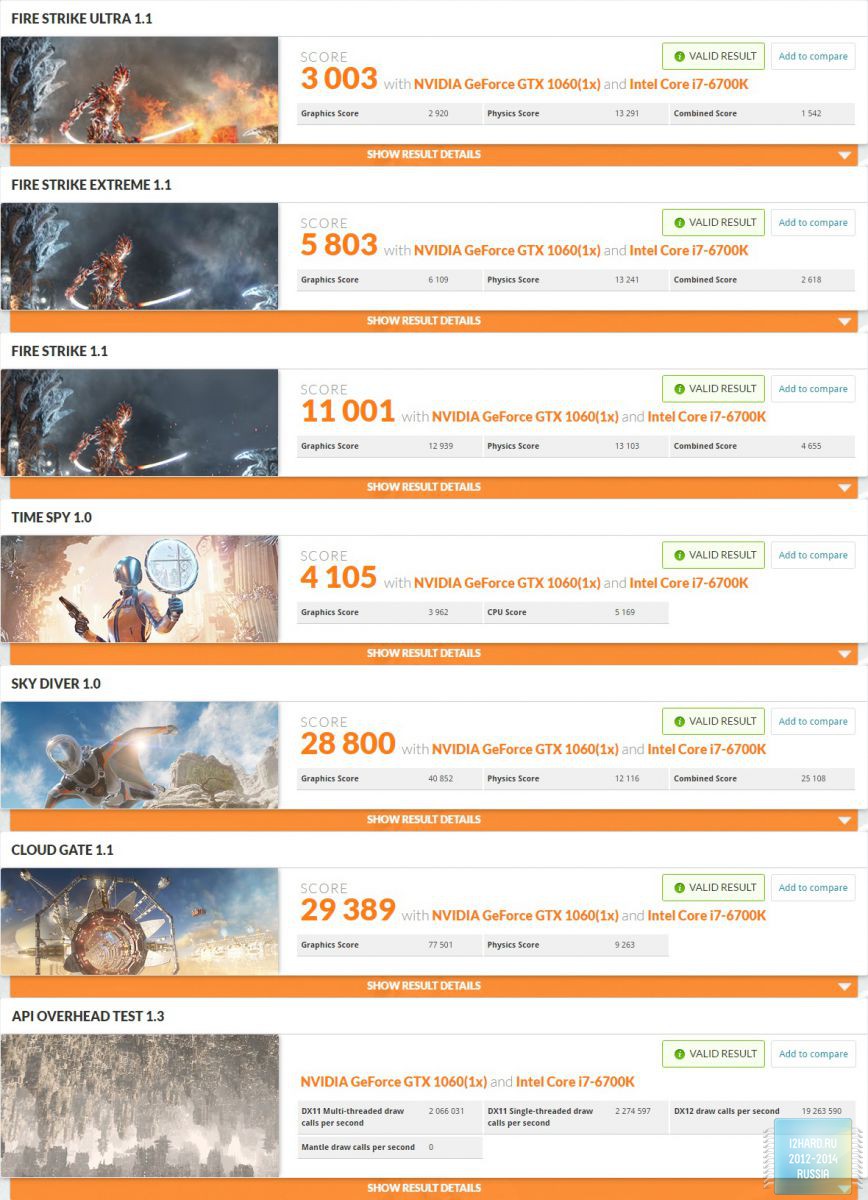
- The frequency of the graphics processor was increased by 200 MHz, which in the final version was 1706 MHz. However, taking into account the GPU Boost, the required value has grown to 2100 MHz, which guarantees a very significant increase in performance.
- The memory frequency was increased by 750 MHz and reached the value of 2376 MHz (9.5 GHz QDR), an excellent increase was obtained.
I propose to get acquainted with the increased performance of Fire Strike Extreme and Fire Strike Ultra:

Conclusion
NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1060 will certainly become one of the most popular models on our market, especially when prices are lowered as a result of competition with AMD RX 480. This model is optimal for owners of FullHD monitors and is able to provide decent performance even when installing the maximum possible graphics settings. Along with this, one can not help but note the low power consumption of the video card, which is able to work in tandem with four hundred watt power supplies. We will add to this the reduction in heat generation and, as a consequence, the absence of the need for the use of bulky cooling systems. Pleased and the possibility of overclocking, which will certainly take advantage of enthusiasts and advanced users to get a solid increase in FPS.
Should I buy Founders Edition or wait for the release of alternative versions? In the opinion of the author, it is not necessary to hurry with the purchase. To begin with, the options from the partners of NVIDIA will be equipped with a semi-passive cooling system and will work noticeably quieter. Another plus in the piggy bank of alternative options is factory overclocking, which will have a significant impact on performance. Let's also recall all sorts of design delights, such as RGB backlighting, color design and so on. The last argument for buyers may be the price. It is for certain that some models will cost less than the Founders Edition, which, with all the above pluses, makes buying a reference not the most profitable option. And if you really sum up, it's not easy to buy NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1060 on the territory of the Russian Federation, since the Founders Edition version is not officially sold for us.
Pros:
- Design, appearance;
- Good level performance;
- Excellent overclocking potential;
- Economical consumption;
- Quiet in idleness and under load;
- Good cooling system efficiency.
Minuses:
- Lack of SLI support.
![]()
According to the editors, taking into account all the pros and cons, NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1070 Founders Edition receives the Silver award.
20.07.2016 19:01
Ooops: The essence of the claims is that without tests for new APIs, which already go igrodely (and which in a year will already be the main ones), and in which the alignment of forces between 1060 and 480 changes significantly, the conclusions you have sewn with white thread are not worth it either a broken penny (well, or stand and a lot more) Reputation earned a long and hard, but lost rapidly. Udachi.Lichno for themselves, I have already concluded all conclusions.
20.07.2016 19:40
dchekanov: The conclusions are based on games that you can play today. And not on the basis of what (maybe) will appear tomorrow or the day after tomorrow. We do not test anyone's fantasies and forecasts, we test what is relevant today in the market.
If you like to eat breakfasts DX12 or Vulkan - your right. In my memory with Mantle was exactly the same situation. There will be games originally written for DX12 and Vulkan - then we will rely on this API as the main one.
While I see a couple of games from which they made a fetish and rush with them, like with a written baggage. And put these games above the much more popular games on the market. We do not do that.
I would not say that a couple of games: Total War: Warhammer, AoS, Hitman, Rise of the Tomb Rider, Gears of War, Killer Instinct. These are the projects on the DX12.
Doom, Talos Principle - on Vulcan. A patch is made for DotA.
Work you have no end!))
20.07.2016 22:03
dchekanov: The conclusions are based on games that you can play today. And not on the basis of what (maybe) will appear tomorrow or the day after tomorrow. We do not test anyone's fantasies and forecasts, we test what is relevant today in the market.
If you like to eat breakfasts DX12 or Vulkan - your right. In my memory with Mantle was exactly the same situation. There will be games originally written for DX12 and Vulkan - then we will rely on this API as the main one.
While I see a couple of games from which they made a fetish and rush with them, like with a written baggage. And put these games above the much more popular games on the market. We do not do that.
Such an argument would have gone down in 5B, but not on a resource dedicated to IT. I note that what is fetish for you, then for the rest of the world is a trend. And these games are already available, and they already have a serious increase with respect to the old API. the approach is serious titles like Deus Ex and Battlefield, I'm already silent about the exclusives from Microsoft, which come out on 10 windows (who would have thought) on dx12, and again make a reservation that they are both already available, and are expected in the near future.
Yes, and a comparison of the mantle developed by one company and Vulkan with DX12, developed and supported by a myriad of players in the big league of the IT industry, which is not even worth mentioning, before they are all heard - this is a highly correct comparison of the professional journalist in this field.
It's just brave.
I applaud standing up.
20.07.2016 23:29
I can not remain silent, I will write.
I'm not an ardent fan of NVidia, not AMD, but I choose their products based on the price of it and tests of the esteemed editorial of highly respected sites, such as this one. However, at the moment I am somewhat amazed.
Concerning the test procedure: "The driver version is Radeon Software 17.2.1". Good. Suppose you are sealed in the figure. But only in one? As far as I know, the numbering is deciphered as Year. The release date of the driver. That is, the 16th year. The tests feature the RX480, a video card released a month ago, and is tested on a video driver released six months ago. Those. the driver installed on the stand does not officially support the video card, since the latter came out after six months. Can these tests be called correct and fair relative to the RX480? Or am I somewhere wrong? If so, please correct.

| Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060 6 GB 192-bit GDDR5 PCI-E | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Value | Nominal value (reference) | |
| GPU | GeForce GTX 1060 (GP106) (P / N 900-1G410-2530-000 G2) | ||
| Interface | PCI Express x16 | ||
| Frequency gPU work (ROPs), MHz | 1507—1860 | 1507—1860 | |
| Memory frequency (physical (effective)), MHz | 2000 (8000) | 2000 (8000) | |
| Width of memory bus, bit | 192 | ||
| Number of computational units in the GPU | 10 | ||
| Number of operations (ALU) in the block | 128 | ||
| Total number of ALUs | 1280 | ||
| Number of texturing blocks (BLF / TLF / ANIS) | 80 | ||
| The number of rasterization blocks (ROP) | 48 | ||
| Dimensions, mm | 270 × 100 × 35 | 270 × 100 × 35 | |
| Number of slots in the system unit, occupied by the video card | 2 | 2 | |
| Color textolite | the black | the black | |
| Energy consumption | Peak in 3D, W | 117 | 117 |
| In the 2D mode, W | 28 | 28 | |
| In the "sleep" mode, W | 11 | 11 | |
| Noise level | In 2D mode, dBA | 20,0 | 20,0 |
| In 2D mode (video viewing), dBA | 20,0 | 20,0 | |
| In the maximum 3D mode, dBA | 26,5 | 26,5 | |
| Output sockets | 1 × DVI (Dual-Link / HDMI), 1 × HDMI 2.0b, 3 × DisplayPort 1.2 / 1.3 / 1.4 | ||
| Multiprocessor support | No | ||
| Maximum number of receivers / monitors for simultaneous display of images | 4 | 4 | |
| Additional power: the number of 8-pin connectors | No | No | |
| Additional power: the number of 6-pin connectors | 1 | 1 | |
| Max Resolution 2D | Display Port | 4096 × 2160 | |
| HDMI | 4096 × 2160 | ||
| Dual-Link DVI | 2560 × 1600 | ||
| Single-Link DVI | 1920 × 1200 | ||
| Max resolution 3D | Display Port | 4096 × 2160 | |
| HDMI | 4096 × 2160 | ||
| Dual-Link DVI | 2560 × 1600 | ||
| Single-Link DVI | 1920 × 1200 | ||
| Composition with local memory | |||
|---|---|---|---|
The card has 6 GB of GDDR5 SDRAM allocated in 6 8 Gb chips on the front side of the PCB. As synthetic tests for DirectX 11, we used examples from the SDK packages of Microsoft and AMD, as well as the demonstration program Nvidia. First, it's HDRToneMappingCS11.exe and NBodyGravityCS11.exe from the DirectX SDK (February 2010). We took the applications of both manufacturers of video chips: Nvidia and AMD. Of ATI Radeon SDK samples were taken DetailTessellation11 and PNTriangles11 (they also exist in the DirectX SDK). In addition, the demonstration program of Nvidia - Realistic Water Terrain, also known as Island11, was used. Synthetic tests were conducted on the following video cards:
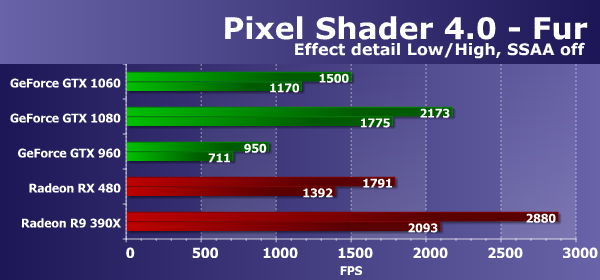
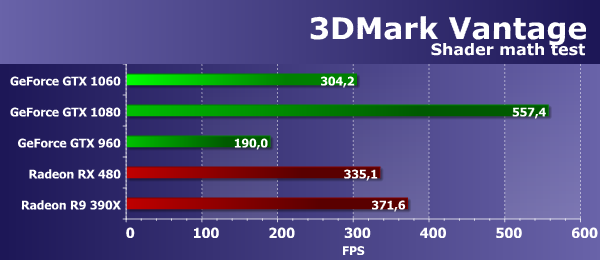
To analyze the performance of the new GeForce GTX 1060 graphics card, we selected several solutions from both GPU manufacturers. The GeForce GTX 960 is a direct predecessor of the novelty, based on the approximately analogous positioning and area graphics processor from the previous generation of Maxwell. The GeForce GTX 1080 video card is taken as the top-generation solution with the maximum performance, based on the GP104 chip - a comparison with it will show how much less theoretically doubled the stripped-down GTX 1060. From the video cards of the competing AMD company for our comparison, we chose two video cards of different generations. Technically, in terms of complexity and GPU area, the real rival for GeForce GTX 1060 from AMD is the new single-chip video card of the Radeon RX 480 model, but it costs less than the California novelty in question. Therefore, we also took the Radeon R9 390X, based on the old Hawaii graphics processor, which is still on the market and is quite competitive with many new solutions in synthetic tests. Direct3D 10: PS 4.0 pixel shader tests (texturing, loops)We refused the outdated DirectX 9 tests, and the second version of RightMark3D included two previously known PS 3.0 tests for Direct3D 9, which were rewritten for DirectX 10, and two more new tests. The first pair added the possibility of turning on self-shadowing and shader supersampling, which additionally increases the load on video chips. These tests measure the performance of performing pixel shaders with loops with a large number of texture samples (in the heaviest mode up to several hundred samples per pixel) and a relatively small ALU load. In other words, they measure the speed of texture samples and the efficiency of branching in a pixel shader. The first test of pixel shaders will be Fur. With the most low settings It uses from 15 to 30 texture samples from the height map and two samples from the main texture. Mode Effect detail - "High" increases the number of samples to 40-80, the inclusion of "shader" supersampling - up to 60-120 samples, and the mode "High" in conjunction with SSAA differs maximum "severity" - from 160 to 320 samples from the height map. Let's first check the modes without the included supersampling, they are relatively simple, and the ratio of the results in the "Low" and "High" modes should be approximately the same.
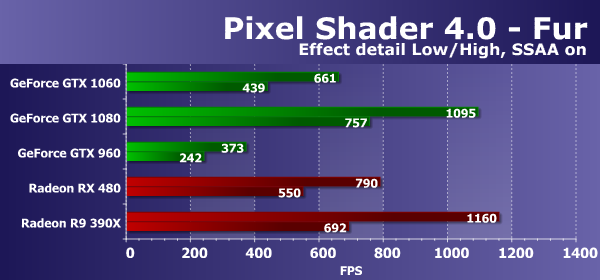
The performance in this test depends on the number and efficiency of TMU units, and the performance of complex programs also affects the result. And in an option without supersampling, an additional effect on performance is also provided by effective fill rate and memory bandwidth. The results for detailing the "High" level are obtained somewhat lower than with the detailing "Low". In problems of procedural visualization of fur with a large number of texture samples, AMD has been leading since the release of the first video chips based on the GCN architecture. It is the Radeon cards that are still the best in these comparisons, which indicates that they are more efficient in implementing these programs, especially for the GPU of the previous generation. Conclusion is confirmed by comparing today - the new Nvidia graphics card we considered lost both solutions competitor, including the Radeon R9 390X on older GPUs. However, the comparison with the RX 480 is not as deplorable as it was before, because the novelty lost only 15-16%. In our first Direct3D 10 test, the new GeForce GTX 1060 video card showed a performance of 66-69% of the speed of the top-generation model of the current generation, and seriously bypassed its predecessor based on the GM206 chip. In general, this can be considered a good result. Let's take a look at the same test, but with included "shader" supersampling, which increases the work four times: in this situation something should change, and the PSP with the fillrate will affect less:
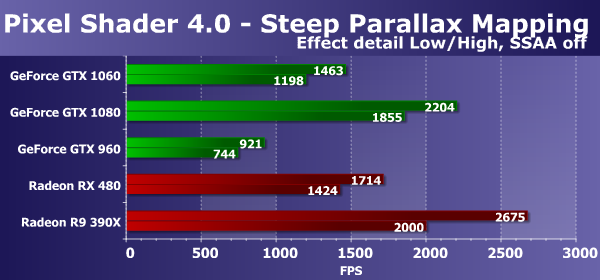
In more complicated conditions, the test results are more interesting. The new video card model GeForce GTX 1060 this time ahead of the similar positioning model from the previous generation GTX 960 almost twice. But from the top-end GTX 1080, it lagged a bit more - losing already up to 42%, which corresponds to the theory. Not surprisingly, the novelty fell behind competitors in the form of Radeon RX 480 and R9 390X, but the lag was about the same. The next DX10 test measures the performance of performing complex pixel shaders with loops with a large number of texture samples and is called Steep Parallax Mapping. At low settings, it uses 10 to 50 texture samples from the height map and three samples from the basic textures. With the inclusion of heavy duty with self-shadowing, the number of samples increases twice, and supersampling increases this number fourfold. The most complex test mode with supersampling and self-shadowing selects from 80 to 400 texture values, that is, eight times more compared to the simple mode. We first check out simple versions without supersampling:
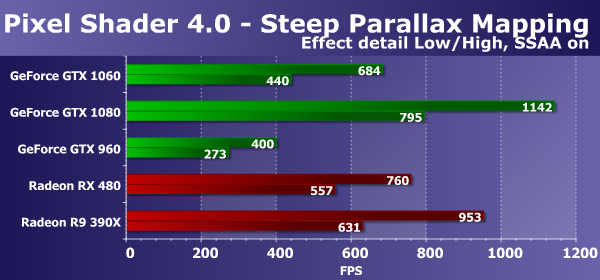
The second pixel shader test Direct3D 10 is more interesting from a practical point of view, because the varieties of parallax mapping are widely used in games, and heavy variants like steep parallax mapping have been used for a long time in many projects, for example, in games of the Crysis series, Lost Planet and many others. In addition, in our test, in addition to supersampling, you can turn on self-shadowing, increasing the load on the video chip by about two times - this mode is called "High". The diagram as a whole is similar to the previous one if we consider the option without including supersampling, and this time the new model of the GeForce GTX 1060 again proved much faster than its direct predecessor GTX 960, and again showed a speed of 65-66% of the top model speed on the GP104 GPU , which is close to theory. If we consider the comparison with AMD video cards, then in this case the novelty is inferior to both Radeon cards, but if we take RX 480, then the difference between them is the same 15-16%. Let's see what will change the inclusion of supersampling:
When supersampling and self-shadowing are enabled, the task becomes harder, the simultaneous inclusion of two options simultaneously increases the card load by almost eight times, causing a serious drop in performance. The difference between the speed indicators of the tested graphics cards has slightly changed, although the inclusion of supersampling affects less than in the previous case. And our comparison today, these conditions almost did not change the balance of power, if you do not look at the top-end video card Nvidia. Graphic solutions AMD Radeon in this D3D10-pixel shader test work more effectively than competing GeForce cards, although the new GeForce GTX 1060 model, based on the second Pascal chip, managed to get closer to the Radeon RX 480 level. Although the competitor's outdated solution proved even faster, the GTX 1080 became obvious leader. In comparison with Nvidia solutions, the novelty showed a speed 40-45% slower than the GeForce GTX 1080 and overtook the GTX 960 by more than 1.5 times. Direct3D 10: PS 4.0 pixel shader tests (calculations)The next couple of pixel shader tests contain the minimum number of texture samples to reduce the performance impact of TMUs. They use a large number of arithmetic operations, and they measure exactly the mathematical performance of video chips, the speed of execution of arithmetic instructions in a pixel shader. The first mathematical test is Mineral. This is a complex procedural texturing test that uses only two samples of texture data and 65 instructions of the type sin and cos.
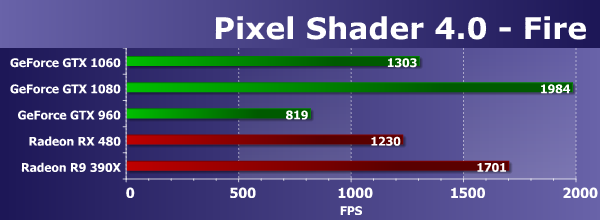
The results of the maximum mathematical tests most often just approximate the difference in frequencies and the number of computational blocks, the results are affected by the different efficiency of their use in specific tasks, and the optimization of drivers, and the newest systems frequency and power management, and even an emphasis in the memory bandwidth. In the case of our Mineral test, powerful video cards clearly did not show actual results - it seems that the test does not reflect the real difference in performance. In such conditions, the GeForce GTX 1060 considered today could even outrun the direct competitor in the form of Radeon RX 480 in this test, which can be considered a small but important victory. Although the old model R9 390X has bypassed everyone in this test. But the predecessor on the basis of the chip architecture Maxwell was about a half times slower, and the top version on the GP104 is only 29% faster than the novelty, which is not so much. Consider the second shader test, which is called Fire. It is heavier for ALU, and there is only one texture sample in it, and the number of instructions of the type sin and cos is doubled, to 130. Let's see what has changed with increasing load:
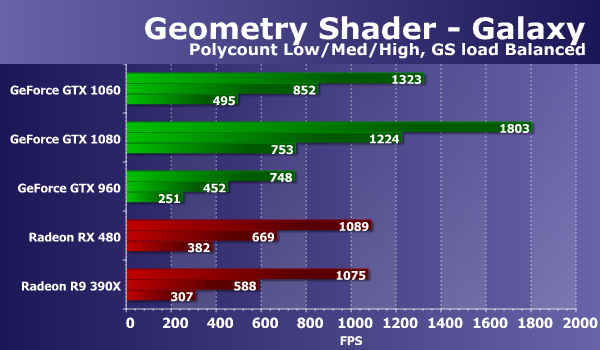
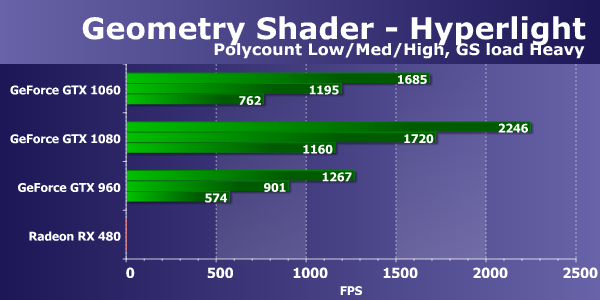
The second mathematical test from our RigthMark usually shows the results of video cards that are more or less similar to the real state of affairs relative to each other. So, the new model GeForce GTX 1060 this time is 60% ahead of the direct predecessor GTX 960, and shows the speed at 66% of the top model GTX 1080 - it seems that this is the real difference between them with a twofold difference in the number of execution units. If we compare the second GPU of the Pascal architecture with the Radeon cards, the newer model from the video cards on the AMD chips again showed a slightly smaller result, and the difference between the GeForce GTX 1060 and the Radeon RX 480 was again in favor of the novelty. Although the Hawaii graphics processor, despite the fact that it was released a long time ago, is still very strong in mathematical tests, and therefore the Radeon R9 390X is clearly faster than this pair of fresh medium-priced GPUs. Direct3D 10: Geometric shader testsAs part of the RightMark3D 2.0 package, there are two speed tests for geometric shaders, the first one is called "Galaxy", the technique is similar to "point sprites" of previous versions Direct3D. It animates the particle system on the GPU, the geometric shader from each point creates four vertices that form a particle. Similar algorithms should be widely used in future games under DirectX 10. Changing the balancing in the tests of geometric shaders does not affect the final rendering result, the resulting image is always exactly the same, only the ways of processing the scene change. The parameter "GS load" determines in which shader the calculations are made - in vertex or geometric. The number of calculations is always the same. Consider the first version of the test "Galaxy", with calculations in the vertex shader, for three levels of geometric complexity:
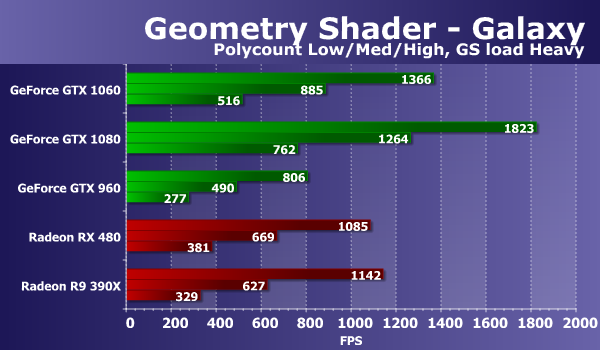
The ratio of speeds for different geometric complexity of scenes is approximately the same for all solutions, the performance corresponds to the number of points, with each step the FPS drop is close to two times. This task for powerful modern video cards is quite simple, and the performance in it is limited by the speed of processing the geometry, and sometimes by the memory capacity and / or fill rate. The observed difference between the results of video cards on Nvidia and AMD chips this time is clearly in favor of the solutions of the California company and it is caused by differences in the geometric pipelines of the chips of these companies. The geometry tests GeForce boards have always been competitive the Radeon, in this case shows clearly that modern GPUs Nvidia have a larger number of blocks of geometry processing and win with a noticeable advantage. The new model GeForce GTX 1060 lags behind the GTX 1080 by only 27-30%, being up to twice as fast as the previous generation GeForce GTX 960. The Radeon graphics cards show results between the GTX 960 and the novelty, the difference between the Radeon R9 390X at The old GPU and the new RX 480 are quite small. Both of them lost the GeForce GTX 1060, though not at times. Let's see how the situation changes when you transfer some of the calculations to a geometric shader:
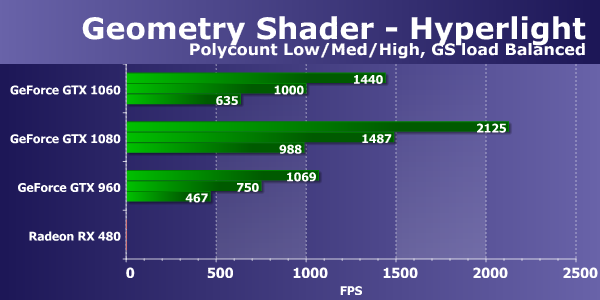
When changing the load in this test, the numbers changed slightly for AMD cards and for Nvidia solutions. And it does not change much. The video cards in this test of geometric shaders react poorly to the change in the GS load parameter, which is responsible for transferring part of the calculations to the geometric shader, and therefore our conclusions remain unchanged. The GeForce GTX 1060 in this subtest showed an excellent result, overtaking all other video cards, except for the top-end GTX 1080, from which it lagged 25-32%. The lag of the fresh Radeon RX 480 from the novelty turned out to be about the same - 25-33%. Unfortunately, Hyperlight is the second test of geometric shaders, demonstrating the use of several techniques at once: instancing, stream output, buffer load, which uses dynamic geometry creation with the help of rendering in two buffers, and also new opportunity Direct3D 10 - stream output, on all modern video cards AMD does not work. This test has long ceased to run on the motherboard of this company, and the bug has not been fixed for several years. So we consider in this test only the results of video cards Nvidia:
In this diagram, we see almost the same thing as in the Galaxy test. The new video card based on the GP106 chip turned out to be a quarter faster than the previous generation GeForce GTX 960, but from the top-end motherboard of its Pascal generation in the form of the GTX 1080 model, it fell 32-36% - again we see about two-thirds of the GP104 speed, that approximately and it is necessary to count in real conditions. Perhaps in a difficult mode something will change:
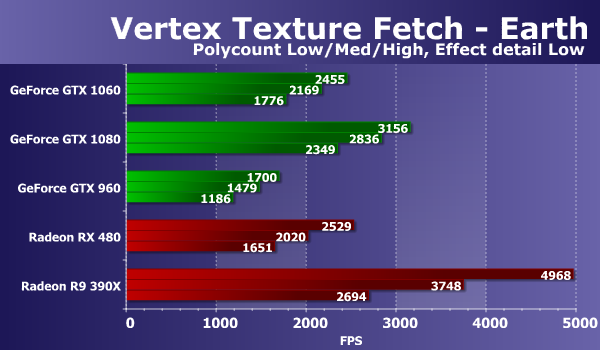
In such conditions, the results of Nvidia's video cards have changed, but this did not greatly affect their mutual position. At the GTX 1060 we see the same 66-70% of the speed of the top GeForce GTX 1080, and the motherboard from the previous generation Maxwell, based on the similarly positioned GPU, lost about 33% to the novelty. In general, we can say that in the tests based on geometric shaders the novelty proved to be quite good. Direct3D 10: the speed of selection of textures from vertex shadersVertex Texture Fetch tests the speed of a large number of texture samples from a vertex shader. The tests are similar, in fact, so the ratio between the results of the maps in the "Earth" and "Waves" tests should be approximately the same. In both tests, displacement mapping is used based on texture sample data, the only significant difference is that the "Waves" test uses conditional transitions, and "Earth" does not. Consider the first test "Earth", first in the "Effect detail Low" mode:
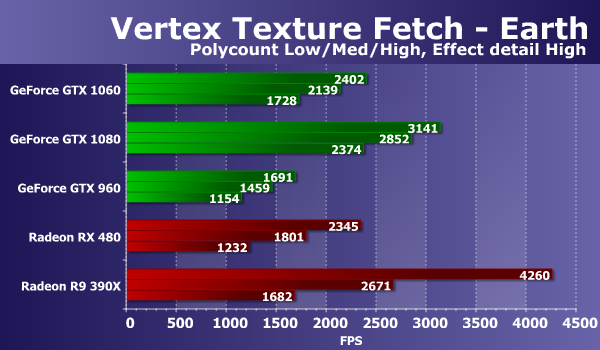
Our previous research has shown that the results of this test can be affected by both fill-rate and memory bandwidth limiting performance, which is clearly visible from the results of Nvidia boards in simple modes. All the new video cards from Nvidia in this test show the speed is obviously too low - this test is not very well executed on all GeForce cards. The clear leader in this test is old fee AMD based on the Hawaii video chip - this time it was stronger than all other comparison cards, from Nvidia and AMD innovations. By the way, if you compare the GTX 1060 with a direct competitor RX 480, then they are very close to each other, and the GeForce is only slightly faster than Radeon. Let's look at the performance of the video cards presented in comparison in the same test, but with an increased number of texture samples:
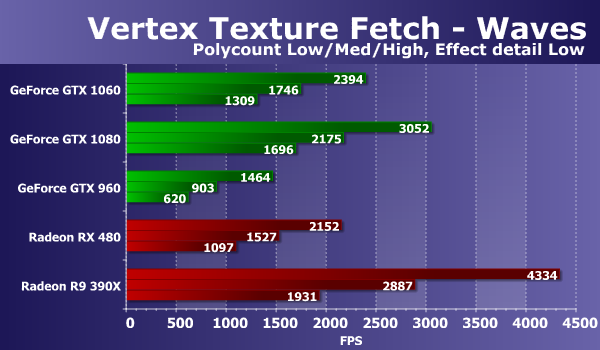
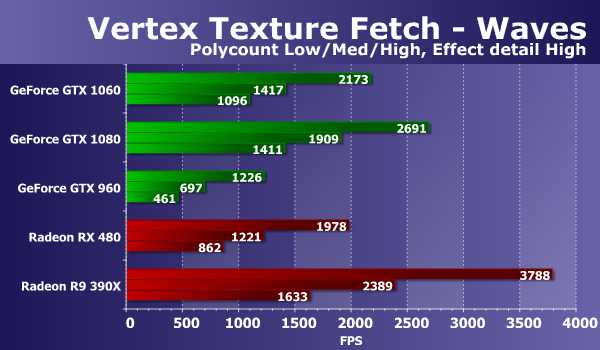
The situation on the diagram has slightly changed, and AMD's solutions in heavy modes have lost significantly more GeForce cards. The new model GeForce GTX 1060 in difficult conditions showed a speed of about 75% of the performance of the GTX 1080, significantly overtaking the predecessor in the face of the GTX 960. By the way, if we compare the novelty with the new Radeon model, then the GeForce GTX 1060 clearly wins the AMD card already in all modes, but especially - in the heaviest, where the difference reaches 40%. Consider the results of the second test of texture samples from vertex shaders. The test "Waves" differs in fewer samples, but it uses conditional transitions. The number of bilinear texture samples in this case is up to 14 ("Effect detail Low") or up to 24 ("Effect detail High") on each vertex. The complexity of the geometry changes similarly to the previous test.
The results in the second vertex texturing test "Waves" are in many respects similar to what we saw in the previous diagrams. The GeForce GTX 1060's performance in this test is clearly higher than the performance of the Radeon RX 480, although the old Radeon R9 390X was faster than all of them, and even the GTX 1080 outperformed. If we compare the new solution of Nvidia with GeForce, then the GTX 960 lagged behind, and the top-end GTX 1080 was only 20-22% faster. Consider the second version of the same problem:
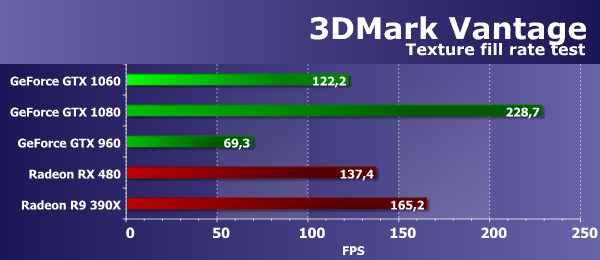
With the complication of the task in the second test of texture samples, the speed of all decisions became lower, and video cards Nvidia suffered somewhat more. But nothing changes in the conclusions, the new model GeForce GTX 1060 again somewhere 20-26% slower than the top-end video card on the GP104 chip of the same generation, and more than twice as fast as its predecessor from the previous generation Maxwell. If we compare the GeForce GTX 1060 with the Radeon RX 480, then the Nvidia solution is still faster - up to 27%. True, the old Radeon R9 390X is again ahead of everyone. 3DMark Vantage: Test FeatureSynthetic tests from the package 3DMark Vantage can show us what we have previously missed. Feature tests from this test package have the support of DirectX 10, are still relevant and interesting in that they are different from ours. When analyzing the results of the latest graphics cards GeForce GTX 1060 this package we will make some new and useful findings, escaped from us in the tests of RightMark family packages. Feature Test 1: Texture FillThe first test measures the performance of texture sample blocks. The filling of a rectangle with values read from a small texture using multiple texture coordinates is used, which change each frame.
Efficiency video cards AMD and Nvidia in the texture test company Futuremark is quite high and the final figures different models are close to the corresponding theoretical parameters. The difference in speed between the GeForce GTX 960 and GTX 1060 was almost twofold in favor of a newer solution based on the Pascal architecture chip, naturally. Well and in comparison with GTX 1080, the novelty has lagged behind the top model almost twice, as approximately and should turn out, proceeding from a theoretical difference. As for comparing the speed of texturing a new video card from Nvidia with the available solutions on the market of the competitor, the novelty is still inferior radeon video card RX 480 about 10%, well, the model of the previous generation 390X ahead of them both. So, the results of this test showed once again that AMD video cards with texturing are doing very well, and the GP106 card could not get Polaris 10 from the competitor in texturing - the last blocks of TMU are much larger. Feature Test 2: Color FillThe second task is the fill rate test. It uses a very simple pixel shader that does not limit performance. The interpolated color value is recorded in the off-screen buffer (render target) using alpha blending. A 16-bit off-screen FP16 format buffer is used, most often used in games that use HDR rendering, so this test is quite timely.
The figures from the second 3DMark Vantage subtest show the performance of ROPs, without taking into account the amount of video memory bandwidth (so-called "effective fill rate"), and the test measures exactly the performance of ROP. The GeForce GTX 1060 card considered by us today has lagged behind the best of the comparison boards for the same almost 50%. Unsurprisingly, the GeForce GTX 1080 is almost twice as fast as it should be in theory. But the direct predecessor GTX 960 is more than 1.5 times slower than today's novelty, so with the efficiency of the ROP units in Pascal everything is fine. Well, if we compare the filling speed of a scene with a new GeForce GTX 1060 graphics card with AMD solutions, then the board considered in this test again showed a slightly lower fill rate in comparison with the Radeon RX 480 (the difference was only 6%). Well, R9 390X is very much behind both modern graphics cards. Apparently, the result was affected not only by a large number of ROP units, but also by effective data compression optimization for modern GPUs of both manufacturers. Feature Test 3: Parallax Occlusion MappingOne of the most interesting feature tests, as this technique has long been used in games. It draws one quadrilateral (more precisely, two triangles) with the use of special techniques Parallax Occlusion Mapping, imitating complex geometry. Use quite resource-intensive ray tracing operations and a map of the depth of a large resolution. Also this surface is obscured by the heavy Strauss algorithm. This test is a very complex and heavy pixel shader for the video chip, containing numerous texture samples for ray tracing, dynamic branching and complex calculations of lighting by Strauss.
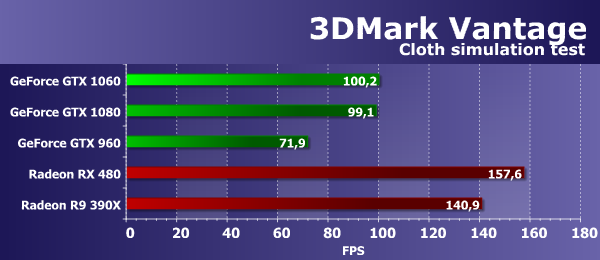
This test of 3DMark Vantage package differs from earlier conducted so that the results of it depends not only on the speed of mathematical calculations, the efficiency of execution of the branch or the speed of texture samples, and on several parameters simultaneously. To achieve high speed in this task, the correct balance of the GPU is important, as well as the efficiency of performing complex shaders. In this case, both mathematical and texture productivity are important, and in this "synthetics" of 3DMark Vantage the new GeForce GTX 1060 board showed quite a good result, being 78% faster than the similar model of the previous generation, based on the similar graphics processor of the Maxwell-GTX architecture 960. And the older model of the current generation GTX 1080 based on the GP104 is still almost twice as fast as the new ones. The average price of Nvidia in this test was almost the same as the Radeon RX 480 (the difference was only 4%), but both of them were behind the R9 390X. Feature Test 4: GPU ClothThe fourth test is interesting in that it calculates physical interactions (imitation of tissue) using a video chip. Vertex simulation is used, using combined work of vertex and geometric shaders, with several passes. It uses stream out to transfer vertices from one simulation pass to another. Thus, the performance of vertex and geometric shaders and the rate of stream out are tested.
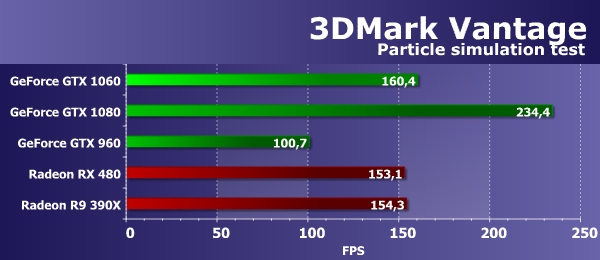
The speed of rendering in this test also depends on several parameters at once, and the main factors of influence should be the performance of geometry processing and the efficiency of performing geometric shaders. That is, the strengths of Nvidia chips should be shown, but we have already noted very strange results for a long time, alas. In this test, another new video card Nvidia showed low speed, exactly at the level of the older sister GeForce GTX 1080, so it's hardly possible to judge the real speed of geometry processing on this test. Comparison with Radeon cards in this test for a novelty in such conditions is far from the most joyful. Despite the theoretically smaller number of geometric execution units and the lag in geometric performance among AMD chips, compared to competing solutions, both Radeon cards in this test work very efficiently, overtaking all the GeForce video cards presented in comparison. Accordingly, the RX 480 in such conditions is already 36% faster than the novelty. Feature Test 5: GPU ParticlesThe test of physical simulation of effects on the basis of particle systems, calculated using a video chip. Vertex simulation is also used, each vertex represents a single particle. Stream out is used for the same purpose as in the previous test. A few hundred thousand particles are calculated, all are animated separately, and their collisions with a height map are also calculated. Similar to one of our RightMark3D 2.0 tests, the particles are drawn using a geometric shader that creates four vertices from each point that form the particle. But the test most loads the shader blocks by vertex calculations, also it is tested stream out.
But in the second "geometric" test from 3DMark Vantage the situation has changed. This time new GeForce already shows very good results, slightly overtaking both the opponent's boards, and the Maxwell architecture solution. The new GeForce GTX 1060 board this time fell behind the GTX 1080 by only 32%, overtaking its predecessor from the previous generation by almost 60%. Comparison of the novelty from Nvidia with AMD's competing graphics cards is more positive this time - the new board on the second GPU of the Pascal family showed the result slightly better than both single-chip video cards of the rival company. Feature Test 6: Perlin NoiseThe last feature of the Vantage package is a mathematically-intensive test for the GPU, it calculates several octaves of the Perlin noise algorithm in a pixel shader. Each color channel uses its own noise function for greater load on the video chip. Perlin noise is a standard algorithm, often used in procedural texturing, it uses a lot of mathematical calculations.
In this mathematical test, the performance of solutions, although not entirely consistent with the theory, is very close to what should be, based on the peak performance. In the mathematic test from the package of the company Futuremark, showing the peak performance of video chips in the limiting tasks, we see the distribution of the results, which is very different from the similar tests from our test package. Although AMD GPUs with GCN architecture still cope with similar tasks better than competitors' solutions in cases where intensive math is performed, the latest models of graphics processors from Nvidia based on Pascal architecture almost reach their direct competitors in speed. So, the GeForce GTX 1060 did not even get the Radeon R9 390X and RX 480, but only 9% behind the latter, which can be called a good result, given the lower complexity of the GPU from Nvidia - they finally got very productive solutions from the point of view the view of intensive computing, and in many respects you need to say a very high clock speed of the chip. Compare the novelty with the previous model of the company from the family GeForce GTX 900 sense is not very much, in this test the difference is quite large. The video card considered today showed a 60% better result than the similar GeForce GTX 960 from the previous generation. These are very good indicators in such tests, which hint at quite strong performances of the GeForce GTX 1060 and in gaming applications. Direct3D 11: Computational Shaders and Tessellation PerformanceUsually, for tests of new solutions in tasks using such features of DirectX 11, as tessellation and computational shaders, we use examples from developer packages (SDK) and demonstration programs from Microsoft, Nvidia and AMD. But alas, all our usual tests using computational shaders and tessellation on a test system with DirectX 12 running operating system Windows 10 do not work correctly. They do not really work either in windowed mode or full screen. And they do not give permission to change, crashing work. For future materials, a new methodology will be developed with actual synthetic tests DirectX 11/12 and OpenCL - in the comments to the article on our forum you can write your wishes on the test suite. Based on the results of synthetic tests new video card Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060 based on a completely new GP106 GPU, already the second representative of Pascal architecture, as well as the results of other video card models from both manufacturers of discrete video chips, we can conclude that the video card we are considering today can become one of the most productive solutions in its class, ahead of even such solutions of the previous generation of a higher price level, like the GeForce GTX 980. The new video card from Nvidia showed fairly strong results in most synthetic tests, roughly at the level with the main competing solution from AMD in the person of Radeon RX 480. Although in some tests we observed obvious losses, but practice showed that the games will be slightly different in games , since not all synthetics can be transferred to games. Once again, we note that Radeon and GeForce have different strengths: if AMD solutions traditionally differ by very effective execution of relatively intensive computational tasks, Nvidia graphics processors are played back in geometric tests using tessellation and tests with more complex computations. In real gaming applications, the situation will still be slightly different, in comparison with synthetic tests. Judging by the experience of previous comparisons, the GeForce GTX 1060 model should show in games speed slightly above the level of the GeForce GTX 980 and clearly outstrip the Radeon RX 480, albeit not with an overwhelming advantage. At first glance, the novelty from Nvidia seems to be a good balanced solution, especially for countering the Radeon RX 480, even taking into account the existing price difference. And if you touch on the topic of energy efficiency and performance per 1 mm² of GPU space or on a transistor, then the GeForce GTX 1060 will be a clear winner. The architecture of Pascal was really effective! In the next part of our material, we suggest to evaluate the performance of new items in games in comparison with its competitors. We tested GeForce GTX 1060 in our usual set of modern game tests and compared its performance with the speed of the main competitors and predecessors. The Corsair Obsidian 800D Full Tower for the test stand is provided by the company Corsair |
Memory modules G.Skill Ripjaws4 F4-2800C16Q-16GRK for the test stand are provided by the company G.Skill | Corsair Hydro SeriesT H100i CPU Cooler for the test stand provided by the company Corsair | |
| The Dell UltraSharp U3011 monitor for test stands is provided by the company Yulmart | The ASRock Fatal1ty X99X Killer for the testbed is provided by the company ASRock | Seagate Barracuda 7200.14 hard drive 3 TB for the test stand provided by the company Seagate | 2 sSD drive Corsair Neutron SeriesT 120 GB for the test stand provided by the company Corsair |

ASUS DUAL-GTX1060-O3G Test procedure Test results Single page
The video card GeForce GTX 1060 has received two incarnations. In detail about the older version of 6 GB we told in a separate article. The younger version with 3 GB differs not only the reduced amount of video memory, but also the smaller number of computational units. Earlier, both video cards appeared in the tests for individual games. Now we decided to bring them together in a big comparison to find out how much the GeForce GTX 1060 3GB differs from the GeForce GTX 1060 6GB. The minor modification is in about the same price category with the Radeon RX 470, but in this article we have placed emphasis on comparison with older video cards. Therefore, AMD will take part in the testing Radeon RX 480 8GB.
Consider the general features of GeForce GTX 1060 3GB and the capabilities of a particular model of this series in the face of ASUS DUAL-GTX1060-O3G. Let's estimate the temperature and noise characteristics, check the overclocking potential.
At the heart of all variations GeForce GTX 1060 graphics processor GP106 architecture Pascal, which is made on a 16-nm process technology. This chip has 1,280 CUDA cores, 80 TMU texture units and 48 ROPs. Compared to the previous generation, an intermediate configuration of the computational blocks between the GeForce GTX 970 and the GeForce GTX 960 is obtained. But thanks to a serious increase in frequencies and a new architecture, the GeForce GTX 1060 6GB is faster than the GeForce GTX 970.
The GeForce GTX 1060 3GB video card should be closer to the GeForce GTX 970 in its capabilities. The younger version left 1152 active CUDA cores at 72 texture blocks. The frequencies remained unchanged. The most serious simplification is a memory reduction of up to 3 GB. And this is also a card closer to the GeForce GTX 970. Due to the peculiarities of the memory subsystem organization, the GeForce GTX 970 has an effective capacity of 3.5 GB, and the last memory segment operates at lower bandwidth and is not always effectively used by applications.
Compare the technical specifications of the two versions of the GeForce GTX 1060 with the GeForce GTX 970 on the lower table.
|
GeForce GTX 1060 6GB |
GeForce GTX 1060 3GB |
||
|
Architecture |
|||
|
The GPU code name |
|||
|
Number of transistors, mln. |
|||
|
Process technology, nm |
|||
|
Core area, sq. mm |
|||
|
Number of texture units |
|||
|
Number of ROPs |
|||
|
Core frequency, MHz |
|||
|
Memory bus, bit |
|||
|
Memory type |
|||
|
Memory capacity, Mbytes |
|||
|
Interface |
|||
|
TDP level, W |
It's no secret that many modern games, even for Full HD, require up to 4 GB of video memory. Therefore, the question of the real difference between the GeForce GTX 1060 3GB and the GeForce GTX 1060 6GB is very urgent. We tried to answer it in this test, comparing different versions of the GeForce GTX 1060 with each other and with the Radeon RX 480 in 16 test applications at a resolution of 1920x1080. But first let's look at the representative of the GeForce GTX 1060 3GB series.
ASUSDUAL-GTX1060-O3G
The ASUS graphics card comes in a small box. It is not equipped with any additional adapters. But the buyer will receive a code with bonuses for the game World of Warships for 15 days of premium mode.

Ruler graphics cards ASUS DUAL stands out for its special style with white color. Usually in the design of videoart dominated by dark colors, so the snow-white body of this model looks unusual. It will look organic together with motherboards ASUS X99-A II or in combination with other boards that use white radiators or light textolite.

ASUS DUAL offers and good system cooling. A large cooler covers the entire board, two fans are used. Additional power is connected to one 8-pin connector in the corner of the board.

The board itself is the usual black color. This is not a shortened version, as happens with cheap versions of the GeForce GTX 1060. It is evident that the production did not save.

There are five connectors for outputting the image: two HDMI, two DisplayPort and one DVI.

After dismantling the cooler, it becomes clear that the radiator is not as large as it seems in the assembled state. But the design uses two thick heat pipes with direct contact - their surface is directly in contact with the surface of the graphic chip.
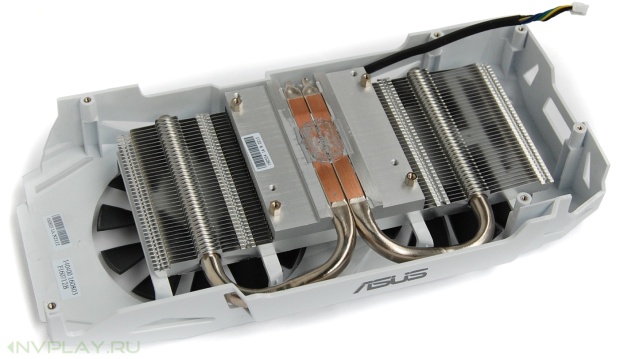
The radiator is recruited from a series of small thin plates fixed in a massive base. Heat pipes are threaded along the edges of the plate. The plastic housing is screwed on top by a pair of 90 mm fans.

For the elements of the supply chain has its own radiator. Given the size of the fans, we can talk about the excellent blow-out of both this additional radiator and all electronic components on the board.

The power supply subsystem of the graphics chip has four phases. Qualitative components are used, which can be seen and no more expensive ASUS video cards.

Full marking of GP106-300-A1 chip. Three gigabytes of memory is collected by six GDDR5 chips Samsung K4G41325FE-HC25.
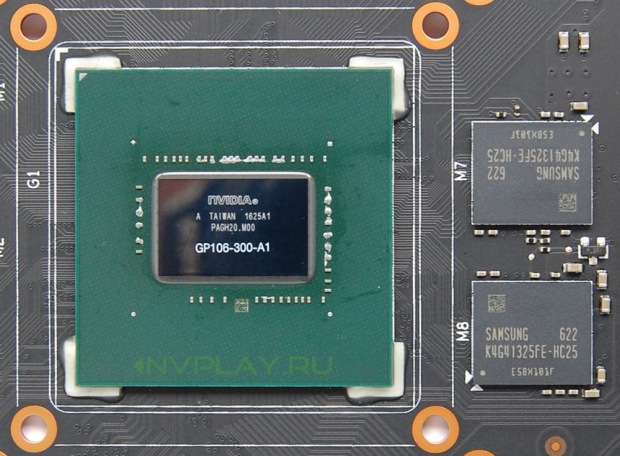

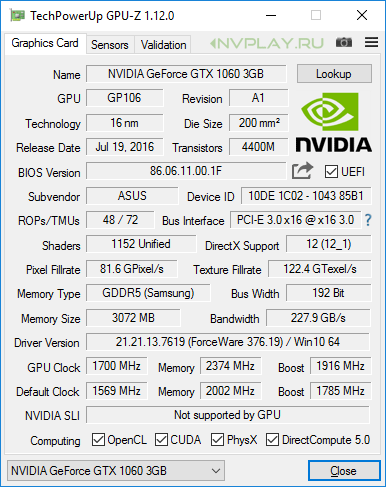
Standard specifications provide a base frequency of a graphics chip of 1506 MHz with an average Boost Clock of 1708 MHz. ASUS operates at frequencies of 1569/1785 MHz. The effective memory frequency corresponds to a standard value of 8 GHz.

Factory overclocking is small, but there is also a software profile with higher core frequencies of 1594/1809 MHz. To select working profiles, use the proprietary utility ASUS GPU Tweak II, which also allows for parameter monitoring and manual overclocking.
We tested ASUS with standard factory settings. In the game mode at a room temperature of 23 ° C, the core was heated to 73 ° C. The fans spun up to 1500 rpm and slightly higher, creating extremely low noise. Peak value of Boost could reach 1974 MHz, but the average frequency was at 1934 MHz, which is illustrated below by the screenshot of monitoring in MSI Afterburner program during multiple passage of Gears of War 4.
Traditionally, for tests on standard frequencies, we bring the GeForce GTX 1060 to Boost frequencies at 1860 MHz. Similarly, this time, the base value was adjusted in such a way that Boost frequencies were kept within 1848-1873 MHz. In order to avoid disagreements on the performance graphs, the maximum Boost value for both versions of the GeForce GTX 1060 is indicated as 1860 MHz.
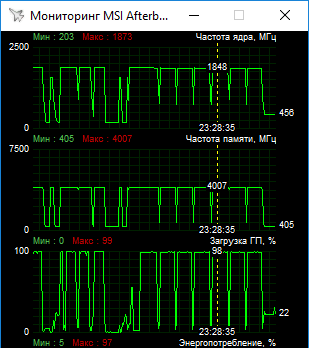
The overclocking potential of ASUS turned out to be at the level of the older GeForce GTX 1060 6GB models. The core frequency was raised to 1700 MHz with the maximum Boost up to 2101 MHz. The memory could be overclocked to 4743 (9486) MHz.
With the increase in the power limit to a maximum and the slight manual acceleration of the fans, it was possible to achieve that the core frequency kept at the level of 2088-2101 MHz, with rare deviations from the lower side.
At a fan speed of more than 2000 rpm, a distinct buzz appears. And if, in terms of acoustic comfort, you are very demanding, you will have to slow down and possibly slow down the acceleration.
As a result, the video card was tested as a standard version with standard frequencies, at higher factory frequencies and in overclocking. The older version of GeForce GTX 1060 and Radeon RX 480 are positioned as more expensive and productive solutions. Therefore, they were tested only at standard frequencies.
Characteristics of the test participants
|
GeForce GTX 1060 6GB |
ASUS DUAL GTX 1060 3GB |
GeForce GTX 1060 3GB |
||
|
Architecture |
||||
|
The GPU code name |
||||
|
Number of transistors, mln. |
||||
|
Process technology, nm |
||||
|
Core area, sq. mm |
||||
|
Number of stream processors |
||||
|
Number of texture units |
||||
|
Number of ROPs |
||||
|
Core frequency, MHz |
||||
|
Memory bus, bit |
||||
|
Memory type |
||||
|
Effective memory frequency, MHz |
||||
|
Memory capacity, Mbytes |
||||
|
Interface |
||||
|
TDP level, W |
Video accelerator Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060
The winner of the top-generation solutions of the previous generation
- Part 2 - Practical acquaintance
We present the basic detailed material with the study of Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060.
Object of study: 3D graphics accelerator (video card) Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060 6 GB 192-bit GDDR5 PCI-E
Information about the developer: Nvidia Corporation (Nvidia trademark) was founded in 1993 in the USA. Headquarters in Santa Clara, California. Develops graphics processors, technologies. Until 1999, the main brand was Riva (Riva 128 / TNT / TNT2), from 1999 to the present - GeForce. In 2000, the assets of 3dfx Interactive were acquired, after which the 3dfx / Voodoo trademarks were transferred to Nvidia. Its production is not. The total number of employees (including regional offices) is about 5000 people.
Part 1: Theory and Architecture
Back in the spring, Nvidia started another wave of new graphics processors entering the market, but these were video cards of the upper price segment - GeForce GTX 1080 and GTX 1070, designed for enthusiasts. Their competitor, in turn, has released a less efficient, but much cheaper solution in the form of Radeon RX 480, which is clearly aimed at a more mass buyer. Of course, Nvidia could not fail to respond to this announcement, on July 7, announcing the imminent release of a new graphics processor - GeForce GTX 1060, which is now replenished with a family of gaming solutions based on Pascal architecture.
Recall that the latest graphic architecture Nvidia Pascal uses a 16-nanometer FinFET technology process, which plays a special role in achieving higher performance and energy efficiency. This made it possible to make chips that have a greater number of execution units and operate at a higher clock speed, in comparison with their predecessors - similar solutions of the Maxwell architecture. In addition, Nvidia engineers have worked with the design of specific Pascal chips to achieve high clock speeds with the lowest possible power consumption. As a result, this architecture has become a clear record for speed and energy efficiency.

Today's novelty is based on the new GP106 chip, unlike the previous two, using the same GPU GPU. Like the top-end Pascal video cards, the mid-price GeForce GTX 1060, is seriously different from the solutions from the previous line of the company with increased performance and energy efficiency. From its older counterparts, the GeForce GTX 1060 differs mainly in that it has only 1280 cores and 6 GB of GDDR5 memory with a 192-bit bus.
In the production of a new graphics processor, the 16 nm process technology of TSMC is also used, so even with fewer functional units, the novelty provides performance at least at the level of the GeForce GTX 980 - with almost one and a half times less power consumption! Well, most importantly, the GeForce GTX 1060 has a recommended price for the US market of only $ 249 (for Russia - 19 thousand rubles), so it is intended for a wider range of consumers compared to the older models of the GTX 1080 and GTX 1070.
The GeForce GTX 1060 graphics card is an excellent opportunity to upgrade the video subsystem for those who still use outdated video cards of previous generations. Thanks to the high efficiency of Pascal architecture, the novelty provides performance at the level of the previous top model GeForce GTX 980, consuming only 120 W of energy. In addition, the new GPU supports many new features, such as asynchronous computing, the level of support for Feature Level 12_1 for DirectX 12, as well as the company's own technologies: Simultaneous Multi-Projection and others.
Since the new model of the Nvidia video card considered today is based on the Pascal graphics processor, which has much in common with the previous Maxwell architecture, before reading this material, we recommend you read our articles about the company's early video cards:
- Nvidia GeForce GTX 1070 - 75% of the new leader of gaming 3D-graphics on the PC
- Nvidia GeForce GTX 1080 - the new leader of game 3D-graphics on the PC
- Nvidia GeForce GTX 980 Ti - the most productive uniprocessor accelerator game class
- Nvidia GeForce GTX Titan X - the most powerful single-processor accelerator
- Nvidia GeForce GTX 980 - follower of GeForce GTX 680, overtaking even GTX 780 Ti
- Nvidia GeForce GTX 750 Ti - Maxwell starts small ... despite Maxwell
Consider the detailed characteristics of the GeForce GTX 1060 video card based on the new GP106 GPU.
| Graphics accelerator GeForce GTX 1060 | |
|---|---|
| Parameter | Value |
| Code name of the chip | GP106 |
| Production technology | 16 nm FinFET |
| Number of transistors | 4.4 billion |
| Core area | 200 mm² |
| Architecture | Unified, with an array common processors for streaming processing of numerous types of data: vertices, pixels, etc. |
| Hardware support for DirectX | DirectX 12, with support for the level of features Feature Level 12_1 |
| Memory bus | 192-bit: six independent 32-bit memory controllers with support for GDDR5 memory |
| GPU frequency | 1506 (1708) MHz |
| Computing units | 10 streaming multiprocessors, including 1280 scalar ALUs for floating point calculations within the IEEE 754-2008 standard; |
| Texturing blocks | 80 blocks of texture addressing and filtering with support for FP16- and FP32-components in textures and support for trilinear and anisotropic filtering for all texture formats |
| Blocks of raster operations (ROP) | 6 wide blocks ROP (48 pixels) with support for various modes of smoothing, including programmable and with FP16 or FP32-format buffer frame. Blocks consist of an array of configurable ALUs and are responsible for the generation and comparison of depth, multisampling and blending |
| Support for monitors | Integrated support for up to four monitors connected via Dual Link DVI, HDMI 2.0b and DisplayPort 1.2 (1.3 / 1.4 Ready) |

| Specification of reference video card GeForce GTX 1060 | |
|---|---|
| Parameter | Value |
| Kernel frequency | 1506 (1708) MHz |
| Number of universal processors | 1280 |
| Number of texture units | 80 |
| Number of Blending Blocks | 48 |
| Effective memory frequency | 8000 (4 × 2000) MHz |
| Memory type | GDDR5 |
| Memory bus | 192-bit |
| Memory | 6 GB |
| Memory bandwidth | 192 GB / s |
| Computing performance (FP32) | about 4 teraflops |
| Theoretical maximum fill speed | 72 gigapixel / s |
| Theoretical texture sampling rate | 121 gigatexel / s |
| Tire | PCI Express 3.0 |
| Connectors | One Dual Link DVI connector, one HDMI and three DisplayPort |
| Typical power consumption | 120 W |
| Extra food | One 6-pin connector |
| Number of slots occupied in the system casing | 2 |
| Recommended price | $ 249 ($ 299) in the US and 18 990 in Russia |
The video card GeForce GTX 1060 released today received a logical name, similar to the same solution from the previous GeForce series. Unsurprisingly, it differs from its direct predecessor GeForce GTX 960 only by the changed first digit of the generation. The novelty was in the current line of the company one step lower than the previously released solution GeForce GTX 1070, which is the average speed in the new series.
The recommended prices for Nvidia's new video card are $ 249 and $ 299 for regular versions of the company's partners and for the special edition of Founder's Edition, respectively. Compared to the two older models, this is a very advantageous price, since the new GTX 1060 model is inferior to the top-end cards, but far from being as low as it is cheaper. At the time of the announcement, today's novelty has definitely become the best-in-class solution in its class and one of the most profitable offers in this price range. As always, the Russian recommended price is less attractive, since it invests additional costs: taxes, logistics, etc.
It's clear that the third model of Nvidia's Pascal video card came out to counter the fresh solution of the competing AMD company, which earlier released the Radeon RX 480 to the market. It's possible to compare Nvidia's novelty with this video card, although not quite directly, as they are still quite noticeable differ in price. The GeForce GTX 1060 is more expensive ($ 249-299 vs. $ 199-229), but also clearly faster than the competitor. And how much they are comparable in speed - we'll talk about this in the next parts of our material.
The GP106 GPU has a 192-bit memory bus, so the amount of memory installed on the graphics card with such a bus can be 3 or 6 GB. Less importance in modern conditions is frankly insufficient, and many game projects, even in Full HD-resolution will be limited by the lack of video memory, which will seriously affect the smooth rendering. To ensure maximum performance of the new solution in conditions of high settings, the GeForce GTX 1060 model was equipped with 6 GB of video memory, which is enough to run any 3D applications with any quality settings. Moreover, for today there is simply no difference between 6 and 8 GB, and this solution will save some money.
The only thing that worries us is the persistent rumors about the existence of less expensive variants of GTX 1060 with 3 GB, which some Nvidia partners allegedly prepared. If it is just a less expensive version of the GTX 1060, then we would not advise buying a 3 GB version of this board. But if the rumor spreading confused the secret board with a less productive model as a whole (for example, the hypothetical GTX 1050), then everything is in order - for a much less expensive option, enough and 3 GB of memory.
The value of typical energy consumption for the novelty is 120 W, which is less than the value for the GTX 1070 by 20% and is equal to the energy consumption of the previous generation GeForce GTX 960 graphics card, which has much less performance and capabilities. The reference board has the usual set of connectors for connecting image output devices: one Dual-Link DVI, one HDMI and three DisplayPort. And there was support for new versions of HDMI and DisplayPort, which we wrote about in the review of the model GTX 1080.

The length of the GeForce GTX 1060 reference board is 9.8 inches (25 cm), and, unlike the older versions, we note separately that the GeForce GTX 1060 does not support the SLI multichip rendering configuration, and does not have a special connector for this. Since the board consumes less power than the older models, one additional 6-pin PCI-E external power connector is installed on the board for additional power.
GeForce GTX 1060 video cards will appear on the market starting from today in the form of partners' products: Asus, EVGA, Gainward, Gigabyte, Innovision 3D, MSI, Palit, Zotac. In a limited number will be released and a special edition GeForce GTX 1060 Founder's Edition, produced by the company Nvidia, which will be sold at a price of $ 299 exclusively on the site of Nvidia and officially in Russia will not be presented. Founder's Edition is distinguished by the fact that it is made of high-quality materials and components, including an aluminum casing, and uses an efficient cooling system, as well as power circuits with low resistance and voltage regulators of special design.
Architectural changes
The GP106 video chip is similar in its device to the top Pascal chip and similar solutions of the Maxwell architecture, and detailed information about the modern GPU device can be found in our reviews of previous solutions of Nvidia. Like the previous GPUs, the chips of the new architecture have different configurations of the processing clusters Graphics Processing Cluster (GPC), streaming multiprocessors Streaming Multiprocessor (SM) and memory controllers:
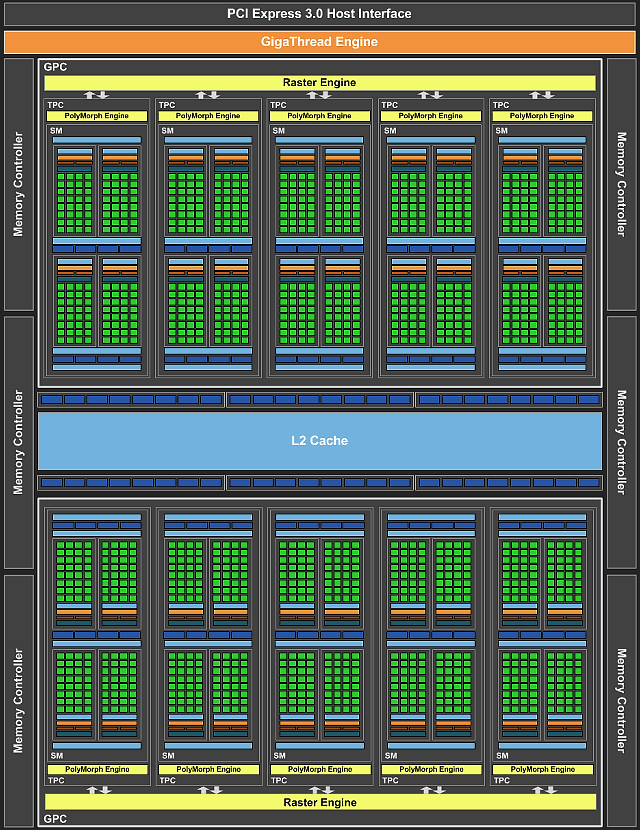
GP106 GPU includes two GPC clusters, consisting of 10 Streaming Multiprocessor (SM), that is exactly half of what is available in GP104. As in the older GPU, each of the multiprocessors contains 128 cores, 8 TMU texture units, 256 KB of register memory, 96 KB of shared memory and 48 KB of L1 cache. As a result, the GeForce GTX 1060 contains a total of 1280 cores and 80 texture modules - half the size of the GTX 1080.
But the GeForce GTX 1060 memory subsystem was not halved with respect to the top-end solution, it contains six 32-bit memory controllers, which give the final 192-bit memory bus. At an effective frequency of GDDR5 video memory for GeForce GTX 1060 equal to 8 GHz, the throughput reaches 192 GB / s, which is quite good for solving such a price segment, especially considering the high efficiency of its use in Pascal. Eight ROPs and 256 KB of L2 cache are tied to each of the memory controllers, so in general full version GP106 GPU contains 48 ROPs and 1536 KB L2 cache.
To reduce memory bandwidth requirements and more efficient use of the Pascal architecture available, the intra-chip lossless data compression was further improved, which is able to compress data in buffers, gaining in efficiency and productivity. In particular, new delta-compression methods with a ratio of 4: 1 and 8: 1 were added in the new family chips, providing an additional 20% to the efficiency of the memory bandwidth compared to previous solutions of the Maxwell family.
The base frequency of the new GPU is 1506 MHz - below this mark the frequency should not drop in principle. Typical turbo frequency (Boost Clock) is much higher and equal to 1708 MHz - this is the average value of the real frequency on which the GeForce GTX 1060 graphics chip works in a large set of games and 3D applications. The actual Boost frequency depends on the game and the conditions in which the testing takes place.
Like the rest of the Pascal family, the GeForce GTX 1060 does not just run at a high clock speed, providing high performance, but it also has a decent amount of overclocking capability. The first experiments indicate the possibility of reaching frequencies of the order of 2 GHz. Not surprisingly, the partners of the company are preparing, including the factory overclocked variants of the GTX 1060 graphics card.
So, the main change in the new architecture was the 16 nm FinFET process, whose use in GP106 production significantly increased the chip complexity while maintaining a relatively low area of 200 mm², so this Pascal architecture chip has a noticeably larger number of execution units compared to the Maxwell similar positioning chip , produced using a process technology of 28 nm.
If GM206 (GTX 960) with an area of 227 mm² had under 3 billion transistors and 1024 ALU, 64 TMU, 32 ROP and 128-bit bus, the new GPU accommodated 4.4 million transistors in 200 mm², 1280 ALU, 80 TMUs and 48 ROPs with a 192-bit bus. And even at almost a half times higher frequency: 1506 (1708) against 1126 (1178) MHz. And this at the same energy consumption of 120 watts! As a result, the GP106 GPU became the most energy efficient graphics processor. Most likely, this indicator is superior to GP104, as younger chips are usually more efficient than more complex ones.
New technologies Nvidia
One of the most interesting technologies of the company, which is supported by the GeForce GTX 1060 and other solutions of the Pascal family, is technology Nvidia Simultaneous Multi-Projection. We already wrote about this technology in the GeForce GTX 1080 review, it allows us to use several new techniques to optimize the rendering. In particular - simultaneously project VR-image at once for two eyes, at times increasing the efficiency of using GPU in virtual reality conditions.
To support SMP in all GPUs of the Pascal family there is a special engine that is located in the PolyMorph Engine at the end of the geometric pipeline in front of the rasterizer. With its help, the GPU can simultaneously project a geometric primitive onto several projections from one point, while these projections can be stereo (that is, it supports up to 16 or 32 projections simultaneously). This feature allows Pascal GPUs to accurately reproduce a curved surface for VR rendering, as well as correctly output images to multi-monitor systems.

It is important that Simultaneous Multi-Projection technology is already being integrated into popular game engines (Unreal Engine and Unity) and games, and to date, technology support has been announced for more than 30 games in development, including such well-known projects as Unreal Tournament , Poolnation VR, Everest VR, Obduction, Adr1ft and Raw Data. It's interesting that although Unreal Tournament is not a VR game, SMP is used in it to achieve better picture quality and performance.
Another long-awaited technology has become a powerful tool for creating screenshots in games Nvidia Ansel. This tool allows you to create unusual and very high quality screenshots of games, with previously inaccessible capabilities, keeping them in very high resolution and complementing with various effects, and share your works. Ansel allows you to literally build a screenshot as the artist wants, allowing you to set the camera with any parameters to any point of the scene, superimpose powerful post-filters on the image, or even make a 360-degree snapshot for viewing in the virtual reality helmet.

Nvidia has standardized the integration of the Ansel user interface into games, and it's very easy to do it - just add a few lines to the code. You do not need to wait for this feature to appear in the games, you can evaluate the Ansel abilities right now in the game Mirror's Edge: Catalyst, and later it will be available in Witcher 3: Wild Hunt. In addition, many game projects with support for Ansel are in development, including games such as Fortnite, Paragon and Unreal Tournament, Obduction, The Witness, Lawbreakers, Tom Clancy's The Division, No Man's Sky and others.
Also, the new GeForce GTX 1060 graphics processor supports a tool package Nvidia VRWorks, helping developers create impressive projects for virtual reality. This package includes many utilities and tools for developers, including VRWorks Audio, which allows you to perform a very accurate calculation of reflections of sound waves from objects in the scene using ray tracing on the GPU. Also, the package includes integration into VR and physical effects PhysX to ensure physically correct behavior of objects in the scene.
One of the most vivid virtual games, which gained the advantage from VRWorks, was VR Funhouse - a game in the virtual reality of Nvidia itself, which is available for free in the service Valve Steam. This game is based on the engine Unreal Engine 4 (Epic Games), and it works on video cards GeForce GTX 1080, 1070 and 1060 in conjunction with the VR-helmets HTC Vive. Moreover, the source code of this game will be publicly available, which will allow other developers to use ready-made ideas and code already in their VR-attractions. Believe us, this is one of the most impressive demonstrations of the possibilities of virtual reality.
Including thanks to SMP and VRWorks technologies, the use of GeForce GTX 1060 graphics processor in VR-applications provides quite sufficient for the initial level of virtual reality reality, and today released GPU corresponds to the minimum required hardware level including for SteamVR, becoming one of the most successful acquisitions For use in systems with official support for VR.
Since the GeForce GTX 1060 model is based on the GP106 chip, which is in no way inferior to the graphics processor GP104, which became the basis for older modifications, it supports absolutely all the technologies described by us in the review of the first-born of the new line of Nvidia. To get more details about the architecture of Pascal, as well as the technologies supported by it, such as improved video output and processing units, support for Async Compute asynchronous computing, Simultaneous Multi-Projection multiprojection technology and a new type of Fast Sync synchronization, you should definitely familiarize yourself with this material.
Conclusions on the theoretical part
The GeForce GTX 1060 video card has already become the third model in the new line of Nvidia, based on the graphics processors of the Pascal family. The new 16 nm FinFET technological process and architecture optimization allowed all new video cards to reach a high clock speed and to place more functional units in the GPU in the form of stream processors, texture modules and others, in comparison with video chips of the previous generation. That's why the GTX 1060 released today was the most profitable and energy-efficient solution in its class and in general.
Although Pascal repeats Maxwell's solutions in many respects, numerous improvements are made to the new graphics processors in terms of the possibilities of outputting images to display devices, the functionality of the blocks of encoding and decoding of video data is improved, asynchronous execution is improved different types GPU calculations, a new Fast Sync synchronization method was implemented, etc. VRWorks support, in particular VRWorks Audio, is also possible - the possibility of high-quality sound counting, taking into account multiple reflections of sound waves using hardware ray tracing. It is very important for the future VR and the technology of multiprojection Simultaneous Multi-Projection, which helps to improve performance in virtual reality systems and get correct display of scenes on multi-monitor systems.
But more importantly, the GeForce GTX 1060 offers quite high performance and support for new features and algorithms at a much lower price, compared with older solutions on the GP104. GP106 graphics chip, used in the new model, provides the best in class performance and energy efficiency. Model GeForce GTX 1060 is specially designed and perfectly suited for all modern games at high and maximum graphical settings In 1920x1080 resolution and even with full-screen anti-aliasing enabled various methods (FXAA, MFAA or MSAA).
For those who want to get even higher performance with ultra-high resolution displays, Nvidia has top models video card GeForce GTX 1070 and GTX 1080, which are also very good in performance and energy efficiency. Still, the combination of low price and sufficient performance is very advantageous for GeForce GTX 1060 against the background of older solutions. And what about the competing Radeon RX 480? Before the tests it's difficult to answer the question, but theoretically Nvidia's board should be somewhat faster with less complexity and GPU space, not to mention energy efficiency. True, it is more expensive, so each video card has its own niche.
In the following parts of this article, we will evaluate the performance of the new Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060 in practice, comparing its speed with the performance of Nvidia and AMD competing with the novelty of single-chip video systems. Let's compare its speed with the older model GeForce GTX 1080, to get the real difference between the GPU of different positioning. Before proceeding to the game tests, let's first consider the data obtained in our set of synthetic tests.