Information technology is constantly evolving and new programs require more and more computing resources of the computer. Machines that were very powerful a few years ago are now considered average or even very weak. Therefore, whether you like it or not, from time to time you have to buy new equipment or at least update the old one.
It is not always prudent to buy a new device if it is still possible to make the old one comply with a small amount of money. One of the critical components, the requirements for which are growing rapidly, is RAM. Previously, 4 Gigabytes was quite enough, but now 6-8 Gigabytes is considered the optimal amount.
When choosing RAM, you need to take into account a lot of nuances in order for it to work in the best possible way or even work on your board. In this article, we will look at how to choose RAM for your computer. But first you need to understand what characteristics the memory bars differ in and what is more important to pay attention to.
A small introduction for beginners, random access memory (RAM) is a volatile and very fast memory in which most of the computer's operations are performed. The fact is that before information is written to disk, received from devices or processed by the processor, it enters the RAM, and all programs that are currently being executed by the processor and all their data are stored here.
Random Access Memeory stands for random, direct access memory. The processor can access any block of memory without affecting other blocks, and the data read speed does not depend on the location of the block. Unlike volatile memory, RAM works much faster and has no restrictions on the number of read-write operations, which is why it is used for temporary data storage.
Types of RAM
RAM has several characteristics and all of them must be taken into account when choosing an additional strip or new memory. It is very important that your RAM is compatible with each other as well as with the motherboard. Therefore, before answering the question of how to choose RAM for a computer, let's consider all your parameters.
DDR, DDR2 and DDR3
At different times, RAM has been produced in different standards. With each new standard, the quality, speed of work and the amount of RAM increased with each new standard. But the motherboard only supports one specific standard.
Initially, it was DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random Acces Memory), it allowed to significantly increase the data transfer rate than the previously used SDRAM technology. DDR2 added memory data cache and some other improvements.
But this was all a long time ago, but now the DDR3 standard, which was proposed in 2005, gained the greatest popularity. Compared to DDR2, it needs 1.5 Volts instead of 1.85, the heat dissipation is reduced by 40%, and the operating speed is also much increased - the bandwidth is twice as high as that of DDR2.
More recently, a new standard has emerged - DDR4, which has even more significant advantages over previous generations. Here, performance has been increased by 50%, power consumption has been reduced by 35%, data transfer rates have been increased, and many other parameters. But now it is quite rare.
Memory frequency
Memory frequency is measured in hertz and characterizes the number of data operations that a block of memory can perform in one second. For DDR, frequencies of 200-400 were used, for DDR2 - 400-1066 MHz, DDR3 - 800 - 2400, and for DDR4, frequencies above 2133 MHz were used. In fact, the higher the frequency, the better the performance.
But this is not entirely true, because the higher the frequency, the greater the latency of the RAM - the timings, which means the performance decreases. Therefore, a balance is obtained, the frequency increases, and the performance remains at the same level.
Bandwidth
The memory bandwidth depends on the frequency and bandwidth of the bus. In fact, this parameter characterizes how many megabytes of data the RAM bar can skip per second. The speed is calculated by multiplying the bus bandwidth by the frequency. For example, if the frequency is 1600, the bus bandwidth for DDR3 is 8 bytes, then the memory speed will be 12800 MB / s.
The speed of work is recorded in the format PC speed... For example, PC3-12800. PC - means standard - Personal Computerand the number 2 or 3 means the DDR type version.
Now that we have examined the main parameters and characteristics of memory, let's move on directly to the question of how to choose the right RAM.
Which RAM should you choose?
If you need to choose RAM for a new motherboard, then this is one question, but if you need to select compatible RAM for a bracket already installed in the system, then this is a little more complicated.
DDR type
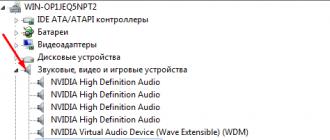
In both cases, you need to consider the type of DDR memory, since the motherboard supports only one standard, and most likely it is DDR3. On Windows you can see the memory type using CPU-Z, and on Linux you can run the command:
sudo dmidecode -t 17
Please note that there will be several blocks of information and only one of them will be filled with information about your memory bar. In CPU-Z, open the Memory folder:

Supply voltage
The next very important parameter is memory voltage. You can see the parameters of your motherboard or find out at what voltage the installed bracket is currently working. To do this, use the command:
sudo dmidecode -t 5
As I said, the DDR3 standard uses a voltage of 1.5 volts, but various modifications have been released, including memory for notebooks, which can consume 1.35 volts, so you need to be careful here too. In CPU-Z, you can find out the voltage on the SPD tab, you may have to select a slot:

Intel and AMD compatible
Recently, memory sticks began to appear that are compatible only with Intel processors or only AMD processors, they are cheaper than regular memory sticks, but in order to choose the right RAM, you need to pay attention to which processor you have, because such memory boards will be optimized for bus commands from one manufacturer and for the other will not work.
To achieve maximum compatibility with the installed memory, it is better to take memory with the same instruction set as it already has. For example, if you have a bar that supports all processors, then this should be taken.
Frequency and baud rate
These parameters are not so important for compatibility, but they are very important for performance, because if you set two bars of different frequencies, then both of them will work at the same frequency - and at a lower one. Therefore, if you want to achieve maximum performance, then it is better to take two bars of the same frequency. We can find out the frequency of the existing bar with the same command:
sudo dmidecode -t 17

Second, if you are looking for new strips, then you need to look at the maximum data transfer rate for the processor bus. You can find this information on the manufacturer's website. For example, for my Intel Pentium (R) CPU B960, the page looks like this:

As you can see, the maximum processor bandwidth is 21.3 GB / s. At the same time, I use memory with a frequency of 1033, in fact it is 1600, but the processor only supports 1033. Then we can calculate the memory bandwidth - 1033 * 8 \u003d 8264 MB / s or 8 GB / s.
The memory bandwidth can be half that of the processor if you use two memory strips, since in this case the processor can write to both simultaneously. But if you want everything to work like this, then you need to choose the strips that are as similar in parameters as possible. Thus, if I use two identical bars, the total data transfer rate will be 16 Gb / s in dual-channel mode. And that's pretty good. It is also important to note here that since the bandwidth of the RAM depends on the frequency, the same tendency is observed here, if you take two bars with different bandwidth, then both of them will work at a smaller one.
To find out if you are using two-channel mode, you can again use dmidecode:
sudo dmidecode -t 20

Here Interleaved Data Depth shows the number of channels, in this example the dual channel mode is not used. In CPU-Z, the number of active channels is shown on the tab Memory, parameter Channel:

Memory size
We will not talk much about the memory size. You yourself know how much you need. My opinion is that 6-8 Gigabytes is enough now. Just before buying, see what the maximum amount of memory your processor supports. Also, for the dual-channel mode to work, it is necessary that both memory strips are of the same size.
Manufacturer
Of course, it's best if you get both RAM cards from the same manufacturer. But it really doesn't really matter. The RAM chips are produced in only three factories, and only two of them make it to the masses - Micron and Samsung. The rest of the manufacturers just buy these chips, install them on a memory card, and add power and cooling supplies.
Therefore, there is no fundamental importance in this, although it is advisable to choose devices from one manufacturer.
conclusions
We have considered all the main aspects and you now know exactly which RAM to choose for your computer. When choosing a memory bar, you need to be very careful if you want not only everything to work, but also to give maximum performance. And after the purchase, it is advisable to immediately check the new RAM in your device to make sure that it is working and compatible. If the bar is not working, then sellers usually go to a meeting and you can change it. If you have any questions, ask in the comments!
To complete the video on the topic:
The internal memory of a computer is divided into operative and permanent memory. Unlike the external one, which is represented by plug-in devices HDD, USB-flash, SD-cards, optical disks, it is one of the main elements of the system that ensures its operation. Devices of this type are located directly on the motherboard and do not require user access to them. Let's see how RAM differs from persistent memory.
Random access memory (RAM) - volatile variable random access memory, which stores data processed by the processor at a particular point in time. It is implemented in the form of random access memory and is often referred to simply as RAM.
Permanent memory (ROM) - non-volatile memory storing unchangeable data. It is implemented in the form of microcircuits soldered on the board, which are called read-only memory devices.
 ROM
ROM ROMs are often confused with the storage devices to which users write files. In fact, this memory is not available to them: the ROM contains BIOS and other firmware designed to control the interaction of hardware elements, and in mobile devices there is also an operating system. Technically, the ROM also includes CD-ROMs, magnetic tapes, punched cards and other media with once placed information, but they, of course, are not part of the computer's internal memory system.
Comparison
Imagine that you are writing, for example, a report. To read an article, you get up, go to the closet, pick up a book or magazine, carry it at the table, look for information, close it, carry it back, put it on the shelf. And so over and over again. Slow and uncomfortable, especially if the closet is in another room. And if you sit down at a large free desk? Here you have three magazines open on the necessary pages, here is the volume of the encyclopedia, there is a manual, and on the monitor is a browser with links to literature. Everything is available, just reach out and read. In the same way, files of running programs and open documents are stored in RAM. Compared to drives, even the most promising ones, RAM is much faster, the access time is measured in nanoseconds.
RAM is used in computer operations after it is started and the OS is loaded. Data is read from ROM mainly during system startup, and applications do not access them. Recording information into permanent memory can be either factory (ROM itself) or one-time programmable (PROM, in everyday life manipulation is called "firmware").
The main technical difference between RAM and permanent memory is volatility. When the power is turned off, the RAM is completely cleared of data, no matter how much of it and no matter how important it may seem. Everyone at least once got into a situation when, while working at the computer, the light suddenly turned off, and then changes in the document, open pages in the browser, the playing video were not saved. This is because before the new revision is written to external memory, it is stored in the operational memory, which, being de-energized, is reset to zero.
Permanent memory is non-volatile. A complete power off does not affect its content in any way, therefore programs launched from ROM (BIOS, POST, OS) require only a single write.
If we compare, for example, the process of typing in an editor and uploading firmware or updates to a smartphone, it is noticeable what the difference is between RAM and permanent memory. Symbols appear on the screen immediately (RAM is used), and in the second case it will take several minutes, and sometimes hours (written in ROM).
In modern systems, solid-state dynamic RAM (DRAM) is used, made in the form of strips with microchips and contacts soldered on them. They can be extracted and exchanged for others, say, of a larger volume. ROMs are placed directly on the board and can only be replaced for repair purposes. The RAM can store up to 64 GB of information in one module, the capacity of one permanent chip is significantly less - a few MB.
Table
| RAM | Persistent memory |
| Volatile, cleared when power off | Non-volatile, data is saved |
| Used in computer operations, works with applications | Used at system startup, does not interact with applications |
| Stores data about open documents and running applications | Stores firmware for managing components |
| Provides fast reading and fast writing | Recording is slow |
| Placed on discrete modules that must be replaced | Integrated on the device motherboard |
| Can accommodate a large amount of information | One chip contains several MB of data |
Now, in the characteristics of smartphones, very large amounts of RAM are often indicated. For example, now the usual amount of RAM for an average smartphone is 3-4 GB, while flagship smartphones generally get 6 or more gigabytes of memory. But, not all users understand what the RAM in a smartphone affects and why there is so much of it. In this article, we will try to deal with these issues.
In order to understand what a smartphone's RAM is, you first need to give a general definition of RAM.
RAM chips for smartphones
(random access memory) is a type of memory that is present in any computer hardware. This is a volatile memory that is used to store the data that the computer needs to work. The advantage of this memory is that it is very fast. RAM is much faster than hard drives and flash drives. Thanks to this, the exchange of data between the RAM and the processor is very fast. The disadvantage of this type of memory is that it depends on the power supply. In other words, it cannot store data without a constant supply of power. As soon as the power supply is lost, the entire contents of the RAM are erased. Therefore, RAM is not used for long-term data storage (like hard drives or flash drives), but only for temporary storage of the data that the computer needs right now.
In a smartphone, RAM performs exactly the same functions as in any other computer. It stores the data that the smartphone needs to work right now. These are data of running applications, operating system data, open files, loaded web pages, etc. There are no fundamental differences in the use of RAM on a smartphone.
What is the difference between RAM and built-in memory
As mentioned above, the RAM of a smartphone is a very fast volatile memory, the contents of which are deleted when the power is turned off (for example, when the smartphone is turned off). Due to this characteristics, RAM can only be used for temporary storage of data with which the smartphone is currently working.
Built-in memory (also called persistent or internal memory) is memory that is built on completely different principles. This memory does not depend on power supply and continues to store the data written into it even after a complete power outage. It is the built-in memory that is used to store operating system files (Android, iOS), application files and user data.
What affects the RAM in a smartphone
The characteristics of smartphones often indicate large amounts of RAM. Now, 3-4 GB is considered the usual volume, and flagship smartphones generally receive 6 or more gigabytes of memory. But, not all users understand what the RAM in a smartphone affects and why there is so much of it.
In short, the entire smartphone system. First, the speed of the RAM itself affects. RAM can operate at different frequencies and the faster it is, the faster the processor receives the data it needs and the faster it performs the necessary operations. More modern smartphones are equipped with faster memory, which speeds up the entire smartphone as a whole.
Secondly, the amount of RAM affects. The larger the amount of RAM, the less often you have to access the slow built-in memory. This saves time and allows the processor to do the job faster.
All of this affects the user experience. Faster memory with more capacity allows the smartphone to respond more quickly to user actions. In particular, it reduces delays when launching applications, switching between tabs in the browser, etc.
How to find out how much RAM is on a smartphone

The amount of RAM of the smartphone in the AIDA64 program
The easiest way to find out how much RAM is on a smartphone is to enter the name of the smartphone into a search engine and view the specifications on any website. But, if you do not know the exact model name of your smartphone, then you can install a special application to view the technical specifications.
For example, if you have a smartphone with an Android operating system, then you can use the free AIDA64 application. Launch this application on your smartphone and go to the "System" section. Here, among other characteristics of the smartphone, the amount of RAM (RAM) will also be indicated.
In this case, the smartphone has 2 GB of LPDDR3 RAM.
How to increase RAM on a smartphone
After reading the information described above, you may have a question, is it possible to increase the RAM of the smartphone. Unfortunately, this is almost impossible. The smartphone's RAM is soldered on the board and its replacement by the user is not provided.
Of course, theoretically, you can find suitable memory chips and solder them to the board in the conditions of the service center. But, in practice, it is unlikely that such a smartphone upgrade will work. To do this, you need to make sure that the smartphone's processor supports more memory, find suitable chips, find a service center, etc. And as a result, the procedure will be more expensive than buying a new smartphone.
The situation with the built-in memory is a little better. If your smartphone supports microSD cards, then you can install such a card in the smartphone and increase the amount of internal memory. This will free the internal memory from storing photos, music and other user files.
History random access memory, or RAM, began back in 1834, when Charles Babbage developed the "analytical engine" - in fact, the prototype of the computer. The part of this machine, which was responsible for storing intermediate data, he called the "warehouse". Memorization of information there was organized in a purely mechanical way, by means of shafts and gears.
In the first generations of computers, cathode-ray tubes and magnetic drums were used as RAM, later magnetic cores appeared, and after them, in the third generation of computers, memory on microcircuits appeared.
Now RAM is performed using technology DRAM in form factors DIMM and SO-DIMM, it is a dynamic memory organized in the form of semiconductor integrated circuits. It is volatile, meaning that data disappears when there is no power.
The choice of RAM is not a difficult task today, the main thing here is to understand the types of memory, its purpose and main characteristics.
Memory types
SO-DIMM

Memory of the form factor SO-DIMM is intended for use in laptops, compact ITX-systems, all-in-ones - in short, where the minimum physical size of memory modules is important. It differs from the DIMM form-factor by approximately 2 times the length of the module, and by a smaller number of pins on the board (204 and 360 pins for SO-DIMM DDR3 and DDR4 versus 240 and 288 on boards of the same types of DIMM memory).
In terms of other characteristics - frequency, timings, volume, SO-DIMM modules can be any, and do not differ from DIMMs in any fundamental way.
DIMM
DIMM is RAM for full-size computers.The type of memory you choose must first be compatible with the connector on the motherboard. RAM for a computer is divided into 4 types - DDR, DDR2, DDR3 and DDR4.

DDR memory appeared in 2001, and had 184 contacts. The supply voltage was from 2.2 to 2.4 V. The operating frequency was 400 MHz. It is still found on sale, however, the choice is small. Today the format is outdated - it is suitable only if you do not want to update the system completely, and in the old motherboard there are only DDR connectors.
The DDR2 standard came out in 2003, it got 240 pins, which increased the number of threads, decently speeding up the data transfer bus to the processor. The DDR2 operating frequency could be up to 800 MHz (in some cases - up to 1066 MHz), and the supply voltage from 1.8 to 2.1 V is slightly lower than that of DDR. Consequently, the power consumption and heat dissipation of memory have decreased.
Differences between DDR2 and DDR:
240 pins versus 120
New slot not compatible with DDR
Less power consumption
Improved design, better cooling
Higher maximum operating frequency
Also, like DDR, the outdated type of memory is now suitable only for old motherboards, in other cases it makes no sense to buy, since the new DDR3 and DDR4 are faster.
In 2007, the RAM was updated with the DDR3 type, which is still widely used today. The same 240 pins remain, but the connection slot for DDR3 has changed - there is no DDR2 compatibility. The frequency of the modules is on average from 1333 to 1866 MHz. There are also modules with frequencies up to 2800 MHz.
DDR3 differs from DDR2:
· DDR2 and DDR3 slots are not compatible.
· The clock frequency of DDR3 is 2 times higher - 1600 MHz versus 800 MHz for DDR2.
Differs in a reduced supply voltage - about 1.5V, and lower power consumption (in the versionDDR3L this value is even lower on average, about 1.35 V).
· The latencies (timings) of DDR3 are higher than those of DDR2, but the operating frequency is higher. In general, the speed of DDR3 is 20-30% higher.
DDR3 is a good choice today. In many motherboards, DDR3 memory slots are on sale, and due to the massive popularity of this type, it is unlikely to disappear soon. It is also slightly cheaper than DDR4.

DDR4 is a new type of RAM that was only developed in 2012. It is an evolutionary development of the previous types. Memory bandwidth has improved again, now reaching 25.6 GB / s. The operating frequency has also increased - from an average of 2133 MHz to 3600 MHz. If we compare the new type with DDR3, which held out on the market for 8 years and became widespread, then the performance gain is insignificant, besides, not all motherboards and processors support the new type.
DDR4 Differences:
Incompatibility with previous types
Reduced supply voltage - from 1.2 to 1.05 V, power consumption also decreased
Working memory frequency up to 3200 MHz (can reach 4166 MHz in some trims), while, of course, proportionally increased timings
May slightly outperform DDR3
If you already have DDR3 strips, then there is no point in rushing to change them to DDR4. When this format spreads massively, and all motherboards already support DDR4, the transition to the new type will happen by itself with the update of the entire system. Thus, we can summarize that DDR4 is more of a marketing than a really new type of RAM.
Which memory frequency should I choose?
Frequency selection should begin by checking the maximum supported frequencies for your processor and motherboard. It makes sense to take a frequency higher than that supported by the processor only when overclocking the processor.Today, you shouldn't choose memory with a frequency below 1600 MHz. The 1333 MHz variant is acceptable in the case of DDR3, if these are ancient modules not lying around at the seller, which will obviously be slower than the new ones.
The best option for today is memory with a frequency range from 1600 to 2400 MHz. A higher frequency has almost no advantage, but it costs much more, and as a rule, these are overclocked modules with raised timings. For example, the difference between the 1600 and 2133 MHz modules in a number of working programs will be no more than 5-8%, in games the difference may be even less. Frequencies of 2133-2400 MHz are worth taking if you are engaged in video / audio encoding, rendering.
The difference between the frequencies of 2400 and 3600 MHz will cost you quite a lot, while not adding noticeably speed.
How much RAM to take?
The amount that you need depends on the type of work performed on the computer, on the installed operating system, on the programs used. Also, do not overlook the maximum amount of memory supported by your motherboard.
Volume 2 GB - for today, it may be enough only to browse the Internet. More than half will be consumed by the operating system, the rest will be enough for the leisurely work of undemanding programs.
Volume 4 GB - suitable for a medium-sized computer, for a home pc media center. Enough to watch movies and even play undemanding games. Modern - alas, will hardly pull. (Best choice if you have a 32-bit Windows operating system that sees no more than 3GB of RAM)
Volume 8 GB (or a set of 2x4GB) - the recommended volume for today for a full-fledged PC. This is enough for almost any games, for working with any resource-demanding software. The best choice for a general purpose computer.
A volume of 16 GB (or sets of 2x8GB, 4x4GB) - will be justified if you work with graphics, heavy programming environments, or constantly render video. It is also perfect for online streaming - there may be freezes with 8 GB, especially with high quality video broadcast. Some games in high resolutions and with HD textures can perform better with 16GB of RAM on board.
Volume 32 GB (a set of 2x16GB, or 4x8GB) - so far a very controversial choice, it will be useful for some very extreme work tasks. It would be better to spend money on other computer components, this will have a stronger effect on its performance.
Operating modes: is it better 1 memory stick or 2?
RAM can operate in one-channel, two-, three- and four-channel modes. Definitely, if your motherboard has a sufficient number of slots, then it is better to take several of the same smaller size instead of one memory stick. The access speed to them will increase from 2 to 4 times.
For the memory to work in dual-channel mode, you need to install strips in slots of the same color on the motherboard. Typically, the color is repeated across the connector. It is important that the memory frequency in the two strips is the same.
- Single chanell Mode - single-channel operation mode. It turns on when one memory stick is installed, or different modules operating at different frequencies. As a result, the memory operates at the frequency of the slowest bar.
- Dual Mode - two-channel mode. Works only with memory modules of the same frequency, increases the speed of work 2 times. Manufacturers release specially for this a set of memory modules, which can have 2 or 4 identical strips.
- Triple Mode - works on the same principle as two-channel. Not always faster in practice.
- Quad Mode - four-channel mode, which works on the principle of two-channel, thus increasing the operating speed by 4 times. It is used where extremely high speed is needed - for example, in servers.

- Flex Mode- a more flexible version of the two-channel operation mode, when the strips are of different sizes, and only the same frequency. In this case, the same volumes of modules will be used in the two-channel mode, and the remaining volume will function in the single-channel mode.
Does the memory need a heatsink?
Now is not the time when at a voltage of 2 V the operating frequency of 1600 MHz was reached, and as a result a lot of heat was released, which had to be removed somehow. Then the radiator could be a criterion for the survival of an overclocked module.
At present, the memory power consumption has dropped significantly, and the heatsink on the module can be justified from a technical point of view only if you are fond of overclocking, and the module will work at frequencies that are beyond its limits. In all other cases, radiators can be justified, perhaps, by a beautiful design.

If the radiator is massive and noticeably increases the height of the memory bar, this is already a significant disadvantage, since it can prevent you from installing a processor supercooler into the system. By the way, there are special low-profile memory modules designed for installation in compact cases. They are somewhat more expensive than regular-sized modules.

What are timings?
Timings, or latency (latency) - one of the most important characteristics of random access memory, which determines its performance. Let us outline the general meaning of this parameter. Simplified, random access memory can be represented as a two-dimensional table in which each cell carries information. Cells are accessed by specifying the column and row numbers, and this is indicated using the strobe pulse of the row access RAS(Row Access Strobe) and column access strobe CAS (Acess strobe) by changing the voltage. Thus, for each cycle of work, calls occur RAS and CAS, and between these calls and the read / write commands, there are certain delays, which are called timings.

In the description of the RAM module, you can see five timings, which for convenience are written in a sequence of numbers separated by a hyphen, for example 8-9-9-20-27 .
· tRCD (time of RAS to CAS Delay)- timing, which determines the delay from the RAS pulse to the CAS
· CL (time of CAS Latency) - timing that determines the delay between the read / write command and the CAS pulse
· tRP (time of Row Precharge) - timing that determines the delay in transitions from one line to the next
· tRAS (time of Active to Precharge Delay) - timing, which determines the delay between the activation of the line and the end of work with it; considered the main value
· Command rate- defines the delay between the command to select a separate chip on the module until the command to activate the line; this timing is not always indicated.

To put it even simpler, it is important to know only one thing about timings - the lower their values, the better. At the same time, the bars can have the same operating frequency, but different timings, and the module with lower values \u200b\u200bwill always be faster. So you should choose the minimum timings, for DDR4 the average values \u200b\u200bwill be 15-15-15-36, for DDR3 - 10-10-10-30. It is also worth remembering that the timings are related to the memory frequency, so during overclocking, you will most likely have to raise the timings, and vice versa - you can manually lower the frequency, while reducing the timings. It is most advantageous to pay attention to the totality of these parameters, choosing a balance rather, and not to chase the extreme values \u200b\u200bof the parameters.
How do you decide on a budget?
With more money, you can afford more RAM. The main difference between cheap and expensive modules will be in the timings, frequency of operation, and in the brand - well-known, advertised ones can cost a little more than noname modules of an unknown manufacturer.In addition, a radiator installed on the modules costs extra money. Not all bars need it, but manufacturers are now not stingy with them.
The price will also depend on the timings, the lower they are, the higher the speed, and, accordingly, the price.
So, having up to 2000 rubles, you can buy a 4 GB memory module, or 2 2 GB modules, which is preferable. Choose whichever allows your pc's configuration. DDR3 modules will cost almost half as much as DDR4. With such a budget, it makes more sense to take DDR3.
To the group up to 4000 rubles includes modules with a volume of 8 GB, as well as sets of 2x4 GB. It is the optimal choice for any task, except for professional video work, and in any other difficult environment.

In the amount up to 8000 rubles will cost 16 GB of memory. Recommended for professional purposes, or for avid gamers - enough even in reserve, in anticipation of new demanding games.
If it's not a problem to spend up to 13,000 rubles, the best choice would be to put them in a set of 4 x 4GB sticks. For this money, you can even choose prettier radiators, possibly for subsequent overclocking.
I do not recommend taking more than 16 GB without the purpose of working in professional heavy environments (and even then not in all), but if you really want to, then for the amount from 13000 rubles you can climb Olympus by purchasing a 32 GB or even 64 GB kit. True, there won't be much sense for an ordinary user or gamer in this - it's better to spend money on, say, a flagship video card.

Random access memory (RAM) is one of the main parts of a computer. It is a volatile component that stores machine code, input / output and intermediate data while the computer is running. The process of choosing RAM only at first glance seems clear, but it contains many nuances that need to be considered in order to purchase quality components.
The easiest way to choose a RAM bar is to use the list of recommended modules on the website of the manufacturer of the motherboard installed on your computer. Since these parts of the PC are inextricably linked (including the processor), it makes sense to pay attention to the manufacturer's advice. The recommended RAM modules listed on his website will definitely work on your PC.
Another tip to follow when purchasing RAM strips is to match another hardware. When buying an inexpensive motherboard and budget processor, do not go for expensive RAM, because it will not reach its potential during operation. But it is very important to pay attention to the technical characteristics of the RAM.
Main settings
When buying a new RAM, pay attention to the main parameters that will help you make the right choice.
First, determine what type of RAM is right for your motherboard. This parameter is indicated in the description for it. There are four types today: SDRAM, DDR (DDR1), DDR2, DDR3, and DDR4.
The most common type of RAM today is DDR3. Unlike the modules of the previous generation, it operates at a clock frequency of up to 2400 MHz and consumes 30-40% less power than its predecessor. In addition, it has a lower supply voltage, so it emits less heat.
All types of random access memory are incompatible with each other in electrical (different supply voltage) and physical parameters (test holes are located in different places). The photo shows why the DDR3 RAM module cannot be installed in the DDR2 socket.

Helpful! The DDR4 standard is gaining popularity now. It features lower power consumption and higher operating frequencies (the prospect of growth up to 3200 MHz).
The form factor characterizes the size of the RAM strips. There are two types:
- DIMM (Dual Inline Memory Module) - installed on stationary PCs;
- SO-DIMM - for installation in laptops or monoblocks.

Bus frequency and bandwidth
RAM performance depends on these two parameters. Bus frequency characterizes the amount of information transmitted per unit of time. The higher it is, the more information will pass through the bus in the same time period. There is a direct proportional relationship between the bus frequency and the bandwidth: if the RAM frequency is 1800 MHz, theoretically it has a bandwidth of 14400 Mb / s.

Don't chase high RAM frequencies on a "more is better" basis. For the average user, the difference between 1333 MHz and 1600 MHz is imperceptible. It is important only for professional users who are engaged in video rendering, or overclockers seeking to "overclock" RAM.
When choosing a frequency, start from the tasks that you set for the computer and from its configuration. It is desirable that the frequency of the RAM modules coincide with the frequency at which the motherboard operates. If you connect the DDR3-1800 bracket to a motherboard that supports the DDR3-1333 standard, the RAM will run at 1333 MHz.
In this case, the more the better - this is the optimal description of the parameter. Today the minimum amount of RAM that must be installed on a computer or laptop is 4 GB. Depending on the tasks that are performed on the device, the amount of RAM can be 8, 32 or even 128 GB. An ordinary user will need 8 GB, for a specialist working with video processing programs, or for a gamer, 16-64 GB of "RAM" is needed.

RAM timings are characterized by delays in work. They are calculated in nanoseconds, and in the description they are indicated by a sequential set of numbers: 9-9-9-27, where the first three parameters are: CAS Latency, RAS to CAS Delay, RAS Precharge Time and DRAM Cycle Time Tras / Trc. They characterize the performance in the "memory-processor" segment, which directly affects the efficiency of the computer. The lower these values, the lower the latency and the faster the PC performance.

Some companies in the description of RAM modules indicate only one number - CL9. It characterizes CAS Latency. Basically, it is equal to or below other parameters.
Good to know! The higher the frequency of the RAM, the higher the timings, so you need to choose the optimal ratio for yourself.
RAM strips with the designation "Low Latency" are on sale. This means that at high frequencies they have low timings. But their cost is higher than that of conventional models.
Modes
To increase the performance of the computer, special modes of operation of the RAM strips are used: one-, two-, three-channel and Flex-Mode. In this case, the speed of the system is theoretically increased by two, three or more times.
Important! The motherboard must support these modes of operation. The description for it indicates in which connectors you need to install the brackets to enable the desired mode.
- Single channel mode starts when one RAM module is used or all strips differ in parameters. In this case, the system operates at the bar speed with the lowest frequency.
- Dual channel mode turns on when two RAM modules with the same characteristics (frequency, timings, volume) are installed in the slots. The performance gain is 10-20% in games and 20-70% when working with graphics.
- Three-channel mode is activated when three identical RAM strips are connected. In fact, it does not always outperform dual-channel in speed.
- Flex-Mode (flexible) - increases PC performance when using two RAM strips of the same frequency, but different in volume.

Important! It is desirable that the memory strips are from the same delivery batch. On sale there are kits consisting of two to four modules, which are fully compatible with each other in operation.

When buying digital equipment, pay attention to the manufacturer. Among the companies involved in the production of RAM modules, the most popular are: Corsair, Kingston, GoodRam, Hynix, Samsung and others.

Interestingly, the market for the production of memory chips for RAM modules is almost completely divided between three large companies: Samsung, Hynix, Micron. And large manufacturers use their chips to make their own models.
Modern RAM strips operate with low power consumption, so they generate little heat. In view of this, it is not necessary to buy models with installed radiators. But if you are a fan of overclocking hardware, then take care of purchasing RAM modules with heatsinks. They will not let them burn out during overclocking.
If necessary, the user can purchase a cooling system for RAM, consisting of radiators and fans. It is also intended for use by overclockers.

Choice to an existing bar
When purchasing a new RAM module for the one already installed in your PC, remember that often such combinations do not work together. But if you decide to buy, make sure that the timings and bus frequencies are the same. In addition, choose RAM sticks from the same manufacturer.
Video
If you don't fully understand how to choose RAM, watch this video.