A distinctive feature of the World Wide Web is the availability of means of transition from one document to another, thematically related to it, without an explicit indication of the address. The link between documents is carried out using hypertext links (or simply hyperlinks). A hyperlink is a selected fragment of a document (text or illustration) with which the address of another Web-document is associated. When you use a hyperlink (usually you need to point the mouse pointer over it and click once), the hyperlink is followed - opening the Web page to which the link points. The mechanism of hyperlinks allows you to organize a thematic journey on the World Wide Web without using (or even knowing) the addresses of specific pages.
Document addressing.
A form called a URL is used to record the addresses of Internet documents (Web pages). The URL contains indications of the application transfer protocol, the address of the computer, and the search path for the document on that computer. The computer address consists of several parts separated by dots, for example www.amik.ru. The parts of the address on the right indicate the network belonging of the computer, while the left-hand parts indicate a specific computer on the network. The conversion of the URL to the numeric form of the IP address is performed by the Domain Name Service (DNS). The forward slash character is always used as a separator in the search path for an Internet document.
Web viewers.
Internet documents are intended to be displayed in electronic form, and the author of the document does not know what the capabilities of the computer on which the document will be displayed are. Therefore, HTML provides not so much document formatting as a description of its logical structure. Formatting and displaying a document on a specific computer is performed by a special program - a browser (from the English word browser).
The main functions of browsers:
Search engines.
The Internet is growing at a very fast pace, and finding the information you need among tens of millions of documents (web pages, files, etc.) is becoming increasingly difficult. To search for information, special search engines are used, which contain more or less complete, but constantly updated information about Web pages, files and other documents stored on tens of millions of Internet servers.
Different search engines can use different search engines to find, store and present information to the user. However, it is common that at the time of the user's request, all information about the Internet documents is stored in a compact form in the database of the search server.
The available search engines can be roughly divided into three groups:
Internet Handbookis analogous to the subject index in a library: it allows you to find the most relevant WWW documents on a given topic. An example of such systems is the Yahoo search engine:
http://www.yahoo.com
General purpose search engines allow you to find documents on the WWW by keywords. The principle on which most of these systems are based is that special robotic programs automatically bypass WWW servers, read and index all documents they encounter, while highlighting keywords related to a given document, and remembering them along with the URL of this document in the database. Most search engines also allow the author of a new Web page to enter information into the database himself.
Referring to such a search engine, we display one or more keywords that, in our opinion, could lead us to the information of interest, and send a request with one click of the mouse on the on-screen button, usually called Submit. After a few seconds, the search engine will return us a list of URL documents in which the keywords we specified were found. An example of such a search engine is Rambler:
http://www.rambler.ru
Specialized search engines allow us to find information on specific sciences, specializations, in areas of interest to you. An example of such a search engine is http://www.avatarsearch.com/. The AvatarSearch search engine is designed for people who are interested in occult and mystic issues. Links to pages whose authors are particularly successful in covering this topic receive a special distinction from the creators of this site.
Fig. 1 InterfaceRambler
Since information on the Internet is constantly changing (new documents are created, old ones are deleted, etc.), search robots do not always have time to track all these changes. The information stored in the database of the search engine may differ from the real state of the Internet, and therefore, sometimes the user may receive a link to a document that does not exist or has been moved.
The search engine interface is usually roughly the same, and
Fig. 2 Search results
 therefore, consider it using the example of the Russian search server RAMBLER ( http://www.rambler.ru).
therefore, consider it using the example of the Russian search server RAMBLER ( http://www.rambler.ru).
The search engine home page contains a list of topics that refine the search area and a search field. In the search box, the user can enter keywords to search for the document, that is, words that the user thinks will identify the document.
Let's set the task to find information about computer science textbooks. However, before entering keywords in the search field, it is advisable to narrow your search by selecting the Education category from the list of sections.
As keywords, we will select the words: informatics, textbook, catalog - and enter them in the search field. As a result, we will receive clearly redundant information, a list of almost 90 thousand documents, since the word informatics is contained in 519249 documents, the word textbook is in 885564 documents, and the word catalog is in 12622835.
The computers in your computer science office are networked. This network ...
Local
Regional
The global
What device is needed to transfer data over telephone lines?
Drive
Modem
Scanner
A network printer is installed on one of the computers in the office. Will other students be able to use this printer from their computers?
Yes, if access to the printer is allowed
What type of access can be set for the My Documents folder on your computer so that other classroom students can use documents from this folder?
Local
Only for reading
Full
5. The greatest opportunities for access to information resources are provided by the method of connecting to the Internet:
a) terminal connection via a dial-up telephone channel;
b) remote access via telephone communication channels;
c) permanent connection via fiber optic channel;
d) permanent connection on a dedicated channel.
6. Computer telecommunications is:
a) connection of several computers into a single network;
b) transferring information from one computer to another using floppy disks;
c) remote transmission of data from one computer to another;
d) exchange of information between users about the state of the computer;
7. The server is:
a) a network program that conducts a dialogue between one user and another;
b) a powerful computer to which other computers are connected;
c) a computer of an individual user connected to a common network;
d) a standard that defines the form of presentation and method of forwarding the message.
8. M dress is:
a) a powerful computer to which other computers are connected;
b) a device that converts digital signals of a computer into an analog telephone signal and vice versa;
c) a program with which a dialogue is carried out between several computers;
d) personal computer used to receive and send correspondence.
9. The baud rate is:
a) the amount of information transmitted per second;
b) the number of bytes of information transmitted per minute;
c) the number of bytes of information transferred from one computer to another;
d) the number of bits of information transmitted through the modem per unit of time.
10. Addressing is:
a) the method of identifying subscribers in the network;
b) server address;
c) postal address of the network user;
d) the number of baud (characters / sec) sent by your modem.
11. Local computer networks are:
a) the network to which all computers in your city are connected;
b) the network to which all computers in your country are connected;
c) the network to which the computers of your computer science office or one building are connected;
d) the network to which all computers are connected.
12. The network adapter is:
a) a special program through which several computers are connected;
b) special hardware for effective interaction of personal computers on the network;
c) a special system for managing shared network resources;
d) a system of information exchange between different computers.
13. Domain is:
a) part of the address that determines the address of the user's computer on the network;
b) the name of the program for communication between computers;
c) the name of the device that communicates between computers;
d) unit of measurement of information.
14 ... Which of the following methods of connecting to the Internet provides the greatest opportunities for accessing information resources:
a) permanent connection via fiber optic channel;
b) remote access via telephone channels;
c) permanent connection on a dedicated channel;
d) terminal connection via a dial-up telephone channel;
e) temporary access via telephone channels.
15. The exchange of information between computer networks in which different standards for the presentation of information (network protocols) are in force is carried out using:
a) host computers;
b) email;
c) gateways;
d) modems;
e) file servers.
16.P mailbox subscriber email represent t yourself:
a) an ordinary mailbox;
b) a certain area of \u200b\u200bthe file server's RAM;
c) a part of the memory on the hard disk of the mail server allocated for the user;
d) part of the memory on the hard disk of the workstation;
e) a special electronic device for storing text files.
17. A distinctive feature of a Web document is:
a) the lack of a strictly defined format for the presentation of the document;
b) the fact that its replication is carried out by the originator of the document;
c) the presence of hypertext links in it;
d) the presence of illustrations in it;
e) its compactness.
18. The set of hardware and software tools that allow computers to exchange data is:
a) highway;
b) interface;
c) adapter;
d) computer network;
e) data buses.
19. The global computer network is:
a) information system with hyperlinks;
b) a lot of computers connected by information transmission channels and located within the same room, building;
c) a set of host computers and file servers;
d) a system for exchanging information on a specific topic;
e) a set of local networks and computers located at long distances and connected using communication channels into a single system.
20. A set of computers, connected by information transmission channels and located within the same room, building, is called:
a) global computer network;
b) an information system with hyperlinks;
c) local computer network;
d) by e-mail;
e) regional computer network.
21. Information resources include:
a) a set of documents in paper form of information;
b) the entire set of individual documents, as well as all documents located in special repositories (libraries, video libraries, funds, archives);
c) all documents kept in archives;
d) books and other printed publications;
e) information stored on paper and magnetic media.
22. To store files intended for general access by network users, the following is used:
a) host computer;
b) file server;
c) workstation;
d) client-server;
e) switch.
23. The network protocol is:
a) a set of agreements on interactions in a computer network;
b) sequential recording of events occurring in the computer network;
c) rules for interpreting data transmitted over the network;
d) n rules for establishing communication between two computersand online;
e) coordination of various processes in time.
24. Activities aimed at collecting, storing, processing, transferring and using information are called:
a) labor activity;
b) sports activities;
c) information activities;
d) artistic activities;
e) scientific activities.
25. Transport Protocol (TCP) provides:
a) splitting files into IP packets during transmission and assembling files during receiving;
b) reception, transmission and issue of one communication session;
c) providing the user with already processed information;
d) delivery of information from the sending computer to the receiving computer;
e) collecting files from IP packets during file transfer.
26. Routing Protocol (IP) provides:
a) delivery of information from the sending computer to the receiving computer;
b) data interpretation and preparation for the user level;
at) preservation of mechanical, functional parameters of physical communication in a computer network;
d) control of data transmission equipment and communication channels;
e) splitting files into IP packets during transmission and assembling files during receiving.
27. A computer connected to the Internet must have:
a) IP address;
b) WEB-page;
c) home WEB-page;
d) domain name;
e) URL.
28. Electronic mail (e-mail) allows you to transfer:
a) messages and attached files;
b) exclusively text messages;
c) executable programs;
d) www-pages;
e) exclusively databases.
29. WEB-pages have the extension:
a) * .HTM;
b) * .THT;
c) * .WEB;
d) *. EXE;
d ) *. WWW.
30. HTML (HYPER TEXT MARKUP LANGUAGE) is an
a) a means of creating WEB-pages;
b) programming system;
c) a graphic editor;
d) database management system;
e) an expert system.
Test number 6 "Informatization of society"
Answers:
Practical task.
Using any Internet search engines, find information on the following topics by options (at least 5 A4 pages):
Application of the Internet.
The computer of the future.
Information society.
Legal protection of programs and data.
Information culture.
Protection of information.
Classification and Use of Websites.
Internet services.
Internet search engines.
The use of computers in life.
Form the found information in the form of text with parameters:
Font - Times New Roman.
The size – 14 fri .
Fields - 2 cm each.
Orientation is bookish.
Line spacing is one and a half.
Cprotect it on the Desktop under the name "Task3_Surname" or send it over the local network to the teacher's computer.
Lecture 17. Principles of formation of web-documents
Ways to connect to the global network
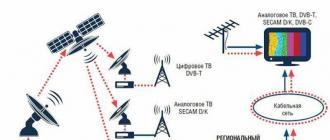
The connection to the network is made through organizations that are Internet service providers called providers ... Providers provide different connection options, relations with the provider are built on a contractual basis.
Modem connection with service provider carried out via telephone networks using a modem that provides modulation-demodulation of signals. High-frequency modems, in contrast to low-frequency modems, provide simultaneous transmission of Internet traffic and telephone calls. The main disadvantage of the connection is the poor quality of the telephone networks and the limited data transfer rate. For this reason, the original modem connection is gradually giving way to modern methods.
Leased line connection based on the transmission of a signal over a cable connecting the provider with the service user. The leased line provides a direct, permanent high-speed connection that is used only to connect to the network. The disadvantages include the high cost of connection and subscription fees, especially for high-speed tariffs.
Radio access refers to a wireless connection method based on the use of transceiving radio equipment, including the use of wireless modems. Radio access provides high user mobility, for example, in the field. One of the disadvantages of radio access is the limitation of radio coverage areas. Reliability of radio access is inferior to a connection over a dedicated line .
Satellite connection most often based on a combined access method, in which a request for communication is sent over a telephone line, and a response is sent through a satellite dish. The method is affordable and has a high data transfer rate. At the same time, as a rule, you can receive satellite TV channels. Each transmitting satellite has its own coverage map, which limits the satellite coverage area.
Web documentIs an electronic document containing text, graphic and other data, which is formatted taking into account the peculiarities of receiving and transmitting information on the Internet. To create web-documents, you can use ordinary text and graphic editors, but web-editors, which are used at a professional level, are more effective.
The basis of web documents is hypertext Is an extended text that includes additional elements, for example, illustrations, links, insert objects. To place hypertext on the Internet use the operation markup , which changes the form of presentation of an electronic document by introducing special markup codes. The application of codes is subject to the rules of the text markup language. The use of markup is due to the fact that during transmission on the Internet it is impossible to achieve absolute fidelity of the document in its original form. In other words, the Internet does not preserve the original formatting of the document, so we can only talk about the functional markup of the document.
Marked up electronic documents are viewed using browsers – software tools designed to work with web documents.
A web document presented on the Internet is called web page ... Content-related web pages form website - thematic web-document, which has its own network address, storage location and owner responsible for the creation and maintenance of the document. The materials presented on the site, or the content of the site are called content .
The presence of hypertext links in it;
What extension do WEB pages have?
What is the purpose of the FTP service on the Internet?
For receiving and transmitting files of any format.
To organize the storage of public access archives.
What is office equipment?
A set of technical means for the preparation of documents, their copying, processing, storage and automatic search;
What is a plotter?
Large format device for printing large-scale images on paper.
What are the Resolution Modes for a fax machine?
Standard, detailed, super detailed, grayscale.
What is paging?
Communication system using a pager.
How are PC drives classified?
Laser, magnetic, ZIP and floppy disks, magneto-optical.
What type of device is an inkjet printer?
Shockless type, ink is used for printing;
What type of device is the dot matrix printer?
Impact type, needle-type printing principle.
What type of device is a laser printer?
Shockless type, drum printing principle;
What PC hardware can be classified as peripheral?
Printer and scanner.
What characterizes the totality of one or more databases and data management tools?
Database.
What characterizes the set of hardware, software and rules that ensure the interaction of various devices that make up a computing system and / or programs?
Interface.
What is multimedia?
Interaction of virtual and audio effects under the control of interactive software using modern and software tools.
84. What is the Wcb Server content?-WEB page.
What is a "corporate information system"?
Human-computer system for decision support and production of information products using computer information technology;
What is the essence of the principle of openness of the corporate information system?
Changes to the system are due. For the most varied reasons, it must be done. only by supplementing the system without reworking the created;
Openness, i.e. the possibility of integration with other components of the information. systems - control. Database.
Which of the above principles are the main ones for building a corporate information system?
Reliability, efficiency, availability, informational comfort, low cost, openness;
What is the purpose of automating service enterprises?
Information support for the formation and decision-making by management;
What are the functions of the module of the internal organization of the enterprise, which is part of the structure of the corporate information system?
What are the functions of the e-commerce system module included in the structure of the corporate information system?
Providing customers with on-line access to the services of the enterprise, drawing up commercial offers and forming orders via the Internet.
What functions are performed by the personnel management module, which is part of the structure of the corporate information system?
What are the components of a 3-way PC speaker?
2 satellites on each of which there are 2 speakers and a subwoofer;
What is PC Acoustic Performance?
The band of sound frequencies reproduced by the PC speaker system and the sound power generated by it;
What kind of service process in the tourism industry was accelerated by computer reservation systems CRS (Computer Reservation System), which appeared in the mid 60s. XX century?
Reservation of air tickets in real time;
What is Amadeus, Galileo Worldspan?
Computer reservation systems;
96. What computer systems not only speed up the process of settlements and the formation of documents, but can also reduce the cost of services (tour package) by choosing the best price option for customer delivery and accommodation?
Amadeus, Galileo Worldspan;
What firms in Russia are developing specialized software products for the tourism business?
Tourism Technologies, ANT-Group;