(about 287 - 212 BC)
Archimedes was one of the most remarkable scientists in ancient Greece. You've probably heard the legend about how one of the laws of physics was discovered.
Once, immersed in a bath in a bath, Archimedes noticed that with his body he displaced some of the water and it splashed out, and at the same time the water seemed to support him. The scientist immediately realized that this was the solution to the problem that tormented him. Shouting "Eureka!" (Found! ") He jumped out of the bath and rushed down the street: he was impatient to make calculations. This is how the famous Archimedean law of buoyancy force was discovered. This man built unprecedented throwing war machines to defend the city of Syracuse on the island of Sicily (where he was and lived), which sowed panic and terror in the ranks of the Roman legionnaires and put them to flight.He also came up with a way to set fire to enemy ships - with the help of thousands of large mirrors held by the soldiers of the besieged city. These mirrors the sunbeams were focused into a single beam , which ignited the enemy's ships.
The parallelogram of forces or speeds, which they talk about in physics lessons, is also an invention of Archimedes. The theory of simple mechanisms, developed by the great scientist, led to the development of important branches of mechanics. The Archimedes screw is used in various machines, serves to lift bulk cargo, and moves parts in factories. The huge (at that time) ship "Syrakosia" was launched using a block system controlled by one warrior. The Archimedean rule of the lever is now sometimes called the golden rule of mechanics. And it is to him that the legend attributes the words: "Give me a fulcrum, and I will turn the world!"
It is somewhat less known that Archimedes was not only a remarkable mechanic and physicist, but also a brilliant mathematician. What did he do in this area of knowledge, what thoughts and theories of his entered the golden fund of science today? Here, first of all, it is necessary to say about the calculation of lengths. It is known that the length of a circle with a radius R is equal to 2? R, where? - some number, slightly more than 3. This can be seen from considering a regular inscribed hexagon: its perimeter is 6R, and the circumference is slightly larger! How to calculate the value more precisely ?? It was Archimedes, in his elegant study related to the examination of inscribed and described polygons, who gave a remarkable estimate of the number n for his time. He found this number to be between 3 10/71 and 3 1/7. Equip yourself with a micro calculator and you will easily find that these numbers are written as 3.140845 and 3.142857. Thus, an approximate value was found by Archimedes? ? 3.14, which we still use for calculations with not very high accuracy.
Another remarkable discovery by Archimedes, also connected with the measurement of lengths. You want to measure the length of the bench as accurately as possible. You first determine how many times a meter is laid on the bench; if there is a remainder, you will find out how many decimeters it contains; if there is a remainder again, find how many centimeters, millimeters there are. Such a measurement process was logically investigated by Archimedes, who in this connection formulated an axiom, which is now called the Archimedes axiom. It consists in the fact that by taking some segment (unit of measurement) and postponing it on another segment (no matter how large it is), after a certain number of postponements we will definitely reach the end of the measured segment and "jump" over its end. Isn't it so obvious that it seems there is no need to talk about this trifle ?! But an amazing thing! It is the axiom of Archimedes that is now especially exciting the minds of scientists. We are now talking more and more often about "non-Archimedean" geometry, about "non-Archimedean" systems of numbers, about "non-Archimedean" analysis. The fact that Archimedes was able to isolate and formulate precisely such an axiom, which is important and relevant today, in hoary antiquity, testifies to his great insight and scientific foresight. Another discovery of Archimedes is associated with the measurement of areas. Solving the problem of how to construct a segment, the length of which is equal to the circumference of a given circle, the scientist calculated the ratio of the circumference to the diameter and found that it is enclosed 3 10/71 and 3 1/7. The method he created for calculating the circumference and area of a figure, with the help of which he obtained the result, anticipates the ideas of a special integral calculus, discovered (two millennia after Archimedes!) By two other geniuses - I. Newton and G.V. Leibniz. It was Newton, who knew the work of Archimedes well and relied on them, who explained his scientific achievements by the fact that he "stood on the shoulders of giants." There are many important discoveries in the scientific heritage of Archimedes. He established the theorem that the three medians of a triangle intersect at one point; found remarkable properties of the curve, which is now called the Archimedes spiral; calculated the volume of the ball; created a formula for the sum of a decreasing geometric progression. There is a legend that the Roman warrior conqueror stepped on the blueprints that Archimedes made on the wet sand. "Don't you dare touch my blueprints!" - exclaimed the scientist. The Roman soldier had no idea that he was a genius, whose glory would survive for millennia. He pierced the scientist with a sword. Bleeding, Archimedes fell on his drawings, possibly concluding a new discovery.
Module I. Principles of operation and components of a personal computer
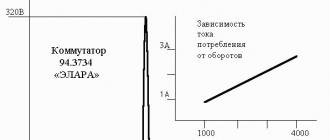
1. In accordance with the classification of parallel architectures, computers built according to the von Neumann principles are classified as a computing system with the first processor
2. The expansion slots can be connected to video cards, sound cards, network cards, post cards
3. Regeneration is an attribute of dynamic random access memory
4. The resolution of the monitor is the size of the image obtained on the screen in pixels.
5. Harvard computing system architecture differs from Princeton Harvard has a single memory and print several
6. The main characteristics of the microprocessor include the amount of RAM clock frequency
7. Programs for initial testing and computer boot are stored in the internal memory of the computer.
8. To the main characteristics of the monitor relate response time viewing angle contrast brightness diagonal size
9. The minimum set of devices required for the operation of each computer architecture von Neumann, includes a system unit keyboard and mouse
10. An intermediate buffer with fast access, containing a copy of the information that is stored in memory with less fast access, but is most likely to be requested from there, is called a cache
11. A plotter is a device used for automatic deletion of graphic images with high precision.
12. The main components of computer networks include the communication channel nodes
13. Processors based on x86 instructions, up to Pentium 4, had ________cisc_ architecture.
14. The system bus includes a set of connectors for connecting devices
15. The fastest memory is RAM
16. Image registration can be provided by scanners
17. One of the physical input-output channels of a computer - a connector - is called a hardware carrier.
18. The characteristic of the scanner, which determines the quality of the resulting digital images, is the number of dots per inch.
19. A processor architecture based on the concept of "smaller and simpler instructions run faster" is the _print_ _______ architecture.
20. Devices for coordinate data input include a joystick mouse
21. The basic PC configuration includes the system unit keyboard mouse
22. USB flash drives use electronic memory
23. The logical organization and structure of hardware and software resources of the computing system is the system unit
24. It is true that the mouse is a cord input device.
25. One of the parameters of the hard drive is the capacity
26. Characteristic of liquid crystal monitors PC is the type of matrix
27. Functional diagram of the computer 
was suggested by Neumann
28. On the motherboard of the PC is placed the processor RAM RAM
29. The principle of recording on rewritable optical CDs is ...
30. RAM refers to the type of memory ...
31. Printer resolution is ...
32. In the von Neumann computer architecture, the part of the processor that executes instructions is called ...
33. To devices only withdrawal information include ...
34. To the principles of the computing system, formulated by John von Neumann, relate principles ...
35. External storage devices are hard disk
36.1 GB contains _1024_______ bytes.
37. The main characteristic of the microprocessor is the clock frequency
38. By the type of computing process, computing facilities are subdivided into digital
39. To the main characteristics of the microprocessor relate clock frequency
40. The unit denoted as dpi, characterizes the indicator of the allowed ability
41. To store the programs required to start and test the computer when it is turned on, you need a ROM
42. For scans with acceptable color quality and good detail at home, ____________ and _____________ types of scanners are used.
43. An electronic computer (ECM) is ...
44. From CDs for the user to burn their files intended …
45. The principle of changing the magnetic induction of the carrier surface is used in drives of the type ...
46. For long-term storage of information intended …
47. The possibility of data exchange between computers via regular telephone lines is provided by ...
48. The largest amount of information can be stored (type of memory) ...
49. Ribbon use is at the heart of ____________ and ____________ printers.
50. Information input devices include ...
51. To computer hardware relate…
52. Peripheral devices perform the function ...
53. The EPROM electronic microcircuit is ...
54. To display bitmap (raster) images created by the user, you can use ...
55. To increase the speed of performing mathematical operations in the PC is used ...
56. CCDs are used in peripherals such as ...
57. In an empty block of the general scheme of the computer it is necessary to write the device ... 
58. High-speed memory, which belongs to any functional block of the computer and serves to reduce the load on the main memory, is called ...
59. Among computer architectures, one can distinguish ...
60. The architecture of a modern personal computer implies such a logical organization of hardware components of a computer, in which ...
61. As you know, the bitness of the processor is determined by the bitness of the registers in which the processed data is placed. If the register has a width of 4 bytes, then the processor capacity is ...
62. Parameters such as resolution and performance are characteristic of ...
63. At runtime, the application is stored in ...
64. He combined the idea of a mechanical machine with the idea of programmed control ...
65. The parameters of any type of computer memory are ...
66. The quality of the sound digitized by a sound card is determined by such parameters as ...
67. The principle of homogeneity of memory is that ...
68. Signals that determine the nature of the exchange of information are transmitted over the bus ...
69. Parameters such as resolution and viewing angle are specific to devices ...
70. The main components of the architecture of a personal computer are the processor, internal memory, video system, input-output devices, ...
71. A computer with a 64-bit data bus and a 32-bit address bus has 16 MB of memory. The bit depth of this processor is ...
72. The main parameters of laser printers are ...
73. The speed of the storage device is characterized by ...
74. To the command system of electronic computers do not apply …
75. The internal memory of the processor is _______________ memory.
76. To the provisions of classical architecture (von Neumann) relate …
77. Printers are ...
78. To the functions of the processor relate …
79. The hardware connection of peripheral devices involves ...
80. Direct memory access (DMA) is a mode in which ...
81. The bit depth of the central processor is determined ...
82. BIOS (Basic Input Output System) is ...
83. To enter bitmaps, you can use ...
84. Flash drives use ____________ memory.
85. A computer with a 64-bit data bus and a 32-bit address bus has 16 MB of memory. Based on the data of this configuration, it can be argued that the processor ...
86. The main parameters of flatbed scanners include ...
87. The highest speed of information exchange is ...
88. In the mode creation sound in the sound card uses the methods ...
89. When you turn off the power of the computer, information not saved in the memory device ...
90. PC architecture, the main features of which are the presence of a common information bus, modular construction, compatibility of new devices and software with previous versions on a "top-down" basis, is called ...
91. The classical principles of computer architecture were proposed in the 40s of the twentieth century by J. von Neumann. To these principles relate…
92. Modems are ...
93. Long-term storage of user information provides ...
94. Dynamic memory serves as the basis for building ...
95. Information on magnetic disks is recorded ...
96. For the processor to execute the program, it must be ...
97. A streamer is a device for ...
98. The division into lanes and sectors is typical for ...
99. Static memory serves as a base for building ...
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
Stavropol Technological Institute of Service
Branch of YURGUES
Test
topic___________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
by discipline Informatics
Completed by a student of group IST 031 ZU _______________ ""
Checked by Ph.D., Associate Professor _______________ ""
Stavropol 2003
Introduction ................................................. ...............................................
1. Types of magnetic disk drives .........................................
2. Floppy disk drives .......................................
3. Hard disk drives .....................................
Conclusion................................................. ...........................................
Sources of information used ..............................................
Introduction.
Produced data storage devices represent a range of storage devices with different operating principles, physical and technical performance characteristics. The main property and purpose of information storage devices is its storage and reproduction. Memory devices are usually divided into types and categories in connection with their principles of operation, operational, technical, physical, software and other characteristics. So, for example, according to the principles of functioning, the following types of devices are distinguished: electronic, magnetic, optical and mixed - magneto-optical. Each type of device is organized on the basis of a corresponding technology for storing / recording digital information. Therefore, in connection with the type and technical performance of the information carrier, they are distinguished: electronic, disk and tape devices. Let's pay special attention to magnetic disk drives - hard disk drives.
1. Types of drives on magnetic disks
Magnetic disks are used as storage devices that allow you to store information for a long time, when the power is off. To work with Magnetic Disks, a device called a magnetic disk drive (MRD) is used.
The main types of drives:
· Floppy disk drives (floppy disk drives);
· Drives on hard magnetic disks (HDD);
· Magnetic tape drives (NML);
· Drives CD-ROM, CD-RW, DVD.
They correspond to the main types of carriers:
Floppy magnetic disks ( Floppy disk) (3.5 '' diameter and 1.44 MB capacity; 5.25 '' diameter and 1.2 MB capacity also discontinued)), removable media disks;
Hard magnetic disks ( Hard disk);
· Cassettes for streamers and other NML;
CD-ROMs, CD-Rs, CD-RWs, DVDs.
Memory devices are usually divided into types and categories in connection with their principles of operation, operational, technical, physical, software and other characteristics. So, for example, according to the principles of functioning, the following types of devices are distinguished: electronic, magnetic, optical and mixed - magneto-optical. Each type of device is organized on the basis of a corresponding technology for storing / reproducing / recording digital information. Therefore, in connection with the type and technical performance of the information carrier, they distinguish: electronic, disk and tape devices.
Main characteristics of drives and media:
· Information capacity;
· Speed of information exchange;
· Reliability of information storage;
· price.
Let's take a closer look at the above drives and media.
Principle of operation magnetic storage devices based on methods of storing information using the magnetic properties of materials. As a rule, magnetic storage devices consist of the actual devices for reading / writing information and magnetic carrier, to which, directly write and from which information is read. It is customary to divide magnetic storage devices into types in connection with performance, physical and technical characteristics of the information carrier, etc. The most commonly distinguished are: disk and tape devices. The general technology of magnetic storage devices consists in magnetizing sections of the carrier with an alternating magnetic field and reading information encoded as areas of variable magnetization. Disc media are typically magnetized along concentric fields - tracks located across the entire plane of a discoidal rotating media. Recording is made in a digital code. Magnetization is achieved by creating an alternating magnetic field using the read / write heads. The heads are two or more magnetic controllable circuits with cores, the windings of which are supplied with alternating voltage. A change in the voltage value causes a change in the direction of the lines of the magnetic induction of the magnetic field and, when the carrier is magnetized, means a change in the value of the information bit from 1 to 0 or from 0 to 1.
Typically, NMI consists of the following parts:
- floppy controller
- the actual drive,
- interface cables,
- magnetic disk
The magnetic disk is a magnetically coated base that rotates about an axis inside the disk drive.
The magnetic coating is used as a storage device.
Magnetic Disks are available: hard (Winchester) and flexible (Floppy).
Hard disk drive - hard disk drive (HDD).
Floppy disk drive - floppy disk drive (FDD).
In addition to hard disk drives and floppy drives, removable media are often used. Zip is a fairly popular drive. It is available as built-in or stand-alone units that connect to the parallel port. These drives can store 100 MB and 250 MB of data on cartridges that resemble a 3.5 '' floppy disk, provide 29 ms access times and transfer rates up to 1 MB / s. If the device is connected to the system through the parallel port, then the baud rate is limited by the speed of the parallel port.
The Jaz drive is a type of removable hard disk drive. The capacity of the cartridge used is 1 or 2 GB. The disadvantage is the high cost of the cartridge. The main application is data backup.
In tape drives (most often such devices are streamers) recording is made on mini-cassettes. The capacity of such cassettes is from 40 MB to 13 GB, the data transfer rate is from 2 to 9 MB per minute, the length of the tape is from 63.5 to 230 m, the number of tracks is from 20 to 144.
2. Floppy disk drives.
Floppy disks(floppy disks, floppy disks) allow you to transfer documents from one computer to another, store information. The main disadvantage of the drive is its small capacity (only 1.44 MB) and unreliable storage of information. However, this method is the only way for many Russian users to transfer information to another computer. On computers of the last years of release, floppy disk drives with a size of 3.5 inches (89mm) are installed. Previously, 5.25-inch drives were used. They, in spite of their size, have less capacity and are less reliable and durable. Both types of floppy disks are write protected (jumper on the protective casing of the floppy disk). Recently, alternative devices have begun to appear: external drives, with disks with a capacity of up to 1.5 GB and a much faster read speed than a floppy drive, but they are still not widely used and are very expensive.
Removable floppy disk drive. The floppy disk has a plastic base and is in a special plastic casing. The floppy disk is inserted into the FDD along with the casing. The floppy disk (in the FDD) spins inside the casing at 300 rpm. At the moment, the IBM PC uses 2 types of FDDs: 5.25 "and 3.5". The 5.25 "floppy disk is enclosed in a flexible plastic casing. The 3.5" floppy disk is enclosed in a rigid plastic casing. HDDs are faster devices than FDDs.
A floppy disk or floppy disk is a compact, low-speed, low-capacity means of storing and transferring information. There are two sizes of floppy disks: 3.5 ”, 5.25”, 8 ”(the last two types are practically out of use).
3.5 "floppy disk 5.25" floppy disk
Structurally, a floppy disk is a magnetic-coated floppy disk enclosed in a case. The floppy disk has a hole for the drive pin, a hole in the case for accessing the read-write heads (3.5 ”is covered with an iron shutter), a cutout or a write protection hole. In addition, a 5.25 "floppy disk has an index hole, and a 3.5" high density floppy disk has a specified hole density (high / low). The 5.25 ”floppy disk is write-protected if the corresponding slot is closed. The 3.5 ”floppy disk is reversed - if the protection hole is open. Currently, 3.5 ”high density floppy disks are practically only used.
The following conventions are used for floppy disks:
SS single side - single sided disc (one work surface).
DS double side - double sided disc.
SD single density - single density.
DD double density - double density.
HD high density - high density.
A floppy drive is fundamentally similar to a hard drive. The rotational speed of the floppy disk is about 10 times slower and the heads touch the surface of the disk. Basically, the structure of information on a floppy disk, both physical and logical, is the same as on a hard disk. From a logical structure point of view, there is no disk partitioning table on the floppy disk.
Work of the controller NGMD it is convenient to consider separately in the modes of writing and reading a data byte.
The recording mode is turned on by the low level of the PC0 line (pin 14 of DD1). In this case, the floppy disk drive is switched to the "Record" mode (the WRDATA signal is active). The byte to be written is entered into port A and its eight-bit code is fed to the input of the multifunctional register DD2. The operating mode of this register is controlled by the DD9 bit counter and DD10 decoder. After writing the previous byte, the counter is in the reset state, and logic zero signals are present at all of its outputs. With this state of the input signals, the decoder DD10 at pin 7 generates a logical zero signal, which, together with a low level at pin 2 of DD17.1, allows writing parallel code to register DD2. Any other state of the counter puts the register into shift mode.
Low PC0 level on element DD13. 4, the channel for reading information from the RDDATA floppy disk is blocked. A logical zero, arriving at the S inputs of the DD11.1 flip-flop after the blocking signal is inverted by the DD14.1 element, sets a logical one at pin 5 of the DD11.1 flip-flop. Through the DD14.3 inverter, a low level signal is sent to the reset inputs of the DD7 and DD8 counters, which ensures their continuous operation. The signals taken from the 8th and 9th outputs of the DD8 counter on the elements DD14.4, DD15.1, DD15.2 form the ISS and ISD sequences, respectively. The ISD pulse, after being inverted by the DD14.6 element, is fed to the clock input of the DD2 register. When a clock pulse arrives, the parallel code written to the register is shifted to the right, and the next bit of this code appears at pin 20. Recording signals are formed by elements DD13.1, DD13.2 and DD13.3. At the moment of action of the high level of the ISD on pin 2 of DD13.1 there is a write bit. Through the elements DD13.1 and DD13.2, the bit is fed to the input of the buffer amplifier DD6, and then to the recording signal line of the floppy disk drive (WRDATA). According to the timing diagram shown in Fig. 8, the CCIS signal is at this time in a state of logical zero. Therefore, the passage of signals through the element DD133 is prohibited. After the ISD signal goes to the state of logical zero, the passage of the information bit for writing through the element DD13.1 will become impossible. When the ISS level is active through the open elements DD13.3, DD13.2 and the DD6 buffer, a logical unit formed at pin 12 of the DD10 decoder will be sent to the WR DATA line. Thus, at the moment of the ISD action, information bits will be received on the recording line of the floppy disk drive, and at the moment of the ISS action, single synchrobits will be received. The counting of the number of written bits is kept by counter DD9. After the passage of the eighth pulse of the ISD, its outputs will go to the zero state, which will cause the readiness trigger to be set: a logical unit will appear on pin 9 of DD12.2. The state of the readiness trigger is programmatically interrogated by the DOS through the PB7 line. When a unit is found in this bit, the PC will write a new byte to port A DD1 (address F000H), while on the elements DD15.4, DD16.4, DD16.1, DD16.2, a reset trigger ready signal will be generated. Thus, the recording and reading of information on the floppy disk drive takes place.
3. Hard disk drives (HDD)
Hard disk drives (hard drives) are intended for permanent storage of information used when working with a computer: operating system programs, frequently used software packages, document editors, translators from programming languages, etc. The presence of a hard disk significantly improves the convenience of working with a computer. For the user, drives not on a hard disk differ from each other, first of all, in their capacity, i.e. by how much information fits on the disk. Now computers are mainly equipped with hard drives of 520 MB or more. Computers that work as file servers can be equipped with a 4 - 8 MB hard drive and more than one.
The drive on a non-removable magnetic disk, created on the basis of special. technology (Winchester technology - hence the name). The Winchester magnetic disk (on a metal base) has a high recording density and a large number of tracks. A Winchester can have several Magnetic Disks. Hard disk drives of Winchester type were created in 1973. All Winchester magnetic disks (combined in a disk package) are hermetically sealed in a common casing. Magnetic disks can NOT be removed from the HDD and replaced with similar ones !!!
The magnetic heads are combined into a single unit (magnetic head unit). This block moves radially in relation to the discs. While the PC is running, the Disk Pack rotates at a constant speed (3600 rpm) all the time. When reading / writing information, the block of magnetic heads is moved (positioned) to a predetermined area, where sector-by-sector information is read / written. Due to the inertia of the information processing process and the high rotation speed of the disk package, a situation is possible when the block of magnetic heads does not have time to read the next sector. To solve this problem, the method of alternating sectors is used (sectors are numbered not in order, but with gaps). For example, instead of numbering the sectors in order: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ..., they are numbered as follows: 1 7 13 2 8 14 3 9 ...
Recently, more high-speed SCSI controllers have appeared, which provide sufficient processing speed, and there is no need for sector interleaving.
So, the drive contains one or several disks (Platters), i.e. it is a carrier that is mounted on an axis - a spindle driven by a special motor (part of the drive). The engine speed for conventional models is about 3600 rpm. It is clear that the higher the rotation speed, the faster the information is read from the disk (of course, at a constant recording density), however, the plates of the carrier at high speeds can simply physically collapse. Nevertheless, in modern models of hard drives, the rotation speed reaches 4500, 5400 or even 7200 rpm.
The discs themselves are precision-machined ceramic or aluminum plates, on which a special magnetic layer (coating) is applied. In some cases, even glass plates are used. It should be noted that in recent years, the manufacturing technology of these parts has gone far ahead. In older drives, the magnetic coating was usually iron oxide. Currently, gamma ferrite oxide, isotropic oxide and barium ferrite are used for coatings, but the most widespread are discs with a sprayed magnetic layer, or rather, with a metal film (for example, cobalt).
The number of disks can be different - from 1 to 5 and more, the number of working surfaces is correspondingly 2 times more, however, not always. Sometimes the outer surfaces of the outer disks or one of them are not used for storing data, while the number of working surfaces is reduced and may turn out to be odd.
The most important part of any storage device is the read / write head. They are usually located on a special positioner that resembles a pickup lever on a turntable (tonearm). This is the head actuator. By the way, there are also linear positioners, which in their principle of movement resemble tangential tonearms.
Currently, at least several types of heads used in hard drives are known: monolithic, composite, thin-film, and magneto-resistance (MR). Monolithic heads are usually made of ferrite, which is a fairly brittle material. In addition, the design of such heads fundamentally does not allow high recording densities. Composite heads are smaller and lighter than monolithic ones. This is usually glass on a ceramic base; for example, alloys are used that include materials such as iron, aluminum and silicon. Ceramic heads are more durable and provide a closer distance to the magnetic surface of the media, which in turn leads to an increase in recording density. In the manufacture of thin-film heads, the photolithography method is used, which is well known to the semiconductor industry. In this case, a layer of conductive material is deposited on the non-metallic substrate.
Magnetic-resistive heads developed by IBM are considered one of the most promising at present. Fujitsu and Seagate also began their production. The actual magneto-resistive head is an assembly of two heads: a thin-film head for recording and a magneto-resistive head for reading. Each of the heads is optimized for its own task. It turns out that a magnetoresistive head is at least three times more efficient than a thin-film head when reading. If the thin-film head has a conventional inductive operating principle, i.e. an alternating current generates a magnetic field, then in a magnetically resistive (by definition) change in the magnetic flux changes the resistance of the sensitive element. Magnetic resistive heads in comparison with others allow to increase the recording density on the medium by almost 50%. All modern hard drives from IBM are equipped with only these heads. New developments from IBM in the field of hard drives allow for a recording density of 10 Gbps per square inch, which is about 30 times higher than today. We are talking about Giant MR-heads.
Note that in modern hard drives the heads seem to "fly" at a distance of a fraction of a micron (usually about 0.13 microns) from the surface of the disks, without touching them. By the way, in hard drives produced in 1980, this distance was another 1.4 microns, in perspective models it is expected to decrease to 0.05 microns.
On the first models of hard drives, the head positioner was usually moved using a stepper motor. Currently, for this purpose, mainly linear (of the type voice coil, or "voice coil") motors, otherwise called hydrochloric ones, are used. Their advantages include a relatively high speed of movement, practical insensitivity to changes in temperature and position of the actuator. In addition, when using hydrochloric motors, automatic parking of the read / write heads is realized when the hard drive power is turned off. Unlike drives with a stepper motor, there is no need to periodically reformat the surface of the media.
The drive of the head movement is a closed servo system, for the normal functioning of which pre-recorded servo information is required. It is she who allows the positioner to constantly know his exact location. For recording in servo information, the positioning system can use dedicated and / or working surfaces of the medium. Depending on this, a distinction is made between dedicated, embedded and hybrid servo systems. Dedicated systems are quite expensive, but they have high performance, since they practically do not waste time for receiving servo information. Built-in servo systems are significantly cheaper and less critical to mechanical shock and temperature fluctuations. In addition, they allow you to save more useful information on disk. However, such systems are generally slower than dedicated systems. Hybrid servo systems take advantage of the two above, i.e. large capacity and high speed. Most modern hard drives for mass use use built-in servo information.
In addition to all of the above, inside any hard drive there is necessarily a printed circuit board with electronic components that are necessary for the normal functioning of the drive device. For example, the electronics decode the commands of the hard disk controller, stabilize the rotation speed of the engine, generate signals for the write heads and amplify them from the read heads, etc. Currently, a number of hard drives even use digital signal processors DSP (Digital Signal Processor).
An indispensable component of most hard drives are special internal filters. For obvious reasons, the frequency of the ambient air is very important to the operation of hard drives, since dirt or dust can cause the head to hit the drive, which will definitely lead to its failure.
As you know, for the installation of disk drives in the system unit of any personal computer, special mounting bays are provided. The overall dimensions of modern hard drives are characterized by the form factor. The form factor indicates the horizontal and vertical dimensions of the hard drive. Currently, the horizontal size of a hard disk can be defined by one of the following values: 1.8; 2.5; 3.5 or 5.25 inches (the actual size of the hard drive case is slightly larger). The vertical size is usually characterized by parameters such as Full Height (FH), Half-Height (HH), Third-Height (or Low-Profile, LP). "Full" drives have vertical dimensions over 3.25 "" (82.5 mm), "half" - 1.63 "" and "low-profile" - about 1 "". It must be remembered that to install a drive that has a smaller form factor than the mounting bay in the system unit, you will have to use special mounts.
Conclusion
The development of the electronic industry is carried out at such a rapid pace that literally in one year, today's "miracle of technology" becomes morally obsolete. However, the principles of the computer structure remain unchanged.
According to experts, soon the company will not equip personal computers with floppy drives - they will be replaced by USB drives with flash memory with a capacity of 16 megabytes, which are initially supposed to be installed on hi-end computers, and then, with a positive reaction from customers, on all desktops. ... Dell has already dropped floppy drives as standard in notebooks. Floppy drives have not been installed in Macintosh computers for five years.
CDs and DVDs may be at the forefront of storage technology, but the rather old-fashioned mechanical tape drives still play an important role in storing large amounts of information. Not only that, this role is so great that IBM scientists have developed a mechanism for writing 1 terabyte (which is 1 trillion bytes of data) on a linear digital tape cartridge. This figure, according to the developers, is about 10 times more than any other tape drive currently available. This amount of information is equivalent to 16 days of continuous DVD-video playback, or 8,000 times more than the amount of information that the human brain retains throughout its entire life. Although it is difficult to imagine a tape drive in a home environment on desktop PCs, for medium and large businesses this technology remains quite relevant for data backup, moreover, tape is less vulnerable to hacking and information theft. The latest technology makes it possible to package the drive at a high data density so that it becomes quite compact. In the long term, it is possible to reduce the cost of data storage for companies. While the average cost of storing information on tape is currently around $ 1 per GB, it is possible that this cost can be reduced to 5 cents per GB. For comparison, the cost of storing 1 GB of information on a hard disk is now $ 8-10, and on devices based on semiconductors - about $ 100 per GB. New technologies for data storage on ML will take on an important role in such information-intensive industries as, for example, mining or archives. Also, the need to increase the amount of stored information arises from corporations and scientists in all disciplines, from geophysics to sociology. For example, academic pursuits require a system that allows long-term re-access to data, with the ability to create multiple copies and easily move them to any location. The first tape drive was invented 50 years ago, when the development of the IBM Model 726 could store only 1.4MB of information, about as much as now fits on a regular floppy disk, and the tape reel was about 12 inches in diameter. In comparison, the latest IBM development with 1TB storage capacity fits in a mail envelope-sized cartridge and contains the equivalent of 1,500 CDs. According to company representatives, the plan for a possible mass production of terabyte cartridges will include the release of intermediate products over several years. During this time, it is planned to release cartridges with a volume of 200,400, and then 600GB.
The researchers managed to make a magnetic film from an alloy of cobalt, chromium and platinum. Then, using a focused ion beam, they cut the film into rectangular magnetic "islands" measuring only 26 millionths of a millimeter across. This corresponds to a recording density of 206 GB per square inch. However, in this case it will not be possible to write and read information directly, since the size of the heads is much larger than the size of the "islands". Hence, newer, more miniaturized heads are needed. In addition, efficient synchronization of read and write procedures with head movement will be required. A prototype developed by IBM implements such synchronization, but widespread adoption of such systems will require significant improvements in hard disk technology.
Sources of information used
1. Leontiev V.P. PC: universal user guide Moscow 2000.
2. Figurnov V.E. IBM PC for the user. ed. 5th S.-Peretburg, JSC "Koruna" 1994.
Tutoring
Need help exploring a topic?
Our experts will advise or provide tutoring services on topics of interest to you.
Send a request with the indication of the topic right now to find out about the possibility of obtaining a consultation.
External (long-term) memory
The main function of the external memory of a computer is the ability to store a large amount of information (programs, documents, audio and video clips, etc.) for a long time. A device that records / reads information is called drive, or disk drive, and information is stored on carriers(for example, floppy disks).
Magnetic principle of recording and reading information. In floppy disk drives (floppy disks) and hard disk drives (HDDs), or hard drives, information recording is based on the magnetization of ferromagnets in a magnetic field, information storage is based on the preservation of magnetization, and information reading is based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
In the process of recording information on flexible and hard magnetic disks, the head of a disk drive with a core made of soft magnetic material (low residual magnetization) moves along the magnetic layer of the hard magnetic medium (high residual magnetization). The magnetic head receives a sequence of electrical pulses (sequences of logical ones and zeros), which create a magnetic field in the head. As a result, the elements of the carrier surface are sequentially magnetized (logical unit) or not magnetized (logical zero).
In the absence of strong magnetic fields and high temperatures, the elements of the carrier can retain their magnetization for a long time (years and decades).
When reading information when the magnetic head moves over the surface of the carrier, the magnetized sections of the carrier cause current pulses in it (the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction). Sequences of such pulses are transmitted through the highway to the computer's RAM.
Flexible magnetic disks. Flexible magnetic disks are housed in a plastic case. This storage medium is called a floppy disk. In the center of the disk there is a device for gripping and rotating the disk inside the plastic case. The diskette is inserted into a disk drive, which rotates the disk at a constant angular velocity.
In this case, the magnetic head of the disk drive is installed on a certain concentric track of the disk, on which the recording is performed or from which the information is read. The information capacity of the floppy disk is small and amounts to only 1.44 MB. The speed of writing and reading information is also low (only about 50 KB / s) due to the slow rotation of the disk (360 rpm).
In order to preserve information, flexible magnetic disks must be protected from the effects of strong magnetic fields and heating, since such physical influences can lead to demagnetization of the medium and loss of information.
Hard magnetic disks. A hard magnetic disk consists of several dozen disks located on one axis, enclosed in a metal case and rotating at a high angular velocity (Fig. 4.6).
Due to the much larger number of tracks on each side of the disks and the large number of disks, the information capacity of a hard disk can be hundreds of thousands of times larger than the information capacity of a floppy disk, and can reach 150 GB. The speed of writing and reading information from hard disks is quite high (it can reach 133 MB / s) due to the fast rotation of the disks (up to 7200 rpm).
 |
| Rice. 4.6. Hard magnetic disk |
Hard disks use rather fragile and miniature elements (media plates, magnetic heads, etc.), therefore, in order to preserve information and operability, hard disks must be protected from shocks and sudden changes in spatial orientation during operation.
Optical principle of recording and reading information. Laser CD-ROM and DVD-ROM drives use an optical principle to read and write information.
In the process of recording information on laser discs, various technologies are used to create surface areas with different reflection coefficients: from simple stamping to changing the reflectivity of the disk surface areas using a powerful laser. Information on a laser disc is recorded on one spiral track (like on a gramophone record), containing alternating areas with different reflectivity.
Subject to the rules of storage (in cases in an upright position) and operation (without causing scratches and dirt), optical media can retain information for tens of years.
In the process of reading information from laser disks, the laser beam installed in the disk drive falls on the surface of the rotating disk and is reflected. Since the surface of the laser disk has areas with different reflection coefficients, the reflected beam also changes its intensity (logical 0 or 1). Then the reflected light pulses are converted by means of photocells into electrical pulses and are transmitted through the line to the RAM.
Laser drives and discs. Laser drives (CD-ROM and DVD-ROM - Fig. 4.7) use the optical principle of reading information.
Laser CD-ROM (CD - Compact Disk) and DVD-ROM (DVD - Digital Video Disk) discs store information that was recorded on them during the manufacturing process. Writing new information to them is impossible, which is reflected in the second part of their names: ROM (Read Only Memory). Such discs are produced by stamping and have a silver color.
The information capacity of a CD-ROM disc can be up to 650 MB, and the speed of reading information in a CD-ROM drive depends on the rotation speed of the disc. The first CD-ROM drives were single-speed and provided a read speed of 150 KB / s. Currently, 52-speed CD-ROM drives are widely used, which provide 52 times faster information read speed (up to 7.8 MB / s).
DVDs have a much higher storage capacity (up to 17 GB) than CDs. First, lasers with a shorter wavelength are used, which allows the optical paths to be placed more densely. Secondly, information on DVDs can be recorded on two sides, with two layers on one side.
 |
| Rice. 4.7. CD-ROM and DVD-ROM |
The first generation of DVD-ROM drives provided a read speed of approximately 1.3 MB / s. Currently, 16-speed DVD-ROM drives achieve read speeds of up to 21 MB / s.
There are CD-Rs and DVD-Rs (R for recordable) that are golden in color. Information on such discs can be recorded, but only once. CD-RW and DVD-RW (RW - ReWntable, rewritable) discs, which are "platinum", information can be recorded many times.
For recording and rewriting onto discs, special CD-RW and DVD-RW drives are used, which have a powerful enough laser to change the reflectivity of surface areas during the disc recording process. Such drives allow you to write and read information from discs at different speeds. For example, labeling a CD-RW drive "40x12x48" means that it writes CD-R discs at 40x speed, writes CD-RW discs at 12x speed, and reads it at 48x speed.
Flash memory. Flash memory is a non-volatile type of memory that allows you to write and store data on microcircuits. Flash memory cards (Fig. 1.8) do not have any moving parts, which ensures high data safety when used in mobile devices (laptop computers, digital cameras, etc.).
 |
| Rice. 4.8. Flash memory cards |
Flash memory is a microcircuit housed in a miniature flat case. To read or write information, a memory card is inserted into special drives built into mobile devices or connected to a computer via a USB port. The information capacity of memory cards can be up to 512 MB.
The disadvantages of flash memory include the fact that there is no single standard and different manufacturers produce memory cards incompatible with each other in terms of size and electrical parameters.
Questions to Think About
1. What are the basic rules for storing and using various types of media?
Practical tasks
4.4. Compile a comparative table of the main parameters of information storage devices (capacity, exchange rate, reliability of information storage, storage price of one megabyte).
Long-term storage of user information is provided by OCD (external storage device). External memory includes: hard magnetic disks (HDD), floppy disk drives (floppy disk drives), magneto-optical CDs, optical drives, magnetic tape drives, etc.
The principle of changing the magnetic induction of the carrier is used in drives of the " Winchester"(HDD). Winchesters are designed for permanent storage of information used when working with a computer: operating system programs, frequently used software packages, document editors, etc. (fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Hard disk.
The main parameters of a hard drive (hard disk) are: disk capacity, number of surfaces, spindle rotation speed, built-in cache memory, interface.
Disk capacity . For the user, hard disk drives differ from each other primarily in their capacity, i.e. by how much information fits on the disk. Now computers are mainly equipped with hard drives of 80 GB or more.
Information on magnetic disks is recorded in concentric tracks and sectors, which are formed on the disk as a result of the formatting operation.
The first mainframes and even the first personal computers functioned without a hard drive. In modern control computers, programs can be "wired" directly into circuits, and such computers function without hard drives.
USB flash drives (flash cards) use electronic, non-volatile, rewritable memory. Flash memory is based on semiconductor elements. Its variety based on cells with NAND elements (NAND) has the highest density and speed.
Streamer (from the English streamer), also a tape drive - a storage device based on the principle of magnetic recording on tape, with sequential access to data (Fig. 7); the principle of operation is similar to that of a household tape recorder.
Rice. 7. Streamer and cartridge for it.
CD-ROM drive intended for reading records on CDs. The advantages of the device are large disk capacity, quick access, reliability, versatility, and low cost. The main concept that characterizes the operation of this device is speed. The main drawback is the impossibility of recording information. This requires other devices.
A non-erasable optical disc designed for user re-readable only is a CD-ROM ( Compact Disk – Read Only Memory). A CD-ROM is commonly used for storing commercial programs and data. You cannot add or erase data on a CD-ROM.
On DVD-R and CD-R optical discs, the user can write files more than once (each recording is called a session), but files cannot be erased from the disc. Each entry is permanent. Recording on these discs is carried out due to the presence of a special light-sensitive layer on them, which burns out under the influence of a high-temperature laser beam.
You can write files to a CD-RW disc multiple times. You can also delete unnecessary files from the disc to free up space and add additional files. CD-RW disc is rewritable and erasable.
Rice. 8. Optical disc (CD or DVD).
One of the main parameters of any type of computer memory is the memory access time, which is defined as the minimum time sufficient to accommodate a unit of information in memory. Speed of information storage - speed of reading - writing data in the storage. It is characterized by two parameters: average access time and data transfer rate.
Direct Memory Access (DMA) is a mode of data exchange between devices or between a device and main memory (RAM) without the participation of a central processing unit (CPU).