All mobile operators (MTS, Beeline, Megafon) broadcast at 900 MHz and 1800 MHz.
Depending on the location, they may broadcast:
- at 900 MHz
- at 1800 MHz
- at 900 MHz and 1800 MHz simultaneously
Typically, the frequency of the network looks like this:
- MTS, Beeline in the city - 900 MHz
- Megaphone in the city - 1800 MHz
- MTS, Beeline, Megaphone in the region - 900 MHz
But there are exceptions, when operators broadcast on other frequencies.
One GSM channel serves 7 simultaneously talking subscribers. The 1800th range prevails mainly for densely populated areas, i.e. cities, because can serve a greater number of subscribers. And the 900th range is used everywhere. The principal advantage of the 900 range is a range of up to 35 km. in line of sight, while at 1800 frequency - only 8 km.
Another important indicator is the level of signals measured in dBm (English dBm). These values are negative, that is, -60 dBm is greater than -65 dBm.
The level of the GSM signal can be measured by a spectrum analyzer or by the NetMonitor program.
1. Call the mobile operator MTS, Beeline, Megafon and clarify at what frequency your cell broadcasts.
Give your address.
Cellular operators, as a rule, do not respond immediately. Sometimes it takes several days to get information.
2. On some phones (especially the old model) there is an option to determine the frequency at which he contacted the base station.
3. In the smartphone to install the program Netmonitor.
The program will show the location of the nearest towers, their number, signal level. On the Internet by the number of the tower you can find information about it.
4. Determine the level of the signal and its frequency can be a spectrum analyzer.
5. Call our specialist to determine the signal in place.
Measurement is performed by a spectrum analyzer.
Call our tech. Department.
Before you start looking for GSM repeaters and selecting an assembly company, answer yourself to the key question: What kind of communication standard should I enhance: only GSM-900 (voice communication), GSM-1800 (voice), GSM-900 + GSM only -1800 (voice) and / or 3G (Internet)?
The thing is that the speech signal operates at 900 MHz and 1800 MHz. And 3G Internet is only at 2400 MHz.
If you only need to amplify the speech radio signal, then you can go outside (outside the amplified room) to measure the signal level (the number of sticks on the phone display). If there are "two or three sticks", then thanks to the system of repeaters and antennas you will receive a stable cellular signal.
| Repeater | Frequency | Gain | Area |
| Vector R-400 | 900 MHz | 50 dBi | 30-100 square meters |
| Vector R-610 | 900 MHz | 60 dBi | 100-300 sq.m. |
| Vector R-710 | 900 MHz | 70 dBi | 200 - 600 square meters |
| Vector R-810 | 900 MHz | 80 dBi | 500 - 1600 sq.m. |
| Vector R-600D | 1800 MHz | 65 dBi | 200 - 600 square meters |
| Vector R-600W | 900/1800 MHz | 65 dBi | 200 - 600 square meters |
If you need only one operator, for example, MTS. Then try to grab a few channels. For example, it is better to catch 2-3 channels with a signal level of -60, than 1 channel -50, and the rest on -70. If you need to provide a signal to all cellular operators, then try to put an external antenna so that the signal to the input of the repeater comes about the same from all cellular operators, otherwise the range from internal antennas will be proportional to the incoming signals. For example, the signals of the MTS "- 70", Beeline "- 60", Megaphone "- 50" get to the input of the repeater, then the output internal antennas We will observe the following situation: 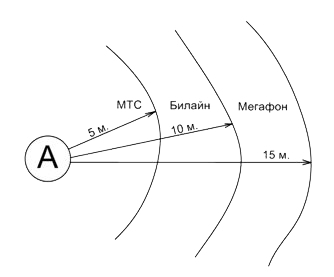
The NetMonitor program will help you to accurately orient the direction of the external directional antenna; it will not only show the level of the GSM signal, but also the location of the nearest base station.
Yours faithfully, CJSC Radioovnimaniye.
(Information provided with the consent of the partner - http://www.exclusive-comfort.ru/uchebnik-gsm-repiter.shtml)
Determination of frequency using Android applications
I. Introduction
The carrier frequency (or frequency range) of a 3G / 4G signal is one of the most important parameters when choosing an antenna. In the end, you can not know the location of base stations in the vicinity - just by turning the antenna, you can determine this direction by the signal level. If you do not know the frequency, then you can not catch the signal at all.
Since the definition of frequency for 3G, 4G and 4G-Advanced (4G +) standards is different, we will consider how to determine frequencies separately.
Ii. Determination of the frequency of the 3G signal
As you know, Russia has adopted two frequency bands for 3G, this is 2100 MHz and 900 MHz. The frequency of 900 MHz is accepted in those regions where for military reasons it is unacceptable to use 2100 MHz. For example, the South-East of Moscow region.
Each smartphone has a hidden program called Netmonitor. For each phone model, this program is activated by its individual code. For Android-smartphones from Samsung it is necessary to enter the code * # 0011 # in the dialing mode. For other Android phones, the codes are as follows: * 4636 # * or * 197328640 # * depending on the version. The most complete list of "secret" codes for activating this hidden program for different models phones, including the iPhone, can be found.
So, in 3G mode, I type on my Samsung dialer code * # 0011 # and get:
Here RX = 10713 is the channel number by which the carrier frequency is determined.
If the channel value is in the range of 2937-3088, then this is 3G / UMTS900.
If the value of the channel is in the range 10562-10838, then this is 3G / UMTS2100.
RI = -64 dB is the signal level from the base station of the cellular operator (RSSI).
Special Android applications for determining the frequency of a 3G signal in the Play Market were not found.
III. 4G signal frequency detection
In 4G LTE mode, cellular operators can operate in three bands - 800 MHz, 1800 MHz and 2600 MHz. To determine the frequency in this mode, you can also use the built-in Netmonitor smartphone. How to do this is described in detail in.
There are only a few applications¹, which are declared by the developers to determine the frequency, in addition to other functions. However, things are not so simple. Some applications (G-NetTrack, Net Monitor, etc.) require operating system not lower than Android 7.X. Others (LTE Discovery) require a smartphone mode Root².
However, there was an application that provides the frequency of the 4G signal. Meet this CellMapper. For the application to work, you need to register on the site, registration is free.
In order for the program to display the value of the carrier frequency, in the settings, tick the "Calculate GSM / UMTS / LTE frequencies" checkbox. In my smartphone (Samsung GT-i9505, Android 5.01) frequencies for GSM and UMTS are not given, for the standard LTE we get what is shown in the screenshot:

The program gives a lot of information about the connected tower and its neighbors, including the frequency of the signal in the form of Band 7. This is the frequency of 2600 MHz. You can identify other possible frequency ranges.
I will not describe each tab of the program, there is (on english language) and FAQ, I will only note that this application gives the frequency for standard 4 signals onlyG. To determine the frequency in the 3G standard, as I said above, no android applications were found.
IV. 4G situation
V. Conclusion
A few remarks at the end of the article.
I would like all the antenna selection tasks to be performed on a handheld device like a smartphone. However, the most reliable and cheapest way to determine the carrier frequency (or frequencies) of the Internet signal is a computer (laptop) with a modem, which has HiLink interface or MDMA program.
The rapid development of the standard 4G + poses difficult challenges for antenna developers. How to combine in one antenna with a good gain (about 17-20 dBi) different frequencies, for example 800 + 2600 MHz? Yes, and that MIMO was. If such a task is not solved, then you have to invent complex designs from antennas of different ranges, combine their signals with diplexers, in general, the task is not simple and cheap. Or stay on 4G and be content with speeds, which in theory can be increased significantly.
Waiting for feedback and comments, your dmitryvv.
1] Only free applications are considered.
2] For those who want to experiment with their smartphone, at the risk of turning it into a brick, I send it here and here (update to Android 7.XX), or to the forum w3bsit3-dns.com
3] I must say that even the best foreign samples of this class (for example, the Australian company Telstra, costing about $ 300), do not exceed 8 ... 11 dBi in gain.
The publication will consider the following frequencies: GSM 900, 4G / LTE2500, DCS 1800, 3G / UMTS 900 3G / UMTS 2100, CDMA 450, 4G / LTE800.
A bit of terminology so that you are better oriented in the article. The communication channel connecting the subscriber with the base station in the direction “subscriber modem - station” is called Uplink. The communication channel, working in the opposite direction - Downlink.
Now about all frequencies in order.
3G frequency:
In our country, this cellular connection - as an example, you can take 3G / UMTS2000 - it uses both the Uplink and Downlink channels, their frequencies are 1920–1980 MHz and 2110– 2170 MHz, respectively. This cellular communication is also called third generation communication. The 3G frequencies are also available from the Skylink operator, it works in the CDMA 450 standard. The frequencies on the Uplink communication channel will be as follows - 453 - 457.5 MHz, and for the Downlink - 463 - 467.5 MHz.
The frequencies in the range of two thousand MHz, now owned by Skylink, are more likely to be transferred to another operator - Rostelecom. But half a year ago services were not provided by anyone on this small segment of communication.
The number of subscribers is constantly growing, which led to the fact that 3G began to use other standards, in particular E-GSM, as well as GSM-900. In other words - Downlink - 925 - 960 megahertz and Uplink - 880 - 915 megahertz.
It should be remembered that 3G and GSM can not be on the same frequency segment, so, the operator cellular communication "Megaphone" the second band is occupied by the standard E-GSM. The band of 3G frequencies, no matter what, is always 5 megahertz. MegaFon has almost everywhere in the capital and Moscow region 3G / UMTS900. In the south of the Moscow region, MTS and Beeline are used, this situation is due to the fact that the military is not allowed to operate at frequencies of 2000, at least that was six months ago.

Fourth-generation communications employ frequencies of 2,500-2,700 megahertz.
To terminology again: let's decipher the abbreviations FDD and TDD and give definitions to these concepts.
Frequency Division Duplex (English - frequency division channels) - when the outgoing and incoming channels are at different frequencies. The same principle is used in GSM.
Time Division Duplex (English - channel separation is temporary) - the incoming channel is on the same frequency as the outgoing one.
The mobile operators Beeline and Rostelecom had 10 megahertz each. MTS in the Moscow region has 35 megahertz and 10 across the country. Megaphone operated with 65 megahertz in Moscow and the region, and 40 megahertz was at the disposal of this operator throughout the country.
Megaphone works with Yota (it’s one and the same holding) virtually, for this the 4G standard is used. The range of TDD throughout our country will allow the broadcasting of various TV channels, for example, Cosmos TV. This feature is not available in the capital of our country.
4G / LTE800
Gos. The Radio Frequency Commission in July last 2012 held a contest, here are its results:
Operator Rostelecom: UpLink - 791 - 798.5 megahertz; DownLink - 832 - 839.5 megahertz; Operator Megaphone: UpLink - 806 - 813.5 megahertz; DownLink - 847 - 854.5 megahertz; MTS operator: UpLink - 798.5 - 806 megahertz; DownLink - 839.5 - 847.5 megahertz; Beeline operator: UpLink - 813.5 - 821 megahertz; DownLink - 854.5 - 862 megahertz.
Subscriber devices using this networkhave not been on sale yet. But this is in the plans for the near future.
4G frequencies from other mobile operators
The operator "Basis Telecom" uses LTE TDD 2300 - 2340 megahertz. 1900 - 1920 megahertz on the LTE TDD frequency is provided by Antares. These are unknown operators to anyone, and it is not entirely clear to whom they provide communication services.
Deputy Development Director Karimov Rostislav.
For the implementation of wireless mobile telephony and data transmission, cellular operators use radio frequencies that range from 250 MHz to 3 GHz. Given that these channels are used for other communications, the manufacturers of cellular telephones were allocated four GSM bands: 850/900/1800/1900 MHz. In Russia, two bands are relevant (band): 900 and 1800.
 The first allows you to cover large areas of service, and the second adapts service in areas of small size with a high density of subscribers. The phones themselves can be as two, so three and 4-band - this is quite important when traveling around the world. In Tele2 gsm, in agreement with other mobile operators, only the 1800 MHz band is used, the deficiencies of which are compensated by the construction of more towers for signal transmission. In Moscow, an agreement on the standard gsm has not been reached to date.
The first allows you to cover large areas of service, and the second adapts service in areas of small size with a high density of subscribers. The phones themselves can be as two, so three and 4-band - this is quite important when traveling around the world. In Tele2 gsm, in agreement with other mobile operators, only the 1800 MHz band is used, the deficiencies of which are compensated by the construction of more towers for signal transmission. In Moscow, an agreement on the standard gsm has not been reached to date.
In this regard, Tele2 is available in the capital only for subscribers whose telecommunications devices support 4G.
The expediency of knowledge of the subject
- Optimizing the selection and tuning of devices designed to amplify the signal.
- Optimize the selection and configuration of devices designed to suppress the signal.
- Optimize mobile phone settings when accessing engineering menu telecommunication equipment.
- Expanding the presentation and improving the understanding of the essence of receiving and transmitting signals to / from subscribers of cellular networks.
GSM standard
 Naturally, the reception and transmission frequencies are presented in a generalized standardized format of 900 and 1800. In fact, they differ in average: 889 - 999 and 1710 - 1899 respectively with minor fluctuations in one direction or another. These frequencies are divided between the operators in order to avoid difficulties in signal transmission and subsequent tariffication of the services provided. In connection with the emergence of the operator in question, the last in the market of telecommunications services in the Russian Federation, the company got only frequencies in the standard 1800 (Tele2 gsm 900 is not in operation): 1710, 1725, 1778, 1784, 1805, 1820, 1873, 1879 MHz. These Tele2 frequencies are used in all regions of Russia, except Moscow.
Naturally, the reception and transmission frequencies are presented in a generalized standardized format of 900 and 1800. In fact, they differ in average: 889 - 999 and 1710 - 1899 respectively with minor fluctuations in one direction or another. These frequencies are divided between the operators in order to avoid difficulties in signal transmission and subsequent tariffication of the services provided. In connection with the emergence of the operator in question, the last in the market of telecommunications services in the Russian Federation, the company got only frequencies in the standard 1800 (Tele2 gsm 900 is not in operation): 1710, 1725, 1778, 1784, 1805, 1820, 1873, 1879 MHz. These Tele2 frequencies are used in all regions of Russia, except Moscow.
In standard 3G and 4G
Due to the high competition among the companies that provide cellular telecommunication services to subscribers, Tele2 was unable to receive frequencies in Moscow in the 900 or 1800 standards. I had to use the new generation 3G networks and. As a result, this operator was unavailable for phones working only in the GSM standard. Below will be presented at what frequencies are valid (these ranges are also used in other regions of the coverage of new generation networks, but are used there, primarily for receiving and transmitting data on the Internet, and not for telephony):
The considered frequencies of Tele2 are relevant for 2016 and may vary depending on the region within the ranges described above. There may be a tendency to create new ranges or expand existing at the federal or regional level. This can happen if one or more operators leave the market, which results in the unloading of certain ranges, or when merging companies that provide telecommunications services.

The same frequency band is also used by television, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. Among the range of frequencies there are those that have been allocated specifically for mobile phones.
Historically, the radio waves used for mobile communication systems in the countries of America, Europe, Africa and Asia differ from each other.
Technology and frequency standards
The first standard of technology used in the US for commercial use was AMPS with a range of 800 MHz. In the countries of northern Europe, NMT-450 technology was first introduced, the range of which was 450 MHz.
Together with the growing popularity of mobile phones, manufacturers faced a problem: they could not provide service to a large number of people. They had to develop existing systems and introduce a new standard with a different frequency range.
In Japan and some European countries, the TACS standard with a range of 900 MHz appeared. The GSM standard, which replaced the NMT-450 technology, also used the 900 MHz band. As demand grows and the cell phone market grows, providers have acquired licenses to use the 1800 MHz band.
Lower frequencies allow providers to cover larger areas, and higher frequencies allow communication to be provided to a larger number of clients in a smaller area.
Modern technology standards
The current generation of mobile devices operates mainly on the GSM standard. Also gaining popularity is the UMTS standard. In some countries, technologies of formats ELT, 3G, 4G are used.
Each standard or format uses a frequency range of two frequencies. The low frequency range transmits information from the mobile device to the station, and the high frequency - from the station to the mobile.
Many GPS phones cover three frequency bands: 900, 1800, 1900 MHz or 850, 1800, 1900 MHz. These are the so-called tri-band phones or tri-band devices. With such a phone it is convenient to travel the world, and it does not require replacement when
moving to another country.
Mobile networks different formats can use the same frequency. Such, for example, is the 800 MHz band used in at least four different formats.
The amount of frequencies available for use by mobile devices is limited. This should be taken into account when the number of users increases. It means that base station can provide a limited number of people, and communication networks need to be constantly expanded.
Cell phones of the main providers in Russia operate at 900 MHz and 1800 MHz. At the same time, Megaphone, Beeline, MTS use both bands, and TELE 2 only 1800 MHz.
Modern life is filled with various technological devices. Daily people check e-mail from their tablets and laptops, communicate in in social networks, call up with their friends and family from anywhere in the world. Although only sixty years ago, the latter could only be dreamed of. After all, what functions does the current smartphone, previously could only afford a computer the size of a small cabinet.
First cell phone
The first official cell phone was the device of the American engineer Martin Cooper, the director of the department mobile communication Motorola. On this device, on April 3, 1973, he first called his competitor from Bell Laboratories Corporation - Joe Engel.
The phone with the sticking antenna weighed a little more than one kilogram and worked in the talk mode for no more than an hour. The cellular device didn’t have any additional functions, just like the usual for a modern human display, only twelve keys (10 numeric, calling and ending a call).
According to the official version, the first commercial cell phone DynaTac was released on June 13, 1983 by Motorola.
However, there is every reason to state that the first cell phone was produced in the Soviet Union. It was the domestic radio engineer Leonid Kupriyanovich who created the mobile phone model "LK-1", which was tested in 1957. The first "mobile phone" had a range of up to thirty kilometers, but its main disadvantage was an unacceptable weight for such a phone - three kilograms.
Therefore, a year later, Leonid Ivanovich improved the cell phone model. The updated device was the size of a pack of cigarettes and weighed only half a kilogram. The phone allowed not only to make outgoing calls, but also to receive incoming calls from fixed phones and street machines.
The first official American mobile phone for sale cost almost four thousand dollars! For example, "Toyota King" of the same year was worth three hundred dollars cheaper. At the same time, the owner of the phone had to shell out monthly for another fifty dollars of subscription fees.
The first mass-distributed cell phone was a Nokia 1011 device. He already had a small display and worked in the GSM standard. The first folding cell phone was the Motorola StarTAC.
Besides, mobile phone Motorola StarTAC was among the very first devices, which had a screen with cells.
The first communicator was the Nokia 9000. It was made like a pencil case, on one side of it was a screen, and on the other a keyboard. This communicator was based on an Intel 386 processor.
A cell phone with an infrared port appeared in 2001 again under the Nokia brand. The first phone with mp3 player was the Samsung SPH-M100.
The receiver can be either a built-in device or a separate device that can be connected to a computer as a special card inserted into an expansion slot.
The same principle of operation is used by many electronic devices - cell phones, wireless networks, garage door drives, remote controls and so on. However, unlike infrared communication, on the basis of which these devices operate, radio frequency communication does not require that the mouse and receiver be located at an accessible distance from each other. The signal of the transmitter of the gadget easily passes through obstacles in the form of a computer monitor or table top.
Sync wireless mouse
As in most modern computer mice, wireless models use in their work not a ball, but an optical system, which significantly improves the accuracy of the gadget. In addition, the optical system allows the user to use a wireless mouse on almost all surfaces, which is very important for a device that is not connected to the computer by the cable at least for a while.
Another advantage of radio frequency communication is the minimal power consumption of radio transmitters and receivers, which also weigh a little, are inexpensive and can run on batteries.
Synchronization of the wireless mouse is necessary for the interaction of its transmitter with the receiver, which must work on one channel, which is a combination of the identification code and frequency. Due to the synchronization, interference is prevented, provoked by other wireless devices and external sources.
Each manufacturer equips its wireless mouse - some models (more expensive in the general rating) are already sold synchronized, and some need to be automatically synchronized by clicking certain buttons on the device. Protection of data transmitted by the mouse to the receiver is provided by encryption mechanisms or frequency hopping technology.
Sources:
- how the mouse works