GBPOU of the Republic of Mordovia
"Saransk Medical College"
Lesson summary on the topic:
“Internet search services. Search enginesWWW»
Prepared by: teacher
Gorina A.D.
Saransk, 2016
Discipline:information technology in professional activities
Lesson number:3.1.1
The pioneering staging of the American Academy of Sciences is still groundbreaking, since most of the information published on the Internet is far from the creative use of the characteristics of digital media. Mention of this work, suggesting more specific comments that should be made in this document, was made in order to draw attention to an aspect that is usually ignored in the use of the Internet. There is much talk about the need to use such media.
Nevertheless, little attention is paid to the recording mediums of knowledge that the Internet has already introduced into the culture, and about future ways of creating, presenting, storing and retrieving information. Recognition of existing configurations and the establishment of the likely contours of digital information for the future are the required educational tasks.
Theme:Internet search services. WWW Search Servers
Note: the name of the lesson appears on slide 1 of the presentation
Purpose:mastering the theoretical foundations of the topic under study (search server, global network protocols, global network hardware)
Providing classes:computer, interactive whiteboard, multimedia projector, lecture notes, presentation
The Internet makes authorship easier; for this reason, in investigative activities related to the use of such an environment, it is always necessary to develop proposals that emphasize the training of teachers and students. In addition to being a source of information, the Internet, in principle, provides an opportunity for anyone to disclose their work through texts, images, videos, sound recordings. Thus, in addition to providing quick access to a huge amount of data, the Internet is an environment for publishing and sharing among all its users.
Occupation Type:lesson - lecture
Learning Technology:developmental education
Teaching methods:lecture, work with a book
Competencies:
OK 1. To understand the essence and social significance of your future profession, to show steady interest in it.
OK 2. Organize your own activities, choose standard methods and methods for performing professional tasks, evaluate their performance and quality.
This characteristic is fundamental in education. Teachers and students should not be just users of technological resources. To use the new media for training, students and teachers must become authors, since some Internet sources come to life only when users are members of an information production network. That is, “reading” the web text in order to create meaningful learning effects must be a collaborative action. This point also deserves further consideration.
OK 3. Make decisions in standard and non-standard situations and bear responsibility for them.
OK 4. To search and use the information necessary for the effective implementation of professional tasks, professional and personal development.
OK 5. Use information and communication technologies in professional activities.
Consider the Internet as an auxiliary educational resource; outside of school, this is an information environment that tends to be hegemonic in our world; Adding to it at school is a mistake. The tremendous opportunities for creating, disseminating and exchanging information on the Internet suggest that its use must be included in systematic education. In fact, even if schools do not integrate it into everyday activities, the Internet has already deeply affected education. In other situations than at school, people are increasingly using the international computer network.
PC 2.1. Present information in a way that is understandable to the patient, explain to him the essence of the intervention.
PC 2.6. Maintain approved medical records.
Interdisciplinary communications:
Used Books:Ugrinovich, N.D. Informatics and information technology. Textbook for grades 10-11
1. Organizational moment: 3-5 min
Economic interests, public services, opportunities for entertainment and communication require the average citizen to use the Internet. A common example of using the Internet is sending tax returns. Similar measures occur with communication systems in public and private service areas. Another example of the current use of the Internet is in the commercial field. More and more companies are offering trading opportunities with virtual resources.
Therefore, they always offer tips and suggestions on what to buy. The site of this large marketing company makes full use of the enormous power of computers to emulate environments, models, and systems. Such a representation of real qualities on a computer screen is an opportunity that can be realized in many other areas of human activity. We must understand that the Internet or cyberspace is a set of environments, not just a repository of information. Today we need to understand how life is in this space and how to participate.
(mark absent, checking the appearance of students, the sanitary condition of the office)
2. Statement of material: 53-58 min
1) Computer network and its types. Technical means of the global network
2) Types of servers. WAN Protocols
3) Internet search services. WWW Search Servers
At present, more and more often computers are not used in isolation, but interconnected for constant or occasional interaction and transmission of information. This interaction is a computer network.
That is, there is a dimension of cyber citizenship that requires participation. Inactive participation in cyberspace leads to a decrease in citizenship. The Internet is not just a place where information is stored; it is an increasingly medium in which various spaces of coexistence are built; therefore, it is necessary not to lose sight of the possibility of creating spaces of cooperation and coexistence in cyberspace in education; Recent research practices include this environmental sense of the international computer network.
In the world of communication and culture, the presence of the Internet is growing. Almost all newspapers have online versions. Museums and cultural centers create pages that not only announce activities, but also provide access to images of their collections. Scientists, such as Stephen Downs, have put their work on websites that also allow you to immediately access the research and messages that they perform. You can use an example to illustrate how this works. In this case, a scanned copy of the volume belonging to the collection of the National Library of Portugal can be studied, copied and processed by students in ways very similar to the actions of researchers who use collections of rare books in a regular library.
A computer network is a set of computers connected by communication channels through which information is exchanged through signals and the user resolves joint information tasks.
Note: on slide 2 of the presentation, the definition for recording by students is given.
The creation of computer networks is caused by the practical need of users of computers that are remote from each other for the same information. Networks provide users with the opportunity not only to quickly exchange information, but also to collaborate on printers and other peripheral devices, and even simultaneously process documents.
The Internet in this case facilitates access and allows any interested person to have contact with cultural products, which before that were, almost always, the privileges of several scientists. What is required in this case is only a suitable research proposal proposed by the teacher. The Internet is not only an instrumental solution, but new media are also changing ways of seeing the world; for this reason, educators must be aware of emerging values \u200b\u200bborn of digital environments; On the other hand, educators must always confront old and new values \u200b\u200bin order to determine what needs to be emphasized in pedagogical projects; without caring about the axiological dimensions favorable to each technology, it risks accepting values \u200b\u200bwithout the necessary judgment, which is required by conscious citizens.
The whole variety of computer networks can be classified by a group of signs:
by geographic location;
depending on the presence of a host computer on the network;
by the method of connecting computers through communication channels;
by type of transmission medium.
Note: on slide 3 of the presentation, this classification is presented, which will be decrypted.
Using the Internet outside of school affects two-way education. The use of digital technology in everyday life introduces new values \u200b\u200band almost always eliminates old values; Information that depended on school attendance is now available on very attractive portals and websites. The presence of any cultural artifact in society changes the values \u200b\u200band ways of seeing the world. Neil Postman solves this issue as follows.
A significant change leads to a complete change. If you remove the caterpillars from a specific habitat, you will not get the same environment except the caterpillars, but with a new environment, and you have restored the conditions of survival; The same is true if you add tracks to an environment in which there is none. This is how environmental ecology works. New technology does not add or subtract anything. We had a different Europe.
By geographic location: local, distributed (corporate), regional and global. Note: on slide 4 of the presentation, this classification is presented, which will be decrypted.
Depending on the availability of the host computer in the network: client-server networks, peer-to-peer networks.
By the method of connecting computers through communication channels (topology): bus, ring, star, snowflake.
After television, the United States was not America, but television; this gave a new color to every political campaign, every home, every school, every church, every industry. The Internet has an environmental impact on a culture that is likely to be deeper than those caused by television and films. And such consequences have not stopped yet. Let's look at something very simple: the immediacy of information. In periods when information depended on the physical transportation of the media, the news could take months to cover all parts of the planet.
Note: on slides 5-7 of the presentation, this classification is presented, which will be decrypted. Connection of computers in each case is shown.
By type of transmission medium, they are divided into coaxial, twisted-pair, fiber-optic networks, with the transmission of information via radio channels, in the infrared range.
Local Area Networks (LAN, LAN)
The Internet, given its technological base of a digital nature, removes several remaining communication barriers. We are used to the “here and now”, which increasingly characterizes our expectations regarding the flow of information. This circumstance is so naturalized that information processing, requiring some delay, is the object of impatience of the population, which has come to be considered direct as a virtue. We see the fury of seemingly irrational immediacy. Everything needs to be done quickly.
Everything must be destroyed as soon as it is produced. This acceleration is occurring mainly in the media. News succeeds in a fast and continuous flow, rapidly aging and not giving people time to reflect on events.
A group of up to 12-15 computers located within one or several rooms, using a common information exchange channel and one set of network equipment and managed by one software package.
A local network unites computers installed in one room (for example, a school computer class consisting of 8-12 computers) or in one building (for example, several dozens of computers installed in various subject rooms can be connected to a local area network). Such networks are used to exchange files between network users, as well as to use shared resources available to all network users.
Reflexes of rhythm acceleration in life can be perceived in the care of middle-class parents about the education of their children. They want their heirs to enter the university early, and that they graduate as soon as possible. Children have a desire to burn steps, anticipating the stages of learning.
The uniqueness noted in the previous paragraphs is a feature of our culture. Even if schools do not consider this valuable, students are already convinced that immediate virtue. The Internet facilitates the realization of this opportunity. Indeed, even before the advent of the global computer network, “here now” was already a sign of the new era.
Each computer connected to the local network must have a special board (network adapter). Between each other computers (network adapters) are connected using cables.
Distributed (Corporate)
Many organizations interested in protecting information from unauthorized access (for example, military, banking, etc.) create their own so-called corporate networks. A corporate network can unite thousands and tens of thousands of computers located in different countries and cities (as an example, the Microsoft Corporation’s network, MSN).
Now, without a comma, without a period. Here, in the favela, in Rio, in Recife, in the suburban police station, in the Palace of Planalto, on the streets of Los Angeles, Rwanda, there is "reality" in thousands of Brazilian houses. The daily life of the viewer is only a background for the truth of life that appears on a small screen. Therefore, the immediacy that characterizes the Internet is not something completely new. In his work, Boorstin shows that a culture that appreciates analysis and fact is replaced by another that appreciates the sight, the image, the immediate.
Regional (MAN)
Local networks do not allow sharing information to users located, for example, in different parts of the city. Regional networks that unite computers within one region (city, country, continent) come to the rescue.
A network of computers that belong to the same region. They have various transmission channels, the number of computers is unlimited.
One of the caveats, apparently, indicates that in practice the relationship between learning and teaching is already marked by directness, because even if it does not explicitly speak of his commitment to new values \u200b\u200bpromoted by the media, the school, and all other examples Our society ultimately reflects relationships that are built because of ways to see the world that come with the entrance to new technologies in our daily lives.
Observations in computer labs in schools show that students no longer read as they used to when using the Internet. Pages and websites quickly intersect in gestures similar to those who view richly illustrated magazines. Students behave much more than people who enjoy images. This happens even when the text prevails on the web page. This behavior is not unique to younger generations. Educated people at a time when the predominance of information through books acts in a similar way.
Global (telecommunications, WAN)
A set of computers located at a great distance from each other, with various channels for transmitting information and exchanging data.
In 1969, the ARPAnet computer network was created in the USA, combining computer centers of the Department of Defense and a number of academic organizations. This network was intended for a narrow purpose: mainly to learn how to communicate in the event of a nuclear attack and to help researchers exchange information. As this network grew, many other networks were created and developed. Even before the era of personal computers, the creators of ARPAnet began to develop the Internetting Project. The success of this project led to the following results. Firstly, the largest internet network in the USA was created. Secondly, various options for the interaction of this network with a number of other US networks were tested. This created the prerequisites for the successful integration of many networks into a single global network. Such a "network of networks" is now called the Internet everywhere (in Russian publications the Russian-language spelling - the Internet is also widely used).
Currently, tens of millions of computers connected to the Internet store a huge amount of information (hundreds of millions of files, documents, etc.) and hundreds of millions of people use the information services of the global network.
The Internet is a global computer network that combines many local, regional and corporate networks and includes tens of millions of computers.
Each local or corporate network usually has at least one computer that has a permanent Internet connection using a high-bandwidth communication line (Internet server).
The reliability of the functioning of the global network is ensured by the redundancy of communication lines: as a rule, servers have more than two communication lines connecting them to the Internet.
The Internet is based on more than one hundred million servers that are constantly connected to the network.
Hundreds of millions of network users can connect to Internet servers using local area networks or dial-up telephone lines.
In small local networks, all computers are usually equal, that is, users decide independently what resources of their computer (disks, directories, files) to make public on the network. Such networks are called peer-to-peer networks.
If more than ten computers are connected to the local network, then a peer-to-peer network may not be productive enough. To increase productivity, as well as to provide greater reliability when storing information on the network, some computers are specially allocated for storing files or application programs. Such computers are called servers, and the local area network is a client-server network.
Unallocated servers - servers to which neither a monitor nor a keyboard is connected.
Dedicated servers - which do not distinguish about the work of ordinary computers, the speed of which is higher than in unallocated; a dedicated server not only manages the network, but also is a stand-alone computer with a high-speed processor, a large amount of memory; Designed for servicing client computers.
Network topology
The general scheme for connecting computers to local networks is called a network topology. Network topologies may vary.
Bus - all computers are connected in parallel to one cable (communication line), and plugs are located at the edges of the cable. With this connection, computers can only transmit in turn. There is no central computer in this structure. On the edges of the cable it is necessary to have special matching devices - terminators.
Advantages:
Simplicity and profitability
Reliability (resistance to damage to one computer)
Disadvantages:
Sensitivity to cable system malfunctions. If the cable is damaged in at least one place, then problems arise for the entire network.
Ring - all computers are connected to one cable, each computer has two neighbors. In such a network, information is transmitted between stations in a ring with a re-reception in each network controller. The retrieval is carried out through buffer drives made on the basis of random access memory, therefore, when they fail, one network controller may interrupt the operation of the entire ring.
Dignity:
Easy implementation of devices
Disadvantage:
Low reliability
High cable consumption
Star (radial structure) - in the center is the server to which workstations are connected, i.e. each computer is connected to its cable.
Tree topology - the implementation of the hierarchical subordination of computers.
Snowflake - combining computers through servers using various topologies.
Technical means of the global network
Note: on slide 8 of the presentation, a list of technical equipment data is presented.
The technical means of the global network include computers, communication channels, special equipment (switches, hubs), modems.
Signals on computer networks are transmitted through communication channels - it can be radio waves, optical fiber, satellite communications. The most common communication channels are cable.
Coaxial cable - the signals are transmitted along the copper core, and the metal shield is grounded at one end; Moreover, the metal shield protects the copper core from external influences.
Twisted pairs are a set of eight wires twisted in pairs so as to provide protection against electromagnetic interference. Each twisted pair cable connects to the network only one computer, so a connection failure affects only this computer, which allows you to quickly find and troubleshoot.
Fiber optic cables - transmit data in the form of light pulses through glass wires. Such cables provide the highest transmission speed; not subject to electromagnetic interference; more convenient transportation.
Wireless communication on radio waves can be used to organize networks within large rooms.
Hub (hub) - a device that provides simultaneous operation of several subscribers on one channel ; grouping the signals of several subchannels and sending them into one channel with higher bandwidth.
Switch (switch) - a device that allows you to share bandwidth between end stations. The switch remembers the addresses of senders and receivers, the port numbers to which the device communication lines are connected, and based on these data, a table is constructed according to which the signal is separated.
A modem (modulator and demodulator) is a device used in communication systems for physically interfacing an information signal with its distribution medium, where it cannot exist without adaptation and performing the function of modulating and demodulating this signal.
All computers in the global network can be divided into:
Note: on slide 9 of the presentation, a list of these computers is presented.
1) Workstations - a computer that uses either its own resources or the resources of another computer, usually a server, to solve information problems.
2) Server - a computer whose resources are available from network workstations. It performs the functions of servicing the network, organizing shared resources, provides centralized management of the entire network, defines message transfer routes, accesses network peripherals through it, and shared programs are located on its disks.
3) A host computer (network server) is a special communication node, which is most often created on the basis of several powerful computers and provides reliable round-the-clock transmission of information, its storage and simultaneous work of many users. In addition to network functions, it can also perform user tasks.
4) Gateway (router, router) - a server that provides communication between local networks using different data transfer protocols. It connects many computers with various operating systems, application programs, and hardware platforms.
5) Firewall - a gateway computer that restricts access to computer networks from the outside. Designed to protect information inside.
Types of servers
Note: on slides 10-11 of the presentation, a list of server data is presented.
File server - stores data files
Print servers - with one or more printers, is used to print documents transmitted over the network.
Application Server - provides access to network applications, thanks to them, users can work in applications that are not on their computers.
Registration servers - designed to ensure the security of databases, they contain information about users.
Web servers provide requests for network resources.
E-mail servers - provide electronic mailboxes for letters addressed to network users.
Remote access servers - provide a dial-up connection, i.e. with their help, another computer can access the server or network over the telephone line.
Terminal servers - provide access to remote computers or terminals.
Telephone servers - act as answering machines, transmit voice messages, redirect calls.
Cluster servers - provide the consolidation of many servers in clusters, i.e. independent groups of computer systems working autonomously.
Proxy servers - serve as intermediate servers between user workstations and the Internet, improve system security.
Fax servers - are the central point of the network, designed for receiving and sending faxes, distribution of received faxes to users.
BOOTH - servers - using the BOOTH protocol, the OS of client computers that do not have hard disks is loaded and provide information on configuring the network protocol.
DHSP servers — Assign IP addresses and configuration parameters to computers that are clients of DHSP servers.
Servers routers (routers) - powerful computers or specialized intelligent devices that connect various networks or sections, they determine the most effective way of information flow, determine the addresses of receivers and senders, minimize line congestion and packet routes.
Bridge servers - devices that provide data transfer between two networks, provide more remote access compared to routers, can connect local networks, and filter packets.
A firewall is a device that restricts access to a computer network from outside.
WAN Protocols
Note: on slide 12 of the presentation, a list of network protocols is presented.
WANs are stable thanks to unified information exchange protocols. WAN protocols are more complex than local ones. This is due to the fact that the servers use different software. The higher the level, the closer it is to the user. There are 7 levels of protocols that define the principles of interaction between computers of global networks:
Physical - the lowest, it determines the type and characteristics of communication lines. Along the communication lines, the signals pass from computer to computer, while their physical nature can change.
Logical - for each protocol of the physical layer, a protocol of the logical layer is developed, which controls the transmission of information on physical lines.
SLIP is the Internet Protocol for the serial channel.
PPP is a protocol of interaction between nodes.
Ethernet is a protocol for local area networks.
Network - is responsible for routing - the choice of the shortest route for following information over the network.
IP - the protocol of interworking, is a system of physical 32-bit addresses of computers connected to global networks.
ARP - Address Resolution Protocol.
Transport - controls the transmission of information over networks.
TCP is a messaging control protocol. It breaks messages into small fragments, supplies each fragment with a header, combines these fragments into a single whole, and at the same time checks for errors.
UDP is a universal data transfer protocol. Used for fast information transfer. Stream protocol. Messages that do not reach the recipient are not repeated.
Session - is responsible for the installation, maintenance and destruction of the appropriate data transmission channels, for their safety. In normal work, such protocols 3 and 4 of the example are almost not used, they are needed for non-standard communication conditions.
UUCP is a copy protocol from Unix to Unix.
SSL is a secure connection layer.
Representative - is engaged in the maintenance of application programs.
SMTP is the mail transport protocol.
POP3 - Office Post Protocol Version 3.
IMAP is an Internet messaging access protocol.
HTTP is a hypertext transfer protocol.
FTP is a data transfer protocol.
NNTP is a network news protocol.
NFS is a distributed file system.
Most often used in pairs. The first two are email. With the advent of the WWW service, HTTP was developed, which provides verification and user identification, protection against interception and confidentiality of information.
Applied - services - network services
Means of providing certain information services for network users are called Internet services. Internet services are divided into information and communication.
Internet communication services
Note: on slide 13 of the presentation, this classification, which will be decrypted, is presented in the form of a list of the Internet service.
Email - e-mail. This is the oldest and most massive network service.
E-mail - e-mail - a system that allows you to exchange electronic messages through a modem.
This service is provided by special mail servers that receive messages from clients and forward them in a chain to the mail servers of the recipient. These messages are accumulated and upon establishing the connection of the addressee with the server are automatically transmitted to the destination computer. When registering on the Internet, each user receives a unique mailing address.
Email structure
<идентификатор_абонента>@<домен>
UserID is the registered username.
The domain defines the mail computer to which this subscriber is connected.
Example email address:
Email Scheme
the mail program puts the letter in the mail-header (envelope) and sends it to the network using SMTP;
the message is transmitted over the network from one computer to another via the Internet protocol;
when a message is sent to a computer, the mail agent (postman) delivers it to the recipient's mailbox. The destination retrieves the message using the POP3 protocol.
Teleconference service (USENET mailing lists). Mailing lists - a special address through which incoming messages are considered by special programs and sent to recipients who have subscribed to messages on this topic. Teleconferences combine both communication and information functions.
Direct communication forums (IRC, chat conferences, ICQ) - real-time communication between participants.
Internet telephony (IP telephony) - real-time voice communication over the network. Skype
Messengers (instant messaging system) - instant messaging service.
Internet Information Services
Data Transfer Services - FTP - storage of a set of files for various purposes.
WWW - The World Wide Web - a distributed information system with hyperlinks that exists on the technical basis of the world wide Internet. Appeared in 1993.
Runet is the Russian-language part of the worldwide Internet.
Web browsers are application programs that provide network services and are used to quickly obtain information from global networks. Web browser is a WWW client program.
Web - browsers provide viewing of almost all types of information and access to global network resources. The browser can be delivered to consumers in the form of an independent (stand-alone) application or as part of bundled software.
Internet Explorer is bundled with the Microsoft Windows operating system.
Mozilla Firefox - individually or as part of Linux distributions.
Safari - as part of the Mac OS X operating system and as a standalone application for Microsoft Windows.
Google Chrome, Opera and other browsers - as stand-alone programs in a variety of options for various operating environments.
Web page - each individual document with its own address. An extension of an html or htm web page.
Web server - a computer on which the WWW server program is running.
A Web site is a collection of interconnected Web pages.
Comprehensive Internet Services
On-line translators and dictionaries
Online stores
Electronic payment systems (QIWI, Yandex.Money, WebMoney)
Ways to actively display information on the World Wide Web:
guest books - software used on websites and allowing their visitors to leave various wishes, comments, short notes addressed to the owner or future visitors. Thus, the guest book is the most simplified version of the web forum;
forums - a class of web applications for organizing communication between website visitors;
blogs is a website whose main content is regularly posted posts containing text, images or multimedia;
wiki-projects - a website, structure and content that users can independently change using the tools provided by the site itself;
social networks - a platform, online service or website designed to build, reflect and organize social relationships, the visualization of which are social graphs. Examples: VKontakte, Odnoklassniki, Moy [email protected], Facebook, Google+, Myspace, Among friends and others;
content management systems.
3. Fastening new material: 15-27 min
Questions for self-control:
1. What is the Internet?
2. List the main Internet services that the user has access to?
3. What are the parts of an email address?
4. What is WWW? What is a web page?
5. What is the function of hyperlinks in WWW technology?
6. List the main elements of the Internet Explorer browser window?
7. What is the address bar of the browser for?
8. How to determine the addresses of recently visited pages?
9. What are browsers? Give examples.
10. What is an email subscriber's mailbox?
4. Homework: 2 minutes
5. Summary: 5-10 min
(marks are given, their comment)
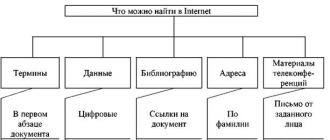
Classification of information (what you can search on the Internet).
From the point of view of the consumer, all information on the Internet can be divided into telecommunication information markets (Fig. 1.).
Search engines (classification and areas of use).
The search for the necessary information in a large amount of sufficiently diverse information is a task that mankind has been solving for many centuries. As the volume of information resources grew, fairly sophisticated search tools and techniques were developed to find the necessary document. As the main tool for finding information in libraries, catalogs are used (alphabetical, systematic and subject). However, each tool has its drawbacks. With large volumes of information (which are characteristic of the Internet), the search for information becomes a very complex procedure. In order to find the information you need in Inernet, you need to have special knowledge and skills. A specialist with such knowledge and skills and searching for information on incoming orders is called an information broker. He knows how classifiers are arranged, how systematizers interpret them, what tools exist for searching for information on Inernet, technological methods and methods of search, features of various search engines, etc. In a conversation with the customer, he studies his informational need and turns it into a search order. In our country, specialists of this profile are still rare, although the need for them is already being felt.
Three types of information retrieval systems (IPS) are available on the Internet: classification, dictionary, and subject.
ClassificationIPS use a hierarchical organization of information, which is described using a classifier. Classifier sections are called rubrics. In librarianship, for example, a systematic catalog is used for this purpose.
The classifier is developed and improved by a team of authors. Then it is used by another team of specialists called systematizers, who, knowing the classifier, read documents and assign classification indexes to them, indicating which sections of the classifier these documents correspond to. As an example of a classification IPS on the Internet, Yahoo! , which simultaneously runs more than 100 systematizers, Excite, Look Smart, Yellow Web, “Constellation Internet”, “Au”.
Classification IPS have a number of specific disadvantages. The development of a classifier is associated with an assessment of the relative importance of various areas of human activity. Any assessment is a social action - it is associated with the society, culture, social group to which the person making the assessment belongs. Therefore, the classifiers created by different teams in different countries are very different. In addition, systematizers have difficulties with interpreting materials written in foreign languages \u200b\u200b(not only source documents, but also classifiers). Since no one can make an absolutely strict classification, there are always documents that can be attributed to several sections of the classifier.
In complex cases (when it is not clear which of the sections the document should be assigned to), systematizers apply two methods: sendingand link.The reference (in Yahoo! It is indicated by the @ sign) is placed in those sections of the classifier that this document did not fall into - it indicates in which section it is assigned by the systematizer. The link is used in cases where similar information can be found in other sections of the classifier.
VocabularyIPSs use a database built from words found in Internet documents a. In such a database, each word contains a list of documents from which it is taken. Since all morphological units in the dictionary are ordered, the search for the desired word can be performed quite quickly, without sequential viewing.
It’s rather difficult to find the required information in one word. Therefore, each dictionary IPS has its own query language, which allows you to combine the words that most fully characterize the information you are looking for.
Vocabulary IPS Internet a include such as Alta Vista, Rambler, I ndex, Aport.
Vocabulary IPSs are capable of producing lists of documents containing millions of links. Even simply browsing such lists is difficult. Therefore, many dictionary IPSs provide the ability to rank search results - the most important documents are placed at the top of the list. In the query language of such IPS, special tools are provided, for example, in the complex search mode in Alta Vista you can specify a list of terms that increase the rank of the document found (which is especially important for this IPS, since it shows only the first 200 documents found). Rambler and I ndex allow you to specify the weight of each of the terms, which allows you to pretty accurately adjust the order of the documents found.
Predictions are the core of any trading system, which is why competently reproduced ones can make you archival money.
AT subjectIPS with the search image linked lists of Web resources containing the necessary information and links to related sites. In such IPS, circular link structures are created. So, the server contains several tens of thousands of thematic rings (the average ring size is about 12 servers, but there are giant rings, which include thousands of servers). While the rings were small, the search for information was not difficult. To facilitate the search on the specified server, their classification and vocabulary IPS are used to help find the necessary information.
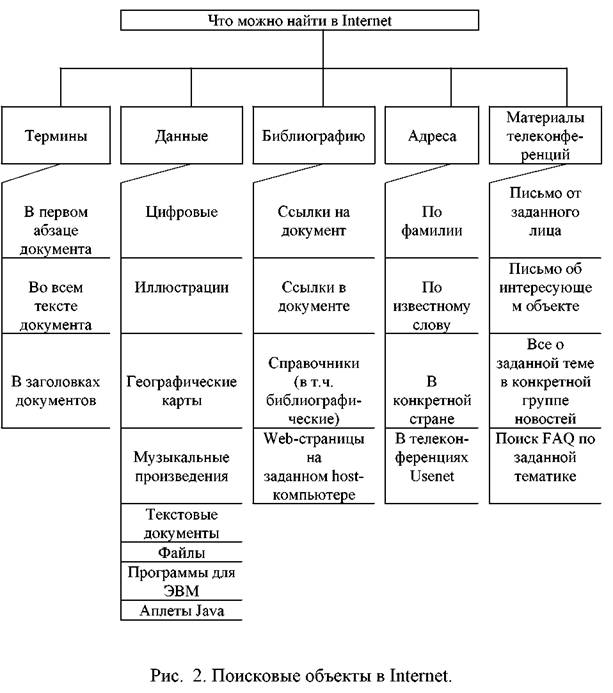
Using information retrieval systems, you can search for very specific information objects, a list of which is shown in Fig. 2.
Description of search engines. Search systemAlta Vista.
Each search engine has its own query language, which defines the rules in accordance with which requests for information search are formulated.
In classification and vocabulary IPS, a request is compiled on the basis of keywords, which are the most striking characteristic of the information sought (in fact, this information cannot do without these words). It is better if these keywords have a specific meaning inherent only in the sought-after information material that distinguishes this material from all others.
The search engine AltaVista belongs to the category of dictionary IPS and is one of the most informative. You can contact her at the addresses:
2) The search image may consist of one or more keywords.
3) Depending on the method of connecting keywords in the search query, simple and complex queries are distinguished.
4) A complex query differs from a simple one in that you can specify the creation date of the document you are looking for (to highlight materials that have the latest update after the specified date), special search logic (defined using AND, OR, NOT, NEAR operators), select one of three options for organizing search results when they are displayed: “only as a result”, “compact form”, and “standard form” (the latter is used by default), and use parentheses to highlight logically independent parts of the query.
5) Keywords can be typed on different keyboard registers - depending on this, the search engine will conduct searches differently.
The presence of a capital letter in the keyword will force the search engine to search for words with exactly the same spelling as in the query with a simple search. If uppercase letters were not used, then the search engine considers any spelling of these words. For example, if the search order consists of one word Computer, informational materials containing this word in this very outline will be found. If this word does not contain capital letters, then the search will take into account words in such styles as computer, COMPUTER, COMPuter, etc. It should be borne in mind that when using a search image consisting of only one word computer, AltaVista provides about 2000 links. Viewing such a number of links is practically impossible, which means that information retrieval cannot be considered effective (with a correctly composed request, the necessary information is among the first two dozen links).
6) In the event that the correct spelling of the word is unknown, or if many root words are of interest, the uncertainty operator “*” (asterisk) is used. Putting this character after any sequence of letters (at least three), the influence of which must be taken into account during the search, you can perform a broad search in which the keyword will be modified: the search will be available for both the set of letters rigidly indicated to the asterisk and for words containing any letters (up to 5) instead of an asterisk. For example, if you specify the keyword comp *, then the search will take into account how the key ones are computer, computers, compute, etc.
7) The operators “space”, “quotation marks”, logical operators “+”, “-”, AND, OR, NOT, NEAR can be used to join several keywords.
8) The “space” operator joins the words in the search prescription in such a way that each of these words is used separately for search. In this case, the word order in the query does not matter. The search process takes into account only the distance of each word from the beginning of the document and the frequency of its use in the document.
9) The “quotation marks” operator concatenates the words so that they form a phrase in which all the words specified in the prescription in the document are next to each other and in the same sequence as specified in the prescription. Therefore, if you specify a search order in the form of the words “personal computer” and in the form of “computer personal”, the search results will be different.
10) The “+” operator connecting the words tells the search engine that it is necessary to search for the main word (first) in the document, but the document should be shown as a result of the search only if the rest of the words from the search instruction are found in the text. An operator is placed immediately before each secondary word. For example, in a search image:
computer + personal + digital will search for the main word computer, but the text will be considered relevant only if it also contains the words personal and digital.
11) The “-” operator before the word indicates that the main word should be used in the text without a secondary one. For example, the search instruction computer - personal tells the search engine that it is necessary to search for the main word computer, but the word personal should not appear in the text (i.e., materials about computers, but not personal ones, are of interest).
12) The AND, OR, NOT, NEAR operators are used in complex queries.
13) The AND operator (you can use the & symbol instead), determines that the words it connects must occur together (that is, in simple queries it is equivalent to the “+” sign).
14) The OR operator (you can use the “|” sign instead) determines that the words it connects are independent of each other (in simple queries, it is equivalent to a space).
15) The NOT operator denotes negation (in simple queries, it is equivalent to the “-” sign).
16) The NEAR operator (the “~” symbol can be used instead) determines that in the searched text the keyword indicated by it is separated from the main one by no more than 10 words (for example, in the search prescription:
* NEAR provider “very cheap” stipulates that in the search text the word “provider” and the phrase “very cheap” are located not at different ends of the text, but next to each other - there can be no more than 10 words between them).
17) To limit the search, special commands (tags) are used: anchor, applet, title, url, host, link, image, from, subject.
18) The anchor command allows you to find on the Web the word contained in the “body” of the link. To do this, after the anchor command, the search word is indicated with a colon. For example, a search image contains:
anchor: home This query will find all the many pages containing the word home inside links, including - and in this link: “If you would like go home, press here”.
19) The applet command allows you to find the Java module specified by the name. For example, if the Java module is called word, then you can find it by writing a search image: applet: word.
20) The title command is used if the search word is in the title of the text. For example, for a query like: title: links, documents will be found containing the word links in the title, including text with the title “Cool Links”.
21) The url command instructs to search for the url address containing the given word. For example, if it is not known which root domain the MESI host computer is located in, you can specify a search prescription: url: mesi. Among the many addresses with such a word there will be an address.
22) The host command allows you to find out what Web sites are on a given host computer. For example, in order to find out what sites are on the host, you need to type the query: host: intel. ru. If in the request to specify only part of the name, then as a result of the search, sites will be found that have other addresses, but containing the specified part of the name.
Using this command, you can search in a given country. For example, for host: *. ru + kreml information about the Moscow, Ryazan and other Kremlin will be found. It should be remembered that the search is conducted only for sites registered in the AltaVista search engine, other sites are not available to it.
23) The link command allows you to find the addresses of pages (sites) that contain a link to a specific (specified in the search image) Web page. For example, in order to find out who links to the site, you need to specify the prescription: link:. The result will be a list of pages that contain links to the mesi website. ru.
24) The image command allows you to find an illustration on the Internet. To do this, you need to know the name of the file in which it is stored. The format of the command is the same.
25) The from command allows you to search in Usenet newsgroups for an email message sent by a specific person whose name is indicated after the colon in the command. For example: from: Ivan + Fedorov (or Ivan + Fedorov).
26) The subject command allows you to search for messages in Usenet newsgroups on a specific topic specified in the search prescription.
The AltaVista search engine can work (and search) in different languages, including Russian.
The described search engine management principles are largely similar to those used in other search engines.
Search systemYandex.
In 1997 at: opened a new Russian search engine Yandex (or I ndex). By the set of its search capabilities, it is not inferior to the most complex search engines of the West, it is specially designed for Russian-language queries and takes into account the peculiarities of Russian vocabulary, it offers several more options for intelligent search.
Like AltaVista, Yandex distinguishes between uppercase and lowercase letters. If the keyword is written in capital letters, then the search engine does not distinguish between uppercase and lowercase letters, that is, when specifying the computer keyword, both Computer and COMPUTER, etc. will be taken into account in the search. Then, as if if the search image contains at least one uppercase letter, in the search will be taken into account only words that have this style.
There is no need for Yandex to use the uncertainty operator (similar to the asterisk in AltaVista), since when specifying a keyword in capital letters, the words used in other cases, in different declensions, in the singular and plural will be used in the search process.
In Yandex, just like in AltaVista, you can build simple and complex queries. But building complex queries requires a higher qualification of the person conducting the search.
To connect keywords in simple queries, operators are used, denoted by the symbols: &, |, ~, (,). Among them, only the tilde (~) has a different purpose - in Yandex it means negation (and is equivalent to the “-” sign in AltaVista). However, these operators have a significant feature: keywords connected by them must be within the same paragraph.
Doubling the telecom operator indicates that the words should be within the entire text (and not just one paragraph).
Yandex provides for “search with distance” - you can specify that the keywords in the search text should be at a distance of no more than, for example, three words (and in one paragraph). The distance is given by / followed by a digit indicating the distance. For example, setting a prescription:
round / 3 ball search engine will search for documents containing within the same paragraph the words “round” and “ball”, moreover, they can be separated by no more than three words. If the distance is given by a negative number, this means that the second word precedes the first.
Instead of a single word in the search prescription, you can use whole expressions. Logically independent elements of these expressions can be enclosed in brackets.
Features of the search for information on the Internet.
The Internet as a global means of exchanging information is often used to find the necessary data. There are many ways to search for information (in brackets there are cases when such a search method is most applicable): Search using search engines(specific things) Catalogs and link collections(more general concepts) Ratings(most popular resources) Conferences, chats and link pages on thematic sites(rare, specialized items). The limited time, physical and financial capabilities of people are forced to most often use special directories and search engines (search engines) for this - librarians of some kind, indexing the array of information available to them on the Internet. In this section, features are highlighted and general rules for the work of the most famous directories and search engines are considered.
Catalogsrepresent a systematic group of addresses, united, as a rule, by topic. The convenience of their use can be attributed to the fact that if the user knows the topic of the document to be searched, he will examine the corresponding branch of the catalog without being distracted by extraneous, irrelevant documents. However, the scope of the catalog is limited by the physical capabilities of the editorial team and its subjectivity in the choice of material. They lack information on narrow, special topics, and the very subject of the desired document cannot always be formulated within the classification of the catalog. Below are the capabilities of foreign and Russian catalogs.
Yahoo! - The most popular directory containing extensive information on tens of thousands of Web sites. The first level of the hierarchy contains 14 thematic categories, which branch into 4-5 sublevels. It has its own search engine, which allows you to: 1) search the Yahoo! database, Usenet, or email addresses; 2) restrict the search to materials posted on the last day, week, month, year or 3 years; 3) to issue articles containing at least one keyword or all keywords; 4) search by cognate words or only by specified key words; 5) display results of 10, 25, 50 or 100 on one page (more details below). Excite Reviews - Contains reviews of 60 thousand Internet sites (hierarchical catalog) City. Net - Information about countries and cities.
Galaxy - A hierarchical catalog with a detailed description of thematic categories on the first page. Searches by search category, by one or several keywords, short and detailed display of search results, transition to Gopher and Telnet pages.
Yellow Pages - Search for information on 16 million American companies in various fields of activity, as well as personal data and email addresses of individuals.
Russia on the Net - The first catalog of Russian resources.
Constellation internet - Covers about 400 servers. Ability to truncate terms. Contains the names and brief characteristics of the servers. Attractive graphics. Small search area, weak hierarchy.
Yellow Pages Internet - About 1200 Web servers. A large amount of information, well thought out structure.
Treasure Internet - Directory of Web resources on the Relcom server. AU! - A young, fast-growing catalog.
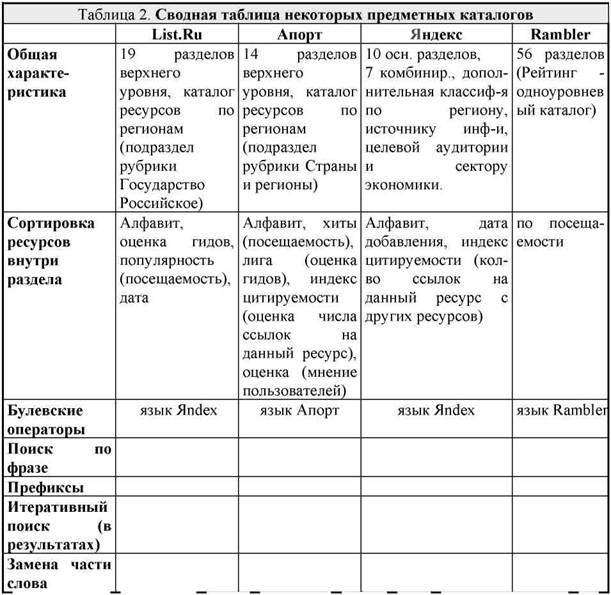
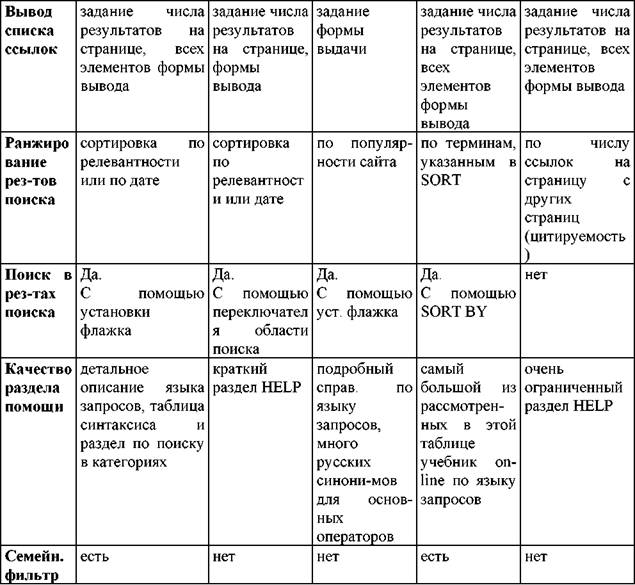
Search serversin total, more than 150 are known that differ by region of coverage, the principles of conducting a search (and therefore by
the input language and the nature of the perceived queries), the volume of the index base, the speed of updating information, the ability to search for "non-standard" information and the like. The main criteria for selecting search engines are the volume of the index database of the server and the degree of development of the search engine itself, that is, the level of complexity of the requests it perceives. Traditionally, search engines have three elements:
1. Robot (crawler, spider, agent) that moves around the Web and collects information; Crawlers look at the headers and return only the first link.
Spiders are programs that perform a general search for information on the Web and report on the contents of a found document, indexing it and extracting the resulting information.
Agents are the most “intelligent” of search tools. They can do more than just search: they can even carry out transactions on your behalf. Already, they can search for sites with specific topics and return lists of sites sorted by their traffic. Search engine administrators can determine which sites or site types agents should visit and index. Agents can process the content of documents, find and index other types of resources, not just pages. Some, for example, index each individual word in a meeting document, while others index only the most important 100 words in each, index the size of the document and the number of words in it, title, headings and subheadings, and so on. They can also be programmed to extract information from existing databases.
The online community has adopted the Robot Exclusion Standard. This standard describes the use of a simple structured text file, available at a known location on the server (" / robots. txt") and used to determine which part of the server’s links should be ignored by robots. All smart search engines first access this file, which should be present on each server. To date, this file must be requested by search robots of only such systems such as Altavista, Excite, Infoseek, Lycos, OpenText, and WebCrawler, which can also be used to alert robots about black holes. Each type of robot can be given specific commands if it is known that the robot It specializes in a specific field, and this standard is free, but it is very simple to implement and there is considerable pressure on robots to try to subordinate them.
1. Database, which contains all the information collected by robots.
Indexing an arbitrary document on the web is very difficult. The first robots simply kept the name of the document and anchors in the text itself, but the latest robots already use more advanced mechanisms and generally consider the full content of the document. Indexed information is sent to the database (DB) of the search engine. The type of the constructed index determines which search can be done by the user of the search engine and how the received information will be interpreted. People can put information directly in the index, filling out a special form for the section in which they would like to put their information. Databases are automatically updated for a certain period of time so that dead links are detected and deleted.
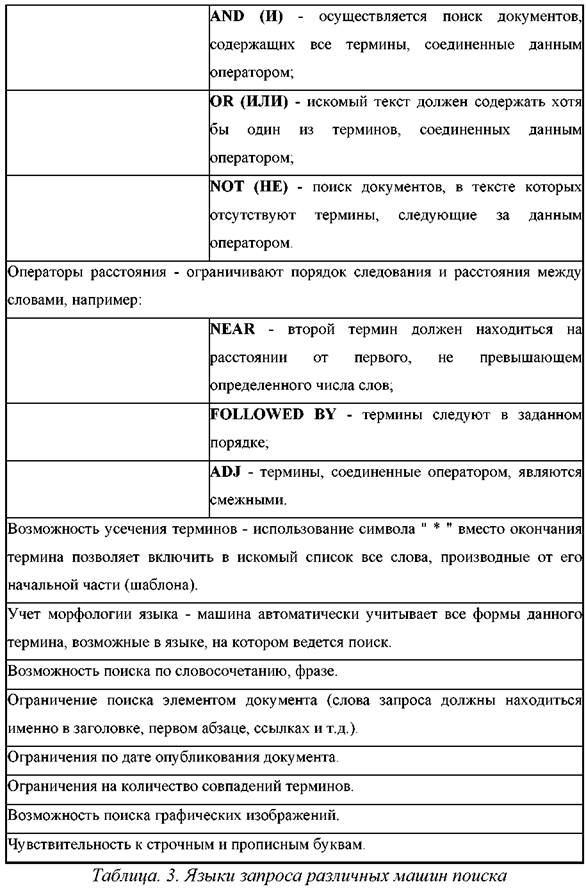
2. User Interfaceto interact with the search engine database. When a user searches for information on the Internet, he fills out a search form on the search engine page. Keywords, dates, and other criteria may be used here. Criteria in the search form must match the criteria used by agents in indexing Web resources. Both the format and semantics of the queries vary depending on the search engine used and the specific subject area. Requests are compiled so that the search area is as concretized and narrowed as possible. The preference is given to using several narrow queries compared to one extended one. Request Languagesdifferent search engines are mainly a combination of the following functions (Table 3).
Boolean algebra operators AND, OR, NOT:
Based on the search string entered by the user, the query subject is searched for in the database and a list of relevant links is displayed. The number of documents received as a result of a search on request,
can be huge. However, thanks rankingdocuments, used in most search engines, on the first pages of the list, almost all documents will be relevant (ideally). Basic principles of definition relevancethe following:
1. The number of query words in the text content of the document (in html code).
2. Tags in which these words are located.
3. The location of the searched words in the document.
4. The specific weight of words (density), relative to which relevance is determined, in the total number of words in the document.
These principles are applied by all search engines. And the ones presented below are used by some, but quite well-known (like AltaVista, HotBot).
5. Time - how long the page has been in the search server database. Many sites live a maximum of a month. If the site exists for quite some time, this means that the owner is very experienced in this topic.
6. Citation index - the number of links to this page from other pages registered in the database.
Exist display featuresthe resulting list - some search engines show only links; others display links with the first few sentences contained in the document or the document title along with the link.
The query result (list of links) is processed in two stages. At the first stage (automatic processing), obviously irrelevant sources that were sampled due to imperfection of the search engine or insufficient "intelligence" of the query are cut off. Further (manual) processing is performed by the user by successively accessing each of the found resources and analyzing the information located there. When a user clicks on a link from the list, before requesting the corresponding document from the server on which he is located, search engines enter a note about user preference in their database. Collected user behavior information(query formulations and resources selected from the list) are successfully used in advertising companies on the Web.
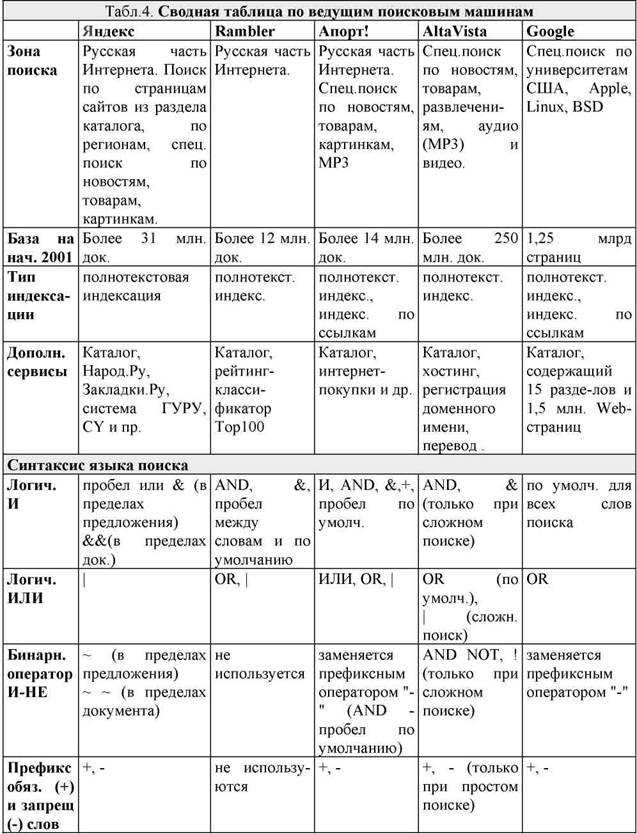
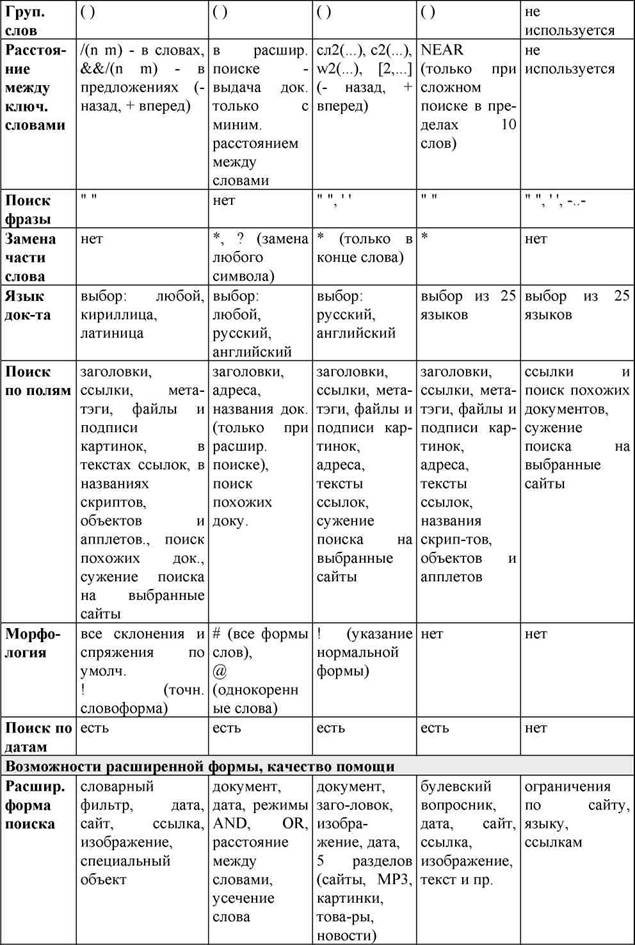
Below are compared the most famous non-Russian search engines.
Altavista . It covers more than 30 million pages on 225,000 servers, provides access to 3 million articles in 14,000 Usenet newsgroups. It has two modes: Simple query and Advanced query. In Simple mode, you can enter patterns for searching with at least three specified characters at the beginning of a word. If the word contains at least one uppercase letter, the search is case sensitive. Below the input line are search tips. In Advanced mode, you can create complex queries based on the logical operators AND, OR, NOT, NEAR and specify criteria for sorting the results. You can specify a range of publication dates. Provides the ability to search for images. User friendly interface. High speed, multivariate search order, the ability to search in Russian, taking into account morphology. The system does not streamline the search results, so it is advisable to apply it for a specific or exhaustive search. Indexing in this system is carried out using a robot. In this case, the robot has the following priorities:
Key phrases in< Meta > tags
Key phrases at the beginning of the page;
Key phrases by the number of occurrences of the presence of phrases; If there are no tags on the page, uses the first 30 words, which are indexed and shown instead of the description (tag description) The most interesting feature of AltaVista is an advanced search. It is worth mentioning right away that, unlike many other systems, AltaVista supports the single operator NOT. In addition, there is also the NEAR operator, which implements the context search option when the terms should be located next to each other in the text of the document. AltaVista allows search by key phrases, while it has a rather large phraseological dictionary. Among other things, when searching in AltaVista, you can specify the name of the field where the word should occur: a hypertext link, applet, image name, title and a number of other fields. Unfortunately, the ranking procedure is not described in detail in the system documentation, but it can be seen that ranking is used both for simple search and for advanced query. Actually, this system can be attributed to a system with advanced Boolean search.
Hotbot - Covers 54 million pages. Search in Russian is possible. It is a popular search tool due to the presence of mechanisms for constructing complex search queries. Basically, the 1st page of the results received in response to the search query comes from Direct Hit, then the results from Inktomi are taken. A list of directories is provided by Open Directory. HotBot began providing its services in May 1996, and in October 1998 it was purchased by Lycos.
Infoseek . It covers 1.5 million pages. The query language allows you to use all possible variants of logical expressions. Less complete than on other servers, search results, inconvenient interface. In this system, a robot creates an index, but it does not index
entire site, but only the specified page. At the same time, the robot has the following priorities:
Words in title< title > have the highest priority;
Words in the keywords, description tag and frequency of occurrences of repetitions in the text itself;
When repeating the same words nearby, throws from the index
Allows up to 1024 characters for the keywords tag, 200 characters for the description tag;
If no tags were used, indexes the first 200 words on the page and uses it as a description;
The Infoseek system has a fairly developed information retrieval language, which allows not only to indicate which terms should appear in documents, but also to weigh them in a peculiar way. This is achieved using special signs "+" - the term must be in the document, and "-" - the term must not be in the document. In addition, Infoseek allows you to carry out what is called contextual search. This means that, using a special request form, you can require consistent joint occurrence of words. You can also indicate that some words should be found together not only in one document, but even in a separate paragraph or heading. It is possible to specify key phrases that are a single whole, up to the word order. Ranking upon delivery is carried out by the number of query terms in the document, by the number of query phrases minus common words. All these factors are used as nested procedures. Summing up, we can say that Infoseek refers to traditional systems with an element of weighting terms when searching.
Infoseek Ultra - 50 million pages of WWW, search in Russian is possible, image search.
Lycos . Covers 68 million pages. You can select the search options: one, several keywords or phrase; truncation of terms; restrictions on the number of matches; the degree to which search results match keywords; form for outputting results (short or detailed); the number of terms found on each page. Low speed and efficiency of updating information. Lycos uses the following indexing mechanism:
Words in< title > The headline has top priority;
Words at the top of the page;
Like most systems, Lycos provides the ability to use a simple query and a more sophisticated search method. In a simple query, a natural language sentence is entered as a search criterion, after which Lycos normalizes the query by removing the so-called stop words from it, and only after that starts to execute it. Almost immediately, information is given on the number of documents per word, and later a list of links to formally relevant documents. The list against each document indicates its measure of proximity to the request, the number of words from the query that got into the document, and an estimated measure of proximity, which can be more or less formally calculated. It is not yet possible to enter logical operators in a string along with terms, but it allows you to use logic through the Lycos menu system. Such an opportunity is used to build an extended request form intended for sophisticated users who have already learned how to work with this mechanism. Thus, it can be seen that Lycos belongs to a system with a query language such as "Like this", but it is planned to expand to other ways of organizing search prescriptions. In October 1998, Lycos acquired HotBot, which is currently being used as a standalone service.
WAIS is one of the most sophisticated Internet search engines. It does not implement only search by fuzzy sets and probabilistic search. Unlike many search engines, the system allows you to build not only nested Boolean queries, consider formal relevance for various proximity measures, weigh the terms of a query and a document, but also correct the query by relevance. The system also allows you to use term truncation, dividing documents into fields, and maintaining distributed indexes. It is no coincidence that this system was chosen as the main search engine for implementing the Encyclopedia Britanica on the Internet.
Yahoo . Yahoo's secret to success lies in people. Yahoo has about 150 editors to compile and edit the contents of its directories. Yahoo has a database of more than 1 million indexed sites. Also, in the event of a shortage of its own database, Yahoo uses the Google database (until July 2000, Yahoo used the Inktomi database). Yahoo is the oldest search engine that began providing its services in 1994. Yahoo's language is quite simple: all words should be entered with a space, they are connected by a bunch of AND or OR. When issuing, the degree of compliance of the document with the request is not indicated, but only the words from the request that are encountered in the document are only emphasized. At the same time, vocabulary is not normalized and no analysis is carried out on "common" words. Good search results are obtained only when the user knows that there is certain information in the Yahoo database. Ranking is based on the number of query terms in the document. Yahoo belongs to the class of simple traditional systems with limited search capabilities.
Prospects for the development of Internet search tools
The following Internet trends are undoubted:
Growth of available information and user information needs
Expanding the borders of the Internet through the accession of new countries
Strengthening the commercialization of services
Increase speed, bandwidth and number of ways to access the network
Deepening the differentiation of services by target audiences (interest circles)
Combining homogeneous services into single portals (places of mass service)
The effects of the “give” protocol affect the development of tools for collecting information about user behavior on the Web
All this will push the automation of search tools and semantic processing of information such as:
Personal Autonomous Intelligent Agents (Type “Search +”)
Personalization and intellectualization of search engines on search portals (setting the method for displaying a list of links, using the Cookies mechanism, filling out special profiles and “subscribing to a request”, semantic ranking of query results)