Many users in pursuit of high performance personal computer forget about the main element of the system unit, which is responsible for the quality and timely supply of power to all components inside the case. We are talking about the power supply, which buyers do not pay attention at all. But in vain! After all, all elements in the computer have certain power requirements, failure to comply with which will lead to failure of the components.
From this article, the reader will learn how to choose a power supply for a computer, and at the same time get acquainted with products of well-known brands that are recognized by all test laboratories in the world. Tips for regular users and beginners, provided by experts in the field of IT technology, will help all potential buyers make their choice in the store.
Definition of need
Before starting to search for a decent power supply, all users need to decide on the consumed one. That is, first the buyer must select the elements of the system unit (motherboard, processor, video card, memory, hard drives and other controllers). Each component of the system in its specification has requirements for power supply (voltage and current, in rare cases - power consumption). Naturally, the buyer will have to find these parameters, add them up and save the result, which will come in handy later.
It does not matter what actions are taken by the user: replacing the computer's power supply or purchasing an element with a new PC - calculations must be carried out in any case. On some elements, such as the processor and video card, there are two requirements for power supply: active voltage and peak load. You need to focus on the maximum parameter in the calculations.
Finger to the sky
There is a strong opinion that for a resource-intensive system, you need to choose the most powerful power supply that is on the storefront. Such a decision has logic, but it does not fit with rationality and saving money, because the higher the power of the device, the more expensive it is. You can buy the price of which exceeds the cost of all elements of the system (30,000 rubles and more), but such a solution will cost the consumer very much in the future.

For some reason, many users forget about the monthly fee, which is necessary for the operation of a personal computer. Naturally, the more powerful the power supply, the more electricity it consumes. Thrifty buyers can not do without calculations.
Standards and power losses
The bigger, the better
Many experts in their advice on how to choose a power supply for a computer recommend that all beginners pay attention to the number of connectors and cables - the more there are in the device, the more efficient and reliable the power supply system. There is logic in this, because manufacturers test before releasing products to the market. If the power of the unit is low, then it makes no sense to provide it with a large number of cables, because they will still be idle.

True, in recent years, many negligent manufacturers have gone to the trick and provide the buyer with a large wire clamp in a low-quality device. Here you already need to focus on other indicators of the efficiency of the battery (weight, wall thickness, cooling system, the presence of buttons, the quality of the connectors). By the way, before connecting the power supply to the computer, it is recommended to visually inspect all the contacts coming from the head unit and make sure that they do not intersect anywhere (we are talking about cheap market representatives).
Hot Selling
The company Seasonic, which specializes in the production of batteries, is known all over the world. This is one of the few brands on the market that sells products of its own production under its own logo. For comparison: a well-known manufacturer of computer components - Corsair - does not have its own factories for the manufacture of power supplies and purchases finished products from Seasonic, equipping them with their own logos. Therefore, before choosing a power supply for a computer, the user will have to get to know the brands better.
Seasonic, Chieftec, Thermaltake and Zalman have their own battery factories. Products under the famous FSP brand are assembled from spare parts produced at the Fractal Design factory (by the way, they have also recently appeared on the market).
Whom to give preference to?
Gold-plated computer power supply connectors are good, but is there any point in overpaying for such functionality, because it is known from the laws of physics that current is better transmitted between homogeneous metals? But it is Thermaltake that offers users such a solution. As for the other products of the famous American brand, they are impeccable. There is not a single serious negative feedback from users about this manufacturer in the media.

The brands Corsair, Aercool, FSP, Zalman, Seasonic, Be quiet, Chieftec (Gold series) and Fractal Design got on the shelf to trusted products. By the way, in the test labs, professionals and enthusiasts check the power and overclock the system with the power supplies mentioned above.
Finally
As practice shows, choosing a decent power supply for a personal computer is not easy. The fact is that many manufacturers go to all sorts of tricks to attract customers: they reduce the cost of production, decorate the device at the expense of efficiency, present a description that does not correspond to reality. There are many mechanisms of deception, it is impossible to list them all. Therefore, before choosing a power supply for a computer, the user must study the market, familiarize himself with all the characteristics of the device and be sure to find positive reviews about the product from real owners.
A power supply is a PC component that converts network 220 V into the 3.3-12 V required for various devices. And, alas, many people relate to the choice of a power supply ... nothing - they just take it for rent from buying other components, often right away along with the hull. However, if you are assembling something more powerful than a multimedia computer, then you should not do this - a bad power supply can easily disable expensive processors or video cards, and so that later it would not be like in the saying “the miser pays twice” - it is better to buy a good PSU right away.
Theory
First, let's figure out what voltage the power supply gives. These are the 3.3, 5 and 12 volt lines:
- +3.3 V - designed to power the output stages of the system logic (and generally power the motherboard and RAM).
- +5 V - powers the logic of almost all PCI and IDE devices (including SATA devices).
- +12 V is the busiest line, it powers the processor and video card.
But the 12 V line is very busy - both the processor (50-150 W) and the video card (up to 300 W) are powered by it, so the most important thing in the power supply is how many watts it can deliver through the 12 V line (and this the figure by the way is usually close in the total power of the power supply).
The second thing you need to pay attention to is the power supply connectors - so that it doesn’t happen that the video card needs a couple of 6 pins, and the power supply has only one for 8 pins. The main power supply (24 pin) is on all power supplies, you can ignore this. Additional CPU power is presented in the form of 4, 8 or 2 x 8 pins - it depends on the power of the processor and the motherboard, respectively, make sure that the power supply has a cable with the required number of pins (important - 8 pins for a video card and a processor are different, do not try swap them!)

Next is the additional power supply for the video card. Some low-end solutions (up to the GTX 1050 Ti or RX 460) can be powered by a PCI-E slot (75 W) and do not need additional power. However, more powerful solutions may require from 6 pins to 2 x 8 pins - make sure that the power supply has them (for some power supplies, the pins may look like 6 + 2 pins - this is normal, if you need 6 pins - then connect the main part with 6 pins, if you need 8 - add 2 more on a separate cable).
Peripherals and drives are powered either through a SATA connector or through Molex - there are no splits into pins, just make sure that the power supply has as many necessary connectors as you have peripherals. In some cases, if the power supply does not have enough pins to power the video card, you can buy a Molex - 6 pin adapter. However, in modern PSUs, such a problem is quite rare, and Molex themselves have almost disappeared from the market.
Power supply form factors - they are selected either for the case, or, conversely, if you have chosen a good PSU of a certain form factor, then you already select the case for it and the motherboard. The most common standard is ATX, which is what you'll most likely see. However, there are more compact SFX, TFX and CFX - they are suitable for those who want to create a very compact system.
The efficiency of a power supply unit is the ratio of useful work to the energy expended. In the case of power supplies, their efficiency can be recognized by the 80 Plus certificate - from Bronze to Platinum: for the former it is 85% at 50% load, for the latter it is already 94%. There is an opinion that a 500W 80 Plus Bronze certified power supply can actually deliver 500 x 0.85 = 425W. This is not so - the unit will be able to give 500 watts, it will simply take 500 x (1 / 0.85) = 588 watts from the network. That is, the better the certificate, the less you will have to pay for electricity and no more, and given that the difference in price between Bronze and Platinum can be up to 50%, there is not much point in overpaying for the latter, saving on electricity will pay off oh how not soon. On the other hand, most of the expensive power supplies have at least a Gold certificate, that is, you will be “forced” to save electricity. 
Power Factor Correction (PFC)
Modern blocks are becoming more powerful, and the wires in the sockets do not change. This leads to the appearance of impulse noise - the power supply is also not a light bulb and, like the processor, consumes energy in impulses. The stronger and more uneven the load on the unit, the more interference it will release into the power grid. To combat this phenomenon, PFC has been developed.
This is a powerful inductor installed after the rectifier before the filter capacitors. The first thing it does is limit the charge current of the aforementioned filters. When a unit without PFC is connected to the network, a characteristic click is very often heard - the current consumed in the first milliseconds can be several times higher than the passport one and this leads to sparking in the switch. During the operation of the computer, the PFC module dampens the same impulses from the charge of various capacitors inside the computer and the spin-up of hard drive motors.
There are two versions of the modules - passive and active. The second is distinguished by the presence of a control circuit associated with the secondary (low-voltage) cascade of the power supply. This allows you to quickly respond to interference and smooth them out better. Also, since there are a lot of powerful capacitors in the PFC circuit, an active PFC can “save” the computer from shutting down if electricity disappears for a fraction of a second.
Calculation of the required power supply power
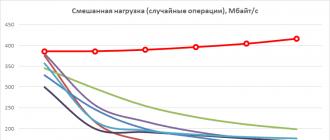
Now that the theory is over, let's move on to practice. First you need to calculate how much power all PC components will consume. The easiest way to do this is to use a special calculator - I recommend this one. You drive in your processor, video card, RAM, disks, number of coolers, how many hours a day you use a PC, etc., and in the end you get this chart (I chose the option with i7-7700K + GTX 1080 Ti):
As you can see, under load, such a system consumes 480 watts. On the 3.3 and 5 V lines, as I said, the load is small - only 80 W, even the simplest PSU will give so much. But for 12 V lines, the load is already 400 watts. Of course, you should not take the power supply back to back - 500 watts. He, of course, will cope, but, firstly, in the future, if you want to upgrade your computer, the PSU can become a bottleneck, and secondly, at 100% load, the power supplies are very noisy. So it’s worth making a reserve of at least 100-150 W and taking power supplies starting from 650 W (they usually have 12 V lines output from 550 W).
But here there are several nuances at once:
- You should not save and take a 650 W PSU built into the case: they all go without PFC, that is, one power surge - and at best you go for a new PSU, and at worst - for other components (up to the processor and video card) . Further, the fact that 650 W is written on them does not mean that they will be able to give so much - a voltage that differs from the nominal value by no more than 5% (and even better - 3%) is considered normal, that is, if the power supply unit gives 12 There is less than 11.6 V in the line - you should not take it. Alas, in noname PSUs built into the case, drawdowns at 100% load can be as high as 10%, and even worse, they can produce a significantly higher voltage, which may well kill the motherboard. So look for a PFC with active PFC and 80 Plus Bronze certification or better to ensure you have good components inside.
- It may be written on the box with the video card that it needs a 400-600 W PSU, when it itself barely consumes 100, and the calculator gave me 200 W under load at all - is it necessary to take a 600 W PSU? No, absolutely not. Companies producing video cards are very reinsured, and deliberately overestimate the requirements for the PSU, so that even people with a PSU built into the case are likely to be able to play (because even the simplest 600 W PSU should not sag at a load of 200 W).
- If you are assembling a quiet assembly, then it makes sense to take a PSU one and a half and even 2 times more powerful than what your system actually consumes - at 50% load, such a PSU may not turn on the cooler at all for cooling.
Measurements of energy consumption of systems turned out to be quite expected. The simplest system without a discrete graphics card could probably get by with any compatible power supply at all. We can also see that the now rather old AMD Phenom II X4 965 processor shows a decent difference in power consumption when compared to the less demanding Intel Core i7-3770K. However, technically, all four systems would be able to function properly even on a 450W power supply (corresponding quality with honest watts).
So who needs 1000W power supplies then? Obviously, they can also find real use, for example, if you have a heaped-up gaming system worth about a hundred thousand rubles with three video cards. Some storage enthusiasts have a weakness to install twenty hard drives with a bunch of additional controllers, but for most ordinary, even powerful systems, an honest (read: high-quality) 550 W power supply will suffice. An office computer without discrete video (or with entry-level devices) can certainly get by with one of the most low-power devices.
Conclusion
The results we got speak for themselves. Even a powerful gaming computer with overclocked components does not consume more than 360 watts at the peak. That is, you obviously won't need a kilowatt power supply until you decide to build a 3-Way SLI configuration. Of course, the results should not mislead you. They do not mean at all that you can use 400 W PSUs from cases with a total cost of 900 rubles for such an assembly. But in the end, there is no reason to take a really high-quality 750-1000 W power supply, you can get by with a cheaper and fairly reliable model that will work on your computer - and at the same time still with a large margin.
Here is another informative article, this time on the topic of iron. Or rather, about choosing the right power supply for your system. Most likely you will think that there is nothing complicated here, just look at the power and choose a manufacturer. But no, this is the most banal mistake of all novice users, since when you come home and start connecting a brand new power supply, you may be unpleasantly surprised when you realize that something is not suitable. And to avoid such mistakes, I strongly recommend that you read this article.
Let's start with the simplest, what is a power supply? The computer power supply is a voltage converter for supplying all computer components with direct current and the voltage necessary for each element. A modern power supply should provide voltages of 3.3V, 5V and 12V.
Power. One of the most important points when choosing a power supply, of course, is the correct selection of power. If you install a power supply with a weaker power than your system needs at peak load, this threatens the instability of the system and with a high degree of probability of failure of any components. If you install a power supply unit of unreasonably higher power, this will affect its efficiency and increase power consumption. There are quite a few calculators on the network for calculating the power of power supplies, but I recommend using the Asus power calculator, as it is updated regularly, and there are always new video cards and processors in its list. You can add 50W to the received power for a reserve, I also recommend looking at a PSU not lower than the 80+ Bronze standard (for more information about the 80 plus standard, see wikipedia.org).
Firm. This is a bit more complicated and it is necessary to seriously study each model, because, as elsewhere, some models are successful, some are not. Still, I strongly advise you not to contact noname PSU, but look towards such manufacturers as Thermaltake, Chieftec, Corsair. Personally, I have been buying components in the OGO.ru store for a long time, but first read the article.
Wires and connectors. Let's move on to the most interesting part. It is because of your inattention to this topic that the purchased power supply may not be suitable. If you pay attention to the specifications of motherboards, you may notice that there are always two important points in the specifications:
1) Main power connector;
2) CPU power connector.
It is because of inattention to these two points that beginners have problems.
In modern motherboards, the 24-pin main power connector is most often found, but the processor power connector is divided into two types: 8-pin ...

On server motherboards, there is also a 20-pin for the main power supply.

A universal option would be to purchase a power supply with a connector for the motherboard 20 + 4pin, and for the processor 4 + 4pin. This will allow you to connect this power supply to any motherboard. But for purely home use, you can often just take 24pin power for the motherboard.
Do not forget about video cards, because if you have a powerful video card installed, then most likely it requires an additional 6-pin power supply, sometimes even 6 + 6 pin. That is, two connectors of 6pin each. The number of hard drives and optical drives is also important, since all modern hard drives and drives are powered by a Sata connector. Although, if you have an old computer, then you should pay attention to the IDE and Floppy connectors.
So, when choosing a power supply, the second most important is the selection of connectors suitable for your system unit assembly:

Summarizing, we can say that you should carefully read the specifications of the motherboard and video card, look at the dimensions of the case and the location of the PSU in it, so that the length of the wires is enough for all the elements. Plus, you can choose a PSU with detachable cables, this will free up some space in the case by disconnecting unnecessary wires.
PFC(power factor Correction). Translated as "reactive power compensation". I recommend choosing a power supply with Active PFC. This will reduce interference in the network, it also stabilizes the incoming voltage and the PSU will be much less sensitive to voltage drops. This essentially allows you to use the power supply in the universal voltage range of 110-230V.
PSU cooling. It is desirable that the fan be at least 120mm in diameter, but this condition is observed in almost all power supplies.
That's all. You can safely go to the catalog of the online store OGO.ru and choose the power supply that suits you.
I hope this article was useful to you, click one of the buttons below to tell your friends about it. Also subscribe to site updates by entering your e-mail in the field on the right.