16.Search for information on the Internet
Information posted on the World Wide Web is calculated in a huge number of bytes. To search for information on the World Wide Web, special websites are used - information retrieval systems. They allow you to find information resources related to keywords by keyword. This can be text containing keywords, or a graphic image of one of the keywords. Examples of information retrieval systems are Google and Yandex.
Search for information - one of the most popular tasks in practice, which has to be solved by any Internet user.
There are three main ways to search for information on the Internet:
1. Specify the page address.
3. Appeal to search engine (search server).
Method 1: Specifying the page address
This is the fastest way to search, but it can only be used if you know the address of the document or the site where the document is located.
Do not forget the ability to search for a web page open in the browser window (Edit-Find on this page ...).
This is the least convenient way, since it can be used to search for documents that are only close in meaning to the current document.
Method 3: Appeal to the search engine
Using hypertext links, one can travel indefinitely in the information space of the Web, moving from one web page to another, but given that many millions of web pages have been created in the world, it is unlikely to find the necessary information on them in this way.
Special search engines come to the rescue (they are even called search engines). The addresses of search engines are well known to all who work on the Internet. Currently, the following search engines are popular in the Russian part of the Internet: Yandex (yandex.ru), Google (google.ru) and Rambler (rambler.ru
Search system - a website that provides the ability to search for information on the Internet.
Most search engines look for information on the World Wide Web sites, but there are also systems that can search for files on ftp servers, products in online stores, and information in Usenet newsgroups.
By the principle of action Search engines are divided into two types: search directories and search indexes.
Search directories serve for thematic search.
The information on these servers is structured by topic and subtopic. Having the intention to highlight some narrow topic, it is easy to find a list of web pages dedicated to her.
Catalog of resources on the Internet or a catalog of Internet resources or just an Internet directory - a structured set of links to sites with a brief description of them.
Search indexes work like an alphabetical index. The client sets a word or a group of words describing his search area, and receives a list of links to web pages containing the specified terms.
The first search engine for the World Wide Web was Wandex, a non-existent index developed by Matthew Gray of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1993.
How does a search index work?
Search indexes automatically, with the help of special programs (web spiders), crawl the Internet pages and index them, that is, they enter into their huge database.
Search robot (“Web spider”) is a program that is an integral part of a search engine and is designed to crawl Internet pages in order to enter information about them (keywords) into the search engine database. At its core, the spider is most like a regular browser. He scans the contents of the page, throws it on the search engine server, which owns and sends the links to the following pages.
In response to a query where to find the necessary information, the search server returns a list of hyperlinks leading to web pages that contain the necessary information or are mentioned. The vastness of the list can be any, depending on the content of the request.
http://www.yandex.ru/
Yandex - Russian search engine on the web. The site of the company, Yandex.ru, was opened on September 23, 1997. The head office of the company is in Moscow. The company has offices in St. Petersburg, Yekaterinburg, Odessa and Kiev. The number of employees exceeds 700 people.
The word “Yandex” (consisting of the letter “I” and part of the word index; the fact that the Russian pronoun “I” matches the English “I”) was beaten up by Ilya Segalovich, one of the founders of Yandex, currently holding the position of technical director of the company.
Yandex search allows you to search the Russian Internet for documents in Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian, Romanian, English, German and French, taking into account the morphology of Russian and english languages and proximity words in a sentence. A distinctive feature of Yandex is the ability to fine-tune a search query. This is implemented through a flexible query language.
By default, Yandex displays 10 links on each page of results output; in the settings of search results, you can increase the page size to 20, 30 or 50 found documents.
From time to time, the Yandex algorithms responsible for issuing relevance change, leading to changes in the results of search queries. In particular, these changes are directed against search spam leading to irrelevant results for some queries.
http://www.google.com/
The leader of the Internet search engines, Google occupies more than 70% of the world market. Today, it now registers around 50 million search queries and indexes over 8 billion web pages. Google can find information in 115 languages.
According to one version, Google is a distorted spelling of the English word googol. “Googol” is a mathematical term for a unit with 100 zeros. This term was coined by Milton Sirotta, nephew of American mathematician Edward Kasner, and was first described in the book by Matner and James Newman, Mathematics and the Imagination. The use of this term by Google reflects the task of organizing vast amounts of information on the Internet.
The Google interface contains a rather complex query language that allows you to limit the search to specific domains, languages, file types, etc.
http://www.rambler.ru/
Rambler Media Group is an Internet holding that includes a search engine as a service, a rating classifier of Russian Internet resources, an information portal.
Rambler was created in 1996.
The search engine Rambler understands and distinguishes the words of Russian, English and Ukrainian languages. By default, the search is conducted for all forms of the word.
Greetings to you, dear readers! In this article we will look at different ways for effective and fast work on the Internet. In the world wide web there is a lot of information on all sorts of topics.
For this reason, the search can be complicated. When using certain methods it can be facilitated. What are the rules to make a request?
How to enter in the search string exactly the phrase that will give you the most accurate information?
Sometimes the search engine does not find any information at all. Consider simple rules for successful information retrieval.
When the search engine gives a large number of links to resources, you need to write your request in more detail and in depth. With a huge number of options for search results, this will help to highlight exactly what you need.
If no matches were found at all in the search results, then simplify the initial search phrase. Although in practice it is difficult to find the right way to search for information.
There are 2 types of information search on the Internet.
1. Search for singular information
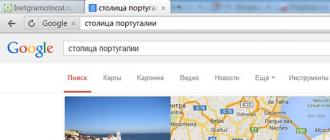
For example, here you can include a request of this type: “What is the capital of Portugal?” To get an answer to it, we enter in our request: the capital of Portugal (for a search engine it does not matter, capital or uppercase letter You will enter in the word - Portugal, which you can easily check if you wish). Press the Enter key, we get the answer:
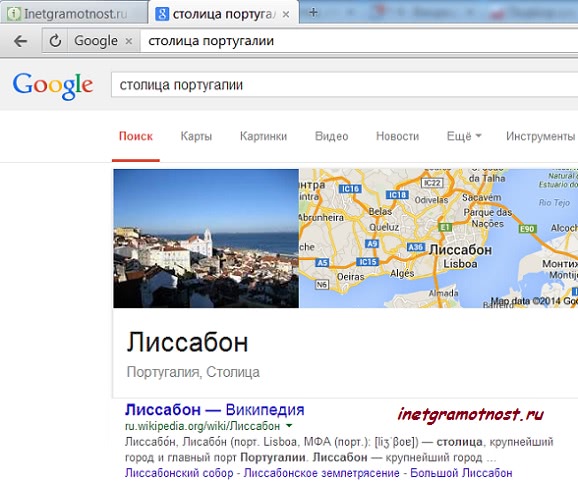 Fig. 1 Search for singular information
Fig. 1 Search for singular information The search results presented in fig. 1, you may differ depending on the search engine and browser you choose.
Or so: “What was the name of Chekhov's writer?” To get an answer, you can change the query a little, for example, enter in the browser: the name of the patronymic Chekhov, after which the search engine returns answers.
Another option: "In what year were the first Olympic Games held?" You can simplify and enter such a query into the browser: the date of the first Olympic Games.
In this case, we find any specific information. For example, it may be in the form of a name, date, or number.
2. Finding Plural Information
An example of such a method of searching for information is the request of the following type: “Which sports nutrition stores are located in the city of Minsk?”. If desired, you can simplify it and enter the following query: sports nutrition stores Minsk. As we can see, in the proposed version we already need to find not one unit of information, but several (2 or more sports nutrition stores).
These methods differ in that in the first of them the search result will be located on a specific page of one website, and in the second - on different pages of several websites.
Let us examine specific examples. First, consider the case of searching for singular information.
For example, you need to know the place and date of birth of Pushkin. What phrase should I enter in the search field of Yandex or Google? Most likely, those users who are not familiar with effective ways to search for information on the Internet will introduce the following option: "The place and date of birth of Pushkin." As a result, we get that on one web page we only know the place of his birth, and on the other - the date.
The first way to search for plural information
But our goal is to find complete information on one single web page. Let us rephrase our search phrase into another variant: “Pushkin was born.” In the very first links of the search we find out when and where this great Russian poet was born. You don’t even have to click on links to other sites. The information we need will be on the main web page of the search engine.
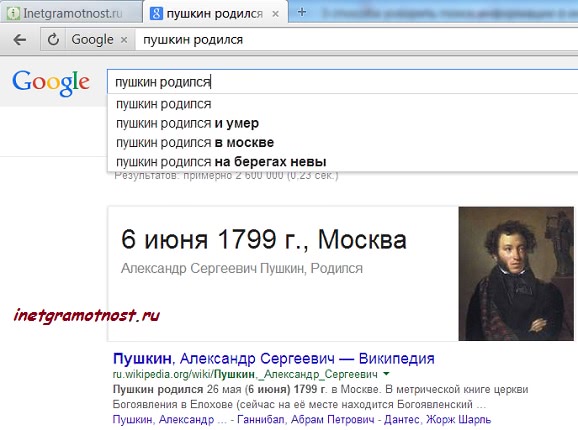 Fig. 2 Example of searching for plural information
Fig. 2 Example of searching for plural information The search results presented in fig. 2, you may differ depending on the search engine and browser you choose.
This way of searching for information not only saves your time, but also Internet traffic. Due to this property of search engines, as relevance, in the search results are displayed the closest documents on this topic, which simplifies the search and saves the Internet user time.
2nd way to search for plural information
To use this method, you need to understand that the initial data may fall on different areas. To find a more accurate option, enter in the search phrase as many items as possible for them. To do this, use individual words or phrases.
For example, we introduce the following query: “Purchase, washing machine, LG, white, Perm”. Thus, the purchase information will be found. washing machine Brand LG white in the city of Perm. You may notice that all the search words of this query are in the singular and nominative case. This is necessary in order to display exactly what you need.
You can use other cases, declensions and numbers of the Russian language, but in this case, you can enclose the search words in quotes. This technique will lead to the fact that the search results will be specific, that is, in the form in which they were specified in quotation marks.
A query enclosed in quotes is a signal to the search engine that it is necessary to look for an exact match to this query, that is, as relevant as possible.
Thank you for your attention, friends. We got acquainted with the 3rd ways to search for information:
- search for singular information
- search for plural information
- use quotes.
And in order for this theoretical information to benefit you, of course, you should apply it in practice. To do this, right now open in your browser and type all the queries given in this article, compare the results, analyze, in general, learn how to find information online. Good luck, love and successful search (surfing) in the world wide web!
P.S. By Internet literacy can still be read.
The problem of search and the means of its organization
Giant and continuously increasing amounts of information available on the Internet, including operational information, make the problem of finding the necessary information very relevant and complex. The speed of searching for the necessary information is largely determined by the professionalism of the Internet user. To automate this task, various, both foreign and domestic search systems have been developed, representing a special type of Web-page. However, despite the presence of numerous search automation tools, this task remains quite laborious, requiring the user to have some experience, intuition, and knowledge of the terminology used in his subject area.
According to an estimate published in Nature magazine dated July 8, 1999, the number of publicly indexed Web pages was 800 million. A year later, the author of the study (Steve Lawrence of the NEC Research Institute) believed that their number almost doubled to 1.5 billion. Even the best search engines index no more than one page out of six. In order to extract useful information from the Internet, you need to know where and how to search.
Internet Explorer's Search tool makes it easy to access search tools, eliminating knowledge of the addresses of search engines. However, it is better to directly contact the search engines by downloading the appropriate page.
According to the method of organizing the search and the possibilities offered, all search tools can be divided into the following groups:
catalogs and specialized databases;
search engines;
metasearch systems.
Catalogs and databases
Catalogs on the WWW are similar to systematic library catalogs. Directory search is a sequential move through a hierarchical list of links called headings or categories. The first page of the catalog contains links to major topics, for example, Culture and Art; Medicine and health; Society and politics; Business and economy; Entertainment and others. Clicking on the appropriate link (category) opens a page containing links detailing the selected theme (category). Going down the detailed categories, you can find a page with the necessary information. On each page opened when moving through the catalog in one way or another, a sequence of viewed sub-headings is indicated, for example, Business World: Finance: Analytics, etc.
All catalogs are created and maintained up to date manually by specialists, in the same way as bibliographers compile and maintain library catalogs. The document description is done either by the compilers of the catalog or by the author. Due to this, the content of the pages included in the catalog most adequately corresponds to the category to which they are assigned. But, taking into account the speed of replenishment and change of information in the Internet, the “manual” method of maintaining directories does not allow equivalently reflecting the real state of Internet resources on this topic.
Search engines
(search engines, search engines, search engines)
There are dozens of large and thousands of small and specialized Web sites designed to search the Internet. The search tools of this group will allow the user to formulate requirements for the information he needs according to certain rules (using the query language to create a query). After that, the search engine automatically scans the documents on sites that are controlled (indexed) by it and selects those that, “according to” the search server, meet the requirements formulated by the user (relevant query). Search engines use their own Internet indexes, which are constantly updated with special programs called spiders. The spider program examines the Web, checking every link on a given page, then on pages that are referenced by links, etc., and informs its owner about all pages for subsequent indexing.
A search results in the creation of one or more pages containing links to documents relevant to the request (Web pages). For each link, the date of creation of the document, its volume, the degree of relevance to the request, fragments of text characterizing the content of the document are also usually indicated. Clicking on this link allows you to load the page of interest. In the case of a very large number of documents found, you can refine the query and repeat the search in accordance with it, but only among the selected pages (such a search is called differently in different machines, but usually it is to look in the found one). In a number of search engines, you can in a certain way change the link to the page, the content of which most suits your needs, and repeat the search, demanding to look for similar ones.
The advantage of automated search is that it provides viewing of very large amounts of information available on the Internet at the moment. However, the complexity of an exact description of a request that adequately reflects your informational needs, as well as the greater complexity of the task of automatically determining the extent to which your request matches the pages you are viewing, leads to the fact that the number of pages selected “from the first visit” is usually very small, or overly large. In general, a search using a search engine is an iterative (multi-pass) process, as a result of which the query form is gradually refined.
Metasearch systems
As noted above, any search engine scans a specific set of servers and selects documents in accordance with its inherent criteria. As a result, a search by different systems for the same keywords gives different results. This led to the idea of creating the so-called meta-search (or multi-search) systems, which themselves do not look for anything, but turn to several search engines for help at once. Each of the metasearch systems has its own query language. The system translates a query formulated in its language into the query languages used by each search engine. Further, the search results by all systems are combined and presented in the appropriate form. Naturally, the search using metasearch systems takes more time compared to conventional search systems.
Overview of the most popular search engines
The Internet has a large number of search engines, and each user is guided by the one he is used to or was advised by his colleagues. We use a brief description of the most popular search engines, which is provided on one of the sites.
1. Google (www.google.com) The fastest and largest search engine. More than 1.3 billion pages are indexed (of which completely - a little more than 700 million, only the address and text of the link is known about the rest). Normally looking for Russian-language resources (of course, without word forms), it is possible to choose an interface language. You can include / exclude results from specific sites and / or domains. Unlike most search engines, Google evaluates the popularity of a resource by the number of links leading to it from other pages. There is a themed-oriented search - Apple Macintosh, BSD UNIX, Linux, the US government and University searches - search in the resources of leading scientific and educational institutions.
2. Yandex (www.yandex.ru) The best of domestic search engines. It indexes mainly Russian-speaking resources, while at the same time it is not inferior to foreign systems by capabilities. The search can be carried out accurately or in any word forms, with a restriction on the date, indicating the site or its subdirectory. You can search with the so-called citation index, search for images, scripts, applets; set the language of the document. The necessary links are usually found already in the top ten results. It has a "lite" version (with a minimum of design elements) on http://www.ya.ru.
3. AltaVista (www.altavista.com) Provides a large expansion of search criteria: in Advanced search there is a choice of the length of time to which the date of creation or change of a resource applies, support for 25 languages; there is the possibility of issuing one result to the site (this narrows the search range without compromising quality). Power search has a standard set of features. Until recently, AV was a large portal, but for reasons of financial (and not only) nature, it significantly reduced the number of services.
4. Yahoo! (www.yahoo.com) One of the first search engines on the Internet. In addition to the standard set of functions, it allows you to select resources by date (4 years, 1, 3, 6 months, week, 1, 3 days). Supports the ability to specify the "*" sign instead of any sequence of characters in keywords. On Yahoo! A large structured catalog of categories has been compiled. First, the search is carried out in them, then in its own archive, then - using Google. Search in categories gives good results - there are few of them and the correspondence is good.
5. Lycos (www.lycos.com) Recently - one of the most popular systems. At the same time, it does not provide any special opportunities - “AND” “OR”, search for phrases, mandatory presence / absence of a word; in advanced options - search in the name, URL, host name and / or domain name; 25 languages, including Russian, in a word, the whole "generally accepted" set. You can specify the content type of the resource — auto, book, ftp, download, news, etc. Obviously, the popularity of Lycos is a consequence of the scale of this major project.
6. Rambler (www.rambler.ru) Until recently, the most famous Russian search engine. Advanced search does not allow searching for phrases, and the usual search until February of this year seldom produced acceptable results. Since February, this system uses an improved search engine, the design has changed, but the quality of the Rambler is still not equal to Yandex and Uport (according to the author, who analyzes the search engines). The site has a rating catalog of Rambler Top 100 resources, one of the recognized sources of statistical information about Internet projects.
7. Aport (www.aport.ru) Another good Russian search server. The search is conducted by text (only in all word forms) and by URL, using logical operators and the operator "..." (however, stop words in the phrase are still ignored), by date and in separate fields (name, description, etc. ), support meta characters * and! The presentation of search results is the most well designed compared to other Russian search engines. Some doubts are caused by the design of the main page, which is clearly overloaded with information. There is a slightly more "light" version on http://aport.ru.
How to choose a search engine
When searching the Internet, two components are important - completeness (nothing is lost) and accuracy (nothing extra is found). Usually this is all called in one word - relevance, that is, the correspondence of the answer to the question.
1. Coverage and depth
Coverage refers to the amount of the search engine database, which is measured by three indicators - the total amount of indexed information, the number of unique servers and the number of unique documents. Depth is understood to mean whether there is a limit on the number of pages or on the nesting depth of directories on one server.
How to check: Some machines write statistics on their site robot. But you can check it yourself - you need to set several search queries consisting of one word (to eliminate the influence of the query language, including a different interpretation of the space), and at the same time look at the statistics of the results produced by the machine - usually at the top of the list it is indicated how many all documents were found. In addition to the fact that words must be from different areas, it is also good to take words of different weights - rare, “medium” and “heavy” (frequency), and compare the number found. Heavy words, in particular, test the full-text (indexation of all the words of a document) search engine.
It is more difficult to check the depth of the robot's walking - for this you need to take some sites, for example, with an extensive archive structure, and check whether the documents are indexed, which can be reached only, for example, after 6 links following the links.
2. Bypass speed and relevance of links
The speed of web traversal shows how quickly the indexing of the newly added resource occurs and how quickly the information in the database is updated. An important indicator of the quality of the search engine (its robot) is not only the seizure of new territories: but also the tracking of the condition already covered. Servers disappear and appear, the pages on them are updated. The links that the search engine gives in the list of those found should, firstly, exist, and, secondly, their content should match the query.
How to check: Objective information can be obtained by analyzing the server logs - the search engine robot is usually represented by the name of your machine (or in a similar way), so you can see how often it happens on the server, how many pages are being viewed, etc. Unfortunately, usually only the site's log is available for study, so there remains an experimental method.
To determine the crawl speed, you need to create a text page somewhere, add it to the search engines and see how quickly it begins to be. Or change the existing page. To determine the relevance of the links, check the documents on at least the first page of the list found by several queries. The Not Found message indicates that the document no longer exists.
3. Search quality (subjective indicator)
Each search engine has its own algorithm for sorting search results. The closer to the top of the list the document you need is, the better the relevance works.
How to check: Only by experiment. It is recommended to make requests of different lengths for comparison. You can also use the query language, while those who are reluctant to read the description can use the expanded query page (“advanced search” in Aport and Yandex, “detailed query” in Rambler - Russian translation options “advanced search”).
In addition to relevance, there are important user characteristics.
4. Search speed
If the search engine responds slowly, working with it is inefficient. It should be added that the speed visible to the user depends not only on the search engine itself, but also on Internet channels.
How to check: By experiment - it is necessary to search for requests of different lengths, different<тяжести> words and at different times of the day (server load is significantly uneven by day, the peak is about three to four hours of the day).
5. Search capabilities (work with document language, query language)
Another comparison item is what exactly and how the search engine indexes. Full-text search engine indexes all words visible to the user of the text. The presence of morphology makes it possible to find the desired words in all declinations or conjugations. In addition, in the HTML language there are tags that can also be processed by a search engine (headers, links, image captions, etc.).
The query language in the form of standard logical operators (AND, OR, NOT) is present in almost all machines. Some are able to search for phrases or words at a given distance - it is often important to get a reasonable result. An additional feature is a search in document areas — headers, links, keywords (META KEYWORDS), etc. An additional feature of the query language is a natural language query that does not require knowledge of operators.
How to check: Usually this information is published on the search engine server (in Help "e). Nevertheless, it is recommended to check on real queries, because sometimes the desired is given for real.
6. Extra amenities
These are additional features that the search engine provides. This includes all sorts of search options (specialized pages, search for similar documents, restriction of the search area), and a list of found servers, and search for dates and servers, and a convenient search engine interface, and the possibility of personalizing it.
How to check: Information may be partially published on the search engine server, but it is best to try to work with these features yourself.
It is clear that this analysis will take some time. In addition, search engines, like the entire Internet, do not stand still. However, given that the search for information is one of the important components of computer technology, this should be given sufficient attention - at least not less than the ability to work in a local network.
A survey was conducted on Yandex.ru: why the Internet is needed and what is missing in it (http://www.yandex.ru/polling/9.html). In descending order, the survey data was distributed as follows: the Internet is used as a reference book (23.76%), a research tool (15, .45%), entertainment (14.15%), and only in fourth place is the source of news (12.32 %). It was optimistic that 10% of users always, and 73% often manage to find the necessary information. But there is not enough of the Internet: information, good search and order (including: orderliness, structure, structure, structuredness, structuring, and also system, systematization, systematic, systematic and systematized).
ANSWER THE QUESTIONS:
What are the ways of organizing the search exist on the Internet?
How to search for information in directories and databases?
How is information recorded in directories and databases?
What does the Internet refer to search engines?
How is the information database formed in search engines?
What begins the search for information in search engines?
What is a request?
How to search for information in search engines?
What is meant by relevance request?
What can be done in case of a very large number of documents found in a further search?
What is metasearch systems?
What is the fundamental difference between metasearch systems and ordinary search engines?
Which of the following systems are metasearch:
Yandex,
AltaVista,
Krasu,
Aport.
What are the most popular domestic search engines?
What are the most popular foreign search engines?
What are the two components that are important when searching for information on the Internet?
What characteristics determine the effectiveness of search engines when searching for information on the Internet?
Information retrieval is one of the tasks that every Internet user has to solve.
Starting to search for data on the Internet, is to determine search target. It is useful to answer for yourself the following questions:
- do you know the addresses of network resources from which to start a search?
- what do you already know about the problem you are looking for information about?
- what keywords should start the search?
- how much time are you willing to spend on finding the right data?
There are three main ways to find information on the Internet:
Method 1:
Specifying the page address
This is the fastest way to search, but it can only be used if you know the address of the document or the site where the document is located.
Method 2:
Hyperlinking
This is the least convenient way, since it can be used to search for documents that are only close in meaning to the current document. But this method is very simple and suitable for a novice user.
Method 3:
Appeal to the search engine
Special search engines come to the rescue (they are also called search engines).
The result of the query is a list of links to Web-pages, next to which there are specified text fragments. Most popular search engines: Yandex
(yandex.ru), Google
(google.com) and Rambler
(rambler.ru). The queries of different search engines are somewhat different from each other.
Yandex search engine
- Hto find information using the Yandex search engine, open the main page. The line for entering a search query is located at the top of the page, in the area highlighted with a yellow background.
After receiving such a command, Yandex will scan its entire database and try to find a web page in it, where the word or phrase entered by us occurs. In this case, it is necessary to take into account in advance that the more extensive our request is, the smaller the number of web pages will correspond to it.
- Pon the default on one page Yandex displays only 10 such links, so to get acquainted with the full search results you will need to scroll through the pages with the help of reference numbers.
- TOeach resource found in the search results is represented by the name of the web page and the text of the link. In addition, in most cases, the search engine shows a small piece of text contained on a particular found web page, in which a match is found with the text of your query. At the same time, the words that we entered for the search will be highlighted in bold in these fragments.
- ATbottom of the search results page, there is a line "In other search engines" . Next to these words are links to several other popular search engines. Therefore, if we do not find the information we need using Yandex, you can use other search engines by clicking on the link.
You can search for information in Yandex
at simple and advanced search mode.
- Simple search
Before you start typing a query in the search engine search bar, carefully formulate .
The clearer the selected wording is, the fewer sites that you do not need will appear in the search results.
- Advanced Search
To get to the web page that provides such opportunities, you must use the link with the name of the type "Advanced Search" .
Following this link, we will see a large search form in which you can specify a variety of parameters.
The Yandex search engine allows, for example, to customize the search parameters for words depending on their location
(side by side, in one sentence, on one page) and forms.
In addition, she can search for web pages by their language
(Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian, etc.), by date of last change and even by file format
web page.
Finally, using Yandex, you can search for information on a particular site. This is useful if there is no built-in search engine on the site you need.
Each search engine has its own query language. We will meet logical query language for Yandex, which allows you to enter additional service commands in the normal search mode that specify your requirements. Consider some such commands.
- Use the signs "+" and "-".
For example, if you want to learn about aquarium fish, but without selling and breeding, then we type in the search box:
"Aquarium fish breeding sale."
- Finding an exact match is a "!"
For example, the query! Ivanov will find only pages with references to this last name, and not the city "Ivanovo".
- Search for an exact phrase - quotes.
The quotation marks force the search engine to select only documents in which words from the query are in exactly the same order in which we indicated them in search query. If there are no quotes, then on request “who is guilty and what to do” the search engine can offer us a page containing the phrase “who is guilty - do what they say” or “well, and who is guilty, that Petr Petrovich does not know how to make dumplings ". Formally, the search system will cope with its work, because in the indicated passages there are all the words from the entered phrase. And the fact that they are not at all in the order in which we need is another question, which is being clarified. using quotes.
When working with search engines, sooner or later we will meet the word "relevance".Relevance - this is the degree of compliance of the found documents with our request. For example, in Yandex, it can be found at the bottom of each web page containing search results, immediately below a set of reference numbers. Here it is used as a parameter for the “Sorted” function. In addition to the parameter by relevance, the option by date is also available.
If the pages in the search results are sorted by relevance, then this means that at the very beginning the sites with the highest level of relevance to your search are indicated, followed by resources with a lower level of relevance, etc.
Children's search engines
- In order to protect children from unnecessary information, special children's search engines have been created that do not index all sites, but only sites with a child or okolitetskaya theme.
AGA is not just a search service. There are all your favorite cartoons, coloring books, watching filmstrips, help with different school subjects, etc.
Quintura for Children - a visual search for children's resources, designed specifically for children and is aimed at primary and secondary school students.
The search uses the Quintura interactive cloud. The colorful and attractive service interface contains several interactive pictures, by clicking on which, children can immediately choose an interesting topic for themselves, for example: science, music, dinosaurs or games.
- Nachalka - Children's search.