Lithium-ion batteries are not as "finicky" as their nickel-metal hydride counterparts, but still require some care. Adhere to five simple rules, you can not only extend the life cycle of lithium-ion batteries, but also increase the operating time of mobile devices without recharging.
Do not allow a full discharge. Lithium-ion batteries lack the so-called memory effect, so they can and, moreover, need to be charged without waiting for discharge to zero. Many manufacturers calculate the life of a lithium-ion battery by the number of full charge cycles (up to 0%). For high-quality batteries, this 400-600 cycles. To extend the life of your lithium-ion battery, charge your phone more often. Optimally, as soon as the battery charge drops below 10-20 percent, you can put the phone on charge. This will increase the number of discharge cycles to 1000-1100
.
Experts describe this process with such an indicator as Depth Of Discharge. If your phone is discharged to 20%, then the Depth of Discharge is 80%. The table below shows the dependence of the number of discharge cycles of a lithium-ion battery on the Depth of Discharge:
Discharge once every 3 months. For a long time, a full charge is also harmful to lithium-ion batteries, as is continuous discharge to zero.
Due to the extremely unstable charging process (we often charge the phone as necessary, and from where, from USB, from a wall outlet, from an external battery, etc.), experts recommend that once every 3 months the battery be completely discharged and after that charge up to 100% and hold on charging 8-12 hours. This helps reset the so-called upper and lower battery charge flags. You can read more about this.
Store partially charged. The optimal condition for long-term storage of a lithium-ion battery is a charge level of 30 to 50 percent at a temperature of 15 ° C. If you leave the battery fully charged, its capacity will decrease significantly over time. But the battery, which for a long time was gathering dust on the shelf discharged to zero, most likely, is no longer a tenant - it's time to send it for recycling.
The table below shows how much capacity remains in a lithium-ion battery, depending on the storage temperature and charge level during storage for 1 year. 
Use the original charger. Few people know that in most cases the charger is built directly inside the mobile devices, and the external network adapter only lowers the voltage and rectifies the current of the household power supply, that is, it does not directly affect the battery. Some gadgets, such as digital cameras, lack a built-in charger, and therefore their lithium-ion batteries are inserted into an external “charger”. It is here that the use of an external charger of dubious quality instead of the original can negatively affect the performance of the battery.
Do not overheat. Well, the worst enemy of lithium-ion batteries is the high temperature - they do not tolerate overheating at all. Therefore, do not expose direct sunlight to mobile devices, and do not leave them in close proximity to heat sources, such as electric heaters. Maximum allowable temperatures at which the use of lithium-ion batteries is possible: –40 ° C to + 50 ° C
You can also watch
Lithium batteries
Lithium or lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are mainly present in cell phones, laptops, and camcorders. Products are expensive, batteries, too, and therefore you need to deal with them even more competently than with any other batteries. So what is Li-Yon's strength? There are probably even more rumors and myths. Firstly, it starts to appear on its own, if only because sellers of equipment with Li-ion batteries do not give special parting words, saying that the battery is “smart” and will do everything right. But not myself. After all, how many cases have owners of new laptops worn out a battery in a month and then paid good ones for a new battery. Of course, lithium batteries are expensive because they are crammed with electronics, but, unfortunately, it does not save you from a fool.
Overdischarge
As with nickel batteries, lithium batteries are also very afraid of overcharging and overdischarging. But, since these batteries are used in smart devices and are equipped with their own chargers, their electronics do not allow overcharging - that is, you can not be afraid of him. But overdischarge is more difficult to control, which is why it is the most typical reason for premature battery failure. Of course, in expensive and complex devices, such as laptops, disconnection occurs before the voltage drops to a critical value. But precedents indicate that this emergency shutdown is better considered as an emergency measure, to which, if possible, it is better not to bring. This is the most important rule - to avoid complete discharge, as low voltage can disconnect the emergency protection circuit. It happens that people "kill" the battery, carried away by training. Training is a good thing, but for lithium batteries, 2-3 full cycles are enough.
There is no memory effect for lithium batteries, so they can be recharged at any time, so after training it is better not to discharge the batteries to the end. The recommended lower threshold is 5-10%. The critical lower threshold is 3%.
Many incomplete cycles or one complete
Lithium batteries have a lifespan of approximately 300 cycles. A full cycle is a cycle of full charge and full (i.e., up to about 3% capacity) discharge, or vice versa. If the battery is discharged to 50% and then charged, it will be 1/2 cycle, if up to 75% and charged - 1/4 cycle, etc. So, for phones and laptops, the difference in benefits between full and incomplete cycles is different. The Internet stubbornly claims that a lot of people charged their phones when they were not fully charged (that is, they recharged the phone every day) and, as a result, ditched them. At the same time, for laptops it is reliably known that full cycles wear out the battery faster than incomplete ones. The situation is clarified by a detailed examination of the device Li-ion batteries (see additional materials). It turns out a lot depends on the controller. It is he who controls the charge current, monitors the state of the battery, etc. So, in laptops, the controller is located in the battery itself and is adjusted by system utilities, such as calibration. In cell phones, the controller is located in the phone itself and so simply cannot be adjusted. Although lithium batteries do not have a memory effect, there is a so-called “digital memory" effect. The fact is that the charge-discharge control electronics located in the battery itself works independently of the device that uses the battery. Internal electronics monitors the cell voltage level, interrupts the charge upon reaching the set maximum value (taking into account the voltage change due to the charging current and battery temperature), interrupts the discharge when the critical value is reached and reports this “up” (a large range of specialized chips). The battery monitoring system “above” calculates the charge level based on information about the moments when the charge and discharge from the battery are turned off and the readings of the current measurement system. But if the operating conditions are such that a complete discharge before a hardware shutdown or a full charge does not occur, these calculations after several cycles may not be entirely correct - the battery capacity decreases over time, and the current meter readings may not always correspond to reality. Typically, deviations do not exceed one percent for each cycle, unless serious changes occur during operation, for example, with the failure of one of the battery cells. The monitoring system has the ability to “learn”, that is, to recalculate the value of the total battery capacity, but for this you need to perform at least one full charge-discharge cycle before the hardware circuits of the battery operate. So it turns out that with very frequent cycles, the controller crashes, and, therefore, incorrectly calculates the battery charge and performs incorrect charging, as a result of which the battery deteriorates. Unlike a laptop, you cannot recalibrate the phone. All that remains in this case is to make a couple of complete cycles to bring the controller in order. I recommend, ideally, combining complete and incomplete cycles, adhering to the principle of the “golden mean”. Personally, I did just that with my cell phone - as a result, after 2 years of operation, the drop in capacity was no more than 40%, which is the norm. In part, time also does not spare lithium batteries - they wear out over time, regardless of operation; their age is short and it is reasonable to change the batteries every 2-3 years.
Storage
If the battery is not used, it is recommended to store it at 40% capacity in a cool place. The lower temperature limit for storage and operation is 00 C. In general, lithium batteries like to be charged, i.e. they are better to store and keep in a charged state, unlike nickels. But with prolonged storage, the maximum charge still wears out the battery more, so 40% of the charge is considered the optimal state.
Battery resuscitation
In general, if the battery is dead, it is better to buy a new one, this is the most logical option, although expensive. I have not seen reliable recipes for reanimating batteries. There are real legends here, especially about laptops, that people reanimated their dying laptop battery and everything is fine with them. One of them sounds like this: “You need to completely discharge the battery, leave the laptop for a week; then fully charge the battery and also leave it for a week; after two months, the capacity should be restored. ”
For cell phones: combine full and incomplete cycles (in the proportion of "HZ").
For laptops: as few complete cycles as possible (after training).
For all: it is recommended to do 80% cycles; do not allow a full discharge (below 3%).
For a long time, an acid accumulator was the only device capable of providing autonomous objects and mechanisms with electric current. Despite the large maximum current and minimum internal resistance, such batteries had a number of drawbacks that limited their use in devices consuming a large amount of electricity or in enclosed spaces. In this regard, lithium-ion batteries are devoid of many negative qualities of their predecessors, although they have drawbacks.
Content
What is a lithium ion battery
The first lithium batteries appeared 50 years ago. Such products were an ordinary battery in which a lithium anode was installed to increase the level of power output. Such products had very high operational characteristics, but one of the most serious drawbacks was the high probability of lithium ignition during cathode overheating. Given this feature, scientists have over time replaced the pure element with metal ions, resulting in significantly increased safety.
Modern li-ion batteries are very reliable and able to withstand a large number of charge-discharge cycles. They have a minimal memory effect and relatively low weight. Due to these properties, a lithium battery is widely used in many devices. The product can be used as a battery, in the form of batteries for household appliances, as well as a highly efficient traction power source.
Today, such devices have several disadvantages:
- high cost;
- do not like deep discharges;
- may die at low temperatures;
- lose capacity when overheating.
How is the production of li-ion batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are produced in several stages:
- The manufacture of electrodes.
- Combining electrodes into a battery.
- Installing the protection board.
- Install the battery in the case.
- Electrolyte filling.
- Testing and charge.
At all stages of production, technology and safety measures must be followed, which ultimately allows you to get a quality product.
As a cathode in lithium-ion batteries, a foil is used with a substance containing lithium deposited on its surface.
The following lithium compounds can be used, depending on the purpose of the battery:
- LiCoO2;
- LiNiO2;
- LiMn2O4.
In the manufacture of cylindrical power sources of sizes AA and AAA, the main electrode is twisted into a roll, which is separated from the anode by a separator. With a large area of \u200b\u200bthe cathode, the film of which has a minimum thickness, it is possible to achieve high energy intensity of the product.
The principle of operation and device li-ion battery
The lithium-ion battery operates as follows:
- When a constant electric current is supplied to the battery contacts, lithium cations move into the anode material.
- During discharge, lithium ions leave the anode and penetrate the dielectric to a depth of 50 nm.
In the “life” of a lithium-ion battery, such cycles can be up to 3,000, while the battery can give off almost all the electric current accumulated during charging. Deep discharge does not lead to oxidation of the plates, which favorably distinguishes such products in comparison with acid batteries.
Not all li-ion batteries tolerate deep discharges well. If such a battery is installed in the phone or camera (type AAA), then when the battery is deeply discharged, the controller board will block the possibility of charging the battery for safety reasons, therefore, it cannot be charged without a special charger. If this is a traction lithium battery for an outboard motor, then a deep discharge will not be at all frightening to it.
Unlike finger-type batteries, complex batteries consist of several separate sources of electricity connected in parallel or in series. The connection method depends on what indicator of electricity needs to be increased.
Sizes and types of li-ion batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are widespread. Such sources of electric current are used in various household devices, gadgets and even cars. In addition, industrial lithium-ion batteries are manufactured, which have a large capacity and high voltage. The most popular are the following types of lithium batteries:
| Title | Diameter mm | Long mm | Capacity mAh |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10180 | 10 | 18 | 90 |
| 10280 | 10 | 28 | 180 |
| 10440 (AAA) | 10 | 44 | 250 |
| 14250 (AA / 2) | 14 | 25 | 250 |
| 14500 | 14 | 50 | 700 |
| 15270 (CR2) | 15 | 27 | 750-850 |
| 16340 (CR123A) | 17 | 34.5 | 750-1500 |
| 17500 (A) | 17 | 50 | 1100 |
| 17670 | 17 | 67 | 1800 |
| 18500 | 18 | 50 | 1400 |
| 18650 (168A) | 18 | 65 | 2200-3400 |
| 22650 | 22 | 65 | 2500-4000 |
| 25500 (type C) | 25 | 50 | 2500-5000 |
| 26650 | 26 | 50 | 2300-5000 |
| 32600 (type D) | 34 | 61 | 3000-6000 |
The first two digits of such designations indicate the diameter of the product, the second pair - the length. The last “0” is set if the batteries are cylindrical.
In addition to cylindrical-shaped batteries, the industry also produces “” type batteries with a voltage of 9v and powerful industrial batteries with a voltage of 12v, 24v, 36v and 48v.
 Stacker battery
Stacker battery Depending on the elements that are added to the product, the following markings may appear on the battery case:
- ICR - containing cobalt;
- IMR - - - - manganese;
- INR - - - - nickel and manganese;
- NCR - - - - nickel and cobalt.
Lithium batteries differ not only in size and chemical additives, but primarily in capacity and voltage. These two parameters determine the possibility of their use in various types of electrical appliances.
Where are li-ion batteries used?
Lithium-ion batteries have no alternative where you need a battery capable of delivering electricity in almost full volume, and make a large number of charge / discharge cycles without reducing capacity. The advantage of such devices is their relatively low weight, because there is no need to use lead grids in such devices.
Given the high performance characteristics, such products can be used:
- As starter batteries. Lithium batteries for cars are getting cheaper every year, thanks to new developments that can reduce production costs. Unfortunately, the price of such batteries can be very high, which is why many car owners cannot afford such a battery. The disadvantages of lithium-ion batteries include a significant drop in power at temperatures below minus 20 degrees, so the operation of such products in the northern regions will be impractical.
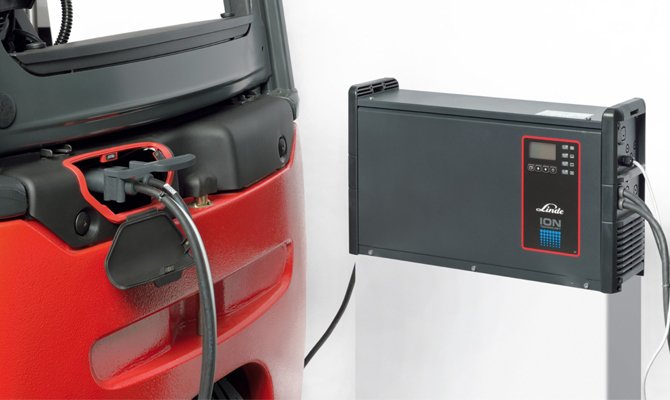
- As traction devices. Due to the fact that lithium-ion batteries easily carry a deep discharge, they are often used as traction for boat electric motors. If the engine power is not too large, then one charge is enough for 5-6 hours of continuous operation, which is quite enough for fishing or taking a boat trip. Traction lithium-ion batteries are also installed on various loading equipment (electric stackers, electric forklifts) operating in enclosed spaces.
- In household appliances. Lithium-ion batteries are used in various household devices instead of standard batteries. Such products have a voltage of 3.6v - 3.7v, but there are models that can replace a regular salt or alkaline battery with 1.5 Volts. You can also meet 3v batteries (15270,), which can be installed instead of 2 standard batteries.
Such products are used mainly in powerful devices in which conventional salt batteries discharge very quickly.
 Traction Battery
Traction Battery Li ion battery operating instructions
The life of a lithium battery is influenced by many factors, the knowledge of which will significantly increase the resource. When using this type of battery, you must:
- Try not to let the battery run out completely. Despite the high resistance of the battery to such an impact, it is advisable not to squeeze all the “juices” out of it. Particular care should be taken when operating such batteries with UPS and high power electric motors. If a full discharge of the battery has occurred, it is necessary to immediately revive it, that is, connect it to a special charger. You can also recharge the battery after a long stay in a deep discharge state, for which it is necessary to make a high-quality charge for 12 hours, then discharge the battery.
- Do not overcharge. Overcharging negatively affects product performance. The built-in controller is not always able to turn off the battery in time, especially when charging is carried out in a cold room.
In addition to overcharging and over-discharging, the battery should be protected from excessive mechanical influences, which can lead to depressurization of the case and fire to the internal components of the battery. For this reason, there is a prohibition on mailing batteries in which the content of pure lithium exceeds 1 g.
 Used as a battery for screwdrivers, laptops and phones
Used as a battery for screwdrivers, laptops and phones How to store lithium-ion batteries
If there is a need for long-term storage of lithium-ion batteries, then to minimize the negative impact on the products, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Store the product only in a cool, dry place.
- The battery must be removed from the electrical device.
- The battery must be charged before preservation. The minimum voltage at which internal corrosion processes will not form is equal to 2.5 volts per 1 cell.
Given the small self-discharge of such batteries, it is possible to store the battery in this way for several years, but during this period the capacity of the cell will inevitably decrease.
Disposal of lithium-ion batteries
Lithium-ion batteries contain substances hazardous to health, so in no case should they be taken apart at home. After the battery runs out of life, it must be returned for further processing. In specialized reception centers, you can receive monetary compensation for an old lithium battery, because such products contain expensive elements that can be reused.
At present, Li-ion batteries and Li-pol (lithium-polymer) batteries are widespread.
The differences between the two are electrolyte. In the first embodiment, helium is used as it, in the second - polymer saturated with a solution containing lithium. Today, due to the popularity of cars on electric motors, the question of finding the ideal type of li ion battery, which is optimal for such a vehicle, is an acute issue.
It, like other batteries, consists of an anode (porous carbon) and a cathode (lithium), separator separating them and a conductor - an electrolyte. The discharge process is accompanied by the transition of "anode" ions to the cathode through the separator and electrolyte. Their direction changes to the opposite during charging (figure below).

Ions circulate during the process of discharging and charging the cell between oppositely charged electrodes.
Ion batteries have a cathode made of different metals, which is their main difference. Manufacturers using different materials for electrodes improve battery performance.
But, it happens that the improvement of some characteristics leads to a sharp deterioration of others. For example, when optimizing the capacity needed to increase travel time, you can increase power, safety, and reduce the negative impact on the environment. At the same time, you can reduce the load current, increase the cost or size of the battery.
You can get acquainted with the main parameters of different types of lithium batteries (lithium-manganese, lithium-cobalt, lithium-phosphate and nickel-manganese-cobalt) in the table:

Rules for users of electric vehicles
The capacity of such batteries during long-term storage is practically not reduced. Li-ion batteries are discharged by only 23% if stored at a temperature of 60 degrees for 15 years. Thanks to these properties, they are widely used in electric transport technologies.
For electric vehicles, lithium-ion batteries with a complete control system built into the housing are suitable.
For this reason, users in operation forget about the basic rules that can extend their service life:
- the battery must be fully charged immediately after its purchase in the store, because the electrodes are charged 50% during the production process. Therefore, the available capacity will decrease, i.e. operating time if there is no initial charge;
- the battery must not be completely discharged in order to preserve its life;
- it is necessary to charge the battery after each exit, even if the charge still remains;
- do not heat batteries, as high temperatures contribute to the aging process. In order to use the resource to the maximum, operation must be carried out at the optimum temperature, which is 20-25 degrees. Therefore, the battery cannot be stored near a heat source;
- in cold weather it is recommended to wrap the battery in a plastic bag with a vacuum lock in order to store it at 3-4 degrees, i.e. indoors not heated. The charge should be at least 50% of the total;
- after the battery has been operated at negative temperatures, it is impossible to charge it, not having stood it for some time at room temperature, that is, it needs to be warmed up;
- you need to charge the battery from the supplied charger.
The PU of these batteries are several subspecies - lithium - LiFePO4 (iron - phosphate), using a cathode of iron phosphate. Their characteristics allow us to talk about batteries, as the pinnacle of technology used to produce batteries.
Their main advantages are:
- the number of charge-discharge cycles, which reaches 5000 until the moment when the capacity decreases by 20%;
- long term of operation;
- the missing "memory effect";
- wide temperature range with constant operating characteristics (300-700 degrees Celsius);
- chemical and thermal stability enhancing safety.
Most commonly used batteries
Among the most common are Li-ion 18650 batteries manufactured by five companies: LG, Sony, Panasonic, Samsung, Sanyo, whose factories are located in Japan, China, Malaysia and South Karee. It was planned that li ion 18650 batteries will be used in laptops. However, due to the successful format, they are used in radio-controlled models, electric vehicles, flashlights, etc.
Like any high-quality product, such batteries have many fakes, therefore, to extend the life of the device, you need to purchase only batteries of well-known brands.
Protected and unprotected lithium-ion batteries
It is also important for lithium batteries whether they are protected or not. The working range of the first is 4.2-2.5V (used in devices designed to work with lithium-ion sources): LED lights, low-power household appliances, etc.
Power tools, electric bicycles, laptops, video and photo equipment use unprotected batteries controlled by the controller.

What you need to know about lithium-ion batteries?
First of all, the restrictions that must be observed during operation:
- recharge voltage (maximum) cannot be higher than 4.35V;
- its minimum value cannot start below 2.3 V;
- discharge current should not exceed more than two times the value of capacitance. If the value of the latter is 2200 mAh, the maximum current value is 4400 mA.
Controller Functions
Why do i need a li ion battery charge controller? It performs several functions:
- delivers a current that compensates for self-discharge. Its value is less than the maximum charge current, but more than the self-discharge current;
- implements an effective charge / discharge cycle algorithm for a specific battery;
- compensates for the difference in energy flows while charging and providing energy to the consumer. For example, when charging and powering a laptop;
- measures the temperature during overheating or overcooling, preventing damage to the battery.

The charge controller li ion of the battery is made either in the form of integrated circuits integrated into the battery, or as a separate device.
To charge the batteries, it is better to use a standard charger for the 18650 li ion batteries, supplied. The 18650 lithium battery charger typically has a charge level indication. More often it is an LED that shows when the charge is on and its end.
On more advanced devices, you can track on the display the time remaining until the end of the charge, the current voltage. For the 18650 battery, whose capacity is 2200mA, the charging time is 2 hours.

But, it is important to know how to charge the li ion 18650 battery. It should be half the nominal capacity, that is, if it is 2000 mAh, then the optimal current is 1A. When charging a battery with high current, it quickly degrades. Using low current will take longer.
Video: How to charge a do-it-yourself Li-ion battery charger
Diagram of a device for charging batteries
It looks like this:

The scheme is reliable and repeatable, and the incoming parts are inexpensive and easily accessible. In order to increase the battery life, competent charging of li ion batteries is required: by the end of charging, the voltage should decrease.
After its completion, i.e. when the current reaches zero, the li ion battery should stop charging. The circuit shown above satisfies these requirements: a discharged battery connected to the charger (VD3 lights up) uses a current of 300 mA.
The VD1 LED on indicates the ongoing process, and the current is gradually decreasing to 30 mA, indicating that the battery is charging. The end of the process is signaled by a lit VD2 LED.

The circuit uses an operational amplifier LM358N (you can replace it with an analog of KR1040UD1 or KR574UD2, which has a different pin arrangement), as well as a transistor VT1 S8550 9 LEDs in yellow, red and green (1.5V).
Can I reanimate the battery?
After a couple of years of active use, batteries catastrophically lose their capacity, creating problems when using your favorite device. Is it possible, and how to restore the li ion battery while the user is looking for a replacement?

There are several ways to restore a li ion battery for a while.
If the battery is swollen, i.e. stopped holding a charge, which means that gases accumulated inside.
Then proceed as follows:
- the battery case is disconnected carefully from the sensor;
- separate the electronic sensor;
- find a cap with control electronics under it and carefully pierce it with a needle;
- then, they find a heavy flat object with an area larger than the area of \u200b\u200bthe battery, which will be used as a press (do not use a vice and similar devices);
- put the battery on a horizontal plane, and press it down, remembering that the battery can be damaged by applying excessive force. If it is not enough, the result may not be achieved. This is the most crucial moment;
- it remains to drip onto the hole with epoxy resin and solder the sensor.
There are other ways that you can read about on the Internet.

You can choose a charger on the site http://18650.in.ua/chargers/.
Video: Li-ion batteries, li-ion battery usage tips

In modern mobile phones, laptops, tablets, lithium ion batteries are used. Gradually, they replaced alkaline batteries from the portable electronics market. Previously, all of these devices used nickel - cadmium and nickel - metal hydride batteries. But their days have passed, since Li─Ion batteries have better characteristics. True, they can replace alkaline not in all respects. For example, currents that can give Nickel Cadmium batteries are unattainable for them. To power smartphones and tablets, this is uncritical. However, in the field of portable power tools, which consume a lot of current, alkaline batteries are still in use. Nevertheless, work on the development of batteries with high discharge currents without cadmium continues. Today we will talk about lithium-ion batteries, their device, operation and development prospects.
The very first battery cells with an anode of lithium were released in the seventies of the last century. They had a high specific energy intensity, which immediately made them in demand. Specialists have long sought to develop a source based on alkali metal, which has a high activity. Thanks to this, a high voltage of this type of batteries and specific energy were achieved. At the same time, the development of the design of such elements was completed quite quickly, but their practical use caused difficulties. They managed to cope only in the 90s of the last century.

Over the course of these 20 years, researchers have come to the conclusion that the main problem is the lithium electrode. This metal is very active and during operation a number of processes took place, which eventually led to ignition. This came to be called ventilation with flame formation. Because of this, in the early 90s, manufacturers were forced to withdraw the batteries released for mobile phones.
This happened after a series of accidents. At the time of the conversation, the current consumed from the battery reached its maximum and ventilation began with the release of a flame. As a result, there have been many cases of users receiving facial burns. Therefore, scientists had to modify the design of lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium metal is extremely unstable, especially when charging and discharging. Therefore, researchers began to create a lithium-type battery without using lithium. Ions of this alkali metal began to be used. Hence their name went.
Lithium-ion batteries have less specific energy than. But they are safe in compliance with the norms of charge and discharge.
Reactions occurring in a Li─Ion battery
A jerk in the direction of introducing lithium ion batteries into consumer electronics was the development of batteries, in which the negative electrode was made of carbon material. The carbon crystal lattice is very suitable as a matrix for intercalation of lithium ions. To increase the voltage of the battery, the positive electrode was made of cobalt oxide. The potential of literated cobalt oxide is about 4 volts.
The magnitude of the operating voltage of most lithium-ion batteries is 3 volts or more. During the discharge on the negative electrode, lithium deintercalates from carbon and intercalates into cobalt oxide of the positive electrode. In the charging process, the processes occur the other way around. It turns out that there is no metallic lithium in the system, but its ions work, which move from one electrode to another, creating an electric current.
Negative electrode reactions
All modern commercial models of lithium-ion batteries have a negative electrode made of carbon-containing material. The complex process of intercalation of lithium into carbon largely depends on the nature of this material, as well as the electrolyte substance. The carbon matrix at the anode has a layered structure. The structure can be ordered (natural or synthetic graphite) or partially ordered (coke, soot, etc.).
During intercalation, lithium ions push apart the carbon layers, penetrating between them. Different intercalates are obtained. During intercalation and deintercalation, the specific volume of the carbon matrix changes insignificantly. In the negative electrode, in addition to the carbon material, silver, tin and their alloys can be used. They also try to use composite materials with silicon, tin sulfides, cobalt compounds, etc.
Positive electrode reactions
Primary lithium cells (batteries) often use a wide variety of materials to make a positive electrode. In batteries, this does not work and the choice of material is limited. Therefore, the positive electrode of a Li─Ion battery is made of lithiated nickel oxide or cobalt. Can also be used lithium manganese spinels.
Today, research is being conducted on materials from mixed phosphates or oxides for the cathode. As experts were able to prove, such materials improve the electrical characteristics of lithium-ion batteries. Methods are also being developed for depositing oxides on the cathode surface.
The reactions that occur in a lithium-ion battery during charging can be described by the following equations:
positive electrode
LiCoO 2 → Li 1-x CoO 2 + xLi + + xe -
negative electrode
C + xLi + + xe - → CLi x
In the process of discharge, the reactions go in the opposite direction.
The figure below schematically shows the processes that occur in a lithium-ion battery during charge and discharge.

The device of lithium-ion batteries
According to their performance Li─Ion batteries are made in a cylindrical and prismatic version. The cylindrical design represents a coil of electrodes with a separator material for separating the electrodes. This roll is housed in an aluminum or steel casing. A negative electrode is connected to it.
A positive contact is displayed as a contact pad on the end of the battery.

Li─Ion prismatic-type batteries are made by laying rectangular plates on top of each other. Such batteries make it possible to make the packaging more dense. The difficulty lies in supporting the compressive force on the electrodes. There are prismatic batteries with a coil assembly of electrodes twisted into a spiral.

The design of any lithium-ion battery provides measures to ensure their safe operation. First of all, this concerns the prevention of heating and ignition. A mechanism is installed under the battery cover that increases the battery resistance with increasing temperature coefficient. When the pressure inside the battery rises above the permissible limit, the mechanism breaks the positive terminal and the cathode.
In addition, to increase the safety of operation in Li-Ion batteries, an electronic board is mandatory. Its purpose is to control the processes of charge and discharge, the exclusion of overheating and short circuit.
Now produced a lot of prismatic lithium-ion batteries. They are used in smartphones and tablets. The design of prismatic batteries can often differ from different manufacturers, because it does not have a single unification. Electrodes of opposite polarity are separated by a separator. For its production, porous polypropylene is used.
The design of Li-Ion and other varieties of lithium batteries is always leakproof. This is a mandatory requirement since leakage of electrolyte is not permissible. If it leaks, the electronics will be damaged. In addition, the sealed design prevents water and oxygen from entering the battery. If they get inside, then as a result of reaction with electrolyte and electrodes they will destroy the battery. The production of components for lithium batteries and their assembly is located in special dry boxes in an argon atmosphere. In this case, complex methods of welding, sealing, etc. are used.
As for the amount of active mass of the Li-Ion battery, here manufacturers are always looking for a compromise. They need to achieve maximum capacity and ensure operational safety. The following is taken as the basis:
A o / A p \u003d 1.1, where
And about - the active mass of the negative electrode;
And p is the active mass of the positive electrode.
Such a balance does not allow the formation of lithium (pure metal) and excludes ignition.
Parameters of Li-Ion batteries
Lithium ion batteries manufactured today have a high specific energy consumption and operating voltage. The latter in most cases is from 3.5 to 3.7 volts. Energy intensity ranges from 100 to 180 watts per kilogram or from 250 to 400 per liter. Some time ago, manufacturers could not release batteries with a capacity above a few ampere-hours. Now the problems holding back the development in this direction have been eliminated. So, lithium batteries with a capacity of several hundred ampere-hours began to be found on sale.

The discharge current of modern Li─Ion batteries is from 2C to 20C. They operate in the range of ambient temperatures from -20 to +60 Celsius. There are models workable at -40 Celsius. But it’s worth mentioning right away that at low temperatures special series of batteries work. Conventional lithium-ion batteries for mobile phones at low temperatures become inoperative.
Self-discharge of this type of battery is 4–6 percent during the first month. Further, it decreases and amounts to percent per year. This is significantly less than that of nickel cadmium and nickel metal hydride batteries. The service life is approximately 400–500 charge-discharge cycles.
Now let's talk about the features of operation of lithium-ion batteries.
Operation of lithium-ion batteries
Charging Li─Ion batteries
The charge of lithium-ion batteries is usually combined. First, they are charged at a constant current of 0.2-1C until they reach a voltage of 4.1-4.2 volts. And then charging is carried out at a constant voltage. The first step lasts about an hour, and the second about two. To charge the battery faster, pulse mode is used. Initially, Li─Ion batteries with graphite were produced and a voltage limit of 4.1 volts per can was set for them. The fact is that with a higher voltage in the cell, side reactions began that shorten the life of these batteries.
Gradually, these disadvantages were eliminated by doping graphite with various additives. Modern lithium-ion cells charge up to 4.2 volts without problems. The error is 0.05 volts per cell. There are groups of Li─Ion rechargeable batteries for the military and industrial sectors, which require increased reliability and a long service life. For such batteries, they withstand a maximum voltage of 3.90 volts per cell. They have slightly lower energy density, but longer life.
If you charge a lithium-ion battery with a current of 1C, then the time for a full set of capacity will be 2–3 hours. The battery is considered fully charged when the voltage rises to maximum, and the current decreases to 3 percent of the value at the beginning of the charging process. This can be seen in the graph below.

The graph below shows the stages of charging Li─Ion batteries.

The charging process consists of the following steps:
- Stage 1. At this stage, the maximum charge current flows through the battery. It continues until the threshold voltage is reached;
- Stage 2. At a constant voltage on the battery, the charging current gradually decreases. This step stops when the current decreases to 3 percent of the initial value;
- Stage 3. If the battery is put into storage, then at this stage there is a periodic charge to compensate for self-discharge. It is done approximately every 500 hours.
It is known from practice that increasing the charge current does not reduce the battery charging time. With increasing current, the voltage rises faster to a threshold value. But then then the second stage of charging lasts longer. Some chargers (chargers) can charge Li─Ion battery in an hour. In such memories, the second stage is missing, but in reality the battery at this point is charged somewhere by 70 percent.
As for jet charging, it is not applicable for lithium-ion batteries. This is because this type of battery cannot absorb excess energy when recharging. Jet charging can lead to a transition of a part of lithium ions to the metallic state (valence 0).
A short charge well compensates for self-discharge and loss of electrical energy. Charging in the third stage can be done every 500 hours. As a rule, it is performed when the battery voltage is reduced to 4.05 volts on one element. The charge is conducted until the voltage rises to 4.2 volts.
It is worth noting the weak resistance of lithium-ion batteries to overcharging. As a result of supplying excess charge to the carbon matrix (negative electrode), lithium metal deposition can begin. It has a very high chemical activity and interacts with an electrolyte. As a result, oxygen evolution begins at the cathode, which threatens to increase pressure in the housing and depressurization. Therefore, if you charge a Li─Ion cell bypassing the controller, do not allow the voltage to rise when the charge is higher than that recommended by the battery manufacturer. If you constantly recharge the battery, its life is reduced.
Security Li-Ion battery manufacturers are paying serious attention. The charge stops when the voltage rises above the permissible level. A charge shutdown mechanism is also installed when the battery temperature rises above 90 Celsius. Some modern battery models have a mechanical type switch in their design. It works when pressure rises inside the battery case. The voltage control mechanism of the electronic board disconnects the bank from the outside world for minimum and maximum voltage.
There are lithium ion batteries without protection. These are models containing manganese. This element during recharging helps to inhibit lithium metallization and oxygen evolution. Therefore, in such batteries protection becomes unnecessary.
Storage and discharge characteristics of lithium-ion batteries
Lithium-type batteries are stored well enough and self-discharge per year is only 10–20%, depending on storage conditions. But at the same time, the degradation of the battery cells continues even if it is not used. In general, all the electrical parameters of a lithium-ion battery may vary for each individual instance.

For example, the voltage during a discharge varies depending on the degree of charging, current, ambient temperature, etc. Currents and modes of the discharge-charge cycle and temperature influence the battery life. One of the main disadvantages of Li-Ion batteries is their sensitivity to charge-discharge mode, which is why they provide for many different types of protection.
The graphs below show the discharge characteristics of lithium-ion batteries. They examined the dependence of voltage on the discharge current and the ambient temperature.


As you can see, with increasing discharge current, the drop in capacitance is insignificant. But at the same time, the operating voltage decreases markedly. A similar pattern is observed at temperatures below 10 degrees Celsius. It is also worth noting the initial drawdown of the battery voltage.