The cooling system is one of the most important parts of every gaming computer. It helps maintain a low processor temperature, providing stability, reliability and efficiency. Unfortunately, in most assemblies this aspect is often not given due attention. Users are stopped by the too high cost of the cooler, and they prefer to invest in other parts of the computer system.
This article is intended to help those who want to overclock their processor, create a silent gaming PC or just give its design the finishing touches. Below is an overview of the best CPU cooling systems, among which there is surely one that harmoniously fits into a system unit of any size.
How to choose a cooler for the processor?
CPU cooling systems come in a variety of sizes. Some of them are limited by socket types, while others are limited by available free space. Therefore, before choosing a cooler for the processor, you should make sure that there is enough free space. For example, the dual-fan PHANTEKS PH-TC14PE measures 159 x 140 x 171 mm. Such parameters force caution when making a purchase, since most midi-tower buildings do not have a place for this. In addition, the use of two fans can be problematic with a height of RAM modules exceeding 40 mm.
When choosing a cooler, you need to consider that assembling a gaming PC or mining farm is a complex process that requires additional costs. The problem is that demanding software exposes the chipset to extreme loads, so using standard components of the cooling system is inefficient. The inevitable increase in temperature and volume becomes a serious problem.
Thus, a cooling device is required that provides efficient cooling and no noise. The cooler for AMD or Intel processors must maintain their low temperature even during overclocking.
The manufacturer usually indicates the maximum load of the CPU in its specification so that the consumer does not overload it. But such restrictions are not always justified - the processor is often able to perform more than is stipulated by safety standards. The operation of the CPU in a mode exceeding its nominal parameters is called acceleration. This makes it possible to increase system performance under heavy load, but the processor temperature also increases. Higher heat causes the computer to malfunction. To prevent this, a cooling system is used. The cooler dissipates heat and ensures stable operation of the computer.
Air or water cooling?
There are two methods to lower the temperature of the processor. Traditionally used air cooling, which is quite inexpensive. In modern coolers, water is also used as a cooling agent. In this case, they are called liquid. Both methods are characterized by cooling capacity and components. Below are brief characteristics of each of them.
In air cooling, air is used as a heat dissipation medium. In a system of this type there are not as many components as in a liquid one. It consists of a radiator and a fan, which drives the air. The entire heat transfer mechanism is controlled only by these two components. Fewer parts mean less cost. This method is considered effective, economical and relatively simple.
On the other hand, to improve the efficiency of coolers for AMD and Intel processors, a liquid cooling system was developed. The fact is that water has a greater heat-absorbing ability than air, and in a hot environment it works better. That is why it is preferable to air cooling. In addition, it uses more components. The water cooling system includes a radiator, a fan, a pump, a tank and, of course, water. All these components make the cooler cumbersome. In perfect working condition, water cooling is more efficient than air cooling. But nothing in this world is given for nothing, and at the moment, higher productivity is expensive. Liquid systems are much more expensive, and also have several disadvantages - installing a cooler on a processor is complicated, and they are prone to leaks.
Water cooling is beneficial only if:
- aTX mini-assembly is used and the appearance of low-profile air coolers is not pleasant;
- the voltage on the CPU rises to squeeze maximum performance out of it;
- additional space is required when installing a more compact system.
In other cases, you should limit yourself to air coolers, because with moderate overclocking, this alternative provides competitive performance and temperature.

Criterias of choice
If we consider an example of a gaming PC, then its main component is a graphics card that experiences maximum heat. It can generate 2-3 times more heat than a standard processor, which is dangerous for the entire system. In this case, a liquid cooler has an indisputable advantage over air cooling - it has the best ratio of performance and efficiency, and it lowers the temperature faster.
However, he has a problem - a water leak. Liquid can leak at any time, which will lead to a malfunction of the computer. Although manufacturers of modern cooling systems take this issue very seriously, the risk factor still remains.
Before choosing a cooler for the processor, it is necessary to compare the characteristics of the best models, taking into account the following factors:
- air consumption;
- cost;
- noise level;
- temperature.
Cooling system replacement
In general, to replace an air cooler, you must perform the following steps:
- Identify the type of socket and select a cooling system.
- Before removing the cooler from the processor, it is necessary to prepare the computer - turn off the power and remove the case cover, disconnect all expansion cards and cables from the motherboard.
- Dismantle the old model. The LGA775 or LGA1366 socket devices are mounted on 4 stands with flat heads, which should be turned counterclockwise and carefully removed. AMD sockets are mounted using a lever located on one side of the radiator, which must be rotated 180 °. After that, disconnect the fan cable and remove the cooler.
- Apply fresh thermal grease, having previously removed the remnants of the old.
- Install a new cooling system according to the instructions for the specific model.
- Connect the power of the processor cooler to the 3- or 4-pin connector on the motherboard.
- Check operation and monitor temperature conditions using the supplied software or third-party utilities.

Fan selection
Many manufacturers of air cooling systems for the central processor, as a rule, pay little attention to the fan and do not attach much importance to it. Although most companies produce high-performance coolers that provide good temperature conditions, this is achieved with very fast rotating and loud fans. The number of revolutions does affect the air flow, but does not necessarily provide sufficient pressure. One quick rotation of the blades is not enough. A fan is needed that can push air with more force. Such devices are commonly called SP static pressure coolers and are specifically designed to move air with greater force.
The only drawback of the SP fan is that it typically provides less airflow. Devices of this type can also be very useful for cooling the computer case, inside of which a large number of wires or drive bays with hard disk drives prevent heat dissipation. Otherwise, it is better to use ordinary models.
When planning to replace an old loud annoying CPU cooler, you should consider replacing the fan, as you can save a lot. Therefore, users recommend checking its characteristics and determining what to replace it with. In addition, many do not even suspect that often the radiator allows you to place a second fan. This will make it possible to reduce speed and, accordingly, the noise level of the cooling system.
Big cooler for the processor: how to choose?
In recent years, many large-sized CPU cooling systems have appeared, but only a few can be called really good. And these are, first of all, Noctua NH-D15, Cryorig R1 Ultimate and PHANTEKS PH-TC14PE. They have the best price-performance ratio on the market. In temperature tests, these models are superior to large monoblock coolers and small 120-mm single-fan cooling systems.
All three devices come with their own PMW adjustment of the processor cooler and quiet fans, which can create good total static pressure. Of these, Noctua NH-D15 is the noisiest, with a volume of 24.60 dB without an adapter. When installing the latter, this figure decreases to 19.20 dB, and Cryorig becomes the loudest (23 dB at a maximum rotation speed of 1300 rpm.). This is not bad, and excellent performance does not require the maximum speed of the processor cooler when browsing websites or streaming video.

These CPU cooling systems have some differences, but not so many. In addition to a slight difference in the volume of the fans, they all work with temperatures varying by 1-3 degrees, but this depends on the specific configuration of the computer. So it all comes down to aesthetics and size. Although Noctua is a favorite of many enthusiasts and gamers, this model does not look very attractive. NH-D15 is available in only one color, and this color is brown. As for the Cryorig R1 Ultimate cooler, it comes in a stylish black version with black aluminum radiators. Finally, the Phanteks PH-TC14PE is available in white, black, blue and red and white, at least offering more variety.
The advantages of these models become apparent, for example, against the background of the Zalman CNPS10X-Performa cooler. Its 120mm fan at 2000 rpm at full speed. produces noise with a volume of 58.7 dB. PWM-control of the processor cooler allows you to reduce the speed to 1350 rpm., But this does not help much. The volume decreases only to 44.8 dB. Thus, the Zalman CNPS10X-Performa cooler is able to demonstrate excellent performance, but at the cost of too noisy operation of the complete fan. Replacing the latter can significantly increase the overall characteristics of the model.
The best mid-range cooler
According to user reviews, one of the most popular cooling systems of this type is Hyper 212 Evo and Cryorig H7. Both coolers are quite small. In terms of performance, they can easily surpass any standard cooling system that comes with i5 or Ryzen chips, but they have some differences. First of all, it is the appearance and design. On the one hand, there is a stylish Cryorig H7 with its black and white fan and a very reliable radiator. But you can choose a much more refined assembly with translucent black blades.
In addition to the external design, the models vary in performance and price. First of all, both coolers for Intel and AMD processors provide the same optimal temperature conditions, but they make noise differently. The Hyper 212 Evo is an older model and suffers from this. It is focused on high performance, surpassing complete coolers in this parameter, but it lags behind in the volume level of the fan from 36 dB against 25 dB in H7. Obviously, during the design process this aspect was not given due attention and, judging by the long-term production, will not be paid in the future. Of course, you can always replace the fan with a much quieter one, but then it is already better to buy the H7.

So, why is the Hyper 212 one of the recommended models if the H7 works the same and sounds quieter? Judging by the annual price changes, the cost of the H7 never fell below $ 30. Unlike Hyper 212, the price of which repeatedly fell below this mark and even below $ 20. Thus, despite the loud fan, Hyper 212 has the right to be considered a profitable acquisition, since it not only performs its job well, but is also the cheapest replacement for a complete cooling system.
The cooler for the Deepcool Gammaxx 400 processor is a budget option with one radiator tower instead of two in the basic design. It copes with normal loads perfectly, but it is not recommended for overclocking, because at fan speeds exceeding 700 rpm, annoying noise is heard.
The best low profile models
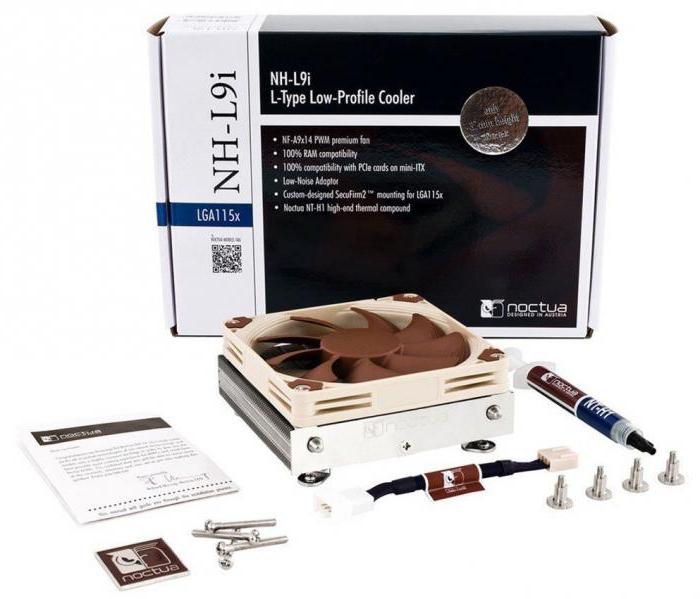
The last category of user-recommended efficient air processor cooling systems are small coolers. The best of them are Noctua NH-L9i and be quiet! Shadow Rock LP. Both models are superior in performance to complete devices, while at the same time taking up very little space. They can easily fit into any mini-ATX assembly. The maximum height of Noctua NH-L9i with a 92 mm fan is 37 mm. Shadow Rock LP comes with a 120mm propeller, and its profile is 50mm thick. Both models provide sufficient clearance with RAM and should not empty the wallet, as they are cheap enough.
Both models do their job of dissipating heat with little noise. The volume level of the NH-L9i fan does not exceed 23.6 dBA at 2500 rpm. without adapter and 14.8 dB at 1600 rpm with adapter. Shadow Rock LP accelerates its propeller to a speed of 1600 rpm. At the same level, the cooler volume is 20 dBA.
Although Noctua looks good on paper, the model is inferior to the competitor in terms of noise. To equal the opponent, the cooler speed on the processor should not exceed 1600 rpm. In addition, do not forget about the 92-mm fan. The size is the reason for the higher temperature of the chipset at low speeds, so users recommend choosing Noctua NH-L9i only if it is necessary to have a very quiet cooler. For the processor, Shadow Rock LP is a more stable cooling system.
Both devices equally claim the title of the best low-profile cooler, but they have in common that they are much inferior to liquid models of monoblock systems.

Water cooling
Currently, the best cooler for this type of processor for monoblock systems is the H110i Corsair. This model can be equipped with two 140-mm fans, and because of this it surpasses many competitors. The cooler is able to keep the temperature stable even when accelerating to high voltages. In addition, it costs only $ 120.
Corsair LINK is a processor cooler program that allows you to track and control its parameters. These include fan and pump rotation speeds, heating temperatures, RGB color, etc. Users recommend leaving the CPU cooler control settings in the default configuration, since it provides the best performance balance and minimal noise level.
The biggest problem with liquid cooling systems for compact computers is their size. How to remove the cooler from the processor, and install it is difficult. The presence of a double 140-mm radiator means that it does not fit in every case, especially in Slim, since liquid cooling systems take up a lot of space. Users who need to install the cooler on the processor in limited conditions have 2 alternatives, the performance of which is equally high, but inferior to the H110i. These are the models H100i and H60. The first one is a dual 120 mm radiator, so it takes up a bit less space. The second is the smallest, because it is equipped with only one 120-mm fan. It copes well with the task of lowering the temperature of the processor, takes up little space and costs only about $ 60.
Some users are convinced that only all-in-one water cooling systems are economically viable. However, this is not so, since everyone can buy a used liquid cooler at a low price. Especially if its cost does not exceed $ 30.
Finally, all the liquid coolers of compact PCs have a common problem, and this is noise. The volume level of all 3 Corsair Liquid options is 35 dB, and it is partially created by the radiator. Thus, coping well with maintaining an acceptable processor temperature, the liquid cooling system also contributes to the overall noise from the PC. You can independently install a good SP-fan, reduce the volume and turn the model into the best water cooler.

Fan replacement
For users who want to upgrade a complete cooler for an Intel or AMD processor, owners recommend considering the Noctua NF-F12 and NF-A14 options.
The first is a 120-mm model that provides an air flow of 92 m 3 / h with a static pressure of 2.61 mm and a low noise level of 23 dB. With the adapter, the speed drops to 73 m 3 / h, and the volume drops to 18 dB with a static pressure of 1.83 mm. Thus, the model is ideal for replacing the annoyingly loud 120 mm fan.
As for the NF-A14, it is a 140 mm version, and provides 143 m 3 / h with higher but still low noise (24 dB) for its performance and static pressure (2.08 mm) without an adapter. Using the latter provides a speed drop of up to 114 m 3 / h, but the volume level decreases to 18.5 dB along with pressure (1.51 mm). Indeed, high static pressure and low noise are good reasons to replace a standard 140mm fan. Noctua NF may not be the best CPU cooler, but it impresses with the results.
According to owners, their only complaint about the model is the company's refusal to use colors other than light brown variations. They would have been bought by more people if there hadn’t been such a restriction, since many people choose components that match the color of the entire gaming platform. As an alternative, you can buy an industrial version of black with a little brown, but its specifications are very different. It operates at a speed of 2000 rpm. and with a noise level of 31 dB, which makes it much louder, although the air flow rate rises to 170 m 3 / h, which is really a lot.
Also note that all Noctua fans have a 5-year warranty.
Conclusion
Finding a good processor cooling system is of great importance, because it is really one of the most important parts of a computer. After the update, it will work hard and for a long time will become one of the few things that do not require modernization.
The time has passed long ago when processors could be cooled passively, without coolers and even heatsinks - modern processors, except perhaps the Pentium and Celeron J-rulers, require at least active air cooling, and at maximum water cooling. And what is better for specific processors, we will consider in this article.
CPU heat dissipation
This is the most important parameter, it is worth paying attention to it first of all. You can find out the heat dissipation (TDP) of your Intel processor on ark.intel.com, AMD - products.amd.com. Also, most coolers indicate how many watts they can take, and this figure should be more than the processor heat.
Processors with heat dissipation up to 35 W (Intel Core T-line or AMD Pro A-series)
Processors from Intel here are essentially mobile Intel Core - a fairly low native frequency, about 2.5-3 GHz, and a significant Turbo Boost up to 3.5-4 GHz. As a result, such processors are well suited for compact systems where it is difficult to make good cooling, but relatively good performance is needed. At AMD, the so-called APUs are presented here - that is, a processor with powerful enough integrated graphics: an ideal solution for a multimedia PC. In both cases, the heat dissipation does not exceed 35 W, so here you can get by with the simplest cooler with an aluminum radiator without any heat pipes:

Processors with heat dissipation up to 50 W (Intel Celeron and Pentium G-line, Core i3)
These are simple dual-core processors, in some of them hyperthreading is activated. Frequencies can reach 4 GHz, however, even in this case, heat dissipation of 50 W is very excessive for them (not to mention Celeron without hyper-threading with a frequency of 3 GHz - there is also 30 watts of the eye). As a result, the same cooling system will suffice as in the previous case - a simple aluminum radiator and fan.
Processors with heat dissipation up to 65 W (Intel Core i5 and i7, AMD Ryzen without index X)
Intel processors here are all quad-core, some with hyperthreading. Frequencies can reach 4 GHz, but there is no overclocking. As a result, 65 W is a reasonable figure for them, and even under stress, the heat generation is unlikely to be higher. In the case of AMD, everything is somewhat better - processors have up to 8 cores, but the frequencies are low, 3-3.5 GHz, so such processors fit into a 65 W heat packet. However, they can overclock, so if it interests you, see the item with overclocked processors.
As a result, a regular heatsink with a simple fan will no longer be suitable for such processors - it makes sense to take a tower cooler with 1-2 heat pipes and a 72-90 mm cooler, like this:

Processors with heat dissipation up to 95 W (Intel Core i5 and i7 with index K, AMD Ryzen with index X)
These processors are considered the top of the user segment - in the case of Intel, the native frequencies can reach as much as 4.5 GHz, in the case of AMD - up to 4 GHz. Alas, in modern realities, increasing the frequency above 3.5-4 GHz leads to an avalanche-like increase in heat dissipation, therefore, at runoff frequencies, the same i7-7700K is only 10% faster than the i7-7700, when the difference in heat dissipation is 30 W - almost half of the i7-7700 !
As a result, if you take such processors and will not overclock them, then you need to take already simple representatives of super-coolers, with 3-4 copper heat pipes and a 90-120 mm turntable:

Processors with heat dissipation up to 200 W (overclocked processors, or Intel Core i7 and i9 X-series lines, AMR Ryzen Threadripper)
As I said above - every hundred megahertz above 4 GHz is given with a fight, and as a result, the i7-7700K at a frequency of 5 GHz can have heat emission of as much as 150-170 watts. The heat dissipation of AMD Ryzen 7 under acceleration to 4-4.2 GHz for all cores can even go beyond the psychological level of 200 watts. This also includes X-line processors from Intel (6-18 core processors) and 16 core processors from AMD - they have a heat dissipation of about 150 watts.
As a result, such processors require either a top-end super-cooler similar to this:

Or already a water cooling system, preferably with two coolers.
The nuances of choosing a cooler
So, we figured out the heat dissipation and the appearance of the cooler, however, some important nuances remained:
- Cooler height: if you take a tower cooler, then see that it fits into the case. Otherwise, it simply will not allow the lid to close.
- Dimensions of the cooler: super-coolers can be so large that they overlap the first RAM slots and the PCI slot, so either take a cooler of a different shape, or take a motherboard where the RAM slots are far from the socket, and the first PCI slot has speed x1.
- Cooler noise: coolers with the same appearance can make a completely different noise, so if silence is important to you, you should look at the reviews and find out how much this or that cooler is noisy.
- Cooler compatibility with the socket: perhaps the most commonplace thing, but they forget about it - the cooler must have a socket for your processor, otherwise you will have to mount the bracket yourself, which is not always possible to do.
- Cooler weight: often the weight of super coolers exceeds one kilogram - such a load can cause deflection and failure of the motherboard. So if you have a heavy cooler - think about the fact that it needs to be additionally attached to the case in order to reduce the load on the motherboard.
- A place for the CBO radiator: if you want to take yourself a water cooling system, then make sure that there is a place for it on the case.
- Using liquid metal: if you decide to use liquid metal as a thermal interface, then choose a cooler with a base made of non-aluminum (otherwise it will corrode). Liquid metal also conducts current - make sure that it does not get on the motherboard.
How to choose a CPU cooler | Basics (why more is better)
Any electrical circuit has a resistance, and it is the principle of electrical resistance that is embedded in both the CPU and toasters. Electric semiconductors have an unusual feature - they can change resistance from low to high when applying electric current in a certain way. These states are represented in the logic diagram as ones and zeros. Although the logic circuits of the CPU are not designed to heat anything, in fact, we use small electric stoves in computers.
Groups of logic circuits, when processing data, become very hot. Therefore, the challenge for developers is to prevent the melting of small pieces of glass on which these patterns are etched. To do this, they came up with heat sinks in the form of massive metal radiators - these are the key elements of the processor cooling system.
And yet, the term “heat sink” means something that absorbs heat. To dissipate a large amount of heat into the relatively cold air, the radiators are helped by their ribs, which increase the area of \u200b\u200bthe scattering surface. Thanks to these fins, the standard CPU heat sink turns into a special type of heatsink, if you do not pay attention to terminology. As with most radiators, their main principle of heat transfer is convection (and a little - thermal radiation), this is when heated air rises, being replaced by cold from below.
The heat dissipation of the processor depends on its clock frequency, voltage, complexity of the circuit and the material on which the circuit is engraved. Radiators with a small number of fins are sufficient for cooling some low-power processors, but most desktop users want more performance, which leads to increased heat generation that needs to be dissipated.

When natural convection does not quickly replace warm air with cold air, the process must be accelerated, which is achieved by installing a fan. The photo above shows a rare, fully copper cooler. Copper transfers heat faster than aluminum, but it also weighs more and costs more. To achieve a better ratio of price to cooling and cooling to weight, manufacturers often use a copper rod surrounded by aluminum fins.

Additional fans and an increased surface area of \u200b\u200bthe radiator increase the efficiency of the processor cooler. Liquid cooling allows you to install huge radiators that are attached not to the motherboard, but to the computer case. A so-called water block is installed on the CPU, which transfers heat to the liquid. The pump is installed on the side of the radiator (as in the photo above) and pumps water (or refrigerant) through the channels of the radiator and water block.

Any of the solutions described above maximizes contact with the circulating air, but they will not work effectively if there is no good contact between the CPU surface and the cooler. To fill the space between surfaces is used heat conductive material It displaces air, which acts as an insulator. It is present in the set of most CPU coolers. In many models, it is immediately applied to the contact surface. But instead of factory materials, enthusiasts often choose third-party heat-conducting compounds, although our tests showed that the difference between them is quite small .

For extreme cooling, compressor units with refrigerant are used. Such systems can reduce the temperature of the CPU far below the ambient temperature. But, as a rule, they use much more energy than the processor itself. There are versions that compress and cool the air to produce liquid nitrogen. However, serious concerns are caused by condensation around cold components, so even the simplest "refrigerators" are usually used only at exhibitions and competitions.
The “more is better” rule, applicable to coolers, in this case is limited by the size of your case, but several other factors must also be taken into account. Since this article is written for beginners, we will only consider models from our list of the best processor coolers . It includes large air coolers (height over 150 mm), low-profile coolers (up to 76 mm), medium-sized coolers (from 76 to 150 mm), as well as ready-made liquid cooling systems.
How to choose a CPU cooler | What about boxed coolers?
“Boxed” or “boxed” coolers are coolers that are supplied by CPU manufacturers complete with their products. Usually they are not designed for increased heat dissipation of the processor during acceleration or for installation in a limited space of narrow computer cases. The motherboard, as a rule, reduces the speed of rotation of the fans to reduce the noise level and first responds to an increase in the temperature of the CPU by increasing the speed of rotation of the fan to the maximum. If at maximum fan speed the cooler is not able to lower the CPU temperature to an acceptable level, the system reduces the clock speed and voltage of the CPU. We call this process thermal regulation (throttling) or throttling. In the worst case, you can observe a picture when a droning computer is not able to provide the necessary level of performance.

Third-party coolers usually have a large scattering surface area, as well as larger fans that allow you to pump large volumes of air with less noise. The photo above shows from left to right: a water cooling system with a radiator for two 140-mm fans, a large air cooler with two radiators, two generations of Intel standard or box coolers, and a wide low-profile cooler designed primarily for HTPC systems.

Complete with FX-8370 processors AMD provides cooler Wraith , which is another attempt to increase the cooling efficiency of boxed coolers.

Temperature change during processor heating
Despite the good performance of the new AMD cooler, customers are still sometimes forced to buy third-party coolers, since some high-performance CPU models come without them.

Recently, AMD and Intel have begun supplying compact liquid cooling systems that meet the demands of very hot processors for cooling, and customers do not need to turn to alternative brands. The growing popularity of mounts for 120-mm fans in modern cases allows you to install small CBO in cases of different shapes and sizes, which compares them favorably with air coolers of similar dimensions.
How to choose a CPU cooler | Finding the best installation position
Tower-type computer cases have the least restrictions on installing large coolers. Modern cases are becoming wider so that they can accommodate high processor coolers, as well as higher, to fit radiators in the upper part, and sometimes longer, for installing radiators and fans on the front panel. Moving the internal compartments or reducing their number allows developers to get more space for installing radiators without the need to increase the size of the case.

The enclosures are still designed to allow air to flow in front-back and bottom-up, but in modern models, the inlet of the power supply is no longer used to help a small exhaust fan (80 or 92 mm) on the rear panel. Now they install a large 140 or 120 mm exhaust fan paired with a fan on the front panel. The direction of the air flow can be changed in the opposite direction, but this way the air will move against convection, and the operation of dust filters, which are usually installed in front and bottom of the housing, will become meaningless.

However, some cheap cases do not take into account current trends. As shown above, the heat pipes of a large air cooler extend beyond the side walls of a tower housing of traditional sizes. The maximum height of the supported CPU coolers is usually indicated in the model specifications on the case manufacturer’s website.

However, the case is not always a limiting factor when choosing a CPU cooler. For example, construction Zalman CNPS12X has an offset of 6 mm towards the video card so that the cooler does not rest against the upper panel of the case. The manufacturer relied on the fact that in many motherboards for gamers, instead of the upper expansion slot, there is free space. In our case, this space does not exist, so we had to mount the cooler back to front in order to test it on an open bench.

Another example, the Thermalright Archon SB-E with a width of 170 mm is not offset and hangs over the top slot in any orientation. It was possible to turn the cooler over to the video card, but then it would touch the RAM modules. This design was designed for motherboards without a card installed in the upper slot, in addition, there must be free space between the motherboard and the upper panel of the case. These are fairly common requirements for gaming systems, but not in our case.

So far we have only talked about the fact that there may be problems installing a large cooler on a large motherboard, but look at the models of motherboards with a smaller form factor. This is where the real problems can be. A variety of mini ITX-format cards bring limits to the space between the CPU socket and memory, expansion cards, voltage regulator radiators, and the left edge of some cases. The widest low-profile coolers usually have an offset of at least one direction from the center to maximize the use of free space.

Some coolers can be biased even in two directions. Please note that the cooler in the photo above is designed so that the fan is located farther from the video card (left shift) and the front edge of the board (backward shift). We always indicate the presence of bias in our reviews of coolers, so you can at least approximately evaluate whether the cooler is suitable for your motherboard.

If the buyer cannot identify possible problems with the installation, you can use a smaller cooler or a cooler, if there is space on the case for mounting the radiator.
How to choose a CPU cooler | Is CBO always the best solution?
Largest cooling systems for the largest enclosures, usually liquid. Flexible hoses allow (depending on the housing design) to install radiators on the front panel - where cold air is taken. In this case, the heat from the CPU returns to the case, but the large amount of air passing through the radiator reduces its effect on other components.

However, the most common mounting option for the CBO radiator is on the top panel of the case. It’s best if the fans are below it and “blowing” up. Problems can occur when heat from a powerful and hot video card goes into the case below the radiator. In this case, warmer air entering the radiator will reduce the efficiency of the operation of the air-conditioning system. It is very important to plan the cooling system in advance, since most high-performance video cards have different versions of their own cooling system, which can remove hot air both into the case and beyond.

If you are worried that the heat from the video card will negatively affect the efficiency of the CBO radiator located on the top panel, you can use a video card that removes the bulk of heat through the ventilation holes in the end part (like the silver card in the photo above). However, video card reviewers often recommend video cards with two or three fans (like the black card in the photo above), which give priority to the best ratio of generated noise to temperature, and do not take into account the effect of thermal air on components that are higher than the video card. From the point of view of air exchange inside the case and the efficiency of the CPU cooler, video cards that remove warm air inside the case can be attributed to harmful factors.

Disputes about the paramount importance of cooling a video card or processor can be resolved using liquid cooling for the CPU and GPU.

An alternative to liquid cooling is large air coolers, in which the radiator fins are in contact with the base through heat pipes. In our tests, some air coolers even circumvented models that use liquid for cooling. Although liquid cooling systems typically provide lower CPU temperatures, the air-to-air coolers are approximately equal in cooling / noise ratio (note that the Kraken X61 liquid cooler and NH-D15 air cooler are roughly the same size).

Acoustic efficiency: relative temperature / relative noise level) - 1, base value \u003d 0
The lack of a pump, in comparison with the SVO, allows you to reduce the cost of an air cooler, however, these two solutions have drawbacks, primarily the size. Firstly, a large air cooler is located directly on the CPU and often blocks access to memory slots and some connectors. A liquid cooler radiator is attached to one of the panels of the case, and only a water block or a combination of a water block and a pump is installed on the processor. On the other hand, the liquid in "closed cycle" systems that do not have openings for topping up may decrease over time due to microscopic leaks. Large air coolers do not have a pump that gradually wears out and constantly buzzes. And although modern pumps work very quietly, noise is still present.

Large air coolers not only make access to RAM and some connectors difficult, but they are also bulky and heavy. Perhaps this is the biggest drawback compared to the CBO. Over time, such coolers can weaken the textolite of the system board and cause irreparable damage to it if it is awkward to handle or just carry over. And bend the CPU pins in the Intel Land Grid Array (LGA) sockets. Cases when during the transportation of the assembled system large air coolers fell off the board and damaged the video card are not rare.
In general, liquid coolers are better than air coolers, although this is not always true in terms of CPU cooling. Usually we use large air coolers exclusively in stationary systems and switch to CBO when we assemble a PC that will move, or when something more than a compact cooler is recommended, which we recommend to beginner collectors.
You now have the information you need to understand our cooler reviews. We hope that it will be useful.
To cool the processor, a cooler is required, the parameters of which depend on how high-quality it is and whether the CPU will overheat. For the right choice, you need to know the size and characteristics of the socket, processor and motherboard. Otherwise, the cooling system may not install correctly and / or damage the motherboard.
If you are building a computer from scratch, then you should think about what is best - buy a separate cooler or box processor, i.e. processor with integrated cooling system. Buying a processor with an integrated cooler is more profitable, because the cooling system is already fully compatible with this model and it costs less to buy such equipment than buying a CPU and a radiator separately.
But at the same time, this design produces too much noise, and when overclocking the processor, the system may not cope with the load. And replacing the boxed cooler with a separate one will either be impossible, or you will have to take the computer to a special service, because a change at home is not recommended in this case. Therefore, if you are building a gaming computer and / or planning to overclock the processor, then buy a separate processor and cooling system.

When choosing a cooler, you need to pay attention to two parameters of the processor and motherboard - socket and heat dissipation (TDP). A socket is a special connector on the motherboard where the CPU and cooler are mounted. When choosing a cooling system, you will have to look at which socket it suits best for (usually manufacturers themselves write recommended sockets). Processor TDP is a measure of the heat produced by CPU cores, which is measured in watts. This indicator, as a rule, is indicated by the CPU manufacturer, and cooler manufacturers write what load this or that model is designed for.
Main characteristics
First of all, pay attention to the list of sockets with which this model is compatible. Manufacturers always provide a list of suitable sockets, as This is the most important point when choosing a cooling system. If you try to install a radiator on a socket that is not specified by the manufacturer in the specifications, then you can break the cooler and / or socket itself.

Maximum operating heat dissipation is one of the main parameters when choosing a cooler for an already purchased processor. True, TDP is not always indicated in the characteristics of the cooler. Slight differences between the working TDP of the cooling system and the CPU are acceptable (for example, the CPU has a TDP of 88W and the radiator has 85W). But with large differences, the processor will noticeably overheat and may become unusable. However, if the heatsink has a TDP much larger than the processor TDP, then this is even good, because cooler capacities will be enough with surpluses to carry out its work.
If the manufacturer did not specify the TDP cooler, then you can find out by “google” the request on the network, but this rule applies only to popular models.
Design features
The design of coolers varies greatly depending on the type of radiator and the presence / absence of special heat pipes. There are also differences in the material from which the fan blades and the radiator itself are made. Basically, the main material is plastic, but there are also models with aluminum and metal blades.
The most budgetary option is a cooling system with an aluminum radiator, without copper heat-conducting pipes. Such models differ in small dimensions and low price, but are poorly suited for more or less productive processors or for processors that are planned to be overclocked in the future. Often comes with a CPU. The difference in the shapes of the heatsinks is noteworthy - for CPUs from AMD, the heatsinks are square in shape, and for Intel round.

Coolers with radiators from precast plates are almost outdated, but still sold. Their design is a radiator with a combination of aluminum and copper plates. They are much cheaper than their analogues with heat pipes, while the cooling quality is not much lower. But due to the fact that these models are outdated, it is very difficult to choose a socket suitable for them. In general, these radiators no longer have significant differences from all-aluminum counterparts.
A horizontal metal radiator with copper tubes for heat dissipation is one of the types of inexpensive, but modern and efficient cooling system. The main drawback of designs where copper tubes are provided is the large dimensions that do not allow installing such a design in a small system unit and / or on a cheap motherboard, as that can break under her weight. Also, all the heat is removed through the tubes towards the motherboard, which, if the system unit has poor ventilation, reduces the efficiency of the tubes to nothing.

There are more expensive varieties of radiators with copper tubes that are installed in a vertical position rather than a horizontal one, which allows them to be mounted in a small system unit. Plus, the heat from the tubes goes up, and not towards the motherboard. Coolers with copper heat sink tubes are great for powerful and expensive processors, but they also have higher socket requirements due to their size.

The efficiency of coolers with copper tubes depends on the number of the latter. For processors from the middle segment, whose TDP is 80-100 watts, models with 3-4 copper tubes are perfect. For more powerful processors at 110-180 watts, models with 6 tubes are already needed. In the characteristics, the number of tubes is rarely written to the radiator, but they can easily be determined from the photo.
It is important to pay attention to the base of the cooler. Models with a through base are the cheapest, but dust is quickly clogged into the radiator connectors, which is difficult to clean. There are also cheap models with a solid base, which are more preferable, albeit a little more expensive. It is even better to choose a cooler, where in addition to the solid base there is a special copper insert, because it greatly increases the efficiency of low-cost radiators.

In the expensive segment, radiators with a copper base or direct contact with the surface of the processor are already used. The effectiveness of both is completely identical, but the second option is smaller and more expensive.
Also, when choosing a radiator, always pay attention to the weight and dimensions of the structure. For example, a tower-type cooler with copper tubes that extend upward has a height of 160 mm, which makes it difficult to place it in a small system unit and / or on a small motherboard. The normal weight of the cooler should be about 400-500 g for mid-range computers and 500-1000 g for gaming and professional machines.

Fan Features
First of all, pay attention to the size of the fan, because noise level, ease of replacement and quality of work depend on them. There are three standard size categories:
- 80 × 80 mm. These models are very cheap and easy to replace. They can be mounted even in small cases without problems. Usually they come with the cheapest coolers. They make a lot of noise and are not able to cope with the cooling of powerful processors;
- 92 × 92 mm is already the standard fan size for the average cooler. They are also easy to install, produce less noise and are able to cope with cooling processors of the middle price category, but they cost more;
- 120 × 120 mm - fans of this size can be found in professional or gaming machines. They provide high-quality cooling, produce not too much noise, it is easy for them to find a replacement in the event of a breakdown. But at the same time, the price of a cooler that is equipped with such a fan is much higher. If a fan of such dimensions is bought separately, then there may be some difficulties with installing it on a radiator.
There may still be fans of 140 × 140 mm and larger, but this is for TOP gaming machines, on which the processor has a very high load. Such fans are difficult to find on the market, and their price will not be affordable.
Pay particular attention to bearing types as the noise level depends on them. There are three of them:
- Sleeve Bearing is the cheapest and most reliable sample. A cooler having such a bearing in its design also produces too much noise;
- Ball Bearing - a more reliable ball bearing, costs more, but also does not differ in low noise;
- Hydro Bearing is a combination of reliability and quality. Has a hydrodynamic design, practically does not produce noise, but is expensive.
If you do not need a noisy cooler, then pay extra attention to the number of revolutions per minute. 2000-4000 rpm make the noise of the cooling system perfectly distinguishable. In order not to hear the computer, it is recommended to pay attention to models with a speed of about 800-1500 per minute. But at the same time, keep in mind that if the fan is small, then the speed of rotation should vary between 3000-4000 per minute, so that the cooler copes with its task. The larger the fan, the less it should do revolutions per minute for normal cooling of the processor.
It is also worth paying attention to the number of fans in the design. In budget options, only one fan is used, and in more expensive ones there can be two or even three. In this case, the rotation speed and noise production can be very low, but there will be no problems in the quality of the processor cooling.

Some coolers can adjust the fan speed automatically, based on the current load on the CPU cores. If you choose such a cooling system, then find out if your motherboard supports speed control through a special controller. Pay attention to the presence of DC and PWM connectors in the motherboard. The required connector depends on the type of connection - 3-pin or 4-pin. Cooler manufacturers indicate in the specifications the connector through which the connection to the motherboard will take place.
In the specifications for the coolers, they also write the item “Airflow”, which is measured in CFM (cubic feet per minute). The higher this indicator, the more efficiently the cooler copes with its task, but the higher the level of noise produced. In fact, this indicator is almost the same as the number of revolutions.
Mount to motherboard
Small or medium coolers are mainly fastened with special latches or small screws, which avoids a number of problems. In addition, detailed instructions are attached, where it is written how to fix and which screws to use for this.

Things will be more difficult with models that require reinforced mounting, as in this case, the motherboard and the computer case must have the necessary dimensions to install a special pedestal or frame on the back of the motherboard. In the latter case, the computer case should not only have enough free space, but also a special recess or window that allows you to install a large cooler without any problems.

In the case of a large cooling system, the means by which and how you will install it depends on the socket. In most cases, these will be special bolts.
Before installing the cooler, the processor will need to be lubricated with thermal grease in advance. If there is already a layer of paste on it, then remove it with a cotton swab or a disk dipped in alcohol and apply a new layer of thermal paste. Some cooler manufacturers put thermal grease in the kit with the cooler. If there is such a paste, then apply it; if not, then buy it yourself. No need to save on this point, it’s better to buy a tube of high-quality thermal paste, where there will still be a special brush for applying. Expensive thermal grease lasts longer and provides better processor cooling.

List of Popular Manufacturers
The following companies are most popular in the Russian and international markets:

Also, when buying a cooler, do not forget to clarify the availability of a guarantee. The minimum warranty period must be at least 12 months from the date of purchase. Knowing all the features of the characteristics of coolers for the computer, it will not be difficult for you to make the right choice.
A lot of articles have been written on the topic of how to decide on the choice of a cooler for a processor, both useful and not very practical and theoretical. The selection of models in stores is huge, they differ in design, size, cooling efficiency and price. Moreover, thanks to the efforts of marketers, the latter parameters are not always identical.
There are times when a super-looking, painted, and highly-advertised supercool shows average performance. There is also the opposite situation, when the manufacturer of the middle hand produces a very successful model. Therefore, when choosing, it is worth considering the various elements of the system from all sides, and only after a thorough analysis make a considered decision.
The main purpose of the cooler is the cooling of the processor, which occurs by removing heat from the processor cover and then dissipating it into the surrounding space. An important point in this case is such an indicator as the thermal conductivity of the radiator material.
Thermal conductivity is the movement of thermal energy in a material from a site with a higher temperature to a site with a lower temperature due to the movement of microparticles, or, one can say, this is simply the ability of an object to transfer heat. The best indicators of heat transfer in silver, however, it would be interesting to look at those who want to buy a cooling system from such a material
For the industrial manufacture of radiators, copper and aluminum are used, slightly inferior in characteristics. In general, an active cooler consists of a metal radiator attached to the processor cover and a fan. There are also passive models - they are without a fan. The fan many times increases the rate of heat dissipation. In no case should not be allowed!
Types of coolers for processors
Such devices can be classified relatively arbitrarily, given that until recently, some types were not produced at all. Having analyzed a lot of information on the Internet and the range of products offered, two large groups can be distinguished:
- Boxed coolers and without heat pipes are the simplest models consisting of an aluminum plate with fins, in some cases having a copper base and a fan attached to it. Often come with a processor for sale, they are called "boxed". They have limited cooling capabilities, but are easy to install, cope with their duties at the nominal processor frequencies. The fan is of poor quality, which is why, with an increase in the rotational speed of the blades, a computer with such a cooler may make additional noise.
- Heat pipes cooling systems - work by removing heat with the help of a fluid circulating in hollow tubes made of aluminum or copper. They have the best performance indicators, but they are often equipped with non-standard fasteners, some are heavy, equipped with fans of various quality.
The first cooling option should not be considered in detail. If you plan to work in normal mode, with a mid-range processor, without overclocking experiments, and the noise level is an uncritical indicator, you can be content with any simple cooler. In principle, it is possible to reduce the noise level if the fan speed is set correctly using the BIOS or.
The second version of coolers requires closer attention and has many additional characteristics that determine, ultimately, the choice of the buyer.
Heatpipe computer coolers
The first idea of \u200b\u200busing heat pipes to lower the temperature of refrigerated units was patented by the United States back in 1942. Its essence was that inside the pipes sealed on both sides there was a liquid substance that evaporated at the heating place, the steam moved to the cold zone, where it condenses, giving off thermal energy, forms a liquid again, which returns to the heating place.
They were used exclusively for industrial purposes, then they did not think about any high-performance computers. The tubes can be without a filler inside, then they must be directed upward so that the condensate drains under the influence of gravity, or with a porous structure, in this case the shape of the tubes does not play a role, and the liquid circulates due to pores.
Now tube coolers occupy a large part of the market. Their device in general terms can be described as follows: there is a base (sole) of the cooler pressed to the processor, tubes are soldered into it, on which aluminum plates are worn, which contribute to heat dissipation. Conventionally, such products can be divided into various subspecies:
- With direct contact, when the tube directly interacts with the heat-distributing cover of the processor;
- Without direct contact, when only the cooler base interacts with the processor.
Which species is better is difficult to say. The majority of users claim that direct contact is more effective. From practice, we can say that the alternative option copes very well with its functions. Here it is necessary to take into account the fact that the working fluid begins to evaporate only at a certain temperature, from 25 to 50 degrees. That is, until this moment, heat removal occurs only due to the metal parts of the radiator, and the base serves as the main heat sink.