Reading time: 11 minute (s)
Technical improvements to the requirements of SEO and optimization of the site structure are the primary points in promoting the resource, but if the search engines do not know about it, that is, it is not indexed, then the promotion is impossible.
What is indexing? This is the addition of the collected information about the resource to the databases by search robots. Further ranking takes place according to the indexed pages. We offer several simple and understandable ways to check pages that search engines "see".
Let's consider each option in more detail.
1. Checking the indexing of the site through the Yandex.Webmaster panel and Google Search Console
Free and reliable way using services for webmasters.
Yandex.Webmaster
After passing the verification, go to the panel and click the "Indexing" - "Pages in search" tab. Here are the website pages that participate in Yandex search.

Also, the number of downloaded and indexed pages can be viewed in the service on the page "My sites".

For analysis, the list of pages can be downloaded from the service as a file in .xls and .csv formats.
Google Search Console
Similarly to the Yandex webmaster, we go through the authorization in the Google account, enter the service https://search.google.com/search-console/about?hl\u003dru, enter the site url and click the "Add resource" button.

After confirming the rights to the site to check the indexing of the resource in the Google Webmaster panel, go to the "Index" - "Coverage" tab.

It should be borne in mind that the information in Google Search Console is approximate, since the report shows statistics after the last crawl, that is, the number of pages may be different at the current time of the scan.
Examples of checking site indexing



2. Checking the number of indexed pages in the PS using operators
Using the document operator "site" it is possible to see the approximate number of pages in the index. To use this parameter, enter "site: site_address" in the search bar, for example "site: https: //www.bordur32.ru".


3. Analysis of site indexing using plugins and extensions
In order not to enter operators in the browser line before the url, this automated method is used. Download a free browser bookmarklet (a small script saved in bookmarks) and click on a special icon while on the site.


4. Tracking indexed pages using online services
Another way to check indexing is to use third-party resources. For example, go to the site a.pr-cy.ru, enter url and click "Analyze".

Site indexing can be checked in other services, for example: seogadget.ru, xseo.in and others.
5. Programs to control the indexing of the site
There are free (Site-Auditor) and paid programs (Semonitor) to analyze the site and check the pages in the index. Download the selected software and install it on your PC. Add the url of the checked site to the input line.

Checking page indexing
Sometimes you need not only to find out how many pages are indexed in Yandex and Google, but you also need to determine whether a particular page is indexed. This can be done in the following ways:
1. In the panel for webmasters:

2. The "url" operator
Enter a special operator in the search bar. The request will look like this: "url: address of the page of interest".

3. Operator "info"
In the Google search engine, you can use the operator "info". The query in the search bar will look like this: "info: address_ of the page of interest"

Why the site may not be indexed
Ideally, resource pages should be indexed and their number in search engines should be approximately the same. But this is not always the case. Consider the reasons for preventing the indexing of the site.
Robots.txt errors
A robots.txt file is a text document in .txt format located in the root directory of a website, which prohibits or permits indexing of pages by robots of the search engine. Therefore, incorrect use of directives can close the entire site or individual pages of the resource from indexing.
Missing sitemap.xml file
A sitemap (file sitemap.xml) is a special document located in the root directory containing links to all pages of the resource. This file helps search robots to quickly and efficiently index the resource. Therefore, only those pages that should be included in the index need to be added to it.
New site
The indexing process of a new resource takes some time. Therefore, in this case, you just need to wait, remembering to control the indexing process.
Private settings
In some CMS, such as WordPress and Megagroup, it is possible to hide pages from indexing through the site admin panel; these settings can be set by default.
Noindex tag
Pages can be closed from the index in the code using the meta tag name \u003d "robots" content \u003d "noindex, nofollow" /\u003e. You need to check for its presence and either remove it from the code, or replace it with "index" and "follow".
Garbage pages
Another reason can be a large number of garbage pages that do not provide useful and unique content within the site. Such pages should be closed from indexing so that there are no problems with indexing the resource and the robot does not waste time visiting these pages.
Also, the reason for not indexing resource pages can be crawling errors, blocking of the site in the .htaccess file, duplicate pages, non-unique content, low hosting uptime, slow site loading speed, bans and filters of the search engine.
Conclusions of the Web Center SEO Specialist
The main goal of both the site owner and the SEO specialist is to achieve indexing of the necessary pages of the resource. To do this, you need to regularly monitor pages in Yandex and Google search, check services for webmasters for errors on the site, fill it with unique and useful content, monitor and optimize the resource loading speed.
To speed up the indexing process, you need to confirm the rights to the site in Yandex.Webmaster and Google Search Console and place a link to the sitemap.xml file in them, you can also send important pages of the resource to crawl.
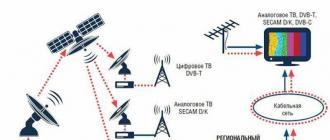
Search engine index is a special database that contains information collected by search robots from site pages. This takes into account text content, internal and external links, graphic and some other objects. When a user sets a query to a search engine, the database is accessed. After that, ranking by relevance is performed - the formation of a list of sites in descending order of their importance.
What is indexing
The process of adding the collected information to the database by robots is called indexing. Then the data is processed in a certain way and an index is created - an extract from the documents. The process of populating the index is carried out in one of two ways: manually or automatically. In the first case, the owner of the resource must independently add the URL of the web resource to a special form that Yandex, Google and other search engines have. In the second, the robot finds the site itself, systematically following external links from other sites or scanning the sitemap.xml file.
The first attempts to index web resources were made back in the mid-90s of the last century. Back then, the database was like a regular subject index, which contained keywords that robots found on the sites they visited. For almost 30 years, this algorithm has been significantly improved and complicated. For example, today, before entering the index, information is processed according to the most complex computational algorithms using artificial intelligence.
Why search engines need an index
Indexing of site pages is an integral part of the work of search engines (not only Google and Yandex, but everyone else). The base obtained in the process of scanning web resources is used to generate relevant results. The main search engine robots:
- main- scans all content on the site and its individual pages;
- quick - indexes only new information that was added after the next update.
There are also robots for indexing rss feeds, pictures, etc.
On the first visit, all new sites are included in the database if they fit the requirements of the search engine. During a return visit, the information is only supplemented with details.
Page indexing speed
The faster the page is added to the index, the better for the web resource. However, search robots cannot perform such a large amount of work as often as the content of sites is updated. Indexing in Yandex takes on average one to two weeks, while in Google it takes several days. In order to speed up the indexing of resources, for which it is very important to quickly get information into the database (news portals, etc.), a special robot is used that visits such sites from one to several times a day.
How to check indexing in Yandex and Google
Use information from the webmaster panel... In the list of Google services, open Search Console and then go to the Google Index section. The necessary information will be in the "Indexing Status" block. In Yandex.Webmaster you need to go along the following chain: "Site indexing" - "Pages in search". Another option: "Site indexing" - "History" - "Pages in search".
Set site search using special operators... To do this, use a request with the "site:" construction, indicating further the address of your resource in full format. This will give you the number of indexed pages. Serious discrepancies in the values \u200b\u200b(up to 80%) obtained in different search engines indicate the presence of problems (for example, a web resource may be under a filter).
Install custom plugins and bookmarklets... These are small browser add-ons that allow you to check the indexing of site pages. One of the most popular among them is the RDS Bar.
How to speed up indexing
Several factors directly affect the speed of site indexing:
- the absence of errors that slow down the process of collecting information by a search robot;
- credibility of the resource;
- frequency of content updates on the site;
- frequency of adding new content to the site;
- page nesting level;
- a correctly filled sitemap.xml file;
- robots.txt restrictions.
To speed up site indexing, follow a few rules:
- choose fast and reliable hosting;
- set up robots.txt by setting indexing rules and removing unnecessary bans;
- get rid of duplicates and errors in the page code;
- create a sitemap sitemap.xml and save the file in the root folder;
- if possible, organize the navigation in such a way that all pages are 3 clicks from the main one;
- add the resource to the Yandex and Google webmasters panel;
- make internal linking of pages;
- register your site in authoritative ratings;
- update content regularly.
Additionally, we recommend evaluating the volume of flash elements in terms of their impact on promotion. The presence of visual objects of this type significantly reduces the share of search traffic, since it does not allow robots to complete indexing in full. It is also not advisable to place key information in PDF files saved in a certain way (only the text content of the document can be scanned).
Search engines, for a number of reasons, do not index all pages of the site or, conversely, add unwanted pages to the index. As a result, it is almost impossible to find a site with the same number of pages in Yandex and Google.
If the discrepancy does not exceed 10%, then not everyone pays attention to this. But this position is fair for media and information sites, when the loss of a small part of the pages does not affect the overall traffic. But for online stores and other commercial sites, the lack of product pages in the search (even one in ten) is a loss of income.
Therefore, it is important to check the indexing of pages in Yandex and Google at least once a month, compare the results, identify which pages are missing in the search, and take action.
Problem while monitoring indexing
It is not difficult to view the indexed pages. This can be done by uploading reports in panels for webmasters:
- ("Indexing" / "Pages in search" / "All pages" / "Download XLS / CSV table");
Tool capabilities:
- simultaneous checking of indexed pages in Yandex and Google (or in one PS);
- the ability to check all site URLs at once using an XML map;
- there is no limit on the number of URLs.
Features:
- work "in the cloud" - no need to download and install software or plugins;
- uploading reports in XLSX format;
- notification by mail about the end of data collection;
- storing reports indefinitely on the PromoPult server.
How to quickly find out if an important page for you got into the index of search engines? Anyway, how many pages of the site are "seen" by search engines? In this post, I described the methods most often used by SEO specialists and prepared a bonus for readers.
When a page is indexed, the search engine robot adds information about the site to the database. Further search is performed on the indexed pages. Indexing and scanning should not be confused.
The robot can crawl the entire site quickly. And adding to the index is slow, not adding part of the pages or removing pages from the index.
1. Check indexing in the webmasters panel
This is the basic verification method for a webmaster or site owner.
Google... You must go to Search Console and on the Google Index tab, select Indexing Status.
Yandex... We pass authorization in Yandex.Passport, go to Yandex.Webmaster and follow the path "Site indexing" - "Pages in search". Another option: "Site indexing" - "History" - "Pages in search". Here you can see the dynamics of changes in the number of pages in the search.
To use this method, you must have a certain level of access to the webmaster's panel. An example of good site indexing. The number of quality pages is growing and they are being added to the index.  Indexing problems look like this:
Indexing problems look like this: 
The screenshot shows a site closed from indexing in the robots.txt file
Want to know more about search engine optimization? Subscribe to the newsletter:
Site indexing in search engines is important for every webmaster. Indeed, for the quality promotion of the project, you should monitor its indexing. I will describe the process of checking indexation in Yandex.
Indexing in Yandex
The Yandex robot scans sites day after day in search of something "tasty". He collects in the top results those sites and pages that, in his opinion, most deserve it. Well, or just Yandex wanted it that way, who knows
We, as real webmasters, will adhere to the theory that the better the site is made, the higher its position and more traffic.
You can check the indexing of a site in Yandex in several ways:
- using Yandex Webmaster;
- using search engine operators;
- using extensions and plugins;
- using online services.
Indexing site pages in Yandex Webmaster
To understand what the search engine has dug up on our site, you need to go to our favorite Yandex Webmaster in the "Indexing" section.
Crawl statistics in Yandex Webmaster
First, let's go to the "Bypass statistics" item. The section allows you to find out which pages of your site the robot crawls. You can identify the addresses that the robot could not load due to the unavailability of the server on which the site is located, or due to errors in the content of the pages themselves.
The section contains information about the pages:
- new - pages that have recently appeared on the site or the robot has just visited them;
- changed - pages that Yandex search engine has seen before, but they have changed;
- crawl history - the number of pages that Yandex bypassed taking into account the server response code (200, 301, 404, and others).
The graph shows new (green) and changed (blue) pages.
And this is a graph of the bypass history.
This item displays the pages that Yandex found.
N / a - URL is not known to the robot, i.e. the robot had never met her before.
What conclusions can be drawn from the screen:
- Yandex did not find the address / xenforo / xenforostyles /, which, in fact, is logical, since this page no longer exists.
- Yandex found the address / bystrye-ssylki-v-yandex-webmaster /, which is also quite logical, since the page is new.
So, in my case, Yandex Webmaster reflects what I expected to see: what is not needed - Yandex deleted, and what is needed - Yandex added. It means that everything is fine with me, there are no blockages.
Pages in search
The search results are constantly changing - new sites are added, old ones are removed, places in the search results are adjusted, and so on.
You can use the information in the "Pages in search" section:
- to track changes in the number of pages in Yandex;
- to keep track of added and excluded pages;
- to find out the reasons for excluding a site from search results;
- to obtain information about the date of the visit to the site by the search engine;
- for information on changing search results.
This section is needed to check the indexing of pages. Here Yandex Webmaster shows pages added to search results. If all your pages have been added to the section (a new one will be added within a week), then everything is in order with the pages.
Checking the number of pages in the Yandex index using operators
In addition to Yandex Webmaster, you can check page indexing using operators directly in the search itself.
We will use two operators:
- "Site" - search in all subdomains and pages of the specified site;
- "Host" - search through pages hosted on this host.
Let's use the operator "site". Note that there is no space between the operator and the site. 18 pages are in Yandex search.
Let's use the "host" operator. 19 pages indexed by Yandex.
Checking indexing with plugins and extensions

Check site indexing using services
There are a lot of such services. I'll show you two.
Serphunt
Serphunt is an online website analysis service. They have a useful tool for checking page indexing.
You can check up to 100 site pages at the same time using two search engines - Yandex and Google.
We press "Start check" and after a few seconds we get the result: