1. Models of objects and processes
2. Classification of models
3. The main stages of modeling

Model -Upresentation of a real object, process or phenomenon.
Modeling - Building models for research and study of objects, processes, phenomena.
Question: Why create a model, why not examine the original itself?

First, in real time the original (prototype) can no longer exist or is not in fact
Secondly, the original can have many properties and relationships. To deeply learn some specific property that interests us is sometimes useful to refuse less significant, not at all given them.

Modeling is amenable
For the same object (process, phenomena), countless models can be created

Signs of classification of models:
- Area of \u200b\u200buse
- Accounting for temporary factor
- Branch of Knowledge
- Method of representation

Classification
models
training
Experienced
game
imitation

Classification taking into account the time factor
models
dynamic
static

Classification according to the presentation method
models
information
verbal
iconic
noncomputer
computer


information
The information model is a set of information that characterizes the properties and state of the object, the process, phenomena, as well as the relationship with the outside world.

iconic
Sign model

verbal
Verbalis (lat. "Verbalis" - oral) model - information model in mental or colloquial form.

Types of information models in the form of representation
wonderful
geometric
mathematical
structural
brain teaser
special
noncomputer
computer

Geometric model
Geometric model
Geometric computer model

Slite model
Slite model

Mathematical model
Mathematical model
Drawing up a mathematical model in many modeling tasks is a very significant stage.
For registration formulas, a special application is a special application - the Microsoft Equation formula editor.

Structural model
Structural model
Structure
structure

Logic model
Logic model

Special models
Special models

Computer model
Computer model is a model implemented by means of a software environment.
Computer simulation tools are technical (handware) and software (SoftWare) provision.

Stage I. Formulation of the problem
Task description
Purpose of modeling
Analysis of the object
Stage II. Model development
Information model
Sign model
Computer model
III stage. Computer experiment
IV stage. Analysis of modeling results
Simulation plan
Modeling technology
Preview:
To enjoy previewing presentations, create yourself an account (account) Google and log in to it: https://accounts.google.com
Signatures for slides:
Computer modeling of physical processes as a means of forming mathematical concepts
The relevance of the knowledge itself becomes necessary, but knowledge about where and how to apply them. But even more importantly, knowledge of how to produce, integrate or create information.
Contradiction Social order formal approach Potential opportunities real practice
Object of study: the process of learning mathematics in a secondary school.
The purpose of the study: to develop a theoretically substantiated method for the training course, where computer modeling of physical processes is being implemented as a means of forming mathematical concepts in the course of the algebra of the main school.
Research hypothesis: Computer modeling of physical processes as a means of forming mathematical concepts will be successfully implemented if it is: - a system of interrelated mathematical concepts and physical processes have been developed, where each physical process serves as an illustration of a particular mathematical concept; - developed a technique for creating computer models of physical processes;
Tasks: To study the theoretical foundations of the formation of mathematical concepts in the course of the algebra of the main school through computer simulation of physical processes. Develop a methodology for creating computer models of physical processes for the formation of mathematical concepts. Make a complex of problems with the physical content aimed at the formation of mathematical concepts to the means of computer simulation.
In this study, the theoretical foundations of the formation of mathematical concepts and computer simulation of physical processes are dismantled: - the essence and psychological and pedagogical foundations of the formation of mathematical concepts are disclosed;
The concept of model and modeling is determined, the use of computer modeling of physical processes is substantiated for the formation of mathematical concepts;
The formation of concepts I stage-sensual perception of objects II - an idea of \u200b\u200bthe object III stage formation of the ABSTR. Concepts IV Stage- gradual assimilation of the content and volume of the concept of the V stage - the application of the concept in the decision-making decision. And the strap. Tasks VI Stage - Classification and systematization of concepts Modeling Intuitive model Structural and dynamic sample model Page. And Dean. Figy-sign model p. And Dean. Sign model inf. Log. Computer model model
Stages of solving the problem The wording problem. Setting the problem. Construction of the model. Model adequacy. Solution of the problem using the constructed model modeling intuitive model Structural and dynamic shaped model page. And Dean. Figy-sign model p. And Dean. Sign model inf. Log. Computer model model
Conclusions: Mathematical concept is a mental model of an object of surrounding; Modeling - means of forming a mathematical concept;
Computer modeling of physical processes acts as one of the effective means of forming mathematical competence, the development of research and creative abilities of students.
Methods of solving problems with physical content using computer simulation; Complex of problems with physical content aimed at the formation of mathematical concepts.
The task of the stone is thrown up vertically up at speed. What time is it from the beginning of the movement, it will be height h?
Quadratic function dependence of the distance from time to equal to the movement T, C Y, M H
Tasks with physical content - illustrations for abstract mathematical concepts showing the use of mathematical knowledge for knowledge and research of the surrounding reality.
Theoretical analysis of philosophical, psychological and pedagogical and methodological literature; - Questioning and observation; - Analysis of educational programs, school textbooks of mathematics and physics; - analysis and synthesis of experience; - Computer modelling.
Educational program of an elective course "Solution of problems with physical content using computer simulation"
Project "The use of simulation modeling of free fall of bodies to study the properties of a square equation".
Course content Concept of model. Types of model. Computer model. Stages of computer simulation. Tasks with physical content. Solving tasks with the help of mathematical modeling. Dynamic modeling of physical processes when solving problems. Laboratory workshop on creating models; - fluctuation of goods deflected from the position of the cargo on the spring (taking into account and without taking into account friction); - oscillation of a mathematical pendulum; - uniform movement of the point around the circle; - free fall of the body; - body movement under the influence of the world's strength; - body movements abandoned at an angle to the horizon; - leakage of water from a vessel with a hole in the wall near the bottom;
The problem of tasks with the physical content of the problem aimed at forming the concept of "linear function": tasks for the compilation of square equations: tasks for the use of a quadratic function
"It is very important that the amazing world of nature, games, beauty, music, fantasy, creativity, surrounding children to school, did not close in front of the child a cool door" V.A.Somkhomli
Slide 3.
Slide 5.
Specialist. programs
"The start of electronics" is a program, which is an electronic designer that allows you to show it in detail on the monitor screen, the assembly process of various electrical circuits. "Electronics Workbench" - from the most well-known packages of a schematic modeling of digital, analog and analog-digital electronic circuits of high complexity.
Slide 6.
Currently, computer simulation in scientific and practical studies is one of the main methods of knowledge. Without computer simulation, the solution of large scientific and economic tasks is now impossible.
Slide 7.
The computing experiment is an experiment on a model of an object on a computer, which is that, according to one model parameters, other parameters are calculated and the conclusions are made on the properties of the phenomenon described by the mathematical model. Computing experiment applies to: physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, environmental psychology, linguistics, phylology economy, sociology, industry
Slide 8.
The advantages of the computational experiment
Difficult laboratory equipment is not required. The time costs of experimentability of the possibility of free control of parameters, arbitrary changes, up to giving them unreal, implausible values \u200b\u200bto conduct a computational experiment where the nutrhea experiment is impossible
Slide 9.
The role of models can act a variety of objects: images, schemes, cards, graphs, computer programs, mathematical formulas, etc. Modeling is the process of replacing the real object using an object model in order to study the actual object or transmit information about the properties of the real object. The replaced object is called the original, replacing the model.
Slide 10.
Goals and objectives of the course "Computer modeling"
As a result of the development of the academic discipline, the student should be able to: work with the packages of applied professional orientation programs; use reference, regulatory and technical documentation together with the capabilities of computer simulation programs in the study of the characteristics of radio-electronic devices and their components; graphically represent and analyze the diagrams of the characteristics of radio-electronic devices and their component parts; apply the means of computing equipment to calculate structural elements and diagrams of the characteristics of radio-electronic devices and their component parts; Analyze electrical circuits of electronic devices and devices. Select measuring instruments and equipment for testing electronic devices and devices, configure and adjust electronic devices and devices, test electronic devices and devices using virtual laboratories.
Slide 11.
As a result of the development of the academic discipline, the student should know:
mathematical methods for calculating various radio-electronic devices and their operation modes; Features and features of the "start of electronics" and "ElectronicSWorkBench"; physical processes when working radio-electronic devices; Features of the structures and the principle of operation of various radio electronic devices, varieties of radio-electronic devices; Methods for calculating elements of structures and diagrams of characteristics of component parts of radio-electronic devices.
Slide 12.
Simulation as a method of knowledge
Modeling is a method of knowledge, consisting of creating and examining models 11/17/2017
Slide 13.
The model is a new object that reflects some of the essential properties of the studied phenomenon or process.
Slide 14.
Model (FR.Sl. Modele, IT. Sl. Modelo, Lat. Sl. Modelus) - Measure, Sample
Slide 15.
The same object may have many models, and different objects can be described by one model.
Slide 16.
Man: doll mannequin skeleton sculpture Real object - original model
Slide 17.
The properties of the object that should reflect the model are determined by the purpose of studying it.
Slide 18.
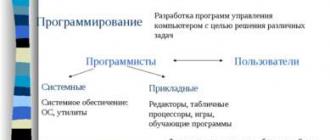
Classification of models according to the presentation method:
Slide 19.
Material models -
Reproduce geometric, physical and other properties of objects in material form Example: Globe (model of the globe) - Geography
Slide 20.
Information models -
Represent objects and processes in the form of schemes, drawings, tables, formulas, texts, etc. Example: Flower drawing - Botany, Formula - Mathematics
Slide 21.
Slide 22.
Classification of models for the area of \u200b\u200buse:
Training models; Experienced models; Scientific and technical models; Game models; Imitation models.
Slide 23.
Classification of models taking into account the time factor:
Static; Dynamic. If the model takes into account the change in the properties of the simulated object from time to time, the model is called dynamic, otherwise static. Examples: Dynamic: Wrinking toys; static: globe; Stuffed Toys; Tutorials.
Slide 24.
Classification of models for the field of use: biological; Historical; Physical; And etc.
Slide 25.
Modeling
Slide 26.
Modeling as a method of cognition what is drawn to the attention of a person (subject, phenomenon, process, attitude), in order to study, is called an object. To explore the object, solving the problem, it is necessary to build a model of a specified object. It is a fashionable man in the process of knowledge of the surrounding world and reflects the essential features of the studied object, phenomenon or process. Modeling is a method of knowledge consisting of creating and examining models. Any model is not an absolute copy of its original, it only reflects some of its qualities and properties. The properties of the model depend on the modeling goal. The models of the same object will be different if they are created for different purposes. Examples: Mendeleev table, model of the structure of the atom, model of the crystal lattice, model of the skeleton, dies, models of technical devices, etc. Next back
Slide 27.
Classification of models Material models are material copies of modeling objects. Examples: Globe, Doll, Robot, Building Layouts, Moulei. Next, we consider the most common features, according to which the models are classified: the purpose of use (training models, experienced, imitation, game, scientific and technical); Knowledge area (biological, economic, sociological, etc.) method (form) of presentation factor in the textbook of informatics N. Jrinovich for grade 9
Slide 28.
Information models Next back to consider information models from the position of the methods of presenting information: mental mental ideas about the object (coding alphabet - a system of concepts, a carrier is a human nervous system, brain); Verbal presentation of the model by means of a natural conversational language (form form - oral or written message Examples: instructions, literary works); Figure Expression of the Properties of the Original Using Images (Pictures, Movies, Geometrical Models) Figyless Markded Figyless Structural Models Drawings Plans Card Graphics Table Networks in the form of graphs Other Mathematical logical software texts Other
Slide 29.
Types and types of models Next Back Types and types of models. Fatural information Technical: car, aircraft, etc. Globus, mannequin, dummy, layout of buildings, etc. Verbal graphic table mathematical description of the modeling object in the natural language Table type object-property, object - Object . Binary card matrices, schemes, drawings, graphics Quantitative characteristics and communication between them General properties of models Simulation objects: - Material objects; - the phenomena of nature; - Processes limited model: - Reflects only a part of the properties of the modeling object. The ambiguity of the model: - Different models of one object created for different purposes The purpose of the model: - limited replacement of the real object; - Using a model to predict the behavior of a real object on the textbook of informatics I. Semakin for grade 9
Slide 30.
Formalization Next Back What is formalization? This word is the essence of information modeling. The information model describes the modeling object in the form of any signs: letters, numbers, cartographic elements, mathematical or chemical formulas, etc. The most formalized science is mathematics. Formalization is the process of building information models using formal languages. Formalization is the result of the transition from the real properties of the modeling object to their formal designation in a specific iconic system.
Slide 31.
Computer models Next back to the textbook of informatics I. Semakina for grade 9 computer models (information models implemented on a computer) Numerical methods: arithmetic ways to solve any mat. Objectives Computer Mathematical Model Computing Experiment: Calculation of the state of modeling object according to the mathematical model Visual representation of the results: Using computer graphics and multimedia to represent the results of calculations Real-time management: fast computer models working at the speed of the physical managed process Computer simulation model Imitation of the state of the real system with Stochastic (random) behavior of its elements of the mass maintenance system Transport systems
Slide 32.
Classification of information models
Slide 33.
Classification of information models:
Slide 34.
In the tabular model, the list of similar objects or properties is placed in the first column (or row) of the table, and the values \u200b\u200bof their properties are placed in the following lines (or columns) of the table
Slide 35.
Table type "Property Object"
One line contains information about one object or event.
Slide 36.
Table type "Object object"
Reflect connections between objects
Slide 37.
Table type "Double Matrix"
Reflects the qualitative nature of the connection between objects
Slide 38.
Table information models
Static price of individual devices of a computer (1997)
Slide 39.
Dynamic Changing Computer Price
Slide 40.
Count is a means of visual representation of the composition and structure of the scheme
Slide 41.
The hierarchical model is a system, the elements of which are located with each other in relation to nesting or subordination. The heierhic model is a graph in which the vertices are interconnected on the principle of "one to many"
Slide 42.
Hierarchical information models
Static Classification of Computers Pocket Desktop Computers Super Computers Workstations Personal Computers Portable
Slide 43.
Dynamic Genealogical Tree Rurikovichi (X-XI century) Izyaslav Vsevolod Svyatoslav Yaroslav Wise Boris Gleb Svyatoslav Yaropolk Vladimir
Slide 44.
The network model is a graph in which the vertices are interconnected on the principle of "many to many"
Slide 45.
Networking information models
Slide 46.
The semantic model - the graph, which is based on what any knowledge can be represented in the form of a set of objects (concepts) and relationships (relationships) between them.
Slide 47.
"Once in the student winter day, I left the forest."
Once from the forest I went out the winter to the student at the time what did you do? Who! Where? When? In which?
Slide 48.
Graphic models
Slide 49.
Purpose of modeling: Creating a menu of simple items to construct from them different objects The simulation tool: Paint work work: 1. Create a menu of simple elements, taking into account the shape and size. 2. Create an object from simple elements. 3. The result is saved in your folder. Building graphic models Menu items Object: Mosaic Menu items Object: Geometric ornament Elements Menu Menu items Menu items: Object: Topographic Map Object: Electrical diagram Menu items: Object: Interior Menu items: Object: Plant ornament Menu items: Object : Design from blocks Object Construction of bricks Next Back Back
Slide 50.
Geometric models Next back to perform a ribbon geometric ornament. Elements used: lines: solid and intermittent: straight, broken, wavy geometric shapes: square rhombus triangle circle semicircle oval semi-finished and other simple figures Computer option: Paint graphic editor. Examples of the expected result:
Slide 51.
Modeling in spreadsheets
Slide 52.
Many objects and processes can be described by mathematical formulas that bind their parameters. These formulas are the mathematical model of the original. You can make numerical calculations with different parameter values \u200b\u200band obtain the quantitative characteristics of the model. Calculations, in turn, make it possible to draw conclusions and summarize them. A tabular processor provides a tool for calculating the quantitative characteristics of the object under study or process, takes on all time-consuming work on calculations. This topic highlighted four main stages of modeling: setting the task, model development, computer experiment, analysis of modeling results.
Slide 53.
Simulation of situations Task Calculation of the number of wallpaper rolls for facing room I stage. Problem Statement Description of the task in the store for sale wallpaper. The names, length and width of the roll are known. Research, which will automatically determine the required number of rolls for pasting any room. The size of the rooms are set high (H), length (a) and width (b). In this case, it takes into account that 15% of the room walls are occupied by windows and doors, and with a 10% roll area goes on trimming. The purpose of modeling establish a link between the geometric sizes of a particular room and the selected wallpaper sample. Analysis of the object modeling object is a system consisting of two simpler objects: rooms and wallpaper. Each of the objects included in the system has its own parameters. The relationship between the system objects is determined when setting the number of rolls for the room paste.
Slide 54.
Stage II. Model Development Information Model
Slide 55.
Mathematical model When calculating the actual roll area, which will go to the pasting of the room, it is necessary to discard 10% of the real area on trimming. The calculation formula has the form: SP \u003d 0.9 * L * D, where L is the length of the roll, D is the roll width, * - a sign of multiplication. When calculating the actual area of \u200b\u200bthe walls, the uncomplicable area of \u200b\u200bwindows and doors (15%) Skom \u003d 0.85 * 2 * (a + b) * h is calculated by the number of rooms required for the room pasting, is calculated by the formula where one spare roll is added.
Slide 56.
Computer model for modeling Select the spreadsheet of the spreadsheet. In this environment, the information and mathematical models are combined into a table that contains three areas: source data - controlled parameters (unmanaged parameters are taken into account in calculation formulas); intermediate calculations; results.
Slide 57.
Task Fill in the sample calculation table. Enter formulas to settlement cells.
Slide 58.
III stage. Computer Experiment Modeling Plan Conduct a test calculation of a computer model according to the data shown in the table. Calculate the number of rolls for the premises of your apartment. Change the data of some samples of wallpaper and trace over the recalculation of results. Add strings with samples and supplement the model by calculating the new samples. The results of the experiment will issue in the form of a report in a text editor. Modeling technology 1. Enter test data into the table and compare the results of the test calculation with the results shown in the table. 2. Alternately, enter the size of your apartment's rooms and the calculation results to copy to the text editor. 3. Make a report. IV stage. Analysis of the modeling results According to the table, you can determine the number of rolls of each wallpaper sample for any room.
Slide 59.
Test modeling in the spreadsheet
See all slides
Description of the presentation on individual slides:
1 Slide
Slide description:
Computer modeling A.N.Petrov, teacher of special disciplines GBPOU "Rzhevsky College"
2 Slide
Slide description:
Initially, the topic "Mathematical modeling" was chosen by me when the computer science of the informatics subject consisted of a greater extent of the QBasic programming language. With the advent of modern PC, this topic, of course, moved to the topic "Computer simulation". The concept of computer simulation is closely connected by such names of models as: mathematical model; economic model; simulation model; interactive; Computer experiment model; etc. And it is natural, as the computer and modeling are closely connected with each other. In essence, each teacher, to one degree or another, is engaged in modeling.
3 Slide
Slide description:
Upaying theoretical calculations of the concept of models can be given such a modeling scheme: the original object - -Prototype, the original modeling is the process of creating a model. Modelable object - substituent object
4 Slide
Slide description:
The basis of the varieties of computer models are such system concepts as an image, sign, characteristics. Modelable object (substituent object) Image Sign Specifications Shaped models: Drawings, mockups, photos, drawings, drawings, etc., provided that they do not have inscriptions or other signs of iconic models: models, based on artificial languages \u200b\u200b(music Signs, language of mathematical formulas - mathematical modeling, language of chemical formulas, etc.) Information models: models that use a set of characteristics
5 Slide
Slide description:
Depending on behavior and state, models can be: animated (computer animation); Imitational: Imitating Movement Imitating Process Solution Process with random numbers (Monte Carlo method) interactive (models in which the interface is added is the connection of the computer and PC user).
6 Slide
Slide description:
More, we are dealing with mixed models. This is primarily due to the purpose of modeling, which, in turn, causes one or another degree of formalization of the modeling facility. For example: ... We simulate the graphics object - "Circle" - using the fill tool, we get the "ball" model
7 Slide
Slide description:
The medium in which the "live" models can be different. In this case, the model acquires a different variety. For example, the same models like Paint or Word objects (autofiguris), in QBasic, as programming objects can be converted from the simple animation model of a moving ball in the image-animation model of the structure of our solar system or a simulation-animated structure of the structure Atom or Brownian movement (depends on the modeling goal). Model as an object environment
8 Slide
Slide description:
Having mastered the simulation algorithm for the movement of graphic primitives QDasic DVIG.BAS, students with great interest continue to simulate, creating more and more complex imitation models. At the same time, an increase in the interest in programming language is noted, to its degrees-to-one study: (organizations of cycles with the simultaneous reproduction of previous software structures. By changing parameters, selecting the trajectory of movement, the student is actively working on numerous calculations. I will give examples of some work of the second year of programming (7 CL) Cvetfr4.bas, Cvetfr6.bas, SKV318.BAS
9 Slide
Slide description:
Pupils who have acquainted in the younger classes with the techniques of imitation and animation-computer simulation, the Internet does not weaken in high schools. There is an interest in the illustration of the typewriter's sound and using the Aleks.bas text functions, the first steps are made to create interactive models in the PAVELM1.BAS dialog mode
10 Slide
Slide description:
In almost every computational task of a particular topic, I try in obligatory, after setting the problem, before algorithmization, proceed to the construction of a mathematical model of the problem, for example, on the topic "One-dimensional arrays. Search mini-max. Fixing the index "Mathematical model of the problem" Search Min / Max in a one-dimensional array "N - the number of elements in an array A A (I) is an element of array A (I) i \u003d 1, n; A (I) \u003d RND * 100 min - the minimum element of the array A; Imin - index (position) of the minimum element in array A; MAX is the maximum array element A; IMAX - index (position) of the maximum element in array A; A (1), originally min \u003d a (i), if A (I)< MIN, для i=1,n; 1, первоначально IMIN = i, если A(i) < MIN, для i=1,n; A(1), первоначально MAX = A(i), если A(i) > Max, for i \u003d 1, n; 1, initially imax \u003d i, if A (i)\u003e Max, for i \u003d 1, n;
11 Slide
Slide description:
According to themes associated with two-dimensional arrays, in addition to conventional mathematical models of tasks, students, under my leadership, interactive-ani-based demo version of the tasks of the "car" type, "Camera storage", models that are from typical information models (Characteristics of the value, name), with the addition of the description of behavior and inter-faces become the above models (Kambag.bas, Vagvag.bas). On the same topics: interactive models "Solution of a system of linear equations by a matrix method (Gauss method)", "Identification of the material on the Jung module").
12 Slide
Slide description:
The "generation of random numbers" theme is well illustrated by solving the tasks: "Calculating the number π" and "calculating area of \u200b\u200ban arbitrary figure" with the creation of a simulation model of the solution.
13 Slide
Slide description:
This task, students can make a competitive work on modeling a simulation model of a graphic mini-editor to create an arbitrary figure, the area of \u200b\u200bwhich must be determined. Litkin on the topic "Sound and Graphics" under my leadership has created a large number of animation models. These developments were demonstrated on one of the open lessons. There was a non-standard lesson "Conference of young professionals." The mathematical model "The method of approximate extraction of roots" was declared for the city scientific-practical conference (3 place) Good results are obtained when modeling in the PowerPoimt environment: activation of studying work with objects in this environment; Improving model formalization skills. The link Nadia during the acquaintance with the Paint graphics editor, the student can familiarize himself with the design of a complex model, making it up, for example, a complex pattern with repeated primary simple objects (cutting, copying, rotation ...).
14 Slide
Slide description:
Paint-design --- type of modeling (Professor Makarova N. V.) Modeling
15 Slide
Slide description:
16 Slide
Slide description:
Interesting is the lessons modeling fragments of pages with built-in animation objects. For example, after an integrated school lesson in the 9th grade "Acquaintance with the electronic encyclopedia for astronomy", the students were trained at the techniques of various pages: "What do we know about the moon?"; "Planets of the Solar System and their satellites"; "Planets in numbers" mass; Diameter; Surface temperature; Star day duration; Orbit. "Comets"; And etc.
17 Slide
Slide description:
Simulation of the page "What do we know about the moon?" (In the PowerPoint environment), the earth shadow near the moon has a greater than that of the moon, angular time, so the crossing of this shadow can last dozens of minutes. First, the moon on the left concerns the barely visible half of the earth (for an observer on the moon, standing in a half, the sun is partially angry with the earth). The intersection of the moon of half can last about an hour, after which, the moon touches the shadow (for the same observer on the moon, in the shade, the sun is fallen completely). Insert movies and sound
18 Slide
Slide description:
Modeling in Excel's Excel spreadsheet environment is an ideal tool for mathematical modeling, as it quickly and virtuoso performs time-consuming work on calculating and recalculating the quantitative characteristics of the object under study or process. Modeling in spreadsheets is carried out according to the general scheme, which allocates four main stages: setting the problem, model development, computer experiment and analysis of results. For example, the problem "The solution of linear equations by the method of inverse matrix" Setting the problem: the solution of the system of linear equations by the specified modeling method is the selection of the necessary formulas to solve the problem by the inverse matrix method and the problem algorithm (task formalization). Computer Experiment - Testing Tasks for various source data. Analysis of the results - is the solution that satisfies the condition of the task
19 Slide
Slide description:
This task for the classification of Professor Makarova A.N. can be attributed to tasks that have the following generalized wording: what is the impact on the object so that its parameters satisfy some given condition. This group of tasks is often called "how to make ...". This group of tasks included such tasks already tested by me on computer practices Excel previous years of study, like "Solution of the system of linear equations tool Search for solutions", "Modeling a situation recognition of a point from entering the coordinates X, Y to the specified region of conditional formatting and constructing the diagram "," Modeling objects (house, shame) in Excel using the formatting of the cells and the simplest macro "," solving systems of nonlinear equations by solutions to the solution "," modeling of recognition of the function intervals in which the function is not defined "
20 Slide
Slide description:
Currently, we work on the simulation of interactivity in Word, over the animation models in Excel Circle / bubble, over the simulation of surfaces in Excel medium, using trigonometric functions of the Radiagra, over mathematical modeling of logical functions, using SDNF and SCFF, mat. Modeling a logical output, logical functions by combinational schemes of the GOST (webbam elements, soffer fragm
21 Slides
Slide description:
Hypertext modeling Hypertext (nonlinear text) is an organization of textual information, in which the text is a set of fragments with explicitly specified associative connections between these fragments. Associative communication between fragments is called a hyperlink that can be written explicitly with the help of a special language of hypertext markup of HTML documents (Hyper Text Markup Language) or using a hyperlink ads in a particular application (PowerPoint, Word) one of the promising directions of development of hypertext systems is technology Hypermedia - connection of hypertext technology and multimedia technology (text integration, graphics, sound, video). Examples of the development of hypermedia applications are various electronic publications - reference books, encyclopedias, training programs.
22 Slide
Slide description:
Modeling the page "What we know about the moon" in Word 2000 Professional environment to highlight the word insert hyperlink ...
23 Slide
Slide description:
Simulation using HTML Hypertext Markup (Hyper Text Markup Language) Let it be necessary to develop a document model in which the task structure can be immediately demonstrated by their implementation in the medium required for them, for example, in Excel, you can select the simplest text editor NotePad (notepad) , enter text using descriptors with the appropriate options Close the Notebook application window with the extension. HTM. In this document, the document will take the type of Internet Explorer icon when the "head HTM-text" starts work with the tasks will be implemented by chain of hyperlink
24 Slide
Slide description:
The above-mentioned material demonstrated the most vibrant modeling developments in order to train schoolchildren modeling skills in various media "Informatics", i.e. Computer modeling category "Model as an environment environment": model as a programming object; Model as a word text processor object; Model as an Excel table processor object; Model as an object of graphic editor Paint; Model as a file with an HTML code; Model as an object PowerPoint
25 Slide
Slide description:
Target modeling Research work on computer modeling, conducted with one or another student (or group) of presums-guaets, assistance and control over a complex complex of preliminary work related to targeted computer simulation: Analysis of the task formulation, description of the task of developing a clear main objective of modeling; Formalization of the task and, as a result, the development of clear intermediate purposes. Often, targets (main and intermediate) are answers to clarifying issues in accordance with the formulation of the problem; Analysis and study of various possible media modeling, comparison of their advantages and disadvantages in order to make a final decision on the choice of modeling environment; Computer modeling with multiple testing model Selecting the model presentation method
26 Slide
Slide description:
Target modeling, depending on the intermediate and intermediate purposes, the novelty of the material and its volume can be very long in time of its execution. For example, computer simulation of the training electronic manual "Work on the Windows Paint standard application environment", made by Pupil Mashkovtsev Vladimir (11 A Class 2003/2004) and declared for the city practical conference 2004. (3 place) one year continued and included the following complex of work:
27 Slide
Slide description:
Stage I. Problem Statement (formal): Development of electronic manual for work in the Paint Graphic Editor. The first basic requirement: simplicity and ease of use of electronic manual. Task formalization: the prototype of the simulation must meet the modern requirements of the development of electronic benefits - should be based on the use of hyperlinks, to have either a standard web-design or its own (unique), possess the interactivity property. The user must be able to simultaneously use the electronic manual and the Paint graphics editor (benefit type " I read did "). The manual interface must comply with the requirements of the transition to any structural part of the manual and return to the starting point; Points of transitions and returns should be a clear unambiguous load stage stage. Modeling in accordance with the formalization of the task in the HTML III Hypertices Markup Language. Multiple Computer Experiment (Debugging Model) IV Stage. Analysis of the results. "Officon" of electronic benefits on basic and elective informatics lessons (allowance received universal recognition).
30 Slide
Slide description:
II. TECHNICAL 05 UCH. The acquisition of video engineering skills; acquisition of scenario planning skills; Acquisition of digitization skills of the footage, testing in practice; Acquisition of the skills of creating a scenario image; Acquisition of mounting skills II. TECHNICAL 05 UCH. The acquisition of video engineering skills; acquisition of scenario planning skills; Acquisition of digitization skills of the footage, testing in practice; Acquisition of the skills of creating a scenario image; Acquisition of mounting skills
Slide description:
III Stage (working) included all other stages of modeling: modeling, computer experiment (model debugging) and, finally, analysis of results. The duration of work on the video project was two academic years. The work was announced twice with the City Scientific and Practical Conference (2003/2004. Year - 3rd place; 2004/2005 uch. Year - 1st place). An interactive video project was dedicated to the anniversary (400 years) Monastery Nilo Council Desert, got the name "The Island of Spiritual Consolation" and was demonstrated on the school lessons of Orthodox culture
33 Slide
Slide description:
Brief conclusions: Computer and modeling are closely connected with each other. The basis of the varieties of computer models are such system concepts as an image, sign, characteristics. Depending on behavior and state, the models can be animated (computer animation), simulating (imitating motion, imitating a real computing process, replacing it with a process based on pseudo-random numbers (Monte Carlo method), interactive (models in which the interface added - Communication of the computer and PC user). The environment in which "live" models may be different. In this case, the model acquires another type. Computer modeling is very fertile soil, since it opens up a huge creative potential of children and, one day, tanning On them sparkles of computer creativity, you can expect good results in the future of children (Vova Fedorov, Alyosha Semenov, Igor Ogarev, Sasha Katkov, Anya Yudashkin, Yura Nikitin, Suvorov Roman, Pavel Alekseev, Volodya Mashkovsky, Seryozha, Sasha Royal, Sysolatina Nadia, Seryozha Mikhailov et al.). Computer simulation can also be viewed as a powerful tool for motivation to train Osti and self-banner is the subject of informati, as it encourages students to independently find deeper knowledge in this area and apply them in practice in the process of numerous computer experiments. As a result, repeated prizes in urban competitions in computer science and urban scientific and practical conferences.
34 Slide
Slide description:
1 Slide
Dim A (5) for i \u003d 1 to 5 Input A (i) Next is \u003d 0 for i \u003d 1 to 5 S \u003d S + A (I) Next I Print S Development: Klinkovskaya MV, Teacher of Informatics and ICT MOU Gymnasium №7 of Baltiysk, 2008-09 Uch.

2 Slide
Represent objects and processes in a figurative or sign form, also in the form of tables, flowcharts, etc.

3 Slide
Dim a (5) for i \u003d 1 to 5 input a (i) next is \u003d 0 for i \u003d 1 to 5 s \u003d s + a (i) Next i Print S in biology: the whole animal world is considered as a hierarchical system (type , Class, detachment, family, genus, view)

4 Slide
The verbal models are oral and written descriptions using illustrations Mathematical models - mathematical formulas displaying the connection of various parameters of the object or process geometric patterns - graphic forms and volumetric structures Structural models - schemes, graphs, tables, etc. Logical models - those in which various options for choosing actions based on conclusions and analysis of conditions Special models - notes, chemical formulas, etc.

5 Slide
N.Qurennik and the image of the heliocentric Copernicus system is not the sun moving around the Earth, and the Earth rotates around its axis and the sun; The orbits of all celestial bodies pass around the sun. Not the sun moves around the earth, and the Earth rotates around its axis and the sun; The orbits of all celestial bodies pass around the sun.

6 Slide
Formalization - the process of building information models using formal languages \u200b\u200bFormal languages: Systems of specialized language tools or their characters with accurate compliance rules Mathematical language Algebraic formulas F \u003d Ma Language of chemical formulas H 2 O

7 Slide

8 Slide
Work 1. Modeling object: classmate. The purpose of modeling: building a verbal model of a person. Simulation parameters. Surname, name, patronymic of the object. Facial features, physique (height and weight) Favorite learning object of object, reasons. Hobby object. Modeling Tool: Microsoft Word Text Processor. Topic: "Building a verbal model in a text editor environment"

9 Slide
Progress. 1. Open the Microsoft Word text editor. 2. Select the modeling object (any classmate). 3. Make it up a thought image in accordance with the simulation parameters. 4. Proceed the mental image with text editor. 5. Show the result to the teacher.

10 Slide
Work 2. Topic: "Building a mathematical model by means of editor formula" Modeling object: Mathematical formula for a straight-line equivalent body movement (change of coordinate X) The purpose of modeling: Building a mathematical model The simulation tool: Editor Microsoft Equation formulas.

11 Slide
Progress. 1. Open the Microsoft Word text processor. 2. Select the Insert Team in the Object 3. Select Microsoft EQation 3.0. 4. Make a formula using symbols and template sets. 5. Below the formula in the document, explain the designations used in the record (description of values). 5. The result of the work. Show the teacher. 1. Open the Microsoft Word text processor. 2. Select the Insert Team in the Object 3. Select Microsoft EQation 3.0. 4. Make a formula using symbols and template sets. 5. Below the formula in the document, explain the designations used in the record (description of values). 5. The result of the work. Show the teacher.

12 Slide
Determine the sequence of a set of formula; All characters are recruited sequentially using the keyboard; Numbers, signs and variables can be entered from the keyboard; You can navigate between the elements of the formula you can use the cursor keys or click the mouse to install the cursor to the desired location; If the formulas are several, separate one from another by pressing the Enter key; If you want to dial the text while in the formula editor, select the style, text. To edit the formula, double-click on it. Instruction Tips for setting formulas 
14 Slide
Know the classification of models in the form of the presentation. Give examples of verbal and mathematical models. With which software tools you can create such models? Make a verbal explanation model with parents in a situation where you received a "deuce". Try to convince the parents in the fact that your "Two" is hardly blessing. According to the given verbal model, make a mathematical model: the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the cathets. Perform this task using a computer.

15 Slide
Literature: N. Ugrinovich "Informatics. Basic course - 9 "S. Beshenkov, E.Rakitina" Informatics. Systematic course - 10 "N.V. Makarova "Informatics 7 -9", O.L.Sokolov. "Universal Purchase Development on Informatics. Grade 10". Moscow. "Wako", 2006.