Computers have long and firmly entered our lives. Most families have at least one computer or laptop. Computers help us work and have fun. Movies, music, games, communication with friends - all this is given to us by the computer and the Internet.
Almost everyone knows how to use the Internet, but sometimes there is a need to connect computers to each other in a local network in order to transfer data between them directly, bypassing the Internet. How to do it yourself, with a magazine Reconomica shared by Alexey, a system administrator from Minsk.
Hello, my name is Alexey Bulatetsky, I am 36 years old. I was born in Moscow, now I live in Belarus, in Minsk.
Several months ago I had the opportunity to get a job as a system administrator at a new place. After a couple of working weeks, I was given the task of designing and building a local enterprise network.
A local network is several computers connected to each other over a short distance to exchange information.
Having started working on the project, I decided to sketch out a small manual on creating a local network. The result is this article, in which I tried to tell in detail what we need and what the procedure for our actions is.
Network topology
First, let's decide on the topology of our network. Network topology is a geometric diagram of how computers are connected to each other. There are three types of topology that are used most often:
- star;
- ring;
- tire.
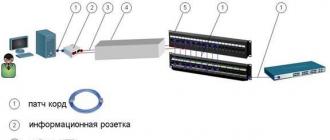
We will use a star topology scheme, in which each individual computer is connected to the switch via a separate connecting cable.
Star network topology.
Required network equipment and cable preparation
What we need for the network:
- connecting cable (twisted pair);
- connectors;
- Computer network cards need to be checked and new ones purchased if necessary.
Network switch and its installation
A network switch (switch) is special equipment designed to connect computer nodes to each other.
I think, no, I’m not even sure, that we need to place the switch somewhere in the center of our computers, then it will be easier to pull the cable and less of it will be needed.
Regarding the choice of a network switch, I want to say that I use only D-Link switches in my work; they have proven themselves to be reliable equipment.

D-Link network switch.
Just don’t think that I’m advertising for D-Link, under no circumstances. At the moment, there is a huge selection of switches and manufacturers that are not inferior in quality to the leading giants in this industry, but I personally prefer D-Link, since over the last five years of work they have never let me down.
Straight cable crimp
At the next stage, we need to crimp the cable (for better signal quality, use only a new cable, do not use one that has already been used).
To do this, we need connectors and a special crimping tool (in extreme cases, you can crimp using pliers and a screwdriver).

Connector and crimping tool.
The network cable has eight cores, each two cores are intertwined, resulting in four pairs, hence the name - twisted pair. We will crimp according to the computer-hub scheme, that is, direct crimping.
You need to act strictly according to the diagram, the connector has eight cells for wires, we lay the wires according to the colors of the cores. The diagram is in the figure below.

Direct crimp color scheme.
All eight cores are used for 1 Gbps communications, but four wires (light orange, orange, white-green and green) can also be used. The data exchange speed will be 100 Mbit/s, and I want to note that this speed is quite enough for comfortable work on the local network and the Internet.
There is an option to use only two wires: light orange and orange, in this case the reception and transmission of data will be carried out alternately, this will significantly slow down the work. Nowadays, almost no one uses such a connection.

How to insert wires into a connector.
So, what we have: we have decided on the network switch, its location, we have crimped our network cable with connectors on both sides and connected the computers to the switch.
All that remains is to correctly configure the computers to communicate with each other through our network switch.
Setting up computers
Every computer needs:
- assign an IP address;
- set the network mask;
- configure a workgroup (all computers on the network in one workgroup);
- configure access to disks and assign appropriate permissions to write and read data.
Setting the IP address and network mask
IP address – in other words, this is the identification number of a computer on the network; it is configured on the network card. It is different for every computer. To configure or change the IP address you need to:
- open Start ->
- Control Panel ->
- Network and Sharing Center ->
- Changing adapter settings ->
- Properties. We select the protocol and in the properties you can change the IP.
Network mask is the part of the IP address that indicates the boundaries of the network. It can also be configured in the properties of the network card.
So, in order for our local network to work fully, we will write down the IP address and network mask (for example, like this):
- IP address 192.168.1.2;
- netmask 255.255.255.0
On the next computer we configure it like this:
- we add 1 to the IP address, that is, the address becomes 192.168.1.3;
- leave the mask unchanged.
And the same on all computers that will be on our local network.
Setting up a workgroup
A workgroup is a group that includes all computers on the same local network.
You can change or assign a group here:
- Start ->
- Utilities ->
- Control Panel->
- System and security ->
- System ->
- Additional system parameters.
Latest settings and network check
Access to disks can be configured in properties, where you can also configure permissions for reading and writing data.
Important!!! It is necessary to check whether the “Server” and “Browser” services are running on the computers, since if these services are not running, then you simply will not see a list of computers in the “Network Neighborhood”. Well, in the end you need to check the current time on all computers and, if necessary, correct it.
Now we can proceed to checking the operation of our network.
We go to “My Computer”, then “Network Neighborhood” and see a list of computers available to us on the network. That's all, we can start exchanging information depending on what drives we have opened and what permissions we have given to read and write data.
How to connect the Internet on a local network
To connect your local network to the Internet, you must already have an agreement with your provider. Of course, you either need to have a modem at home, or simply run a network cable into your apartment. Usually the provider pulls the cable into the apartment from the entrance or simply throws the cable off the roof.

To connect to the Internet on a local network, you need to connect the Internet cable to the switch into a free port. Then register the Default Gateway in the network cards of the computers, and indicate the Primary and Alternate DNS servers. This data can be obtained from your Internet service provider.
How to change network card settings:
- Start > Control Panel ->
- Network and Sharing Center ->
- Changing adapter settings ->
- Properties. In Properties, select Protocol and specify the Default Gateway and DNS server addresses.
Wireless LANs
Nowadays, wireless local area network is gaining popularity. It is much more convenient, there are no wires, no connectors, the price characteristics are not much different from equipment for a wired local network.
To organize this kind of network, it is required that each computer be equipped with Wi-Fi, and also require a Wi-Fi router that will act as a router.
All you have to do is choose and determine for what purposes the local network will be used and what the load on it will be.
Good luck to you in building local networks.
Let's decide on the starting points: a small company, maybe about 15-50 employees. As a rule, there is no qualified network specialist. And most likely it’s the one “dedicated” to working with the network, the network administrator on staff. Let's agree - your own specialist is still necessary. And he needs to be paid money, and good money at that (what a horror, right? This is news for many directors). In this article (possibly with a continuation) I will try to act as a network administrator for such a small company. So, we build the network ourselves. Why not? There are many arguments against self-dealing, and all of them are true (unless, of course, it is an outright “noodle” from a potential contractor). But, still, you can do it yourself. There are also plenty of arguments in favor. We will not present them here - we believe that we decided to do it ourselves. We will not create newfangled radio, Wi-Fi and other networks, but an inexpensive but high-quality cable network of the traditional wire type for the daily work of the company. However, you must understand that the work must be performed by a specialist (or several).
Introduction
Let's decide on the starting points: a small company, maybe about 15-50 employees. As a rule, there is no qualified network specialist. And most likely it’s the one “dedicated” to working with the network, the network administrator on staff. If there is one, he is a jack of all trades, and is often forced to deal with some “urgent” matter, such as installing Windows or drivers on some computer, instead of working with the network. Together with other "computer scientists" (if there are any). Is the network working? Let the deck pass through the stump, oh well, we’ll get to work a little later (we’ll get to work on it).
Let's agree - your own specialist is still necessary. And he needs to be paid money, and good money at that (what a horror, right? This is news for many directors). In this article (possibly with a continuation) I will try to act as a network administrator for such a small company.
Initial data
So, we build the network ourselves. Why not? There are many arguments against self-dealing, and all of them are true (unless, of course, it is an outright “noodle” from a potential contractor). But, still, you can do it yourself. There are also plenty of arguments in favor. We will not present them here - we believe that we decided to do it ourselves.However, you must understand that the work must be performed by a specialist (or several). You cannot train (“even if inferior, but your own”) and raise your specialist using this method. You can give yours to the person doing the work (we won’t take into account drilling holes in the walls with a hammer drill and attaching cable ducts - any man should be able to do this).
One more factor, let’s add the “pepper” so to speak - our company, in addition to the office, has a store and a warehouse, which are quite remote.
We will not create newfangled radio, Wi-Fi and other networks, but an inexpensive but high-quality cable network of the traditional wire type for the daily work of the company. For work, not for surfing news and/or porn sites from a laptop from a hotel sofa. We may return to these questions in the sequel (not to the hotel and its ilk, of course, but to modern technologies).
Last, and also very important: we count money, but don’t be greedy.
Plan
At the very beginning, you must do one very simple, but very important thing - take a few sheets of paper, a pencil and sit down to draft a business plan. It is very important to more or less clearly “take a pencil” of all the keywords that come to mind from the question “what do I want from the network”. Sketch these positions on the first sheet. The second step is to group them into separate categories. For example, the “services” category. What services do we want to receive from the network, and what quality? What do we need? File-, ftp-, print-, internet service?It would seem that everything is clear, why write, draw? But if you don’t take everything into account, it will get worse later. For example, it turns out that you need to go to the director and/or the accounting department: “Sorry, we bought the wrong piece of hardware here, and not for 100 USD. necessary, but for 500.”
Now, after taking a rest, you can add what you need and throw away the excess. And put all this off for at least a day. Next, the draft can be transferred to the third sheet. With "final" additions and corrections. Why the quotation marks - you yourself understand, this is not the last piece of paper, and far from the last “sketches”.
Services are services, however, the base is SCS, that is, a structured cable system. Let's try not to run too far ahead of the horse.
Usually there are two options - an office “from scratch” and an office “ready”. The first case is bare walls and ceiling, the renovation is ours, and that’s good. The second option is “ready”. Those. - we begin the external laying of the SCS. But let's not start with that, for now.
Electricity
An important stage, because God forbid that not just one or two ordinary computers “fly”, everything can “fly”. Okay, we think that everything is fine with the power network in our office. There is only one important point here - uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). They are necessary. Believe me. A diesel generator is, of course, good, but not necessary in all cases, but sparing money on installing a UPS on every server or communication cabinet is simply stupid. However, we will return to the issue of UPS in due time.SCS and basic active equipment
Structured cabling system (SCS) is one of the cornerstones. The SCS must be properly designed and built. Let's divide the question into points:
* Communication cabinet (with “stuffing”)
* Cable lines
* Subscriber sockets
This is where a floor plan, with employee positions clearly marked, comes in handy. One thing to keep in mind is that it’s a good idea to also mark the power outlets. Next, in order, let's start with the closet.
Communication cabinet: We find a convenient place to install a cabinet with equipment. It is important to find the optimal distance to workstations in order to reduce costs for twisted pair cables, cable channels and other “trifles”. There are many factors: limiting the line length to 100 meters (or rather, 90 meters, according to the classic formula 90+5+5); office layout (in what place is it convenient to place or hang a cabinet, is it convenient to go through walls when pulling cables, will the cooling put pressure on the ears of clients or employees, etc.); in fact, the design of the cabinet (floor-mounted, wall-mounted, its height in U, the amount of equipment that needs to be installed in it, whether there will be a cooling unit).
There are a wide variety of cabinets, you need to carefully look at the prices and quality of the proposed purchase, do not forget to make a reserve of capacity (!) in those same U. The presence of at least one shelf is a must. However, in some places it is quite possible to get by with wall brackets to secure the equipment. But this is already specific. We will assume that for the office we have chosen a 12-14 high cabinet with a glass door. Looking ahead a little, it is necessary to mention what will be installed inside:
Shelf: It will always be useful, even if it is empty (I doubt it) - it can be removed. You should not regret 10-20 dollars when you have to “suddenly” put a device or two in the closet, remember these lines.
Switch: 24 ports are the lower limit of company employees in the office - let there be 10-20 people in the office (and don’t forget about servers and other network equipment). However, if there is a high density of jobs, there will be no problems adding the required number of switches and other related equipment.
Distribution panel (patch panel): 24 ports, everything is the same with a switch. It is to the patch panel that all lines from workstations and servers will be connected.
Panel (block) of power sockets: according to the amount of connected equipment in the cabinet, plus a reserve of 1-2 sockets on the panel. Here we may well be faced with an “ambush” if we have to connect power supplies - there may not be enough (remember that 99.9% of the market is filled with surge protectors with sockets placed tightly and obliquely).
You can install a cheap, simple option (that’s when a shelf comes in handy, but you can also install it on the floor of a cabinet), or you can install a 19” UPS designed for installation in a cabinet.

So, having looked at the products offered on the market, we believe that we have decided on a cabinet: 14-high (14 U). For example, Molex MODBOX II 14U:
Possibility of using a 19-inch 1U fan in a cabinet
. Standard cabinet configuration:
. Lightweight steel profile provides the cabinet with greater rigidity and strength
. Aesthetic glass door with lock
. Door of universal design with the possibility of reversing (left, right)
. 19" frame with depth adjustment
. Grounding of all cabinet elements
. The cable entry holes are equipped with a protective brush to prevent dust from entering the cabinet
Switch. His choice is a more complex matter. I don’t want to consider very cheap switches. There are still more expensive (and very expensive) devices, but you still have to choose from two types: unmanaged and managed.
Let's take a look at the following two devices: ZyXEL Dimension ES-1024 and ES-2024:

It is a cost-effective Fast Ethernet solution and can be used to build highly efficient switched networks. The store-and-forward feature significantly reduces latency on high-speed networks. The switch is designed for workgroups, departments, or backbone computing environments for small and medium-sized enterprises. Due to its large address table and high performance, the switch is an excellent solution for connecting departmental networks to a corporate backbone or connecting network segments.
Specifications:
24-Port Fast Ethernet Switch
. Compliant with IEEE 802.3, 802.3u and 802.3x standards
. RJ-45 Ethernet ports with automatic 10/100 Mbps speed selection
. Automatic detection of crossover cable connections on all RJ-45 10/100 Mbps Ethernet ports
. Supports Back-Pressure-Base flow control on half-duplex ports
. Support Pause-Frame-Base flow control on full duplex ports
. Support for store-and-forward switching
. Supports automatic address detection
. Maximum forwarding speed over a wired network
. Built-in MAC address table (8K MAC address capacity)
. LED indicators for power, LK/ACT and FD/COL

Application of the ES-2024 switch will allow you to unite a group of users and connect them to the corporate network via high-speed lines. Additionally, it will be possible, thanks to the use of iStackingTM technology, to combine a group of switches for network management, regardless of their location.
Specifications:
24 RJ-45 ports with auto 10/100 Ethernet speed and auto crossover cable detection
. 2 10/100/1000 Ethernet ports
. 2 mini-GBIC slots combined with ports
. 8.8 Gbps non-blocking switch bus
. Supports IEEE 802.3u, 802.3ab, 802.3z, 802.3x, 802.1D, 802.1w, 802.1p protocols
. MAC address table 10Kb
. VLAN support: Port-based and 802.1Q
. Ability to limit port speed
. 64 static VLANs and up to 2Kb dynamic VLANs
. MAC address filtering
. Supports ZyXEL iStacking™, up to 8 switches (in the future up to 24) controlled by one IP address
. Control via RS-232 and WEB interface
. Telnet CLI
. SNMP V2c(RFC 1213, 1493, 1643, 1757, 2647)
. IP management: static IP or DHCP client
. Firmware update via FTP
. Updating and saving system configuration
. Standard 19" rack mount
As you can see, there is a difference, and a very serious one. There is a difference in price - approximately 100 and 450 dollars. But, if the first switch is a decent, but “dumb” box, then the second is in some sense intelligent, with much greater functionality and controllability, with potentially strong sides. We choose the second option. We want to build a good network, right?
By the way, right now is the time to ask the question, why are we actually building a “hundredth” network? Nowadays, every second computer has not just a gigabit network interface, but two gigabit ones?
This is the case where you can safely save. The fact is that a 100-megabit network is more than enough for office work. If, moreover, the switch is decent! Yes, and on the two gigabit interfaces of the selected switch, we can safely “plant”, for example, two servers. This is just for their benefit, the servers.
Of course, you can take something like the ZyXEL GS-2024 and put everyone on a gigabit channel, but this is just a case of unreasonable spending of money, and for that kind of money we can buy the entire cabinet with a more complete set.

Patch panel. This is also a case where you shouldn’t save much. We choose a panel like Molex 19" 24xRJ45, KATT, 568B, UTP, PowerCat 5e, 1U.
Category 5e compliant. The compensation system is implemented directly on the printed circuit board. The use of KATT type connectors speeds up and simplifies cable installation. Dedicated space for channel marking. The panel is powder coated. All necessary fastening and marking elements are supplied in the kit.
There are many options here, as already mentioned, you can install any cheap one, you can get it more expensive, you can have a 19” rack version - it will be absolutely beautiful. Who doesn't know APC? For example, you can look at this UPS:

APC Smart-UPS SC 1500VA 230V - 2U Rackmount/Tower
Or like this:

Without delving into the specifications, we note that many devices are equipped upon request with guides for installing a UPS in a 19" rack. It is also possible to equip, if desired, an SNMP module for monitoring and managing the UPS over a computer network. Of course, this will cost money, but may turn out to be very convenient. Let's choose IPPON. It should be noted that models 1500, 2000 and 3000 can be equipped with SNMP support, but 750 and 1000 cannot.
Power socket block:

Without any special comments - maybe you can find something cheaper and simpler. But a dozen “strangled raccoons” won’t make a difference.
The only thing left to remember is to decide whether a fan unit is needed in the cabinet? An expensive pleasure, especially when paired with a thermostat unit. However, let’s relate this to the specifics of the location/office.

We’ve more or less sorted out the closet, all that remains are all sorts of “little things”, without taking into account which there will be annoying delays later:
* Screws with nuts for mounting equipment in the cabinet;
* Nylon non-opening ties for laying and fastening cables (packs of 100 pieces, 100, 150, 200 mm long);
* Cable markings (adhesive sheets with a protective layer).
In fact, we got to the SCS itself. A very important “detail” is the cable that will be used to wire the SCS. Yes, again the call not to save. A good twisted pair cable is a good investment. We take Molex, unshielded UTP PowerCat 5e cable.

The cable is the core element of the PowerCat product line. The line is designed for use in high-speed telecommunications networks (for example GigaEthernet 1000Base-T).
We will, of course, come to the subscriber sockets, but what next? Next - buy the required number of patch cords to connect workstations. Naturally, you need to think about the length, look at the mentioned office plan. But that is not all. You also need a strainded cable (regular - solid). This is a special twisted pair, “soft”, from which patch cords are made. After all, sooner or later you will definitely need a patch cord of a greater length than is available ready-made at hand (if there are any left at all by that time). In addition, you can (or necessary - as you wish) it will be to make short - 30-50 cm, patch cords for cross-connecting SCS lines and active equipment in the cabinet itself. Therefore, we “take a pencil” for a couple more packages of RJ45 connectors, in common parlance - “chips.” And packaging of rubber caps for them. It is better to take the caps soft and with a slot for the “chip” retainer, and not with a “pimple” for the retainer.
We have almost reached the network interfaces on user computers, but subscriber sockets are still needed. Is anyone against such a wonderful thing as Molex OFFICE BLOCK 2xRJ45? ;-)

Category 5e compliant. The modules are designed for high-speed telecommunication networks. Possibility of cable entry from the sides, top or rear. As standard, the modules are equipped with dust curtains. Convenient channel marking. The built-in magnet simplifies the installation of modules on metal surfaces. Possibility of fastening with screws. Cable fastening inside the module without cable clamps. Free choice of connection sequence (568A/B). "KATT" type connector for easy installation. The kit includes mounting elements. .
Here you need to decide on the quantity. After all, there are single options. Let's take the office plan again. There is another important point in determining the installation locations for sockets - it is advisable to add one or two additional SCS lines to each office. One - just “just in case”. What if the layout in the office changes a little or someone needs to connect a laptop? The second is a good idea to have for a print server, for organizing network printing. It’s very nice to have one or two network printers per office or office that work without the problems and whims of the owner (or Windows).
Do you think that's it? No. Another factor that is present in any office has been forgotten - telephony. It’s very good to think about this: if telephones must be connected to some workplaces, then why not make the wiring in a common SCS? After all, the issue can be solved simply: throw a line or two to the necessary places, install an RJ-12 socket next to the RJ-45, it can even be in one case (block). In a socket - DECT, for example, with several handsets, and in a cabinet we draw a line (lines) from the PBX - they can be placed on sockets carefully glued with Velcro inside and on the sides. Lines from workplaces are on them.
It seems like it’s time to take on the cable duct and dowel-nails? Yes. It is time. But this is already clear to any handy man; let’s not dwell on this for long. You just need to take into account the number of lines being laid in the cable channel. And, of course, a small supply is needed. It is very good if the office has a suspended ceiling; the lines can be stretched behind it directly to the workplace and lowered in a cable channel along the wall. When drawing lines, it’s a good idea to label them (as well as sockets in the future). The simplest method is the first socket to the left of the door - No. 1, then in a circle.
Having stretched the lines, you can start splitting the patch panel and sockets. Needless to say, this work requires precision and skill. It is at this moment that marking the lines will be useful to us - if all the lines are split in order, then in the further operation of the SCS it will be possible to practically do without an installation map (layout), something like this:
Socket
However, this card is still necessary in the future. It will definitely come in handy.
When laying cables, you need to follow a few simple rules (just simple, we won’t go deep into standards and other ISOs):
* Do not bend, rub or step on the cable. Cable bending is allowed: during installation - 8, and during operation - 4 radii of the cable itself;
* Do not lay lines next to power lines: if there is a need to lay them in parallel - at a distance of at least 20 cm;
* It is allowed to cross power lines at right angles;
* Testing with a cable tester is required.
Separately about the last point. Remember the joke about the Japanese supply of something there? “Dear customers! We don’t know why you need this, but we still decided to put one defective chip in the boxes for every ten thousand, according to your requirements.” Yes, you can just split it and forget it. An experienced installer makes no mistakes. However, a truly experienced installer will definitely check not only the line layout, but also the quality.
Now we have reached the most interesting moment. If we check small things with a simple and cheap tester, then testing and certifying the lines - no, it won’t work:

Which exit? I really don’t want to leave the issue of line quality unresolved. There are three options. The first is to buy a good tester, for example:
But, alas, we really feel sorry for the $6,000, even for such a wonderful and necessary device.

It is a compact, portable tool used to qualify, test and troubleshoot coaxial and twisted pair cables in local area networks. The tester is recommended by leading manufacturers of information cable systems for testing for certification of systems up to Class E inclusive. The high level of reliability, convenience and accuracy of the device ensured it one of the first places among products of this class. For fast and high-quality testing of cable connections in an extended frequency range up to 350 MHz, digital pulse signal processing technologies are used.
The second option is to invite a friend of the admin or installer who has this or a similar device. Of course, first buy a case of good beer. Half an hour of work, plus a beer evening in the pleasant company of a friend.
The third option is to officially invite specialists from any company that provides such services. And pay for these services. This is not so much, especially if you do not require a certificate on paper.
Remote workstations
Having “finished” (quotes because we must first plan everything and make the necessary purchases and negotiations) with the work at the main office, we remember the warehouse and store.
Now (in these notes) we will consider not a “sophisticated” solution like VPN, but the simplest one - organizing the connection of computer networks with subnets (workstations with a network) via a dedicated line. Effective, cheap and cheerful. By the way, dedicated telephones, of course, should be placed in a closet and connected to sockets, just like telephones.

If the distance and, accordingly, the resistance of the dedicated line is small, you can try installing a pair of “bridges”, for example, from the already mentioned company ZyXEL Prestige 841C and ZyXEL Prestige 841. Model “C” is a “master”, so this device is best installed at the head office. These are inexpensive devices that work using VDSL technology, but they provide the necessary results for our task. What ZyXEL says:
Depending on the type and condition of the cable, as well as the distance, the Prestige 841 paired with the Prestige 841C provides the following data exchange speed:
Toward the subscriber - ranging from 4.17 to 18.75 Mbit/s
. in the direction from the subscriber - from 1.56 to 16.67 Mbit/s
. the total line capacity can reach 35 Mbit/s
Specifications:
VDSL Ethernet bridge
. Connection of local networks at a speed of 15 Mbit/s up to 1.5 km
. Plug&Play, transparent for all protocols
. Work in pairs
. Desktop version
. Non-volatile memory (Flash ROM)
. Size: 181 x 128 x 30 mm
This option will give 18 Mb in each direction, ideally, of course. This is VDSL.
There is one more benefit to using the Prestige 841. These devices have a built-in splitter, and we can get “free” telephony from a remote location. It is enough to plug the remote workplace telephone into the “phone” connector on one side, and connect an office mini-PBX on the other side.
If the VDSL bridges do not “stretch” the line, you need to look at other devices, xDSL. For example - something from the 79x series ZyXEL, SHDSL.

Optimization of the hardware and the use of advanced technologies made it possible not only to reduce the dimensions of the device, but also to reduce the cost and improve the functional characteristics. provide a symmetrical connection at speeds up to 2.3 Mbit/s and can operate on a dedicated 2-wire line both in point-to-point mode and as a client of an Internet provider hub.
Specifications:
. SHDSL router
. Supports G.991.2 at speeds up to 2.3 Mbps symmetrically
. Connecting networks or accessing the Internet over long distances
. Encapsulation PPPoA, PPPoE, RFC-1483
. TCP/IP routing, Full NAT, packet filtering
. Support IP Policy Routing, UPnP, connection redundancy
. Management via console, Telnet, Web, SNMP
The ideal speed is 2.3Mb over two wires. If you “charge” 4 wires, the speed will be correspondingly higher. However, these devices will cost a large amount - $400-500 per pair. In any case, roughly speaking, the worse the quality of the line, the lower the speed and the higher the costs. However, we will postpone setting up (tuning) devices for the future; this is a separate conversation, especially since in the case of VDSL 841 this does not make too much sense at all. xDSL devices should be placed on a shelf in the closet. I told you it wouldn't be empty.
Internet connection

ZyXEL Prestige-660
A modern office is unthinkable without the Internet. To connect we can use ADSL technology, for example - ZyXEL Prestige 660.
As ZyXEL describes this device:
Modem P-660R belongs to the fourth generation of ADSL modems and combines in one device the functionality necessary to connect an existing office or home network to the Internet: ADSL2+ modem, router and firewall. The modem will provide your office with a constant Internet connection that is fast and secure. Installation and maintenance of the P-660R modem is simple and will not cause any problems even for untrained users.
Main advantages of ZyXEL Prestige 660:
* High-speed Internet - up to 24 Mbit/s
* Reliable connection on problem lines
* Free phone
* Permanent connection
* Does not require driver installation
* Works with W
Large companies have in circulation a large amount of data of a different nature:
- text files;
- graphic;
- Images;
- tables;
- scheme.
It is important for management that all information is in a convenient format, easily converted and transmitted on any medium to the right hands. But paper documents have long begun to be replaced by digitized ones, since a computer can contain a lot of data, which is much more convenient to work with through process automation. This is also facilitated by the movement of information, reports and contracts to partners or inspection companies without long journeys.
Thus, the need arose to universally supply departments of companies with electronic computing devices. At the same time, the question arose about connecting these devices into a single complex for protection, safety and ease of moving files.
In this article we will tell you how to make it easier to design a local area (computer) network in an enterprise.
What is a LAN, its functions
This is a connecting connection of a number of computers into one closed space. This method is often used in large companies and in production. You can also create a small connection of 2 – 3 devices yourself, even at home. The more inclusions there are in a structure, the more complex it becomes.
Types of networking
There are two types of connection, they differ in complexity and the presence of a leading, central link:
- Equal.
- Multi-level.
Equivalent, or peer-to-peer, are characterized by similarity in technical characteristics. They have the same distribution of functions - each user can gain access to all common documents and perform the same operations. This scheme is easy to manage and does not require multiple efforts to create it. The downside is its limitation - no more than 10 members can join this circle, otherwise the overall efficiency and speed are disrupted.
Server-side design of a company's local network is more labor-intensive, however, such a system has a higher level of information security, and there is also a clear distribution of responsibilities within the web. The computer with the best technical characteristics (powerful, reliable, with more RAM) is designated as the server. This is the center of the entire LAN, all data is stored here, and from this point you can open or deny access to documents to other users.
Functions of computer networks
The main properties that need to be taken into account when drawing up a project:
- Possibility of connecting additional devices. Initially, the network may contain several machines; as the company expands, additional inclusion may be required. When calculating power, you should pay attention to this, otherwise you will need to do redevelopment and purchase new consumables of increased strength.
- Adaptation for different technologies. It is necessary to ensure the flexibility of the system and its adaptability to different network cables and different software.
- Availability of backup lines. Firstly, this applies to the exit points of ordinary computers. If there is a failure, it should be possible to connect another cord. Secondly, it is necessary to ensure uninterrupted operation of the server with a multi-level connection. This can be done by providing automatic migration to the second hub.
- Reliability. Equipping with uninterruptible power supplies and autonomous energy reserves to minimize the possibility of communication interruptions.
- Protection from outside influences and hacking. Stored data can be protected not just with a password, but with a whole bunch of devices: a hub, switch, router and remote access server.
- Automated and manual control. It is important to install a program that will analyze the state of the grid at each moment in time and notify about malfunctions so that they can be quickly eliminated. An example of such software is RMON. In this case, you can also use personal monitoring via Internet servers.

Drawing up technical requirements for the design and calculation of a local network (LAN) at an enterprise
From the properties come the conditions that need to be taken into account when drawing up a project. The entire design process begins with the preparation of technical specifications (TOR). It contains:
- Data security standards.
- Providing all connected computers with access to information.
- Performance parameters: response time from the user request to opening the desired page, throughput, that is, the amount of data in use and transmission delay.
- Reliability conditions, that is, readiness for long-term, even constant work without interruptions.
- Replacement of components - expansion of the grid, additional inclusions or installation of equipment of a different power.
- Support for different types of traffic: text, graphics, multimedia content.
- Providing centralized and remote control.
- Integration of various systems and software packages.
When the technical specifications are compiled in accordance with the needs of users, the type of inclusion of all points in one network is selected.
Basic LAN topologies
These are ways to physically connect devices. The most frequent ones are represented by three figures:
- tire;
- ring;
- star.
Bus (linear)
During assembly, one leading cable is used, from which wires go to user computers. The main cord is directly connected to the server, which stores information. It also selects and filters data, grants or restricts access.

Advantages:
- Disabling or problems with one element does not disrupt the rest of the grid.
- Designing an organization's local network is quite simple.
- Relatively low cost of installation and consumables.
Flaws:
- Failure or damage to the carrier cable stops the operation of the entire system.
- A small area can be connected in this way.
- Performance may suffer from this, especially if communication takes place between more than 10 devices.
"Ring" (ring)
All user computers are connected in series - from one device to another. This is often done in the case of peer-to-peer LANs. In general, this technology is used less and less.

Advantages:
- There are no costs for a hub, router or other network equipment.
- Several users can transmit information at once.
Flaws:
- The transmission speed of the entire mesh depends on the power of the slowest processor.
- If there is a problem with the cable or if any element is not connected, the overall operation stops.
- Setting up such a system is quite difficult.
- When connecting an additional workplace, it is necessary to interrupt general activities.
"Star"
This is the parallel connection of devices to a network to a common source - a server. A hub or concentrator is most often used as a center. All data is transmitted through it. In this way, not only computers, but also printers, faxes and other equipment can operate. In modern enterprises, this is the most frequently used method of organizing activities.

Advantages:
- It's easy to connect another location.
- Performance does not depend on the speed of individual elements, so it remains at a stable high level.
- Just find the problem.
Flaws:
- A malfunction of the central device stops the activities of all users.
- The number of connections is determined by the number of ports on the server device.
- The mesh consumes a lot of cable.
- High cost of equipment.
Stages of LAN software design
This is a multi-stage process that requires the competent participation of many specialists, since the required cable capacity must first be calculated, the configuration of the premises taken into account, and the equipment installed and configured.
Organizational premises planning
The offices of employees and management should be located in accordance with the selected topology. If the star shape suits you, then you should place the main equipment in the room that is the main one and is located in the center. This could be the management office. In the case of bus distribution, the service may be located in the room furthest along the corridor.
Building a local network diagram

The drawing can be made in specialized computer-aided design programs. The products of the ZVSOFT company are ideal - they contain all the basic elements that will be required during construction.
The grid must take into account:
- maximum voltage;
- sequence of occurrences;
- possible interruptions;
- installation efficiency;
- convenient power supply.
The characteristics of the LAN must be selected in accordance with the layout of the organization's premises and the equipment used.
Computer and network device settings
When selecting and purchasing mesh elements, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Compatible with different programs and new technologies.
- Data transfer speed and performance of devices.
- The quantity and quality of cables depends on the selected topology.
- A method for managing network exchanges.
- Protection from interference and failures by winding wires.
- Cost and power of network adapters, transceivers, repeaters, hubs, switches.
Principles of LAN design using computer programs
When drawing up a project, it is important to take into account a large number of nuances. Software from ZWSOFT will help with this. The company develops and sells multifunctional software to automate the work of design engineers. Basic CAD is an analogue of the popular but expensive package from Autodesk - AutoCAD, but surpasses it in ease and convenience of licensing, as well as in a more loyal pricing policy.

Benefits of the program:
- Intuitive, user-friendly interface in black.
- Wide selection of tools.
- Work in two-dimensional and three-dimensional space.
- 3D visualization.
- Integration with files of most popular extensions.
- Organization of LAN elements in the form of blocks.
- Calculation of cable line lengths.
- Visual arrangement of elements and nodes.
- Simultaneous work with graphics and text data.
- Ability to install additional applications.
For ZWCAD - a module that expands the functions of basic CAD in the field of designing multimedia circuits. All drawings are made with automated calculation of local area network cables and their markings.
Advantages:
- automation of selection of switching systems;
- wide library of elements;
- parallel filling of the cable log;
- automatic creation of specifications;
- adding equipment to the library;
- simultaneous work of several users with the database;
- schematic marks for the location of devices and pieces of furniture.
It will help you make a project in three-dimensional form, create it in 3D. Intelligent tools allow you to quickly lay LAN routes to connection points, visually represent the locations of cables, organize intersections of lines, and make cuts of connected equipment and technological furniture (including in dynamic mode). Using the component editor, you can create a library of cabinets, switching devices, cables, clamps, etc., as well as assign characteristics to them, on the basis of which you can later create specifications and cost estimates. Thus, the functions of this software will help to complete the master plan of the organization’s premises with tracing of all LAN lines.
Create a local computer network project in your enterprise together with programs from ZVSOFT.
Due to the large area of the territory, the large number of buildings, workshops, departments and users (about 1500 users), in order to increase the performance and fault tolerance of the network, it is necessary to divide it into logically independent objects, which will be interconnected by node network devices. At the same time, dividing a large network into smaller ones will make it easier to administer. Thus, the enterprise LAN topology will be designed in the form of a hierarchical star. The link layer technology will be a family of high-speed versions of Ethernet.
To ensure separation of responsibilities between switches, a standard architecture will be used, consisting of: network core level switches, distribution level switches and access level switches. Switches installed at the network core level require high performance and fault tolerance. Since the performance of the entire network will depend on them. Distribution switches will be located throughout the enterprise, closer to groups of access switches, to which end users of LAN resources are already connected. Server cabinet switches are connected directly to the network core switch, which serve the so-called SAN (Storage area network), local networks inside the server cabinets.
The enterprise is divided into 5 zones, each of which will be served from its own distribution level switch. Zones are selected depending on location and number of users. The enterprise LAN diagram is shown in Figure 2.
Logically, such a large network should be divided into several smaller networks. With this approach, network performance will increase, since broadcast and other “junk traffic” will not spread across all networks, taking up network bandwidth. In the event of a network failure, such as a broadcast storm, only a small logical fragment of the network will fail, the problem in which can be identified and corrected much faster. That is, in this case, the convenience of network administration is ensured. When carrying out any work to rebuild the network, it will be possible to do this in parts, which simplifies the work of network administrators and allows a small number of users to be taken out of service while the work is being carried out.
Figure 2 - Enterprise LAN topology
Virtual local area network (VLAN) technology will be used to divide the network. Each division, and sometimes a group of smaller divisions, will have its own virtual network. Several vlans will also be created to connect the switches of the network core and the distribution layer. Each such network will use unique network addresses. Virtual networks will use switch ports at the core and distribution levels to place units in their own unique vlans. This will be done during the configuration of active network devices.
As can be seen from the diagram, several logical channels will be used to connect the core and distribution switches. The core topology of the “star + ring” network will be implemented. From the core switch, channels radiate in a star pattern to the distribution switches; they are highlighted in blue in the diagram. This creates a “star”. These channels will be allocated to a separate vlan, which will be used only for communication between backbone switches.
The channels that will connect the backbone switches into a “ring” are highlighted in yellow. Previously, it was not acceptable to create loops in Ethernet networks. But the requirements for network reliability led to the development of technologies capable of supporting redundant connections in the network for channel reservation. Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS) is one of the technologies that allows you to organize fault-tolerant network topologies. It was chosen over Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) due to the quick time it takes to restore the network in the event of a failure of one of the channels. For RSTP the convergence time is less than 10 seconds, while for ERPS it is less than 50 milliseconds. This will also be a separate vlan, used only by backbone switches.
Dynamic routing will be used to unite all virtual networks and find routes between them. Namely, the Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2) protocol. Each of the backbone switches will be able to operate at layer 3 of the OSI model, that is, it will be an L3 switch. In the OSPF protocol domain, one backbone zone will be allocated - the backbone. It will contain only routers (built into L3 switches), which will exchange information with each other about the virtual networks connected to them. This protocol requires the allocation of the OSPF domain root - Designated root (DR), and the presence of a backup root - Backup designated root (BDR). A core-level switch will be used as a DR, and one of the distribution-level switches will be used as a BDR.
Each user access layer switch will be used in its own specific vlan allocated for it on the distribution layer switch. In some cases, such switches can be used to connect switches with fewer ports to them, but this does not matter for the logic of the network.
In this way, a productive, fault-tolerant and easily scalable local area network architecture is organized.
The CADE 2D vector editor for Windows was developed by a company specializing in working with CAD. The program allows you to easily create a detailed network diagram. One of the most useful features, in my opinion, is the ability to sign the IP address, serial number and manufacturer name for each device on the network. CADE includes all the templates necessary for drawing up a diagram and is distributed absolutely free of charge.
Concept Draw Pro is one of the most powerful business tools for drawing diagrams, and not just for network diagrams. It takes a minimum of time to master the program - all operations are carried out by simple drag and drop. Concept Draw Pro comes with a complete set of network symbols, and every aspect of the diagram can be customized. The application costs $249.

Dia is open source diagramming software, the main disadvantage of which is its outdated interface and primitive character set. But the program is very easy to use without being distracted by any extraneous tasks. Dia is free and runs on almost all desktop Linux distributions.

Diagram Designer is another free utility with an outdated interface, but very easy to use, which will surely appeal to many users. Unlike Dia, the program offers a much wider selection of symbols and icons. The only thing I didn't like about Diagram Designer was the need to draw connections between computers manually, because the program uses a free-form shape to do this. Apart from this small drawback, DD is a completely decent solution.

eDraw Max is one of the best tools on this list, with the exception of Visio, of course. The program is easy to learn, has a convenient, and, moreover, the most modern user interface of all the listed options. eDraw Max is a fully functional business diagramming tool for any purpose, not just network diagrams. The cost of the solution is $99.95 per license, and the more licenses, the cheaper each of them.

There are some incredibly bad programs, and GoVisual Diagram Editor is one of them. It is a difficult tool to use and produces less than satisfactory results. While it can still be used to create a network diagram, it won't be particularly easy to read because the GoVisual Diagram Editor lacks some useful features—particularly network device icons. But if someone needs a free diagramming program for any purpose, GoVisual is just the right option because it comes for free.

I would include LanFlow among the best. The program has an excellent interface, offers a rich selection of network objects and allows you to easily create local, telecommunications, external network diagrams, as well as computer diagrams. LanFlow even provides two different network diagram templates: 3D and black and white. To create a diagram, just select a template and drag suitable objects onto it, which can be grouped, deleted, and so on. A single-user license for the program costs $89, so LanFlow can rightfully be called one of the best budget alternatives to Visio.

Although NetProbe can be used for mapping, its primary purpose is to monitor network devices in real time. But the main advantage of NetProbe as a diagramming tool is that network devices can be added to the diagram as needed, even in advance. There is no need to do this manually - the built-in NetProbe component automatically scans the network and compiles a list of all devices available on the network. The Standard version is free, but can only track eight hosts. The Pro version costs just $40 for up to 20 hosts, while the Enterprise version, which can monitor up to 400 hosts, is priced at $295.

Network Notepad (literally "network notepad") is exactly what its name suggests - a notepad for drawing up network diagrams. But despite its apparent simplicity, the program has rich capabilities, including interactive functions (Telnet, network browsing, pinging, etc.). Network Notepad has a simple drag-and-drop interface and can automatically discover Cisco devices. The program is distributed free of charge.

Visio is, of course, the de facto standard in the Windows diagramming application market. The program makes it easy to create beautiful network diagrams and share them via a web browser. Visio includes a rich set of templates, including for data centers, help desks, network racks; for office consolidation, enterprise-wide network planning, data center or home office; for drawing up a fault tree, heating, ventilation, air conditioning plan, etc. Visio is the best solution for drawing up network diagrams, and therefore it is not cheap: $ 249.99 for the Standard version, 559.99 for Professional and 999.99 for Premium 2010. More information about version capabilities can be found on the official Visio page.

| Materials |