Hello, dear readers of the blog site. Today I want to talk about the formats of raster graphics, which were appropriate for applying to pictures displayed on the site, and indeed.
We'll look at Gif, which is popular now because of its support for the animation hyphas, Jpg, which is very suitable for inserting full-color photos and, of course, Png, which allows you to create images with a transparent background and can serve as an excellent replacement for the previously mentioned formats. You can also read about half the graphic, and half the text.
All of them are actively used in, but the subtlety is to choose the optimal format for each particular case, so that the image quality is not affected, and its weight would be minimal. I advise you to take the schedule myself with free services on similarity and other similar that then there would be no problems with infringement of the copyright.
Raster graphics for the web in the face of Gif, Japep and Pong
Now it is very difficult to imagine individual web pages at all without having any photos, icons or pictures on them. By the way, the first browser that could show graphics was Mosaic (mosaic), which appeared almost simultaneously with the appearance.
And, as I mentioned above, not all image formats will fit to the site, but only certain, maximum under it sharpened - Gif, Png and Jpg. Depending on the type of image that you want to add to the web page, you will also need to select one of the mentioned formats, which, in turn, refer to the so-called raster graphics.
By itself, it implies that an image on paper or a monitor will be formed from so-called unit elements called pixels (color points). All images of any format related to the raster graphics have some properties.
The size of the picture is determined by such a concept as resolution, which is horizontal and vertical, for example, 300 to 200. Sometimes, however, they say about the total number of pixels in the picture, for example, manufacturers of cameras (12 megapixels, etc.).
Applied to the web, the physical size of the bitmap can significantly depend on the pixel value (the screen grain) of the device on which the user browses the web page. Images are also characterized by such a notion as number of colors used in it. For example, for Gif only 256 colors are used, which are set in one byte of information.
Well, besides this, various formats can use different color models, with the help of which all possible shades are formed. When we considered writing with you, we discussed in some detail the principles of the formation of the RGB model.
One of the main drawbacks of raster graphics is the large size of the resulting images, even in the formats Gif, Png and Jpg, which are used on the web. Naturally, to reduce the resulting images, different compression algorithms, which work both with deterioration of quality (compression with losses), and without it.
All this is very similar to the principles of the operation of audio compression algorithms - MP3 compresses with losses, and, first of all, any transitions that are most likely not to be perceived by the person's ear are deleted. Such an analogy in the world of raster graphics can serve jpg format, the compression of information in which is carried out with losses. At the same time, the possibilities of visual perception of a person are taken into account, and, first of all, those details that will be particularly and not noticeable are deleted.
But there are also compression algorithms for lossless images - BMP, Gif and Png. BMP most often is not a compressed image, but Gif and Png are compressed without loss by removing duplicate and redundant information (it turns out something like the archiving, but taking into account the features of raster graphics).
There are many graphic editors who can work with raster graphics (for example, all the same photoshop or it), but you should use oriented editors for this, because only then you can get the most optimized images, which then will not create unnecessary load on the server of your hosting when they are downloaded to user's browsers.
Format Gif - design elements and animation for the site
At the moment almost all browsers support three main formats of raster graphics used for the web - Gif, Png and Jpg. Historically, the first appeared Gif and it was with it that in the first browsers it was possible to add and display pictures and media information, which was first expressed in the so-called Gif animation.
The abbreviation Gif stands for Graphics Interchange Format. Pronounced as hypha, but the developers of the standard believed that it was correct to call it jif, but another name came to life in the Russian interpretation.
Because it was developed a long time ago, and most of the users at that time were, oh, what a small, then at its creation did the main emphasis on the maximum reduction in the size of the resulting image (wrote about this in the article about or).
In this regard, Gif may include a palette consisting of only from 256 colors (it is also called an indexed palette). Those. the image converted into this format will always contain no more than 256 shades, and all other colors will be created on the basis of blending (the neighboring pixels from the basic palette are cunningly chosen so that the human eye at a distance would perceive them as the color required in this place).
But, unfortunately, in practice, when converting full-color photos to Gif, a bunch of artifacts (because of this very blending) that make photos unacceptable for posting on the web. Therefore, it is not used to display full-color pictures and photos on the site pages (Jpg or Png is often chosen for this purpose).
Gif-animation and its use on the Internet
Possessing such a significant drawback, Gif should have long ago sunk into oblivion, but it, however, is still livelier than all living ones, and often images in this format can be found on the pages of sites.
Here all the hassle is that gIF format supports animation (the only one used on the Web). Any animated and avatars (including ones) that you can meet in large numbers on the Internet, have the extension GIF.
However, for some time now the alternative format Mng has been developing, adding the possibility of animation to Png, but its development and distribution is not too fast. Therefore, if you do not take into account flash technology, all the animation on the web is created on the basis of Gif and flash.
The essence of this animation is that in the Gif container there is not one picture, but several times and there is also written the time through which these images will replace each other. In this case, you can loop animation, when the last frame will again start showing the first.

There are specialized editors in which you can create Gif animations. The main thing is to create the necessary number of pictures of a certain size, and then they are placed on the timeline and an interval is set for them to change.
As a result, it gets the same effect as the cartoon that we are used to watching on web pages. Sometimes even in the eyes ripples from animated banners (read about how), emoticons, avatars. An example of Gif animation can serve as a goblin from the page "" of my project.
Gif supports a transparent background (almost)
But animation is not the only counter of this format. It can also support a primitive way of generating transparency for the images being created. One of 256 possible colors in Gif is set as transparent and through it will shine through the background of the web page, on which this picture will be located.
But the problem is that for any pixel in the image of this format only two values are possible - transparent or opaque (the two extreme states without the possibility of intermediate variants such as translucent, a quarter transparent, etc.). Those. About such concept, as an alpha channel (used in Png), in transparent Gif speech does not go. Because of this, there are difficulties with displaying a smoothly changing level of transparency.
But still transparent Giff finds application in the web. For example, in this format, very often different markers used on web pages are stored. The background around the marker is made transparent and through it the background of the web page will shine through. For example, this would look like a marker with a gray background:
And so the same marker will look when you change the gray background to a transparent color while saving in GIF:
In order to form smooth edges with a drop in transparency in Gif images, go for one trick. In any an image editor when creating an image in this format, you will be able to specify the so-called MATE color (otherwise it will use the default color, usually white).
The color of MATE is mixed in those areas of GIF where you need to create smooth edges with a drop in transparency, but all this will look good only for the background of the web page that matches the MATE you specified. But on top of another shade, this picture will not look very good.
For which web graphics does it make sense to use the Gif format?
As I mentioned above, in this format, the pictures are compressed (converted) without loss, but only if the original picture was 8-bit (for coding the color was allocated only one byte), i.e. contained 256 colors. If the source was full-color, there will be a deterioration in quality if you save or convert to Gif, it is because of the loss of some of the shades.
The algorithm of compression (conversion) in Gif works in such a way that it will be best to optimize the size of the photo with a vertical color change (gradient). Those. It makes sense to use it to compress pictures, the color in the lines of which does not change much.
But when converting to Gif a photo with a horizontal or oblique gradient, the resulting picture can turn out to be very large, for example, compared to all with the same Png. Well, and besides it's possible to get out of unpleasant artifacts.
In addition, this compression algorithm was patented in its time, and that's why the work on the alternative Png 8 began, but at the moment the terms of Gif patents have expired. APG turned out to be better than Gif's and continues to gain popularity among webmasters.
Jpg (JPEG) - full-color images with low weight
Jpg was designed to compress and store full-color photos. It is the property of the association of American photographers, which, in fact, says the abbreviation Jpeg - Joint Photographic Experts Group. Although the association itself says this is an open format.
As I mentioned above, he compresses images with loss of quality. The whole picture is divided into squares of 8 by 8 pixels and then the compression algorithm starts, which groups various simple figures from these simple squares. All those differences in colors that the human eye can not notice are removed from the picture in Jpg.
Pros and Cons of Japep
By removing a piece of information that still will not be visible to the naked eye, Jpeg lets you sometimes compress full-color images dozens of times even without apparent loss in quality.
But, on the other hand, even if you select the maximum quality, you will not be able to save a photo in this format with the same quality as the original. Losses will be required, but not always noticeable with the eye without magnification.
You can check it yourself by taking some very quality photography and keeping it in Jaipeg with the maximum quality several dozen times in a row. Therefore it is better do not save again in Jpg sources of the same format - there will be serious losses in quality due to the accumulation and overlapping of artifacts. Therefore, do not save the unfinished image in JPEG, and then continue editing it - significantly lose quality.
Here is an example of such mockery (just a few re-saving in the Jpeg format and you will not look at the picture without tears):

But despite these shortcomings Jpeg has become very popular especially after digital photography. Its main advantages are the possibility of fast, non-resource-consuming and very strong compression of full-color images. True, this format of raster graphics is called full-color, it does not quite cover the entire RGB palette, but it can be attributed to insignificant shortcomings.
Which images should be saved in Jpg format?
Jpg is best for saving photos with smooth transitions of brightness and contrast, but to save something like drawings, texts and other photos with sharp contrast transitions, it fits very badly, and in this case, the best option is to use lossless compression in Png.
Look at how unsightly the screenshot of the text in the JPEG format looks (although at the same and even smaller weight in the PNG format, the picture in general would not be different from the original):

Jpg (JPEG), as I have already mentioned, is possible set quality the resulting image, regulating the degree of its compression. When saving photos, for example, with a lot of sky, you should put the quality (compression ratio) of Jpeg close to the maximum (minimum compression) in order to avoid noticeable artifacts in this very sky.
And when saving photos with lots of details different colors quality can be reduced (increase the compression ratio), without fear of the appearance of notable artifacts.
I mentioned that when saving in Jpg (JPEG), the entire image is divided into squares with an eight-pixel side. So, if you have the option to choose the size of the resulting photo, then it's better take a multiple of eight, t. In this case you will get a little less artifacts, which will be especially noticeable in pictures with thin lines, etc.
Png - replacement of Gif and Jpeg, as well as transparent background in Png32
Initially, Png was developed as an alternative to the proprietary Gif at the time (no one from outside was allowed to develop it). The abbreviation stands for "portable network graphics", it was originally imprisoned for use on the web. This format of raster graphics is completely open and its description is on the site of the W3C consortium.
I remind you that he is lossless compression format, so you can safely save the unfinished image in Png, and then continue editing it without fear of getting additional artifacts, as was the case with Jpg.
Png8 and Png24 - a full replacement for Gif and Jpeg
There are three variations of the Png format, each of which is designed to perform its tasks. The first two were originally created as an alternative to the already existing formats Gif and Jaypeg, and the third one brought to web graphics something that it had not had in the past. But first things first.
Png 8 - Eight indicates the color bit and says that when you save a photo in Png 8, only 256 colors will be used, similar to the one already described just above Gif.
Those. it was developed as a full Gif replacement and the results of image compression in these two formats of raster graphics will be almost identical. As well as in Gif - here transparency is maintained, but with an alpha channel.
Png 24 - the number 24 means that for each pixel of the photo in this format, three color channels of 8 bits each (1 byte) are allocated, thereby realizing a full-color image formation. Thus. With the help of Png 24 you can transmit colors without distortion. Even Jpg can not do it by one hundred percent.
While saving the original image in Png 24 you get exactly the same photo, but its size will still be larger than when using Jpeg. But this, however, is not always the case. With large pictures that have sharp transitions, this format can show even better results than Jeepeg of acceptable quality.
Those. as I mentioned a little bit above, for normal pictures Jpeg is best, but for images with text or where the quality can not be degraded in any way, Png 24 will be irreplaceable. , which I use in articles, Png 8 or 24 seems to me the optimal solution.
For example, the same screenshot with text that just above you could see saved in Jpeg (though low quality to emphasize possible artifacts) in Png would look like this:

But the full-color picture at the beginning of each article, I usually save in Jeepega, tk. The quality / size ratio speaks in favor of just such an option. Just say that there are different ways compression of images in Png format, and one of the best algorithms is used, in my opinion, in the online service Puny Png.
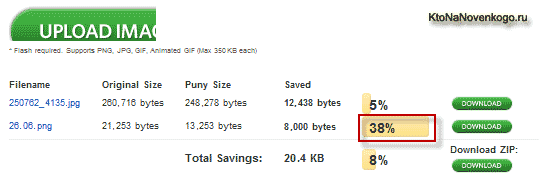
Png 32 - full transparency with alpha channel
Probably, you understood by analogy that in this format of raster graphics for one pixel it is possible to use as many as four bytes of information.
Three are responsible for generating a full-color image similar to Png 24, but the fourth byte is allocated separately to form an alpha channel that allows the use of Png 32 to obtain pictures with transparent background.
In it you will be able to specify the change in the degree of transparency without any MATE colors, which means that such pictures will look equally good on absolutely any web pages with any background. An example of such an image can serve as a logo from the cap of my blog:
Probably, it is clear that Png 32 is simply irreplaceable and has no analogues in terms of the features provided. By the way, the alpha channel can also be used in Png 8, but, unfortunately, not all raster graphics editors allow you to do this. Photoshop, for example, does not know how to do it, but Fireworks or Gimp know how.
In addition, Png 32 and 8 with the alpha channel have such a problem that it is not fully supported in the IE browser, since version 6 and below, and gray color will be mixed in place of the transparent background, and Png 8 with the alpha channel there generally will not be shown. True, there are almost no such archaic browsers for users, but still.
Good luck to you! To fast meetings on pages of a blog a site
Send
Bluff
Link
Recall
Now the leading positions in jpeg format. Due to his ability to compress photos and color pictures several times, he is ahead of the minimum weight formats gif and png, and bmp still "grazes the back".
Now you probably can not find a web page on the Internet without having any photos or pictures on it. Today, it became the norm when making any web pages, because pictures are animated, adorned, supplement the main content of sites and are successfully applied in all areas of the web. By the way, the first browser that could show graphics was Mosaic (mosaic), which appeared almost simultaneously with the appearance of the hypertext markup language Html.
Now almost all browsers support three basic formats of raster graphics used for the web - Gif, Png and Jpg. Historically, the first appeared gif and it was with it that in the first browsers it was possible to add and display pictures and media information. The developers at its creation made the main emphasis on the maximum reduction in the size of the saved image.
After all, at that time the speed of the Internet was so small, and that the downloading of images did not last "forever", and a special "graphic exchange format" was developed and applied (that's what the GIF abbreviation stands for).
The peculiarity of Gif is that it can include a palette consisting of only 256 colors. Those. the image converted into this format will always contain no more than 256 shades, and all other colors will be created based on the mixing. But it is because of this very mixing and there are various unexpected artifacts when converting full-color photos to Gif. Because of this obvious and significant drawback, jpeg and png are increasingly used to display full-color images and photos on the site's pages.
But gif is still popular in the web industry for one simple reason - it supports animation, the only one used on the web. Animated emoticons and avatars, postcards and banners - this is the result of the GIF format. The truth is now no less popular flash technology, but due to its simplicity gif in favorites from webmasters, especially beginners.
The essence of this animation is that in the Gif container there is not one picture, but several times and there is also written the time through which these images will replace each other. At the same time, there is an opportunity to loop the animation and then the last one will start the first one again. Today there are a lot of specialized editors on the Internet in which you can create Gif animations yourself.
Also, gif can support a primitive way of generating transparency for the images being created. Why primitive? Yes, because Giff supports only two transparency values - transparent or opaque, without any intermediate states, which can be achieved by using alpha channels in Png formats.
Because of this, there are difficulties with displaying a smoothly changing level of transparency, so everything regarding the quality transparent background for images is the prerogative of Png. Almost all the elections with a transparent background that we can find on the Internet have an extension of png.
There are several variations of Png, each of which is designed to perform its tasks:
Png 8 - here by analogy with Gif, when saving a photo in Png 8 only 256 colors will be used, so the results of image compression in these two formats of raster graphics will be almost identical. Just like in Gif, transparency is supported here, but with an alpha channel.
Png 24 - here for each pixel of the photo three color channels are allocated to 8 bits each (8 * 3 = 24), thereby realizing a full-color image formation without distortion. By the quality of the color display it surpasses even Jpg, but it will be heavier by weight.
Png 32 - here three color channels are responsible for the formation of a full-color image, and the fourth is separately selected for the formation of an alpha channel, which allows the use of Png 32 to produce images with a transparent background. In Png 32 you can choose any change in the degree of transparency, so that these pictures will look equally good on all web pages with any background.
Now let's summarize all the information and draw some conclusions.
From the author: In March 2017 images account for over 65% of web content. And it's not surprising: images add beauty, convey messages, tell stories and make contact with visitors to your site. The reverse side of the question - when using images incorrectly is often the main reason for slowing down the site and bad user experience.
Correct use of images on the Internet means two things:
choosing the right image format;
image optimization.
In this article I will reveal the first point, in particular I'll tell you about the image formats that are more suitable for the web, and also for what images you need to use these formats.

But first let's briefly go over the terminology.
Raster or vector images
At the heart of raster images is a two-dimensional grid of pixels. In each pixel, the color and the transparency value are stored.
Bitmap images are poorly scaled: if you enlarge a bitmap, it will lose clarity and quality. Popular raster image formats for webs are JPEG, JPG, GIF and PNG.
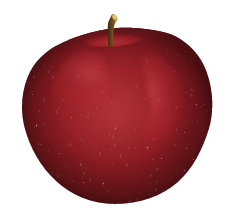
Below are two raster images (JPG) with an apple. The first is a full-size image. The second shows the enlarged part of the first image.

An example of a raster image in a natural size.

Increased bitmap part.
Pay attention to the loss of quality in the enlarged version of the image.
Unlike bitmap images, vector graphics consists of lines, shapes, waypoints. Information about vector images is not stored in pixels, it is stored in mathematical instructions for rendering, which are not connected with pixels in any way. Alex Walker very clearly explained the difference on the example of SVG - the most popular vector image format on the network:
"SVG is not an image format, it's more of an image recipe." - Why are JPEG images similar to apple pie from McDonalds (and SVG is not)
One of the consequences of independence from the screen resolution - vector images can be scaled to the size of the content. The images will be clear, ideal for retina screens.
SVG-graphics on a small scale.

Part of the enlarged SVG image.
Both images from above are an example of a single vector image, but the second image is more than doubled in comparison with the first one. There is no loss of quality.
With loss of quality or lossless (lossy and lossless)
Both lossy and lossless terms refer to media compression techniques, i.e. images, audio and video.
Lossy-compression: "Does not restore digital data to 100% of the original. Methods with loss of quality are characterized by a high degree of compression, which allows you to reduce the weight of compressed files. However, part of the original pixels, sound waves and video frames are permanently deleted. "- PCMag.com Encyclopedia
What this means in practice: the more you compress the file with the loss of quality, the less it will be. Getting less weight of the file, you irreversibly lose quality. With lossy compression, you need to balance between a small file weight and quality.
You often see the format of images with loss of quality, this is JPEG.
Unlike images with loss of quality, lossless-compression saves all data, as in the original. Such compression does not lead to a drop in the quality of the files. Because of this, lossless file formats often have more weight compared to lossy.
In the network it is easy to find lossless-image formats, it's GIF and PNG.
The information presented is useful for selecting better format images for your content.
The first three image formats I will describe below (JPG, GIF and PNG), they have been used for a long time on websites. The last two formats, SVG and webP, are not completely new, they are not popular yet. Nevertheless, they perfectly fit the requirements of adaptability and fast download sites, and their popularity has grown significantly.
JPEG
JPEG or JPG is a lossy format developed by the Joint Photographic Experts Group. JPG-images occupy almost 3% of all types of content on sites. Why this format is so popular:
the JPG format can display millions of colors, which makes it an ideal candidate for displaying photos on the Internet;

Modern trends and approaches in web development
Learn the algorithm of rapid professional growth from scratch in site building
since this is a lossy format, you can use compression to significantly reduce the file size. JPG files have many levels of compression: about 60% will be enough for images on the Internet, anything above 75% degrades image quality;
all devices with the Internet support JPG format, which simplifies the use of the format on the Internet.
One notable disadvantage of JPG is that the files in this format do not support transparency. If you want to use a transparent background to superimpose an image on the background color or texture of the page, the JPG images will not work. Choose one of the options that I will discuss below.
GIF
GIF or Graphics Interchange Format is an 8-bit lossless format with a maximum of 256 colors. Color restrictions make GIF an unsuitable option for displaying photos and images with a wide range of colors.
Factors that have affected such long-term use on the Internet:
due to the limitation of 256 colors, the file size is quite low;
supports transparency;
supports animation, which allows the use of a format for displaying looped images, for example, icons, smileys, banners, etc;
good for simple images with monochrome colors, but not suitable for photos.
PNG
PNG or Portable Network Graphics is an alternative to GIF. The format is developed by W3C. Like GIF, the format uses a compression algorithm without loss of quality, 8-bit and 24-bit options are available. Both options support transparency. However, in a 24-bit PNG image, transparency works on the alpha channel, as well as red, green and blue channels. Therefore, despite the fact that GIF and 8-bit PNG images can be either completely opaque or completely transparent, in PNG each pixel of the image offers 256 levels of transparency.
A 24-bit version of PNG can be used for:
web images with different levels of transparency;
complex photographs and graphics;
graphics that you often need to edit and export: a lessless format will retain quality.
Unlike GIF, the PNG format does not support animation, and the weight of the files can be quite large.
SVG
SVG or Scalable Vector Graphics (scalable vector graphics) is a type of vector files based on XML. The format appeared in 2001, but it was only recently gained popularity among web developers. The reason for this belated love is poor SVG support in browsers for many years. I'm happy to inform you that at the time of writing, SVG is supported in all major browsers, but not without differences and bugs.
In SVG there are a lot of functions that make this format recommended for the web, especially if SVG is used for simple images such as logos, maps, icons, etc.
Pros of SVG format
SVGs often weigh less bitmap images, especially after optimizing for the web and compressing through gzip;
the format is scalable, which provides clarity on any screen resolution;
SVG-code can be placed in HTML and save on HTTP-requests;
SVG-code can be customized through CSS;
SVG images can be animated, including individual parts, both with CSS and JS, which is very cool.
Avoid too complex SVG images, this slightly increases the file size. And finally, SVG does not apply to photos, here the formats JPG and webP are better.
WebP
Despite the fact that the format appeared in 2010, I will not be mistaken if I say that the webP is still a very new format, which is not as well known as JPG and PNG. Nevertheless, the web for this format is in the blood: it was specially designed for the Internet, which makes it extremely interesting.
WebP is an open source image format developed by Google. Key features: "WebP - a modern format of images on the Internet, providing excellent compression with both loss and loss of quality ... lossless versions of webP images weigh 26% less PNG. Lossy versions of webP weigh 25-34% less comparable JPEG images... Lossless webP supports transparency ... due to 22% extra bytes. In cases where lossy RGB compression is applicable, lossy webP also supports transparency, providing a 3x smaller file size compared to PNG. "- WebP site
The crash of webP is that it combines the advantages of JPG and PNG without increasing the file size.
At the moment, the format support is pretty good: Blink-browsers supported the format from the very release, yet webP is the creation of Google. For backwards compatibility with browsers without support, i.e. IE / Edge, Firefox and Safari, folk craftsmen invented workarounds.
Conclusion
In this article, I told you about the image formats for the web, and also briefly looked at the types of images most suitable for the Internet.
JPG, GIF and PNG are very popular formats that have been used for a very long time. SVG and webP are newer, interesting alternatives. SVG is great for illustrations and simple images, webP replaces all niches of applying JPG and PNG.
Have you already used SVG and webP in development? What difficulties did you have? Have you achieved any significant productivity gains? Write in the comments!
Hello everyone on the blog. In general, in this article I want to dispel the myth about two data extensions for pictures, it's jpg and png the best of them has not yet been found. The thing is that both, depending on the application and on the texture itself, can affect the speed of the site, and optimization. What little has left you stumped? Then read on.
Two formats png and jpg what are the differences.
It seems like a picture and what's wrong with it, but it's all about colors. Format jpg the most common, because compared to others:
- It weighs less (but this is a controversial issue to be seen further).
- Easy to compress.
- High number of colors in the transmission.
The most common format of png-8 in site building, because compared to its png-24 counterpart, have a huge difference in the size of the file, so the second is used very rarely.
The main difference between the two formats is that jpeg is a hospital and colors can not be extracted from it to remove unnecessary ones, and thus reduce the volume of the picture, and that jpg does not have a transparent background, this format does not support it.
Destroy the myths.
The most important myth of all saitostroev that in any case not to use png, it's just nonsense, you can compress images of this format and optimize it better than jpg, many times with the right approach.
How to choose the right format?
See for example let's take a picture suppose our Russian flag.

I'll look at all the operations on the example of Photoshop, it's easier. Specially chose a large size and a little color, only three colors, and now I want to save it, see what happens, first I'll take the jpg format.
But what if I save it in png.
The size has decreased 6 times almost. I did not do anything but set the minimum number of colors, just super I think. This method is suitable for those who do not fundamentally color rendition, as I have on the blog, all the screenshots are so made, I expose the minimum of colors to be readable and everything is fine.
This is the moment you need to scan, it's not just about sites. The size of the hard disk is not rubber, my mom's pictures and pictures of the work in general 246 gigs occupied, and she wondered why so much and not enough space. Just have to use my method and that's it.
Of course, if the picture is multicolored with many colors and shadows, then png does not help, and then I advise you to use
- Revise all images on the blog and choose which format is better than jpeg or png apply for different kinds of pictures. Even those who have already compressed and optimized, because they can be further cut back, and without losing quality.
- When writing new articles, to evaluate this moment, I know that time will be more, but.
- Use the riot program mentioned above, or use this to compress jpg.
- Do not be lazy because it's in the truth you need.
And the business will take you two minutes more, and the benefit will be a whole car with a small cart.
Well, as you article, I think for some things I opened my eyes to you, which you do not even know, so use and use, for now, for now, I'm waiting for you in the comments.