Diagnostics of malfunctions of the processor. Common symptoms computer malfunctions
CPU Fault Diagnostics
The term "diagnostics of microprocessor faults" is not erroneous, as it may seem. The first microprocessors, such as the 8088, contained “only” 28,000 transistors. When one of these transistors failed, the whole system failed - it hung or collapsed. In the future, the computer could stop working at the stage of loading the system. Over the past 20 years, computers have become increasingly complex and a new generation of microprocessors, such as the Pentium 4, already contains over 40 million transistors. With such a huge number of transistors, the failure of one of them is less likely to have disastrous consequences for the entire system. Of course, any malfunction of the central processor is a serious matter, but at the same time, the system can load and work, and fail only when performing certain specific functions (for example, when trying to execute protected mode commands). Such symptoms may also be due to software errors or malfunctioning of one or more expansion devices. This part of the chapter deals with issues related to malfunctions of the central microprocessor.
Temperature control
Overheating of the processor is the main enemy of the processor (even during its normal operation), so the main task is to maintain the temperature conditions. Some recommendations are given below:
■ Use a radiator / fan system that coolly supplies your microprocessor.
■ Use a thin layer of heat transfer paste to improve heat transfer between the processor case and the heat sink.
■ To cool a very hot processor, use a cooling device on Peltier elements or similar devices.
■ Choose ball bearing fans with extended service life.
■ Remove the cables from the cooling air circulation area (near the central processor). Remove all obstacles to the free passage of air near the processor.
■ Make sure that there is a reliable contact between the central microprocessor case and the radiator of the cooling system (use special paste if necessary). If such contact fails, replace the cooling system.
■ Use a cooling system with automatic warning of fan failure or processor overheating.
■ To dissipate additional heat after overclocking the processor, use an oversized cooling system, an active cooling device on Peltier elements, or another efficient cooling device.
■ At least once a year, clean the fan blades, its mounting system, and the ventilation hole of the power supply of the system unit from dust and dirt. In this case, a balloon with compressed air or a cleaning nozzle of a vacuum cleaner helps.
■ Increase air circulation inside and outside the system case with an additional fan.
Common symptoms
When problems arise when starting or operating a computer, the following options are possible.
Symptom 5.1. The system does not work completely (while the power indicator is lit normally)
The malfunction of the central microprocessor is always insidious. If it speaks for itself, then the computer will not work. Consequently, if the computer does not start up (or hangs up without warning during the zafuzki process), it’s time to suspect a malfunction of the central processor. A typical symptom in this case is that the diagnostics of the POST procedure does not work, and any diagnostic programs in DOS mode are not triggered.
Before changing the central microprocessor, check the output voltage of the power supply using a universal measuring device. Even if the power indicator is lit, one or several output voltages may be too low or absent. A low power level can easily lead to logical errors that “hang up” the system. If the problem occurs after replacing or installing a new hardware, the power source may be over-powered - try to restore the original configuration. If the computer works, then try to install another power source (more powerful). If the voltage is low or absent, and no hardware changes were made (or if the situation did not change after the changes were restored), replace the power supply.
The next thing you can do is turn off all peripheral devices and start the computer after that. If the computer started to work, then one of the disconnected devices could interrupt the operation of the system. Connect each device one at a time and check the operation of the computer. The last device, after connecting which the computer stopped working, is guilty. Replace this device. If the fault persists, replace the CPU. Do not forget to turn off the computer and unplug the power cord of the system unit. When removing the processor, be careful not to bend its pins (you may need to reinstall it). Also, be careful when installing a new processor. A curved pin almost always means a chip break. If after the installation of a new microprocessor, the situation has not changed, then replace the motherboard.
Symptom 5.2. The sound code or error code of the POST procedure indicates a possible malfunction of the central processor.
The system in this case almost always will not boot. When you start the POST procedure, all key components of the motherboard (including the central processor) are checked. If the POST procedure signals a processor fault (usually by issuing a single-byte error code at address 80h, which can be read using a POST diagnostic card), check each output voltage of the computer's power supply. If one or more of the voltage values is low or missing, then the power source may be the cause of the problem. Try to replace it. If all the voltage levels generated by the power supply are normal, replace the central processor. If this does not help, then replace the system board.
Symptom 5.3. The system boots normally, but crashes or freezes when executing a specific program.
You can be suspected of an error in this program. But try running a diagnostic program such as AMIDAG from AMI or AHMicro's Troubleshooter. Run repetitive CPU tests. The processor can operate normally in real mode, but diagnostic tests can detect an error when executing protected mode commands and perform a check on the operation of registers. The AMIDIAG program stands out among others in that it not only gives out specific error codes, but even if there is an error, it suggests a possible reason for it. When an error code is issued suggesting a processor malfunction, try replacing it. If processor test passes, check other components. motherboard. If all tests pass successfully, then you can suspect an error in the application program.
Symptom 5.4. The system boots normally, but crashes or hangs after a few minutes of operation.
This happens regardless of the application being executed. Diagnostic tests do not detect processor errors. If the computer is turned off, wait a few minutes, then turn it on again, it will work normally for a while, then stop again. This is a typical situation of microprocessor overheating. Check the CPU temperature after the computer stops working. In this case, you must be extremely careful not to get burned. The processor may not have a cooling radiator installed, or the cooling system may be disabled or faulty. As a rule, all processors, starting from 486, have a radiator and a cooling fan. In case of fan failure, replace it.
Make sure that the cooling system is working properly and that the air flow to the CPU area is not blocked. If this does not help, then consider using a more suitable cooling system. If the processor is already equipped with a radiator, make sure that there is a layer of thermally conductive paste between the processor case and the radiator. In many cases, this paste is missing, which prevents the effective removal of heat from the processor, and it overheats. If there is no such layer, let the processor cool down and apply heat-conducting paste between the processor case and the heat sink.
Symptom 5.5. System BIOS incorrectly identifies the processor
This often happens after replacing the processor, and the reason is related to the BIOS. Most BIOS versions interrogate the central microprocessor using the CPUID command, then recognize the processor by looking at the table contained in the BIOS. If the table does not contain a record of this processor, then it is not recognized (or is identified incorrectly). The general rule out of this situation is to update the system BIOS version or replace the motherboard with a new one.
Symptom 5.6. The old computer model refuses to work if the internal cache memory (L1) of the CPU is enabled.
This can happen with older processor models (for example, AMD 486) and almost always the situation is related to the configuration. The processor may give an error if it runs at an incorrect bus frequency (for example, an increased bus frequency). Therefore, it is necessary to check and set the correct frequency of the bus frequency of the motherboard for this processor. The same can happen if the processor is powered by the wrong voltage. Check the voltage level of the processor and, if necessary, correct it using the settings of the motherboard. Finally, the motherboard must be compatible with the type of cache memory of the first level of the central microprocessor. For example, installing a central microprocessor with write-back cache on a motherboard that does not support write-back cache may cause an error in the operation of the processor.
Symptom 5.7. 3.45 V centralized microprocessor does not work on a 5 V system board, although a power stabilizer module is used
Double check the voltage stabilizer module (VRM). It must provide the power level required for the central microprocessor. Otherwise, it may overload and not provide the desired level of supply voltage. Check that the voltage regulator module complies with the recommendations of the processor manufacturer. You can also test the processor with the VRM module on another 5-volt motherboard — it is possible that this module is under-powered or defective. If this combination is working properly on another motherboard, then it is possible that the system BIOS does not support the specific requirements of this processor. Contact the motherboard manufacturer for a new BIOS version for this system.
Symptom 5.8. After installing a new processor, the system does not work correctly under HIMEM.SYS or DOS4GW.EXE
This symptom is often observed when installing old-fashioned processors, and the cause may be the incorrect installation of the power supply voltage of the processor or its type on the motherboard. The same can be observed if a processor with 3.45 V power is powered by 5 V or vice versa - a processor that does not support low power (SL-modification) is powered by a lower voltage. Therefore, it is necessary to make sure that the voltage of the processor is set correctly (if necessary, use the power supply stabilizer module) and the correct mode of its operation is set.
Symptom 5.9. The speed of the processor Pentium 4 or Athlon is determined incorrectly
In all cases, this is due to incorrect setting of the system bus frequency (FSB). The Pentium 4 processor uses QPB (Quad Pumped Bus) buses, which operate at four times the frequency of the system clock, and the Athlon processor uses a double frequency for the system bus. It is necessary to check the correctness of the system bus frequency setting (using the CMOS Setup program or jumpers on the system board). If everything is fine with the system bus frequency, you may need to update the bIOS version.
Symptom 5.10. Second-level cache does not work after installing the Pentium OverDrive processor
Installing an OverDrive processor sometimes results in disabling the operation of a second-level cache (external cache). This is due to a BIOS version that does not support an OverDrive processor. To correct the situation, you need to update the BIOS version. In some cases, it is possible to install a correction driver, which is specified in CONFIG.SYS or AUTOEXEC.BAT (for DOS), and re-enables the second-level cache after the system is booted.
Symptom 5.11. Some programs hang when working on a computer with 5x86 processors
This often happens with various programs, for example with AutoDesk's 3D Studio package. Many programs use software time delays. The 5x86 processors perform latency cycles faster than previous x86 processor models, which sometimes leads to overflow of counters and software errors. In most cases, manufacturers software offer software patches for such cases. For 3D Studio, you can download the FSTCPUFX.EXE file from Kinetix (www.twinhead.com/drivers/P66/ FSTCPUFX.EXE). Run this program and follow the instructions. This program adjusts the executable file of the program 3D Studio.
Another example of software-related issues is Clipper applications. Clipper inserts time-delay cycles into application programs at the time they are compiled, and this also affects the time-dependent program code. For the Clipper software package, you can download the PIPELOOP.EXE file (ftp://np.wiznet.ru/drivers/ CPU / pipeloop.exe) and place it in the AUTOEXEC.BAT file.
Short description
When one of these transistors failed, the whole system failed - it hung or collapsed. In the future, the computer could stop working at the stage of loading the system. Over the past 20 years, computers have become increasingly complex and a new generation of microprocessors, such as the Pentium 4, already contains over 40 million transistors. With such a huge number of transistors, the failure of one of them is less likely to have disastrous consequences for the entire system. Of course, any malfunction of the central processor is a serious matter, but at the same time, the system can load and work, and fail only when performing certain specific functions (for example, when trying to execute protected mode commands).
How do I know that the processor burned?
Answer wizard:
In any, even the most modern personal computer literally every element can fail. Reasons can be different: power surges, poor workmanship, etc. Some of the items can be repaired, some can not. The main thing to know which of the parts failed and in time to replace it for the normal operation of the computer.
Turn on your computer. In the event of a malfunction, the BIOS speaker emits certain sounds. This is the first sign. View the instructions on the signals of the BIOS. It will help determine what the fault is. It is possible that the processor burned down, although, usually, such a problem is rarely accompanied by such alerts. If you started the computer, all the coolers are spinning, and the monitor does not turn on, then you should not hurry to determine the video card as a weak link. When it fails, the BIOS will definitely let you know about it.
Disconnect the power from your PC. Open the system unit. To do this, unscrew the fastening screws from the side panel and move it in the direction of the back side. system unit. Remove the screws securing the cooler to the radiator. And then remove the radiator.
To do this, open the special latch. All this is necessary for conviction in breakage of the processor. After removing the radiator, and in the event that it is confirmed that the processor actually burned out, you can feel the characteristic smell, which cannot be confused with any other.
Also check the surface of the motherboard around the socket for blackening. Try applying thermal paste to the processor. Do this neatly in a thin layer. Then assemble the system unit and try again to turn on the computer. In that case, if the monitor still does not catch fire, then the processor most likely really burned out.
Try connecting your processor to another PC. But remember, if your processor is actually faulty, there is a risk that the motherboard will burn. To avoid this, do not leave the computer on for a long time. Before turning on another computer with your processor installed, you should put a small layer of thermal paste on it and the radiator.
Turn on the computer. If the monitor shows a picture, then all systems work normally and your processor is fine. Otherwise, we can conclude that the processor is still burned and you have to replace it.
It often happens that the processor in the course of work starts to get very hot. Many simply do not pay attention to it. But due to overheating, at best, the computer will start to slow down a lot. In the worst case, a person will have to buy a new one. The fact that due to overheating the computer is unstable is a proven fact. The level of processor performance is significantly reduced, which means that the system does not allow the temperature to rise further. Unlike laptops, a regular computer can have two, or even three cooling coolers. At the laptop, only one. And coolers cool not only the processor, but also the video card.
But the laptop cooler is much smaller, and if it has a powerful processor, overheating will lead to damage. The same is true of a regular computer. But there are coolers on it much more than a laptop. How to know that the processor starts to overheat?
The main signs of processor overheating. The main sign that the processor is warming is an unusual fan sound. As soon as such sound appears, it is necessary to immediately disassemble the computer and pay attention to the fan. Also worth checking out and its play. If the fan is loose, it must be replaced. Also, processor overheating may cause blue screen of death. And it can appear when you turn on the computer, and in the course of work. But<<синий экран смерти>\u003e causes not only the processor. Therefore, this feature is not essential. The next sign is a frequent restart of the computer.
In some cases, the computer is constantly shutting down. Why a reboot occurs If the processor fails, operating system trying to fix it by rebooting. If the processor is to blame for the failure, a reboot occurs constantly. The main signs of a malfunction include the increase in temperature when opening any programs. But the most common symptom is a processor malfunction due to poor cooling. And not only the fan is to blame. It can be healthy, and the processor is heated. In this case, check the cooling system for blockages. The system may contain various debris. The last sign is that overheating occurs due to the drying of the thermal paste. It so happens that the processor heats up so much, a hundred is literally soldered to the radiator. In this case, without damaging the processor, the radiator cannot be removed.
In order to prevent the processor from overheating, it is necessary to constantly check the temperature. There are many programs that show its temperature. In some cases, it is difficult to determine the cause of overheating. It happens that some game starts, and the temperature of the processor soars to the very top. And this is with good fans, and no dust in the radiator. And the parameters of the video card and processor allow you to run it. And the temperature rises rapidly. In this case, the heat dissipation of the video card or processor increases. To do this, you must have a heat sink. You can make yourself some kind of heat sink. Or forget about the game. And in order not to buy a new processor, you need to look in time at the state of the fans and radiators.
Comments
CPU overheated
Today, our theme is processor overheating. We have already touched on it a bit in our previous article devoted to processor burning from overheating. Now we will dwell on this moment in more detail.
First, I want to say: if the processor heats up it is normal, since it is energized by it. But if it overheats, it is no longer good, and we must fight it.
Secondly: modern chips (firms "AMD" or "Intel" - not so important) as well as motherboards, have a built-in system for preventing overheating and forcing the work to be completed if it is detected. So the overheating of the processor and its failure now is not as relevant as before.
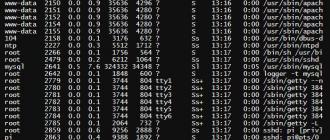
How can we control the CPU temperature? First of all, these are the “bios” indicators. Depending on its model and implementation, the parameter we need may be located in different sections of the BIOS. Most often it is located in the “Hardware” or “Power” sections and is called "Hardware monitor" (monitoring).
In the figure above, we see CPU temperature readings and - motherboard (MB Temperature). Temperatures are in degrees Celsius (C) and in pharyngates (F).
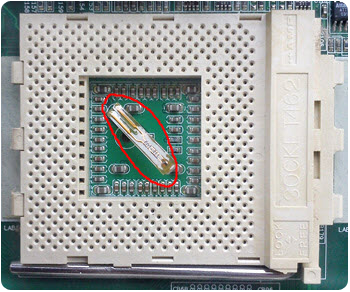
Here, for example, what the external thermal sensor looked like to take temperature readings from old AMD processors (now similar sensors are built into its core itself):
For temperature measurement there are also various system utilitiesThere are a great many, but you have to understand that all programs use the indications of hardware sensors-microchips located on the computer motherboard.
Previously, monitoring functions were performed by specialized heat and electrical sensors. Now this is done by special chips Super Multi IO. They are also called multicontrollers (or - "cartoons"), since they not only remove and process various indicators from the tracking sensors, but also control the speed of rotation of the fans, implement the functions of parallel and serial ports, contain controllers of the mouse and keyboard, FDD, game port, etc.
An example of one such "cartoon" we can see in the photo below. As you can see, the multicontroller is based on the Winbond W83627THF chip.

Note: The normal temperature of a running processor should be in the range of 30
before 60
degrees Celsius (depending on its model), chipset - from 25
before 50
, and the graphics core (video card) - from 40
before 70
degrees Naturally, depending on the load on a particular component!
And now I want to give one example from the practice, when the temperature readings of the BIOS helped me to detect overheating of the processor.
In one of the previous works, I changed a burnt-out motherboard on a computer. Naturally - removed the processor with the cooling system and installed a new one. Collected, screwed, launched - everything works. About a week later, they ask me to come over to look: the computer is buzzing heavily, which prevents the accountant working behind him from self-realization!
I come and I hear a fan howl from the threshold. At first, I confess, I thought - the power supply (it happens with them), but it turned out that the cooling cooler is noisy (a processor was installed under the “LGA 775” socket).
I decided to look at the BIOS-e indicators of the temperature of the motherboard and the core, and was quite surprised that the sensor showed "85" degrees Celsius. Now, at least, it was clear why the fan worked at maximum speed (the motherboard or the "stone" itself, upon detecting overheating, raised its rotational speed).
Another thing is noteworthy here - under the conditions of a week-long operation temperature conditions there were no consequences of such overheating, leading, as a rule, to reboots and "hang".
By the way, the reason that the overheating took place was to be one of the fixtures of the cooling system, which I had not done until the end. As a result, the radiator did not fit snugly against the protective cover of the processor and could not effectively “take” heat from it. After the problem was fixed, the temperature indicators were fixed at "59" degrees.
I must say that the signs of processor overheating on new computers may not appear even if forcibly disconnecting the active cooling system (pull the fan power out of the motherboard). If you do not run at the same time enough "heavy" applications (computer games), such systems can operate stably for a long time.
I remember, we had another case in the IT department: an old Athlon was brought with symptoms of periodic “freezing” and unstable software operation. Asked to reinstall Windows.
Intuitively understanding that the reason is not in Windows, we opened the case and found that the radiator fins of the processor’s cooling system are so densely packed with compressed dust that it formed a kind of “shield” that, in fact, isolated the radiator from the fan who tried unsuccessfully to dissipate the allocated the core is warm.
I had to remove the entire structure, clean the radiator from dust with a screwdriver, apply a new thermal grease and collect everything back. After that, the computer started working steadily and the question of reinstall windows dropped automatically.
What do I want you to understand? With attention to overheating of the processor (as well as any other component of the PC) should be given due attention.
How to avoid processor overheating? When installing (or replacing) the radiator, be sure to use thermal grease. Carefully remove the old and uniform thin layer of paint on its upper protective cover with a new one, as shown in the photo below:
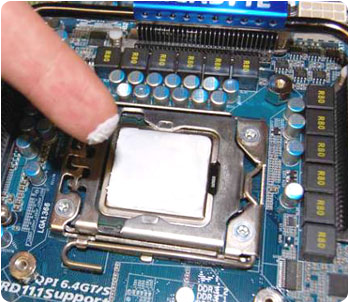
You can evenly spread the paste over the surface with your finger (as shown in the photo). I personally use an old broken credit card. Its hard plastic allows to achieve a uniform distribution of thermal paste on the surface.
I use the paste from the company "Zalman". It is sold in special bottles and equipped with a brush for more convenient application.
Why do I need thermal grease? She plays a very important role in preventing overheating of the processor! To efficiently remove heat from the hot core, the bottom surface of the radiator must be very tight to its protective cover (in older models - directly to the processor chip).
The fasteners provide the proper fit, but the problem is that no matter how good the fasteners are and how well the bottom surface of the radiator itself is not polished, there are still micro-scratches and micro gaps between the processor and its cooling system.
These very “gaps” are designed to fill high-quality thermal grease. Since it is thermally conductive, it significantly increases overall effectiveness cooling, collecting heat from the entire surface and transferring it to the radiator, from which heat is blown away by the fan.
There are also funny cases: one PC got us for repair / prevention. The diagnosis is overheating, the consequence is spontaneous shutdown (overheating protection is triggered). We blew it and decided to change the thermal paste on the processor. Imagine my surprise when, after removing the old pasta under it, I found the following picture:

The computer came to us from China (along with a set of measuring equipment), but why did the stickers not be removed when the computer was assembled? Everything else on the oval was neatly glued polyethylene transparent valepka! What do you think, what coefficient of thermal conductivity have such "pleasant" additions? The processor was heated to 76 degrees Celsius!
With the help of a clerical knife, alcohol, and such and such a mother, this outrage was removed, a new thermal paste was applied, and the heating temperature, as a result, was 61 degrees.
I want to draw your attention also to the fact that good (quality) fans for connecting have three or even four wires. Additional wires allow you to programmatically control the speed of their turns and adjust the pitch of this rotation.
Here, for example, looks like the packaging of an 8 centimeter fan with LED backlight that I recently bought:
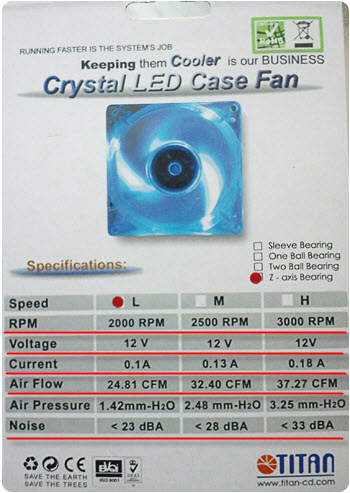
Let's walk on the basic designations:
- RPM - "Rounds Per Minute" revolutions per minute;
- Voltage - device supply voltage;
- Current - current consumption (in amperes);
- Air Flow - the air flow generated by the cooler;
- Noise - the published noise.
Let's say a few words about the general (classical) organization of the cooling system inside the computer case. It can be described as follows: a fan is installed on the front wall of the case (under the front decorative panel); on air blowing inside the system unit. On the back of the case, there is another fan attached, but already working on blowing air out.
In a closed case, such a bundle provides quite substantial traction. Inside, a large turbine begins to work: cool air from the room gets inside and, passing through the entire "stuffing" of the computer, is thrown out.
It often happens that the processor in the course of work starts to get very hot. Many simply do not pay attention to it. But due to overheating, at best, the computer will start to slow down a lot. In the worst case, a person will have to buy a new one. The fact that due to overheating the computer is unstable is a proven fact. The level of processor performance is significantly reduced, which means that the system does not allow the temperature to rise further. Unlike laptops, a regular computer can have two, or even three cooling coolers. At the laptop, only one. And coolers cool not only the processor, but also the video card.
But the laptop cooler is much smaller, and if it has a powerful processor, overheating will lead to damage. The same is true of a regular computer. But there are coolers on it much more than a laptop. How to know that the processor starts to overheat?
The main signs of processor overheating. The main sign that the processor is warming is an unusual fan sound. As soon as such sound appears, it is necessary to immediately disassemble the computer and pay attention to the fan. Also worth checking out and its play. If the fan is loose, it must be replaced. Also, processor overheating can cause a blue screen of death. And it can appear when you turn on the computer, and in the course of work. But<<синий экран смерти>\u003e causes not only the processor. Therefore, this feature is not essential. The next sign is a frequent restart of the computer.
In some cases, the computer is constantly shutting down. Why a reboot occurs If the processor fails, the operating system tries to fix it by rebooting. If the processor is to blame for the failure, a reboot occurs constantly. The main signs of a malfunction include the increase in temperature when opening any programs. But the most common symptom is a processor malfunction due to poor cooling. And not only the fan is to blame. It can be healthy, and the processor is heated. In this case, check the cooling system for blockages. The system may contain various debris. The last sign is that overheating occurs due to the drying of the thermal paste. It so happens that the processor heats up so much, a hundred is literally soldered to the radiator. In this case, without damaging the processor, the radiator cannot be removed.
In order to prevent the processor from overheating, it is necessary to constantly check the temperature. There are many programs that show its temperature. In some cases, it is difficult to determine the cause of overheating. It happens that some game starts, and the temperature of the processor soars to the very top. And this is with good fans, and no dust in the radiator. And the parameters of the video card and processor allow you to run it. And the temperature rises rapidly. In this case, the heat dissipation of the video card or processor increases. To do this, you must have a heat sink. You can make yourself some kind of heat sink. Or forget about the game. And in order not to buy a new processor, you need to look in time at the state of the fans and radiators.