Using the Trade Management 11.3 example, let's consider a simple process of connecting an external printing form. We will also consider the features of the new security system.
Fast passage
Preliminary actions
For starters, you should enable functionality or check availability
1. We go under full rights to the infobase.
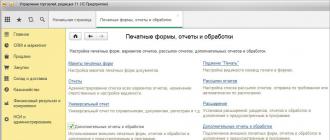
2. Go to the menu "NSI and administration" / Block "Administration" / Command "Print forms, reports and processing".

Addendum
In the opened section:
We add processing by the "Create" button (this is important) or "Update!" existing:
- Select it in the list (if it is not selected or empty, the command will not work, but it will not say anything).
- Click the "Load from file" button.

After the appearance for 1C in external processing, security checks appeared in new configurations.

You should install only processing created independently or received through known communication channels (not from mail, only from a site with a valid certificate, or provided by the developer's employees, confirmed by him by phone).
If everything is written in the processing by the developer, then "Placement" will be set - the objects in which the processing will be involved, the command (s) will appear.
To work, it will be enough to click "Record and close."
Examination
Immediately afterwards, depending on the type of processing:
- The print form becomes available when you open a document or from its list (for an already open one when reopened) by clicking the "Print" button.
- Treatments are available in the "Additional Treatments" sections in each subsystem
- Processing filling by the "Fill" button of the list or the main command panel of the object form.
For the above processing, the launch will look like this:

If the document is new, it should be recorded, the external processing mechanism will warn you about this:

Further behavior depends on the inherent functionality: it is possible to open a form or simple data processing.
Security warnings in 1C
In new releases of the platform and configurations, protection against the launch of malicious programs has been strengthened.
Processing may cause Excel to start to load, in which case the new security subsystem will also warn you:

In this case, the handler code is interrupted.
If you click "Yes", the system will ask you to call the command again:

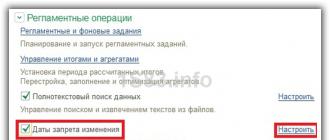
It is possible for an infobase user to disable protection against dangerous actions via the Configurator:

From the "Enterprise" mode, this cannot be changed, perhaps it was done on purpose, it may appear after the update.
You should also note that if processing uses Excel, it must start in unsafe mode (this was the case before the introduction of the new system, this works in parallel):
"Unable to load MS EXCEL!!!" "The safe mode is set. Operation is prohibited"
In external processing, it looks like this:

The developer should set it to "False" in the internal processing description, then everything will be fine:
ExternalProcessingDetails() ExportRegistrationParameters = New Structure; RegistrationParameters.Insert("SafeMode", False);
When updating the configuration, there was also a warning text about the source from which the configuration file was obtained:

When you run the Download Documents program as a normal user, an error occurs "Safe mode is set. Operation is prohibited."
This difficulty arises because there are not enough rights to start external processing. To set access rights, go to the database in 1C Enterprise mode on behalf of administrator and go to section User and Rights Settings / Access Group Profiles, click To create a group.
Enter the name of the group and tick the roles available to users of this group -
- Interactive opening of external reports and processing
- Use of additional reports and processing
Click Write and close

Return to the Users menu and select an employee from the list who will work with the Document Upload program. Click Permissions. In the list of profiles, mark the previously created profile. Click burn.

In order for users to start processing, it is recommended to add Document Upload to the list of external processing. To do this, the menu Administration / Printing forms and processing / Additional reports and processing create a new processing. Specify the path to the "DocumentUpload.epf" file and give it a name. Specify the location of the processing in the menu, from where the user can start it in the future, for example, select the menu Reference books

By clicking on the Quick access item, you specify which of the users is available for processing:

After setting, click Write and close. To start processing, users will only need to re-enter the database and open it from the access menu (in the example - Directories) and click Run.

open Menu - All functions... and find the option "Using security profiles" in the list.

It is enough to uncheck the option "Security profiles are used".

After that, the program will run successfully.
Print (Ctrl+P)
Configuration objects
If it is necessary to use "untrusted" program code on the server: external processing or program code entered by the user for use in the Execute() and Calculate() methods, you can use the safe mode of operation.
In safe mode:
- Privileged Mode canceled.
- Switching to privileged mode ignored.
- Forbidden operations that lead to the use of external tools in relation to the 1C:Enterprise platform (including non-blocking analogues of the above methods):
- COM mechanisms:
- COMObject();
- GetCOMObject();
- WrapperHTMLDocument.GetCOMObject().
- Loading external components:
- LoadExternalComponent();
- ConnectExternalComponent().
- File system access:
- valueToFile();
- CopyFile();
- MergeFiles();
- MoveFile();
- SplitFile();
- CreateDirectory();
- DeleteFiles();
- New File;
- New xBase;
- WriteHTML.OpenFile();
- ReadingHTML.OpenFile();
- ReadingXML.OpenFile();
- WriteXML.OpenFile();
- ReadFastInfoset.OpenFile();
- WriteFastInfoset.OpenFile();
- CanonicalWriterXML.OpenFile();
- XSL Transformation.LoadFromFile();
- WriteZipFile.Open();
- ReadZipFile.Open();
- NewTextReader() if the first argument is a string;
- ReadText.Open() if the first parameter is a string;
- New TextWrite() if the first parameter is a string;
- WriteText.Open() if the first parameter is a string;
- New ExtractText();
- changing the ExtractText.FileName property;
- ExtractText.Write();
- New Image() if the first parameter is a string;
- Picture.Record();
- New BinaryData();
- BinaryData.Write();
- New DataWrite() if the first parameter is a string;
- New DataRead(), the first parameter is a string;
- all methods of the FileStreamManager object;
- New FileStream();
- FormattedDocument.Write();
- GeographicScheme.Read();
- GeographicScheme.Write();
- GeographicScheme.Print();
- SpreadsheetDocument.Read();
- SpreadsheetDocument.Write();
- SpreadsheetDocument.Print(); GraphicScheme.Read();
- GraphicScheme.Write();
- GraphicScheme.Print();
- TextDocument.Read();
- TextDocument.Write().
- Internet access:
- New Internet Connection,
- New InternetMail,
- New Internet Proxy,
- New HTTP Connection,
- New FTP Connection.
ATTENTION! Throws an exception when performing prohibited operations at runtime.
Note. External reports and processing opened using the File ‑ Open menu are executed in safe mode if the user does not have administrative access rights.
The number of safe mode activations must match the number of shutdowns. However, if within a procedure or function, the safe mode was enabled (once or more), but it was not disabled, the system will automatically shutdown as many times as there were pending activations in the procedure or function being abandoned.
If in a procedure or function method calls SetSafeMode(False) done more than method calls SetSafeMode(True), then an exception will be thrown.
Programmatic installation of safe mode may be required when the configuration developer assumes the use of third-party (in relation to the configuration) program code, the reliability of which the developer cannot guarantee. An example of such code is the execution of the Execute() and Calculate() methods in cases where the executable code is received from the outside world. In this case, it is good practice to set safe mode before executing these methods:
// Program code is generated to be executed // It is possible that the code is loaded from external sources // or entered manually ExecutableCode = GetExecutableCodeFrom OutsideWorld(); // Enable safe mode SetSafeMode(True); // Execute potentially dangerous code Execute(ExecutableCode); // Disable safe mode SetSafeMode(False);
In some cases, the safe mode settings may conflict with the privileged mode settings. An example of such a conflict is posting a document that has the Privileged mode on post property set from 1D code that is running in safe mode. In this case, privileged mode is disabled, and attempts to enable it are ignored. As a result, 1C:Enterprise code that "relies" on the enabled privileged mode "collides" with its absence, which leads to errors with non-obvious reasons for appearing. To prevent such a situation, 1C:Enterprise automatically disables safe mode for event handlers that are available in an object module or a manager module, provided that the executable code in the 1C:Enterprise language is not located in the configuration extension. Such handlers are marked in the syntax assistant in a special way.
It also provides the ability to disable safe mode from within the 1st language (if the code from which the disable is attempted is not in a configuration extension). Method to disable safe mode SetDisableSafeMode(). You can check that safe mode is currently disabled (automatically or by calling a method) using the method GetDisableSafeMode().
Within a single 1C:1 method, there cannot be more than one nesting level of setting safe mode (by calling the SetSafeMode() method) and setting disabling safe mode (automatically at the time of execution of metadata object event handlers or by calling the SetSafeModeDisable() method). When trying to increase the nesting, an exception is thrown:
// Correct Usage Procedure ProcedureName() SetSafeModeDisable(True); SetSafeMode(True); SetSafeMode(False); SetSafeModeDisable(False); EndProcedure // Incorrect usage Procedure ProcedureName() SetSafeModeDisable(True); SetSafeMode(True); SetSafeModeDisable(False); // Exception EndProcedure ProcedureProcedureName() SetSafeMode(True); SetSafeModeDisable(False); // Exception EndProcedure
Programmatic discovery of external processing is carried out using the global context object ExternalProcessing, which has the type ExternalProcessingManager. For each operating mode of the 1C platform (regular application mode and managed application mode), different object methods are used to work with external processing.
Starting external processing in normal application mode
In a typical application, you need to use the Create() method of the ExternalProcessing object, which is passed the full name of the externalprocessing file. The method returns an object of type ExternalProcessing, this object is the external processing being opened. If you need to open an external processing form, then call the GetForm() method of the received object, which will return the main form, and then call the Open() method to open it.Processing = ExternalProcessings.Create(FullFileName);
Processing.GetForm().Open();
In external processing, the main form should always be a regular one, and the managed one should always be an additional one, otherwise the GetForm() method will not work in the normal application mode.
Start external processing in managed application mode
Managed forms mode introduces a separation of the algorithm by execution context. On the client, we get binary data by the full name of the external processing file. We transfer the received binary data to the server and place them in temporary storage. Next, you need to call the Connect() method of the ExternalProcessing object, to which the address to the temporary storage is passed. The method returns the name of the connected external processing. We return the name of the external processing on the client, form a string path to the processing form, and use the OpenForm() method to open the external processing form.&On server
GetExternalProcessName(BinaryData) Function
AddressInTempStorage = PlaceInTempStorage(BinaryData);
Return ExternalProcessing.Connect(AddressInTempStorage);
EndFunctions
&AtClient
FullFileName = ""; // Full name of the external processing file.
FileData = New BinaryData(FullFileName);
ExternalProcessingName = GetExternalProcessingName(FileData);
OpenForm("ExternalProcessing." + ExternalProcessingName + ".Form");
Safe mode for external processing
The Create() and Connect() methods of the ExternalProcessing object have the SafeMode input parameter, which indicates that external processing is connected in safe mode. If the parameter is not specified, the connection will be made in secure mode.Safe mode of operation is designed to protect the system from running "untrusted" program code on the server. Potential dangers are external processing or program code entered by the user for use in the Execute () and Calculate () methods.
Safe mode has the following restrictions:
- privileged mode is canceled if it was set;
- attempts to enter privileged mode are ignored;
- operations with COM objects are prohibited;
- loading and connection of external components is prohibited;
- access to the file system is denied (except for temporary files);
- access to the Internet is prohibited.
To prohibit the interactive opening of processings, in all roles assigned to the user, it is necessary to remove the "Interactive opening of external processings" right (see Figure 1).
| Figure 1. Rights to interactively open external processing/reports |
Opening external reports programmatically is similar to external processing, but you should use the ExternalReports global context object, which is of type ExternalReportsManager.
The fact is that when using the client-server version of 1C, external processing / reports are opened in safe mode, in which the use of privileged mode is prohibited. And the privileged mode is used very often in typical configurations: the formation of printed forms, various service checks (registration of exchanges), etc. As a result, even using a regular report on ACS without a form (by default, the general form "ReportForm" is used) and saving the user settings of the report (in the corresponding directory), you will receive an error about insufficient access rights to various constants and session parameters used for official purposes after line SetPrivilegedMode(True) ;
The "correct" solution would be to connect external processors and reports through the BSP "Additional Reports and Processing" mechanisms with disabling safe mode or adding permissions (in my opinion, from BSP version 2.2.2.1). But if for some reason it is necessary to use external report/processing files, then you can configure the cluster security profile used as the safe mode security profile for a particular infobase.
I would like to note right away that this option is not preferred, but due to various circumstances, it can be used in such a simplified form. For example, I have several databases in different cities, a common local network with strictly limited rights, closed USB, etc., Accounting 2.0 is used somewhere, and somewhere 3.0, I make almost all reports using ACS without forms, so that they opened in both versions. Maintaining all these reports for different versions and different databases is a time-consuming and unpromising task, because there are plans to switch to a single configuration and base ...
We create a profile.
In the cluster console, create a security profile in which we set the flags "Can be used as a safe mode security profile" and " under "Full access allowed:" "to privileged mode".

In many cases of using reports and simple processing, this method will be applicable. For more complex situations, it makes no sense to describe the process, because. it is described in the documentation (the ability to configure security profiles for specific external files by specifying its hash sum, etc.).
P.S. I thought that security profiles function only when using licenses for the platform and server of the CORP level, but this functionality also works on the 1C: Enterprise 8.3 platform (we can conditionally call PROF by analogy with the typical configurations Basic / PROF / CORP)