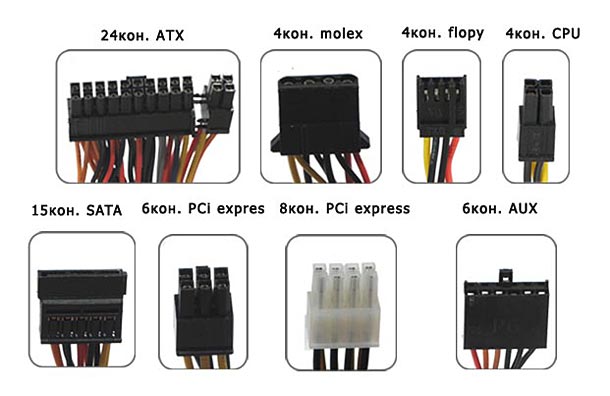
The type of power supply connectors is one of these things, without foreseeing that, you will have to suffer a lot from the PSU. Time, technology and standards are changing, and now, having bought a new power supply in your store for your computer, you may be disappointed that you will not be able to connect it due to a mismatch between the connectors.
In this article, let's look at the power supply connectors. What they are, how they are divided according to standards, and what should be yours. Know about the connectors is necessary for the correct.
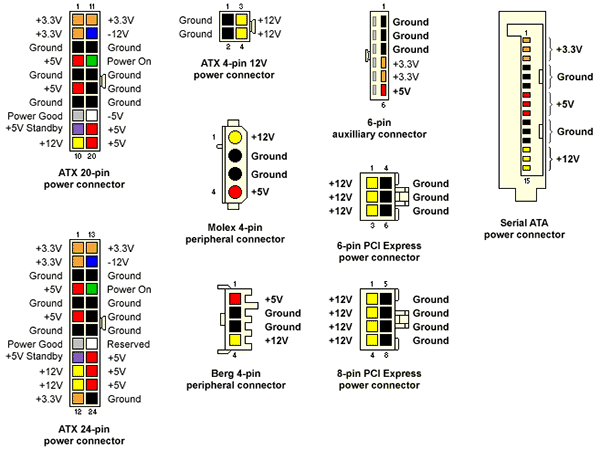
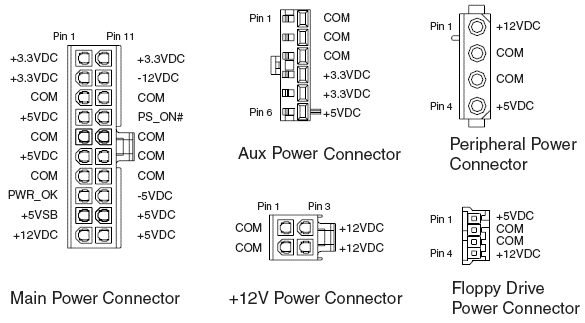
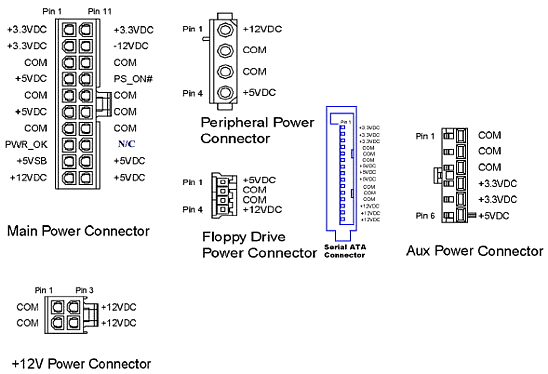
Main Power Connector 20 + 4 pin
Main Power Connector 20 + 4 pin is the main power line in the computer, it is for motherboard. It consists of 24 contacts, 4 of which are sometimes detachable.
This power supply connector is always one. And he is and will always be. The standards for it have not changed.
+ 12V Power Connector
Power line for the motherboard, consists of 4 contacts. Used to ensure the operation of the processor. He too is always, and more often than not one.
But pay attention to your fee. If you need two + 12V Power Connector, then you need the power supply, respectively, with them two. These also happen, but less often.
EPS12V Power Connector
EPS12V Power Connector is also a connector for the motherboard, consisting of 8 contacts. But it is unlikely to be on your home PC, since it is only used for powering large capacities that are commonly used in server machines. This connector is on the blocks that meet the standard EPS12V.
 PCI Express Power Connector
PCI Express Power Connector
Gamers with a heaped video card should pay attention to the presence of this connector power supply computer. PCI Express Power Connector is used to support the operation of powerful video cards. It consists of 6 contacts.
It may not be on the power supply, so look before buying, and then you will be left without games.
 Peripheral Power Connector
Peripheral Power Connector
Peripheral Power Connector is usually on each PSU in a number of pieces. You will need this 4-pin computer power supply connector, if you have an HDD and an old-style drive - IDE ATA. About connection hard disks read.
Also it is usually used for nutrition peripherals, for example, additional coolers.
 SATA Power Connector
SATA Power Connector
The SATA Power Connector is used for SATA drives. If you have such devices installed in your computer, and you buy an old-fashioned power supply, there may not be such connectors. So pay attention to it.
. Where + 12 volts in a computer2016-03-04
Where + 12 volts in a computer
Voltage from the computer power supply. Connectors, powerToday, it is not uncommon to see people throw out computer power supplies. Well, or BP just lay around idly, collecting dust.
But they can be used on the farm! In this article I will tell you what voltages can be obtained at the output of a conventional computer power supply.
A small educational program on the voltages and currents of computer BS
First, do not neglect safety.
If at the output of the power supply unit we are dealing with harmless to health voltages, then at the entrance and inside it 220 and 110 volts! Therefore, observe the safety precautions. And make sure that no one else is hurt by the experiments!
Secondly, we need a Voltmeter or a multimeter. With it, you can measure the voltage and determine the polarity of the voltage (find the plus and minus).
Third, on the power supply you can find a sticker on which the maximum current to which the power supply unit is calculated is indicated for each voltage.
Just in case, take away from the written figure 10%. So you get the most accurate value (manufacturers often lie).
Fourth, the ATX power unit is designed to generate constant supply voltages of + 3.3V, + 5V, + 12V, -5V, -12V. Therefore, do not try to obtain an alternating voltage output. We will expand the set of voltages by combining the nominal voltages.

Well, have you learned? Then we continue. It's time to determine the connectors and voltages on their contacts.
Sockets and voltages of computer power supply
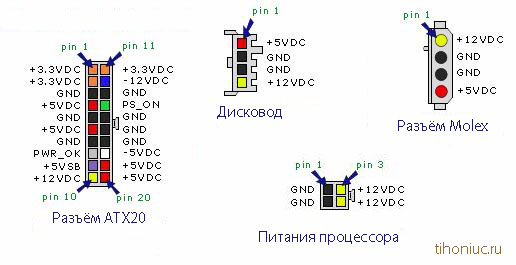
Color marking of voltages of the computer power unit
As you can see, the wires coming out of the power supply have their own color. It's not just that. Each color indicates stress. Most manufacturers try to stick to the same standard, but there are absolutely Chinese power supplies and the color may not match (that's why the multimeter is for help).
In normal PSU marking by the colors of the wires is as follows:
- Black - common wire, ground, GND
- White - minus 5V
- Blue - minus 12V
- Yellow - plus 12V
- Red - plus 5V
- Orange - Plus 3.3V
- Green ON (PS-ON)
- Gray - POWER-OK (POWERGOOD)
- Purple - 5VSB (power on duty).
Pinout of AT and ATX power connectors
For your convenience, I picked up a series of pictures with pinouts of all types of power supply connectors for today.
To begin we will study types and types of connectors (connectors) of the standard power supply.
To "power" the motherboard uses an ATX connector with 24 contacts or an AT connector with 20 contacts. It is also used to turn on the power supply.
For hard drives, sidirums, card readers and other uses MOLEX.
A rarity today is the connector for flopy disks. But you can meet old BPs.
A 4-pin CPU connector is used to power the processor. There are two or more of them, that is, 8-pin, for powerful processors.
SATA connector - came to replace the MOLEX connector. Used for the same purposes as MOLEX, but on newer devices.
PCI connectors are most often used to serve supplementary feeding on various kinds of PCI express devices (most common for video cards).
Let's proceed directly to pinout and marking. Where are our cherished strains? And here they are!
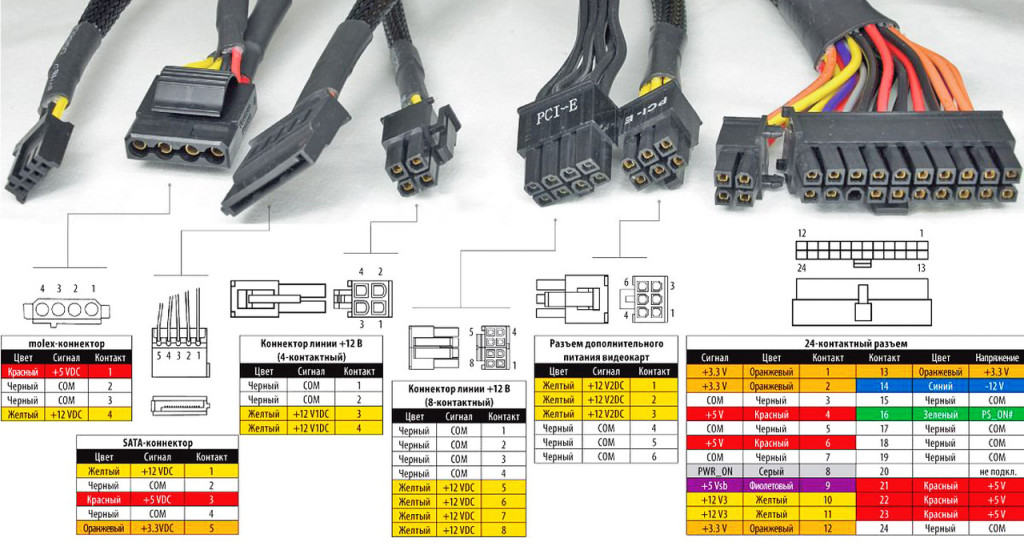
Another picture with pinout and color designation of voltages on the connectors of the PSU.
 The following is a pinout of an AT-type power supply.
The following is a pinout of an AT-type power supply.
 Well. With the pinout computer power supplies figured out! It's time to move on to how to get the necessary voltage from the power supply.
Well. With the pinout computer power supplies figured out! It's time to move on to how to get the necessary voltage from the power supply.
Receiving voltages from the connectors of a computer power supply
Now that we know where to draw the stresses, let's use the table that I mentioned below. Use it as follows: positive voltage + zero = total.
Positive zero total (difference) + 12V 0V + 12V + 5V-5V + 10V + 12V + 3.3V + 8.7V + 3.3V -5V + 8.3V + 12V + 5V + 7V + 5V 0V + 5V + 3.3V 0V + 3.3V + 5V + 3.3V + 1.7V 0V 0V 0V
It is important to remember that the current of the final voltage will be determined by the minimum value for the used values to obtain it.
Also do not forget that for large currents it is desirable to use a thick wire.
The most important thing!!! The power supply is started by closing the wires GND and PWR SW. Works as long as these circuits are closed!
REMEMBER! Any experiments with electricity must be carried out with strict adherence to the rules of electrical safety!
Addition on the connectors. Pinpoint pinout of PCIe and EPS connectors.
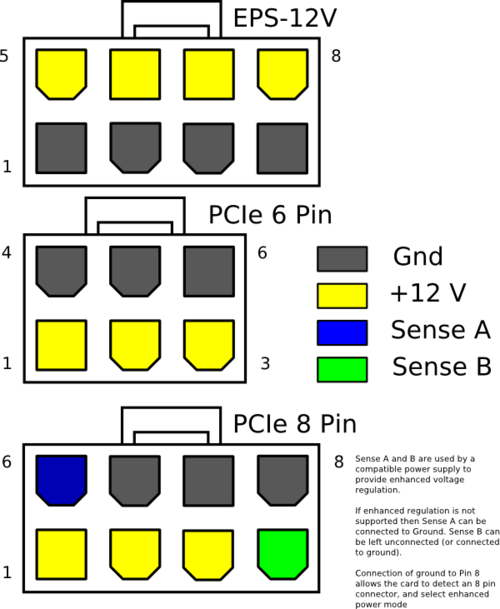 PCIe and EPS
PCIe and EPS - Ryzen Threadripper 1950X 3.4Ghz 16core 40Mb 14nm "\u003e Ryzen Threadripper 1950X 3.4Ghz 16core 40Mb 14nm
- Ryzen Threadripper 1920X 3.5Ghz 12core 38Mb 14nm "\u003e Ryzen Threadripper 1920X 3.5Ghz 12core 38Mb 14nm
- Inexpensive tablet on the characteristics should be so
You can mark you interesting snippets of text,
which will be available through a unique link in the address bar of the browser.
Selecting a BP based on visual characteristics - a guide
nemoW 05/18/2005 01:12 | | printable version | archive
This work was sent to our "perpetual" contest of articles and the author received the award - cooler PENTAGRAM FREEZONE QVC-100 Cu +, a mat from AMD and a branded T-shirt site.
Version 2.01 ( revision history)
Most often novice users do not pay enough attention to the selection of high-quality components, and when choosing a case they are worried, except that the design of its front panel. Even if the buyer is interested in the power installed in the power supply unit (hereinafter BP), the low quality of cheap power supplies (no matter how beautiful the figures on them were drawn), no one will warn him. In the future, with an independent upgrade, a processor, a graphics card, a hard drive are being replaced ... and the power supply remains the same, and if there are problems with the stability of the machine, it is not immediately recalled about its existence. A search for a more powerful BP begins, but in articles on BP and on near-computer conferences (the efforts of individual illiterate and irresponsible authors, as well as their readers), there are many surprisingly enduring myths. Some of these materials will try to expose this material, but at the same time show by examples of the difference between a cheap BP from a quality one (not necessarily expensive).
In the network, you can find quite a lot of articles on the theory of computer BS, their tests and manuals for finalization. This material is an attempt to give some generalized recommendations on the choice of BP without tests, by characteristic external features. The idea itself is inspired by this article.
Introduction
It's no secret that the energy consumption (and accordingly the heat emission) of PC components is constantly growing. TDP (maximum design heat dissipation) of modern desktop platforms in the short term is 130W (LGA755) and 125W (Socket AM2), respectively. The power consumption of top-end video cards has long exceeded the permissible current limits for both AGP (40W) and PCI Express (75W) connectors and reaches 120W (such video cards are equipped with additional power connectors), and the use of two video cards in SLI or CrossFire mode automatically doubles these requirements (lists of BPs certified for SLI and CrossFire systems, see in the section). The transition of DDR-\u003e DDR2 (with a decrease in voltage from 2.5-2.8V to 1.8-1.9V and reference frequencies in half) is gradually compensated by the increase in frequencies (and voltages - in overclocker modules).
In the middle of the year, and Intel (processors based on the new architecture - Conroe), and AMD (processors for the platform AMD Live!) Are going to introduce a line of CPUs with reduced power consumption. But these processors are sure to become popular among overclockers, and the operation of components in abnormal conditions (overclocking) makes the power requirements of the system even more stringent, which complicates the choice of quality and relatively inexpensive power supply.
We will come back to the energy consumption figures for the various components, and now we turn to the power supply unit, which provides power to all components of the PC.
Standard ATX12V. Connectors BP
The main developer of the form factor ATX (and others) is Intel. On the official site - formfactors.org - there are documents regulating requirements and recommendations to manufacturers of cases, power supplies and motherboards. Requirements and recommendations for the BP defines a document ATX12V Power Supply Design Guide (PSDG).
ATX12V was created as an addition to the ATX standard and introduced when switching to the architecture of NetBurst (Pentium 4, which already consumed much more than its predecessor at that time). The main innovation compared to ATX - to get a aboutat lower currents, the VRM (power converter) of the processor was powered from + 12V, not + 5V. The compatibility of the BP with the ATX12V is determined by the presence of a 4-pin + 12V power connector (there should not be a connector if the maximum current is + 12V below 10A). Deviations of stresses (within the limits of the relevant HCV) should not exceed 5% for positive and 10% for negative voltages.
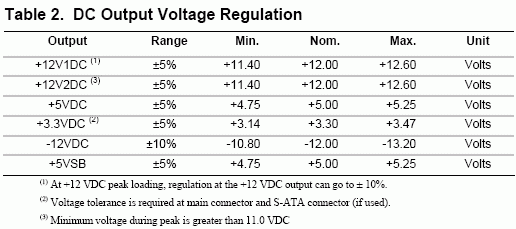 Allowable voltage deviation (ATX12V 2.x)
Allowable voltage deviation (ATX12V 2.x)
Overview (for more details, see the "Chronicles of specifications" section), we'll start with version 1.1, which is dated August 2000 (version 1.0, 1.2 is not on the official site, although they can be found on third-party servers).
 Connectors BP standard ATX12V version 1.1
Connectors BP standard ATX12V version 1.1
Version 1.3 is dated April 2003. Regarding v1.1, the requirements for currents have been changed, the mention of the ATX standard (and voltage -5V) has been removed, the requirements for PS_ON signal processing have been clarified, the mention of the SATA power cable has been added, the efficiency requirements have been slightly increased, etc.
 Connectors BP standard ATX12V version 1.3
Connectors BP standard ATX12V version 1.3
ATX12V PSDG version 2.0 is dated February 2003. Relative to v1.3 there were significant changes in currents (in the direction of increasing consumption by + 12V and correspondingly decreasing by +3.3 and + 5V), 350W and 400W units are standardized (for 300W and more 16AWG wires are recommended), the ATX power cable is changed from 20- pin to 24-pin (added +3.3, +5, + 12V, COM (also ground, ground) contacts for pCI power supply Express devices), SATA power cable is mandatory. The higher-end PDUs can also have 6-pin power connectors (for video cards with power consumption greater than 75W) and an 8-pin + 12V connector instead of 4-pin (for future processors). The 24-pin ATX connector is compatible with the 20-pin ATX both electrically and mechanically and is similar to the server-side SSI (EPS12V).
The next revision continues the line started by the ATX12V PSDG 2.0. In the versions from 2.01 (June 2004) to 2.2 (March 2005) the following changes occurred: 450W block description added; The requirements to the maximum currents on lines + 3.3V, + 5V (strongly), + 12V2 are weakened - while the curves of the KHK have not changed; The requirements to efficiency and currents for + 5V standby (duty source) are increased.
![]() Connectors BP standard ATX12V version 2.x
Connectors BP standard ATX12V version 2.x
 24-pin and 20-pin ATX power connectors
24-pin and 20-pin ATX power connectors

 SATA connectors and peripheral power-\u003e SATA adapter without line + 3.3V
SATA connectors and peripheral power-\u003e SATA adapter without line + 3.3V

![]() 6-pin video card power connector, 2 slots for SLI-enabled units
6-pin video card power connector, 2 slots for SLI-enabled units

 Moved from the servers to the top boxes 8-pin + 12V connector and an adapter to it to 4-pin
Moved from the servers to the top boxes 8-pin + 12V connector and an adapter to it to 4-pin
Power consumption of PC
As mentioned in the previous section, with each new version the standard power of the lines + 3.3V and + 5V is reduced, and + 12V - is increased. This is due to the transfer of the main consumers (CPU and video card) to the bus + 12V. The development of the requirements of various versions of the ATX12V standard for the distribution of currents (i.e., to the load capacities) on 300W busbars is shown on the plate below (the changes are clearly visible in cross-load curve):
| Maximum consumption | + 3.3V amp | + 5V amp | + 12V amp | + 5V standby, ampere | -5V, ampere | -12V, ampere | The total power is + 3.3V and + 5V (*), Watt |
| Standard | |||||||
| ATX | 20 | 30 | 12 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 180 |
| ATX12V 1.1 | 28 | 30 | 15 | 2.0 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 180 |
| ATX12V 1.3 | 27 | 26 | 18 | 2.0 | - | 0.8 | |
| ATX12V 2.0 | 20 | 20 | 8+14 (**) | 2.0 | - | 0.3 | |
| ATX12V 2.2 | 18 | 12 | 8+13 | 2.5 | - | 0.3 |
- (*) the most common + 3.3V formation scheme does not assume its own winding on the transformer, + 3.3V is obtained from the + 5V winding through the auxiliary stabilizer (on the saturated throttle).
- (**) In ATX12V 2.x power supply units, one internal source is + 12V, but for safety reasons it is artificially divided into two with separate overcurrent protection (protection is only necessary to meet safety standards). Wherein line + 12V1 is connected to the power connectors ATX and peripherals, and + 12V2 with 4-pin connector + 12V.
An approximate representation (the data is inaccurate) about the energy consumption of the main components can be obtained from the following table (information is taken here and here):
| Component | Max. power consumption (1 pc.), W | Basic consumption by line: |
| Athlon 1400 / Athlon XP 3200+ | 72/80 | + 5V or + 12V (*) |
| Athlon 64 FX-55 / Athlon 64 X2 | 105/110 | + 12V |
| Pentium 4 XE 3.73 / Pentium XE 3.2 | 110/130 | + 12V |
| Memory modules | 5-10 (512MB PC3200 2.5-2.7V) (**) | + 3.3V or + 5V or + 12V |
| Motherboard | 20-30 | + 3.3V, + 5V, + 12V |
| Video Cards | 20-40 (budget in / cards) | AGP in / cards: + 3.3V, + 5V, + 12V PCI Express in / cards: + 12V |
| 50-80 (in / mid-level maps) | ||
| 90-120 (top-end cards) | ||
| Expansion cards | 5-10 | + 5V |
| HDD | 5-30 | + 5V, + 12V (***) |
| CD / DVD | 10-25 | + 5V, + 12V |
| FDD | 5-7 | + 5V, + 12V |
| Fans | 1-5 (****) | + 12V |
- (*) AMD (and motherboard manufacturers) too late supported and introduced the ATX12V, so most MB Socket A feeds the VRM processor from + 5V pin of the ATX main power connector (which leads to their burning at high currents). The exceptions are some top-end models based on the VIA KT600, KT880 and nVidia nForce 2 chipsets, which have a + 12B 4-pin connector - these models are recommended for purchase. Therefore, for most systems on an aging Socket A platform with top or overclocked processors (and even more so with aTI graphics cards series 9700-9800, creating the main load on the buses + 3.3V and + 5V), the blocks with low currents (load capacity) on these tires will not work. These PSUs are not only budgetary, but also ATX12V 2.2-compliant units, and old, but high-quality ones will cope. For example, my system (Athlon XP 2.06GHz (Vsore 1.55), Epox 8RDA, Radeon 9800Pro, 3HDD, DVD-RW) is running Enermax 300W ATX 99g.v. (+ 3.3V - 20A, + 5V - 30A, + 12V - 12A, without the ATX12V connector). For power consumption of other processors, see here or search here in the impl (ementation) section. By the way, for some time now AMD and Intel have ceased to publish heat dissipation for each model of processors, and publish data for platforms (a group of models). Examples of processors with low heat generation are given.
- (**) Data on the power consumption of memory are inconsistent. Curious document AMD # 26003, Builders Guide for Desktop / Tower Systems (rus) contains examples of energy consumption calculations for typical systems. In it, a 128MB DDR module corresponds to 10W (2A current to + 5V). In other documents, both according to calculations and the results of measurements, different, but numerically smaller figures are given (references: 1, 2, 3, 4). It should be noted that power consumption is highly dependent on the frequency and voltage of the modules, so overclockers can consume more and heat much more.
- (***) The SATA power connector has a + 3.3V line, but there are not any HDDs that require it for operation.
- (****) The power of the fans' motors is obtained by multiplying the declared current by 12 Volts and is related to the number of revolutions, the diameter and the profile of the fan blades. For reference: the rated current of the fan of the boxer cooler P4 3.0 GHz (Prescott) is 0.27A, the nominal current of the unnamed is 80x80x25 ~ 2500ob. - 0.13A (based on the measurement results: 0.13A is the starting current at the peak (as far as it can be measured by a cheap multimeter), and after a set of revolutions the consumption is 0.09-0.10A, if the impeller is blocked - 0.14-0.17A), and currents greater than 0.5 A characteristic only for high-turnover monsters.
Summarizing the energy consumption of PC components, we get that the power consumption of mid-range systems (and the more budgetary ones) does not exceed 250-300 W, and for systems with top processors and top-end video cards in SLI / CrossFire mode it is 400-450 W. In practice, energy consumption tests of modern gaming systems show even slightly lower power. It seems that 300W of the unit should suffice for the average system, with what is the myth connected with the need for a BP of much higher power? First, the case in the already mentioned load distribution on the tires is a high-quality, but low-power block of the old standard simply does not pull new systems with the main consumption along the line + 12V. Secondly, the point is real power and integrity of the block labeling, which will be discussed in more detail below.
To estimate the power consumed by the system, there is a utility from Alexander Lemenkov aka awl - Power Supply Calculator, read about the reasons for its development (and other useful information on the BP) is possible. It contains an extensive database on the passport data of the power supply, the power consumption of various processors and video cards, can determine the components of the system.
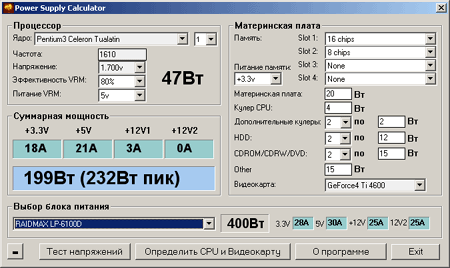
In addition, the program includes a stress test to assess the stability of the voltages during peak processor consumption. Since the test uses indicators unreliable hardware monitoring of voltages, for this purpose it is preferable to use S & M (in FPU burn mode, 100% load) and voltmeter.
There are online calculators for the consumption of the system (links: 1, 2, 3). The fatal flaw of all calculators is that it is impossible to measure the power consumption by software (without additional equipment). In addition, the energy consumption databases of all the mentioned scripts contain overestimated figures, and the PSC has not been updated for a long time. Therefore, the approximate power consumption of the system should be considered manually (references to practical tests of consumption of PC components are collected in the corresponding one).
Introduction №2
The actual task of choosing a BP without tests, according to some visually determined criteria. Because the:
- on our market power units of little-known manufacturers and trade marks get;
- producer (especially brazenly - in blocks of the lower price category), the passport characteristics of the BP are overestimated. Most often low-power budget blocks are labeled as more powerful, leaving unchanged components and correspondingly maximum currents;
- often there is no possibility to take BP for tests.
Of course, only a detailed inspection together with the tests will give an exact answer about the capabilities of the block, but there are also basic signs on which it is possible to determine a qualitative PSU. 100% guarantee this method will not, but the risk of running into lewdness is reduced to a minimum.
Take the BP in hand
Before reading this section, I recommend that you read the article Test Method for Power Supplies Oleg Artamonov (it describes the device and the main components of the PSU), some of the issues are discussed in more detail in the work serj_ - Power Supply.
Taking BP in hand, you can evaluate the following parameters:
1. The thickness of the metal (and the manufacturing quality)
Here, save only in the cheapest blocks.
2. Unit weight
It is often advised that the block can be selected by weight. It seems to be true, but with a number of reservations. First, the weight of low-cost and inexpensive blocks is determined to a greater extent by the thickness of the enclosure's iron and the presence / absence of a passive throttle rather than the "stuffing". Secondly, the large weight of the block does not guarantee high performance and can only be used as a simplest way to assess the quality of BP.
Therefore, do not rely on weight in itself as the main sign of a good BP, it's just an element of an integrated methodology. Nevertheless, if the weight of the BP is noticeably "airy", the inside and the number of parts are minimal. The average BP level, without passive PFC, can not weigh less than 0.9-1.2 kg. By the way, having bought a BP, it is worthwhile to weigh it and check its real weight with the specified in the specifications (on the manufacturer's website).
3. The size and location of the fan (s) and ventilation grilles
80x80 mm fan is put on the rear wall of the BP, 90x90 or 120x120 - on the bottom (with the direction of view from the front panel of the case and the horizontal location of the PSU). In cheap units, one 80x80 fan (with a stamped grate) is used, in more expensive ones one can stand 1-2 (very rarely 3) fans of sizes from 80x80 to 140x140 mm with a wire grill ("grill"), which creates less obstacles to the air flow (and noise).
The grilles for air intake (the fan in the power unit should work on blowing out of the housing) are located in blocks with one 80x80 fan on the opposite fan (front) wall ( type 1), there are fewer holes on the bottom wall of the unit ( type 2). A simple modification of the Type 1 block is possible to improve the cooling of the PSU itself and to reduce the noise from it. In models with 120x120 fan ( type 3) on the bottom wall make frequent holes for ventilation on the back of the unit. For more information on cooling the PSU, see here.

 Power supplies with 80x80 fans (type 1 and type 2)
Power supplies with 80x80 fans (type 1 and type 2)

 Power supplies with 120x120 and 80x80 + 90x90 fans (type 3 and type 4)
Power supplies with 120x120 and 80x80 + 90x90 fans (type 3 and type 4)
Obviously, blocks of types 3 and 4 are most efficiently removed from the housing (but also heated at the same time), but installation in the fan casing for blowing out of the processor zone (under the BP) is recommended in any case.
4. Number and length of cables, thickness of wires
For budget blocks typical 1 FDD connector, 4 connectors for peripherals on two loops, short cables (including the ATX power cable), thin wires (cross section 20AWG-22AWG). In normal PSUs more, cables are longer and wires are thicker (16AWG (very rarely) -18AWG). The minimum recommended cable length is 28 cm for the cable + 12V 4-pin and 25 cm for the remaining cables (from the PSU to the first connector). At the exit point of the bundle of wires from the PSU there should be a plastic ring (however, it is easy to put it yourself), which protects the wires from rubbing. The mains (220V) connector in low-cost units is usually supplemented with an output 220V connector, in normal ones - with a switch-disconnector of the power supply of the power supply unit (since + 5V the duty source works even when the PC is switched off).
Since the connectors of peripheral devices are most often intended for ATA devices (HDD and optical drives), it is reasonable to call them HDD connectors for short. Alas, they are often mistakenly called moleks, although Molex is one of the manufacturers of various connectors and cables, including for the BP.
5. Analysis of the label with the passport data of the BP
Since in the BP of the lower price category (almost always, in the more expensive ones) the passport characteristics (usually power) are brazenly inflated, this information should be treated skeptically. Nevertheless, it already shows what the block manufacturer claims. The declared capacity must be not more sum of the products of the nominal busbar voltages to the loads on these buses. It is necessary to focus attention on how much total power according to the ATX12V standard corresponds to the claimed currents, how this power is correlated with the claimed and with the solidity of the "stuffing" BP. For more details, click here.
Looking at the BP at the lumen (through the ventilation grilles), you can estimate:
1. Radiator thickness and profile
Best of all - thick (4-5 mm, in thinner small thermal conductivity and they ineffectively heat up) with developed finning (punching out "fingers" instead of ribs is worse, because they have a small area and accordingly low dissipated power). Note: although in the new FSP series Epsilon / Optima Pro instead of radiators - aluminum plates, this does not affect the performance of the PSU due to the improved circuitry (including high efficiency).
![]() Example of bad radiators (GIT KP-300UPF)
Example of bad radiators (GIT KP-300UPF)
 Another example of bad radiators (Codegen 250X1)
Another example of bad radiators (Codegen 250X1)
 Example of quality radiators (Delta DPS-300KBD)
Example of quality radiators (Delta DPS-300KBD)
 Example of massive radiators (OCZ PowerStream OCZ-470ADJ)
Example of massive radiators (OCZ PowerStream OCZ-470ADJ)
2. Size of filtering (smoothing) high-voltage capacitors
From their capacity (proportional to the size) depends on the performance of the unit with reduced network voltage, inductive load in the network (vacuum cleaner, refrigerator), sensitivity to interference, reaction to short-term voltage dips and even heating of the capacitors themselves.
3. Power Transformer Dimensions
The size of the transformer is determined by its operating frequency. However, a miniature transformer can limit the maximum power and heat up under a high load. Unfortunately, it is impossible to estimate the height of the transformers in the photographs below because of the camera angle.


 Transformer from PowerMini PM-300W, from Antec TruePower True430P and from OCZ ModStream OCZ-520 12U - in approximately the same scale
Transformer from PowerMini PM-300W, from Antec TruePower True430P and from OCZ ModStream OCZ-520 12U - in approximately the same scale
4. Diameter of the throttle of group stabilization
From the diameter of the throttle, the operating parameters of the PSU are not directly dependent. Another thing is that the smaller throttle is a trivial way cheaper, therefore chokes of the big diameter in cheap blocks do not put.
 The throttle from the nameless BP 235W (not better than the "300W" Chinese) and Chieftec (Powerman Pro) HPC 420-102DF
The throttle from the nameless BP 235W (not better than the "300W" Chinese) and Chieftec (Powerman Pro) HPC 420-102DF
It belongs to all components of the PSU: a high density of installation and solid dimensions and denominations (and weight) of parts do not guarantee a high performance of the unit, but (in general) the higher they are, the higher the level (quality) of performance and the price category of the BP.
5. The availability of output capacitors and output chokes
If you can remove the cover
It is unlikely that when buying a power supply you will be allowed to remove the cover and examine the inside of the unit. In addition, most non-budget models have a fairly tight installation, and it is very problematic to see the denominations of some elements beyond the stockade of others. The task is complicated by the possible availability of warranty labels - both the manufacturer of the BP and the retailer. Therefore, this section will be useful to a person who wants to evaluate the quality of the BP already purchased.
By removing the cover of the PSU, you can determine:
1. The presence of a network filter and a passive / active PFC
A network filter protects other devices connected to the network from interference generated by the PSU.


 "Specially trained jumpers" instead of the mains filter, the network filter, it is also (in part) on a separate board
"Specially trained jumpers" instead of the mains filter, the network filter, it is also (in part) on a separate board
Passive PFC (power factor correction, not to be confused with efficiency! See PFC section here) is a massive (significantly increasing mass of the PSU) throttle and is functionally useless for home computers, besides it worsens the reaction of the unit to sudden changes in load and mains voltage , can buzz and warm with a heavy load. Quite another matter is really useful active PFC. However, for some PSUs with active PFC, probes with UPS are possible.
 Throttle passive PFC, mounted on the cover of the BP (FSP300-60BTV)
Throttle passive PFC, mounted on the cover of the BP (FSP300-60BTV)
 Active PFC board (Thermaltake PurePower HPC-420-302DF)
Active PFC board (Thermaltake PurePower HPC-420-302DF)
2. Capacity of filtering high-voltage capacitors
Condensers (usually 2 pieces in series for a lower voltage (200-250 V), which gives a doubling of the maximum operating voltage and halving of the total capacitance) should be at least 1 μF (each capacitor) per 1 W (unit power). For example, for a budget 300W block is typical - no more than 2x330mkF, and in more solid blocks of the same power put 2x470-2x680 mkF. In the presence of active PFC, capacitor capacitance requirements are much lower.
3. Rectifying diode bridge rating
Documentation of the components of the BP (including denominations) can be found on alldatasheet.com.
4. Nominal of the key transistors of the unit
5. Dimensions and quality of the winding of the power transformer
The maximum power and heating under load depend on the diameter of the wires. However, their diameter is difficult to determine, so be guided by the size of the transformer and the accuracy of its winding.
6. Optimality of air flows in PSUs
The location of the fan (s) must match the shape of the radiators (the airflow must pass through the radiators, ie they must be blown), otherwise temperature regime The BP will be suboptimal. Massive radiators are not always necessary, but they allow maintaining the permissible temperature of the BP components at low fan speeds (and the corresponding noise level). A necessary condition in this case is the high (\u003e 0.8) efficiency of the unit.
Explanation: The efficiency of the unit is determined by the ratio of the load power to the power consumed by the unit from the active power network. Since the efficiency values in practice are less than unity, the remaining power is dissipated in the key transistors, transformer, diodes, inductors, capacitors, which means their heating.
7. Ratings and manufacturers of diode assemblies
Diode assemblies are often marked with the type XXYY, where XX is the maximum current, and YY is the maximum voltage. On them it is easy to determine the true load capacity of the block on individual tires. In this case, keep in mind that XX - amount currents of two diodes, therefore, for example, at the declared current of 30A to + 5V in the block (in a good way) there should be 2x30A assemblies! (In fact, the maximum allowable current is slightly more than half, for more details, see.) Unfortunately, in low-cost blocks such a solution is extremely rare.
Better, if in addition to the insulating film (or mica) assemblies are planted on the thermal paste. In some special budget blocks instead of diode assemblies (and rectifying diode bridge) can be discrete diodes (usually + 12V). Such a "solution" to provide a current of more than 3-5A can not in principle. What to do with such a "miracle of Chinese engineering thought", it is written.


 Diode assembly MOSPEC (30A), diode assembly LT (10A) and 2 diode instead of assembly (5A)
Diode assembly MOSPEC (30A), diode assembly LT (10A) and 2 diode instead of assembly (5A)
When the BP overheats (from fan failure or overload), the first die key transistors or diode assemblies. The remaining components (power transformer, capacitors, etc.) less often lead to the failure of the unit, but anything can be burned in cheap PSUs. As an example, we can cite the epic that took place a few years ago with the cheapening of the on-duty + 5V source in the budget blocks, which at one time (usually when the PC was turned on) led to the issuance of all the overestimated stresses and burnout of the systemic whole (see here and here).
8. Quality of the winding of the group stabilization choke
From the diameter of the wires of the windings of high-current buses (better if the wire is thick (diameter\u003e = 1mm) or several windings are wound in parallel), the output voltage drops.
9. Capacities and manufacturers of filtering capacitors at the output, the presence of chokes
Affect the level of pulsations and the drop (sag) of the output voltages. The same recommendations apply to the wires of the filter chokes as to the wires of the group stabilization choke.
 Jumpers instead of filter chokes, also pay attention to the size of the capacitors and the group stabilization choke
Jumpers instead of filter chokes, also pay attention to the size of the capacitors and the group stabilization choke
Electrolytic capacitors of several manufacturers (GSC, JackCon, Licon, Rulycon (not to be confused with Ru bycon!), etc. ) are of extremely low quality, they were seen in epic with swell condensers (eng). The capacitances of these manufacturers may not correspond to the nominal value of the actual capacitance, maximum voltage and temperature, as well as the internal resistance of the capacitor (ESR, for more details, see "Condensers" and), which is relevant for high-frequency circuits (output filters BP - to cancel pulsations at frequency of operation of the transformer and PWM controller (30-60KHz)). Also pay attention to the operating temperature of the capacitors, it should be 105C (for electrolytes of the network filter - 85C).
10. General assembly accuracy (soldering) and assembly density
It is better if the material of the printed circuit board is a fiberglass (denser, usually has a pale-flesh color), and not the getinax (homogeneous at the end, thicker and darker), which is less resistant to temperature and delamination (and peeling of the tracks). In addition to the accuracy of soldering and the quality of the assembly (assembly of the elements), pay attention to the use of nylon ties, heat shrink tubes, transparent plastic insulating films and fixing glue (an example of a particularly poor-quality assembly, see here.
11. The fan manufacturer, the type of its connection, the presence of a thermoregulation circuit (and a temperature sensor)
The fan wires can be soldered into the board or connected with a 2-pin connector (in more expensive units, 3-pin is possible, in this case a wire of the speed sensor with a connector for connection to the motherboard is output). The thermal control circuit (strictly speaking, the fan speed can be adjusted depending not on temperature, but on the load - stepwise) can be implemented on a separate small printed circuit board. The temperature sensor (thermistor) must be pressed against the radiator on the diode assemblies (or other strongly heating element of the PSU) - this determines the speed of the fan speed response to a sudden increase in the load currents (and the temperature of the components of the PSU).

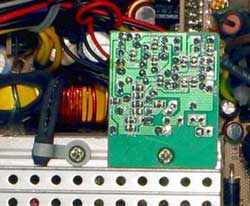 A freely protruding thermistor (Cybermark ATX350W & P4) and clamped to the radiator, next to the control board (FSP300-60BTV)
A freely protruding thermistor (Cybermark ATX350W & P4) and clamped to the radiator, next to the control board (FSP300-60BTV)
Intermediate conclusions
Summing up: bend radiators, miniature capacitors and transformer, discrete diodes instead of assemblies, jumpers in the role of capacitors and chokes are unambiguous the verdict to send the BP to the garbage can. There is no sense in reworking such a BP, it will be necessary to change all, and the PCB (printed circuit board) of such "blocks" may not be designed to set a normal "loose".
However, this opinion of the author, who is not friendly with the soldering iron and all modifications is cautious. In some cases, minimal improvement is reasonable:
A good 300W BP (mid-level) can not cost less than $ 20-25, so it's naive to expect a normal block in cheap cases. The watershed between budget buildings with low-quality BP and normal cases can be considered products of Inwin ($ 50-70), but if possible, you should give preference to the cases Ascot (55-100 $) and Chiftec (100 $ +). Exceptions are possible - sometimes lots of blocks are delivered to our market at bargain prices. For example, 2 years ago such a story occurred with BP Delta, and recently - with several models HIPRO blocks. At the same time, both require a little refinement - Delta needs soldering a resistor between Power OK and + 5V, and in the HIPRO HP-P4017F5 noisy fan.
Price categories of BP
For BP of the lower price category are typical:
- Slim, bending iron casing;
- Low-quality, often high-revving and noisy (to reduce the likelihood overheating and failure block under real load, up to combustion) 80x80 fan, stamped fan grill;
- Thin radiators, practically without finning (or with stamped "fingers");
- Thin wires (20AWG-22AWG), short cables, a small number of peripheral connectors (4);
- Total savings on the number and nominal of parts;
- Semi-empty PCB, low-quality (inaccurate) soldering and installation;
- Low weight (the consequence of a thin iron body, flimsy radiators and total savings on the number and quality of parts);
- The mains filter is incomplete or absent;
- The discrepancy between the passport characteristics of the real load capacity block (and none of the ATX12V PSDG versions).
 IPower LC-B250ATX (250W)
IPower LC-B250ATX (250W)
 PowerMini PM-300W (300W)
PowerMini PM-300W (300W)
For medium-price BPs are typical:
- Qualitative (not deflecting) iron body;
- Fan size 80x80 or 120x120, with thermal control, often wire grill fan ("grill");
- Radiators with pronounced finning;
- The installed wire thickness (18AWG), medium or long cables, a sufficient number of peripheral connectors (5-7);
- A minimum of jumpers instead of parts, it is possible to install a part of the elements on separate (small) printed circuit boards. Qualitative (neat) soldering;
- Tangible weight (a consequence of the normal body iron, increased radiators and small savings in the number and number of parts);
- Network filter, passive PFC possible;
- The conformity of the passport characteristics of the real load capacity block (and one version of the ATX12V PSDG).
- High efficiency is possible;
![]() Fortron / Source FSP300-60BTV (300W)
Fortron / Source FSP300-60BTV (300W)
 Macropower MP360AR Ver. 2 (360W)
Macropower MP360AR Ver. 2 (360W)
For BP of the highest price category are characterized by:
- Quality iron enclosure, often with an additional coating (paint or varnish);
- Qualitative (well-known manufacturer) fans with effective thermal control and wire grating;
- Massive radiators with extensive, thick fins;
- The installed wire thickness (16AWG-18AWG), long cables, a large number of peripheral connectors (7-8), additional connectors;
- Very tight installation, the use of detachable connections instead of soldering, installation of parts of the elements on individual printed circuit boards. High-quality (accurate) soldering and installation;
- The big weight (consequence of the normal iron of the case, massive radiators and absence of economy on quantity and nominal of details);
- The network filter, is possible: active PFC, separate stabilization of voltages;
- Correspondence of the passport characteristics of the block of real load capacity (possibly exceeding the requirements of ATX12V PSDG);
- High efficiency is possible;
- Other necessary and not very features.
 Antec TruePower True430P (430W)
Antec TruePower True430P (430W)
 OCZ Technology ModStream OCZ-520 12U (520W)
OCZ Technology ModStream OCZ-520 12U (520W)
Instead of concluding
Do not take the price categories described in the previous section as rigid frames. In fact, the blocks, which exactly correspond to one of the three descriptions, are comparatively small. All the rest are located between in part, corresponding to one category, in part to another.
In the budget blocks, there can be a case of normal steel, long cables (with enough connectors), a mains filter, a wire grill of the fan, and so on. These elements bring the budget blocks closer to mid-level blocks, but they do not increase the real power of the PSU, they do not reduce the pulsations and the sagging of the output voltages under load. Therefore, I believe that the "code-like" cheap PSUs in principle, you can not use, even in systems with a small total energy consumption (where such units seemingly suitable for currents).
In middle-level blocks, on the one hand, there can be both active PFC, and 16AWG wires, and exceeding the requirements of ATX12V standards. On the other hand, some quality blocks (say, extracted from branded machines or accidentally dropped into retail) can be designed for a specific hardware (chassis, motherboard and total system power consumption), which can mean short cables, a small number of HDD connectors and an ATX12V discrepancy (non-standard wiring in the ATX connector, etc.). In addition, for example, budget FSP models (ATX and Optima series) with a general high quality of performance - short cables with a small number of connectors, which is more common in budget PSUs. They also report on fake FSP blocks.
Even buying an expensive and powerful unit does not guarantee getting rid of all problems. There are blocks with poor load capacity on one or at once on two main buses, with high ripple levels of the output voltages that are not ATX12V compliant, without active PFC, without a 24-pin ATX connector, with rattling fan gratings, with traces of poor-quality manual soldering. .. (see examples here).
I hope I did not seriously intimidate you. Good luck in choosing a quality BP!
Illustrations are taken from sites (in alphabetical order):
- enermax.com.tw
- fcenter.ru (pages) - А.В. Golovkov, V.B. Lyubitsky
- Overclocking the power supply
- POWER SUPPLY (24 hours work)
- Reviews and tests of BP and enclosures on fcenter.ru (catalog of tested BPs)
- Reviews and tests of BP and cases on itc.ua
- Reviews and tests of PSUs and cases on ixbt.com
- BP, tested by Intel for compliance with ATX12V (250-450W)
- BPs tested by Intel for compliance with ATX12V, designed for use with high-end video cards (450-600W)
- Power consumption tests for Pentium 4 processors (Prescott 2.8-3.8GHz) 5xx (E0), 6XX, Pentium 4 EE
- Power consumption tests of Athlon 64 Newcastle and Winchester (1.8-2.4 GHz)
- Power consumption tests for Athlon 64 Newcastle, Winchester and Venice (1.8-2.4 GHz)
- Power consumption tests of single- and dual-core processors Athlon 64, Athlon 64 X2, Pentium 4, Pentium XE
- Power consumption tests for the Athlon 64 FX-55 (CG), Athlon 64 FX-57 (E4), Pentium 4 3.6GHz, Pentium XE 3.73
- Power consumption tests of budget processors Sempron 3000+ (S754, S939), Athlon 64 3000+, Celeron D 351
- Diet HDD: power consumption and heat dissipation - tests 35 HDD 3.5 inches, ATA and SCSI (the data are disputable)
- The main topics of the forum "Enclosures and power supplies" (conference site)
- Guide to Power Supplies (iXBT Hardware BBS)
- Power Supply Terminology
- Manufacturers of enclosures and power supplies (links)
- Standard Certification Marks (eng)
Thanks:
- Igor N. - for patient explanations of the basics of circuitry of the BP;
- Russian scientists presented ferroelectric MELRAM
- Ryzen Threadripper turned out to be so large that the waterblocks lack one sticker
- Virtual spinners for android-devices: a primitive from Google Play or a means to relieve stress?
- Computer power supply
- Power
- Active or passive PFC?
- Cooling the power supply unit
- Connectors and cables
- Brands and Manufacturers
- From the history
- Development prospects
Computer power supply
Choosing the right power supply for your computer - sometimes it may not be as easy as it sounds. This choice depends on the stability, as well as the life of all the components of the PC used, and the choice of the power supply should be approached seriously. In this review, we will try to consider the main points that will help make the right choice.
Power
The output of the power supply unit has the following constant voltages: +5 V, +12 V (also +3.3 V), and - auxiliary (minus 12 V and + 5 V in idle time). The main load is now "accepted" to load the line +12 V.
The output power (W - Watt) is calculated by a simple formula: it is equal to the product of U by J, where U - voltage (in Volts), J - current strength (in Ampere). The voltages are constant, therefore, the more power, the greater the current strength along the lines.
But, it turns out, here, too, not everything is simple. With a strong load on the combined line +3.3 / +5, power can decrease by the line +12. Example - marking the power supply unit of the budget brand Cooler Master (RS-500-PSAP-J3 models):

The maximum total power on the lines +3.3 and +5 is equal to 130W (which is indicated on the package), but the maximum power on the "most important" line + 12V is equal to 360W.
But this is not all. Let's pay attention to the inscription below:
3.3V and + 5V and + 12V, the total power should not exceed 427.9 W. However, theoretically (looking at the "table"), we "see" 490W (360 plus 130), and here - only 427.9.
What this will give us in practice: if the load on the line + 3.3V and 5V is in the sum, say 60W, then taking away from the manufacturer's power of 427.9, i.е. 427.9 - 60, we obtain 367.9W. We get only 360 watts on the + 12V line. From which goes just "basic consumption": the current to the processor, the graphics card.
Automatic power calculation
To calculate the power of power supplies, you can use the calculator in the browser: http://www.extreme.outervision.com/psucalculatorlite.jsp. Although he is english language, you can understand. There are many such services on the Internet.
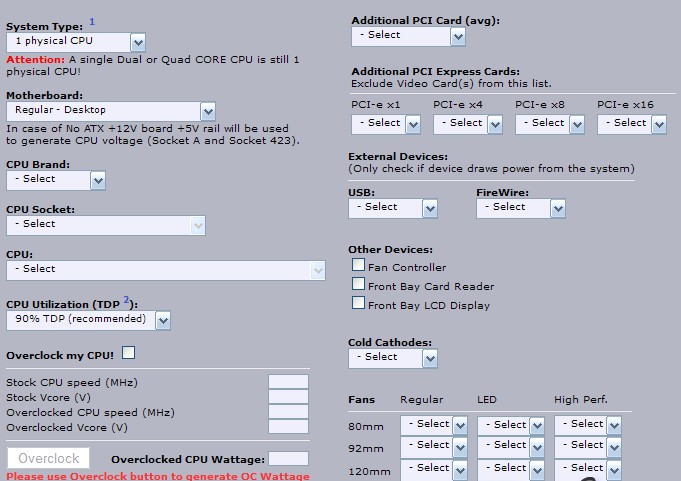
In general, you can choose almost everything you need, including a specific type of CPU, the format of the motherboard (micro-ATX or ATX), the number of memory slots, hard drives, fans ... For calculation, you have to press the rectangular button "Calculate". The service will give out: both the recommended and the minimum possible power (in Watts) for your system.
However, according to experience, we can consider: an office computer (with a dual-core CPU), can be satisfied with a power supply unit at 300W. For home (gaming, with a discrete video card) - suitable BP 450 - 500W, well, and for powerful gaming PCs with the "top" (top) card (or - two, in crossfire mode or SLI) - Total Power (total power) starts from 600 - 700W.
The CPU consumes 100 - 180W (except for 6-core AMD), even at the maximum possible load, a discrete video card - from 90 to 340W, the motherboard itself is 25-30W (the memory bar is 5-7W), hDD 15-20W. Take into account that the main load (processor and graphics card) falls on the line "12V". Well, it is desirable to add a reserve of power (10-20%).
Efficiency - coefficient of efficiency

An important criterion will be the efficiency of the power supply. Coefficient of efficiency (EFFICIENCY) - the ratio of the useful power given out by the power unit to the power it consumes from the network. If the power supply circuit diagram contained only a transformer, its efficiency would be about 100%.
Consider an example where a power supply (with a known efficiency of 80%) provides an output power of 400W. If this number (400) is divided by 80% - we get 500W. A power supply with the same characteristics, but with a lower efficiency (70%), will consume already 570W.
But - do not take these figures "seriously." Power supply most of the time - not fully loaded, for example, this value can be 200W (the computer will be consumed less from the network).
There is an organization, whose functions include testing power supplies to meet the level of the declared efficiency standard. Certification 80 Plus, at the same time, is carried out only for networks at 115 volts (common in the US), starting with the "class" 80 Plus Bronze, all units are tested for use in a 220V-power network. For example, if the certification is passed in the 80 Plus Bronze class, the efficiency of the power supply is 85% with a "half" capacity load, and 81% at the claimed capacity.
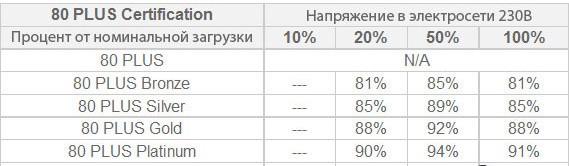
The presence of a logo on the power supply unit says that the product corresponds to the level of certification.
Advantages of high efficiency: less energy is taken away "in the form of heat", and the cooling system, accordingly, will be less noisy. Secondly, there is an obvious saving in electricity (although not very big). The quality of "certified" BP, as a rule, is high.
Active or passive PFC?
Power Factor Correction (PFC) - power factor correction. Power Factor - the ratio of active power to full (active plus reactive).
Load the same, reactive power is not consumed - it is 100% returned back to the network, the next half-cycle. However, with the growth of reactive power, the maximum current value increases (over a period).
Too much current in the wires 220V - is it good? Probably not. Therefore, with reactive power, if possible, fight (especially this is true for really powerful devices, "rolling" the limit of 300-400 watts).
PFC - can be passive or active.
Advantages of the active method:
The power factor is close to the ideal value, up to a value close to 1. With PF = 1, the current in the 220V wire does not exceed the value "power divide by 220" (in the case of smaller PF values, the current is always a little more).
Disadvantages of active PFC:
The complexity increases - the overall reliability of the power supply is reduced. The most active PFC system requires cooling. In addition, it is not recommended to use active correction systems with auto-voltages in conjunction with UPS sources.
Advantages of passive PFC:
There are no shortcomings of the active method.
Disadvantages:
The system is ineffective at high power values.

What to choose? In any case, buying a power unit with a lower power (up to 400-450W), in it you will most often find PFC of the passive system, and more powerful units, from 600 W - are more often found with active correction.
Cooling the power supply unit
The presence of a fan in the cooling fan is considered the norm. The diameter of the fan - can be equal to 120 mm, there is an option for 135 mm and, finally, 140 mm.

The system unit provides for the installation of a power supply at the top of the housing - then, choose any model with a horizontally located fan. More diameter - less noise (with the same cooling capacity).
The speed of rotation should vary with the internal temperature. When the BP does not overheat - why do you need to turn the "valve" at all speeds and annoy the user with noise? There are BP models that completely stop their fan when the power consumption is less than 1/3 of the calculated one. What is convenient.
The main thing in the BP cooling system is its silence (or - a complete absence of a fan, this also occurs). On the other hand, cooling is then necessary to prevent overheating of parts (high power, in any case, entails heat generation). At high power, without a fan - can not do.
Note: in the photo - the result of modding (removal of the standard grid-slot, installation of a Noktua fan and a 120 mm grill).
Connectors and cables
When buying and selecting, pay attention to the number of available connectors and the length of wires coming from the power supply. Depending on the geometry of the housing, you need to choose a PSU with a sufficient length of the cable harness. For standard ATX cases, a 40-45 cm bundle will suffice.

Power supply, working in the home and office computer, has connectors:
 This is the 24-pin power connector of the PC motherboard. Usually here - separately 20 and 4 contacts, but sometimes - and monolithic, 24-pin.
This is the 24-pin power connector of the PC motherboard. Usually here - separately 20 and 4 contacts, but sometimes - and monolithic, 24-pin.
 CPU power connector. Usually it is 4-pin, and only for very powerful processors use 8 contacts. You can select the correct power supply for the computer by focusing on the corresponding connector of the motherboard itself.
CPU power connector. Usually it is 4-pin, and only for very powerful processors use 8 contacts. You can select the correct power supply for the computer by focusing on the corresponding connector of the motherboard itself.
The connector for powering the video card looks similar, and differs in that it is 6 or 8-pin.
Connectors (connectors) for powering SATA-devices (hard disks, optical drives), four Molex contact (for IDE), and to enable FDD (or card reader) - are familiar to most users:

Note: the number of all additional connectors (SATA, MOLEX, FDD) should be sufficient to connect devices located inside the system unit.
Montage demontage

To dismantle the old power supply, disconnect its 220-volt wire. Then, it is necessary to wait 2-3 minutes, and only then to start to work. Attention! Failure to comply with this requirement may result in electric shock.
The power supply in any PC is fixed to the rear wall on 4 screws (screws). You can unscrew them only by disconnecting all internal connectors and plugs of the power supply unit (2 motherboard connectors, video cards, connectors of additional devices).
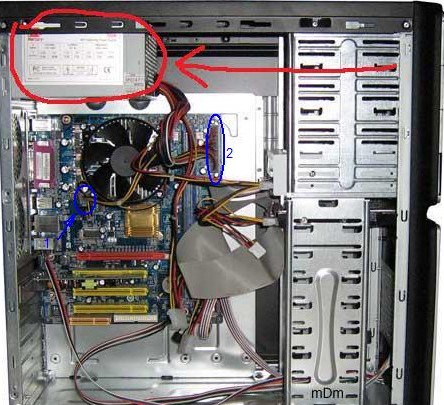

Connect the power supply to the computer in the reverse order: first - mount it into the case, fix it with screws, then connect the connectors.
Note: when manipulating the power supply, the CPU cooler may interfere. If it is possible to dismantle it - use this (put in place - then, before turning it on).
Enabling the computer with a new PSU
By supplying 220 volts to a new PSU, you do not need to immediately turn on the computer. Wait for 10-15 seconds first: you will listen to whether something "extraordinary" is happening. If we hear a squeak, choke the throttles - go and change the power supply unit under warranty. If you hear a recurring "metallic" click - do not turn on the computer with such a power supply.
If in the standby mode, the power unit "clicks" - this is the system of protection. Disconnect such a power supply, disconnect its connectors (connectors). You can try to collect the same thing again - if the problem repeats, we carry the power unit to the service center (possibly the unit itself is defective).
A computer with a working PSU is turned on almost immediately, by pressing the "Power" button of the ATX case. You should see an image on the monitor - now you can continue working, but already - with a new power supply.

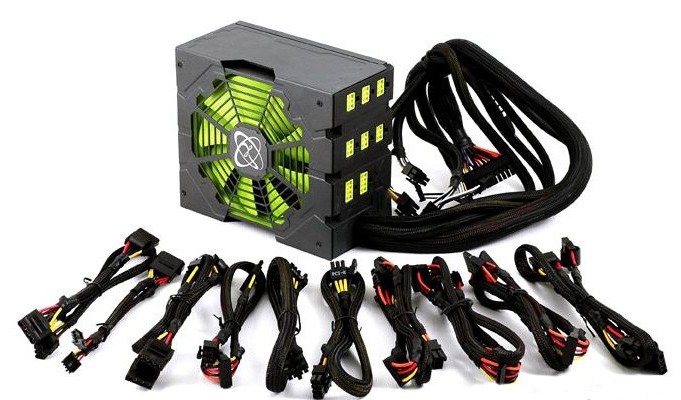
Modular Cables and Connectors

Many more powerful power supply models now use the so-called "modular" connection. Adding internal cables with matching mating connectors - occurs as needed. This is convenient, because in the computer case it is no longer necessary to keep unnecessary (unused) wires, in addition, so - less confusion. And the absence of extra wires, also improves the circulation of hot air. In modular power supplies, only cables with a connector for the motherboard / processor make "permanent" ones.

Brands and Manufacturers
All companies (manufacturers of power supplies for the computer) belong to one of the three main groups:
- They produce completely their products - such brands as Hipro, FSP, Enermax, Delta, also HEC, Seasonic.
- They produce products, shifting part of the manufacturing process to other companies - Corsair, Silverstone, Antec, Power & Cooling and Zalman.
- Resell ready blocks under own brand (some - produce "selection", some do not): Chiftec, Gigabyte, Cooler Master, OCZ, Thermaltake.
Each brand, mentioned above, can be safely recommended. On the Internet, in addition, there are many reviews and tests for "branded" power supplies, which you can navigate the user.
Before buying a PSU, it's worth weighing it (enough and holding it in your hand). This will allow you to more or less understand what is inside of him. Of course, the method is inaccurate, but it allows you to immediately "sweep away" the obviously "cheap" BP.
The weight of the power unit depends on the quality of the steel, the dimensions of the fan, and (most importantly): the number of throttles and the weight of the radiators inside. If there are not enough inductors in the power supply unit (or, let's say, capacitors of reduced capacitance), this indicates a "cheapening" of the electrical circuit: the PSU will weigh 700-900 grams. A good BP (450-500W) weighs usually from 900 gr. up to 1.4 kg.
From the history
On the market personal computers, that is, not only IBM-compatible, but - more generally, "computers", the standardization of components (BP, motherboard) originally went to IBM. The rest then began to copy it. All known form factors for power supplies of IBM-compatible PCs are based on any of the BP models: PC / XT, PC / AT, and Model 30 PS / 2. All compatible PCs, one way or another, could use one of the three original standards developed by IBM. These standards were popular until 1996, and even later - the modern standard ATX goes back to the physical layout of PS / 2 Model 30.
The new form factor, that is known to us ATX, was determined in 1995 by Intel (then IBM's partner), having introduced a standard for the board and power supply. The new standard has gained popularity since 1996, and manufacturers have gradually begun to move away from the outdated standard AT. ATX and some "offshoots" of the standard that followed it, use different connectors from the form factor AT. boards (not only with additional voltages, but also signals that allow to provide more power and additional capabilities).
All IBM standards provided physically the same connector, feeding power to the motherboard. To turn on and off, to power the computer, a toggle switch (or button) was used, a breaker wire with a voltage of 220 volts. That was not very convenient (especially when parsing / repairing the PC). Therefore, a new standard appeared that "does not allow" a voltage of more than 12 volts inside the system unit (inside the case).

It must be said that the power circuit itself (the principle of its construction), starting from the first PC XT, did not receive significant changes. The principle of energy conversion used in computer BS is called "impulse" (220V is made of "constant" voltage, then it is converted, reduced to lower values by pulse method). The first power supplies for personal computers had a power of 60 W (XT), or, say, 100-120 W (AT 286). Simply, then the computer provided for the installation: 1-2 drives, one hard drive (and the processor itself - "consumed" very little).
Development prospects

800 Watts, 900 Watts, 1000 Watts ... The power supply for the PC, giving one Kilowatt of energy to the load, does not surprise anyone. Of course, the price is significantly different (from "standard" boxes to 450-500 W), however, such a power supply provides a sufficient level of reliability (and - low noise level) even at full load! Well, it's just a miracle.
If you calculate how much energy such a computer will consume from the outlet - it turns out that this is nothing more than the equivalent of a permanently switched on full power iron. A good one, in capacity - above average, heavy ...
Recently, with the transition to new production processes for the production of "main" microcircuits for a computer (CPU, 3-D module), the movement was just the "reverse" - that is, a reduction in the total capacity while maintaining the same level of performance. Two years ago, the average 4-core "percent" consumed at least 90 W, now - already 65 ("new", at the same time - faster). In any case (as 2 years ago, and now), the choice is for the user.
The type of power supply connectors is one of these things, without foreseeing that, you will have to suffer a lot from the PSU. Time, technology and standards are changing, and now, having bought a new power supply in your store for your computer, you may be disappointed that you will not be able to connect it due to a mismatch between the connectors.
In this article, let's look at the power supply connectors. What they are, how they are divided according to standards, and what should be yours. Know about the connectors is necessary for the correct.
Main Power Connector 20 + 4 pin
Main Power Connector 20 + 4 pin is the main power line in the computer, it's for the motherboard. It consists of 24 contacts, 4 of which are sometimes detachable.
This power supply connector is always one. And he is and will always be. The standards for it have not changed.
+ 12V Power Connector
Power line for the motherboard, consists of 4 contacts. Used to ensure the operation of the processor. He too is always, and more often than not one.
But pay attention to your fee. If you need two + 12V Power Connector, then you need the power supply, respectively, with them two. These also happen, but less often.
EPS12V Power Connector
EPS12V Power Connector is also a connector for the motherboard, consisting of 8 contacts. But it is unlikely to be on your home PC, since it is only used for powering large capacities that are commonly used in server machines. This connector is on the blocks that meet the standard EPS12V.
 PCI Express Power Connector
PCI Express Power Connector
Gamers with a heaped video card should pay attention to the presence of this connector power supply computer. PCI Express Power Connector is used to support the operation of powerful video cards. It consists of 6 contacts.
It may not be on the power supply, so look before buying, and then you will be left without games.
 Peripheral Power Connector
Peripheral Power Connector
Peripheral Power Connector is usually on each PSU in a number of pieces. You will need this 4-pin computer power supply connector, if you have an HDD and an old-style drive - IDE ATA. On the connection of hard disks, read.
It is also used to power peripheral devices, for example, additional coolers.
 SATA Power Connector
SATA Power Connector
The SATA Power Connector is used for SATA drives. If you have such devices installed in your computer, and you buy an old-fashioned power supply, there may not be such connectors. So pay attention to it.