The computer configurator with compatibility check allows you to quickly assemble a system unit with the technical characteristics required by the user. With the help of our online construction set, you can easily build a reliable office machine, home multimedia system unit or a powerful gaming configuration.
Assembling your computer online
Nowadays, like many years before that, assembling a computer from self-selected components is popular. This is a good opportunity to find what exactly you want. Nothing limits you, hundreds of options are available for assembly, among which there will definitely be one that you like.
Our online store offers the possibility of assembling a computer online through the configurator. It presents this process in the form of categories of components, from the processor to the power supply. Each category contains an expanded assortment of models with descriptions of characteristics for easy selection.
To simplify the selection of components, a compatibility filter for the main components of the assembly is configured in the configurator. For example, by selecting a specific processor, the following components are automatically filtered by compatibility. Also, you will be presented with a choice to install the operating system. After completing the assembly process, you get the final result in three parameters: price, technical data, rendered image. After placing an order and confirming it by phone, our specialists assemble this complete set, check its functionality.
The advantage of this method of buying a system unit is that you not only choose the components you want, but also have the opportunity to choose the brand or company of the part manufacturer.
After collecting a certain configuration, completing by pressing the assemble / buy buttons, the assembly is assigned a certain serial number, by typing which in the product search bar, you can find this PC and send a link to it to friends or acquaintances for consultation or recommendation to them for purchase.
An important feature of our configurator is the function “find out an expert's opinion”. By sending your request through this form, you will receive a detailed response with a recommendation to the e-mail specified by you.
Try it and see for yourself - assembling a computer online is easy and simple! In case of difficulties, you can always get advice from our specialists on all issues of interest to you.
In this essay, we will try to briefly explain some of the features of IBM PC-compatible computers, and also introduce some basic concepts, which we will later refer to more than once.
Open architecture (block-modular construction principle)
The appeal of IBM PC-compatible computers lies in their open architecture. This, in particular, means that such computers have a modular construction principle, that is, their main units and blocks are made in the form of separate modules. Thus, installing new or replacing old devices that are part of the computer is not particularly difficult. Improvement of such computers is within the power of the users themselves.
As part of an IBM PC-compatible personal computer, there are three main components: a system unit, a monitor and a keyboard. The system unit contains all the main electronic stuffing of the computer: the power supply, the motherboard (system) board, and storage drives (floppy drives) with removable or non-removable media. The keyboard is a standard input device that allows the computer to transmit certain characters or
control signals. The monitor (or display) is designed to display monochrome or color, symbolic or graphic information on its screen. All of the above main components are connected to each other by means of special cables with connectors.
The type of case of the system unit depends, in particular, on the size and location of the motherboard used, the minimum power supply unit (that is, the possible number of connected devices) and the maximum number of installed storage drives. Computer cases are available in tower and desktop versions. The main difference between these types of cases can be considered a different number of mounting places for drives and, accordingly, the power of the power supply. By the way, mounting locations (mounting bays) for drives can be of two types: with external access and internal access. Thus, by definition, access to drives installed in the mounting bays of the latter type can be carried out only when the cover of the system unit case is open. Such mounting locations can only be used for drives with non-removable media, such as hard drives.
The motherboard is the basis of the computer and is a flat sheet of foil-clad fiberglass, on which the main electronic elements are located: a basic microprocessor, random access memory, a quartz resonator and other auxiliary microcircuits.
In accordance with the principle of open architecture, most
IBM PC-compatible computers have motherboards that contain only the main components, and there are no communication elements, for example, with storage drives, a monitor and other peripheral devices. In such
in this case, these missing elements are located on separate printed circuit boards, which are inserted into special expansion slots provided for this on the system board. These additional boards are called daughter boards, and the system board is called the motherboard. Functional devices on daughter cards are often called controllers or adapters, and daughter cards are often called expansion cards.
Microprocessors and system buses
IBM PC-compatible computers use only Intel microprocessors or their clones with a similar architecture.
The microprocessor is connected to the main devices of the computer through the so-called system bus. This bus is used not only to transfer information, but also to address devices, as well as to exchange special service signals. As a rule, additional devices are connected to the system bus via expansion connectors.
To connect expansion cards on the system bus of computers based on the i8088 microprocessor (IBM PC and IBM PC / XT), 62-pin connectors are used. In particular, this system bus includes 8 data lines and 20 address lines, which limit the address space of a computer to a limit of
1 MB. The PC / AT286 was the first to use the new ISA (Industry Standart Architecture) system bus, through which it was possible to transmit 16 data bits in parallel, and thanks to 24 address lines, it was possible to directly access 16 MB of system memory. This system bus differs from the previous one by the presence of an additional 36-pin connector for the corresponding expansion cards. Computers based on i80386 / 486 microprocessors began to use special buses for memory, which made it possible to maximize its performance. However, some devices connected through the system bus expansion connectors cannot achieve baud rates comparable to a microprocessor. This mainly concerns working with storage controllers and video adapters. To solve this problem, they began to use the so-called local (local) buses, which directly connect the microprocessor with the controllers of these peripheral devices. Currently, two standard local buses are known: VL-bus (VESA Local-bus) and PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect). There are special connectors on the computer's motherboard to connect devices to such buses.
Ports, interrupts, direct memory access
All devices on the system bus are treated by the microprocessor as either addressable memory or I / O ports. Generally speaking, a port is understood as a kind of interface circuit, which usually includes one or more I / O registers (special memory cells).
The microprocessor can find out about the commission of a certain event by a signal called an interrupt. In this case, the execution of the current sequence of commands is suspended (interrupted), and another sequence corresponding to this interrupt begins to execute instead. Interrupts are typically classified as hardware, logic, and software.
Hardware interrupts (IRQs) are transmitted over special lines on the system bus and are associated with requests from external devices (for example, pressing a key on the keyboard). Logic interrupts occur during the operation of the microprocessor itself (for example, division by zero), while software interrupts are initiated by the executable program and are usually used to call special subroutines.
The first IBM PCs used the i8259 (Interrupt Controller) interrupt controller chip, which has eight interrupt signal inputs (IRQ0-IRQ7). As you know, at the same time the microprocessor can serve only one event and the interrupt controller helps it in choosing this event, which sets a certain level of importance for each of its inputs - priority. The IRQ0 interrupt request line has the highest priority, and IRQ7 has the lowest priority, that is, the priority decreases in ascending order of the line number. In the IBM PC / AT, eight interrupt lines were no longer enough and their number was increased to 15. In the first models, cascading of two i8259 microcircuits was used for this. It was carried out by connecting the output of the second controller to the IRQ2 input of the first.
The following is important to understand here. Interrupt lines IRQ8 - IRQ15 (that is, the inputs of the second controller) have a priority lower than IRQ1, but higher than IRQ3.
In direct access mode (DMA, Direct Memory Access), the peripheral device is connected to the RAM directly, and not through the internal registers of the microprocessor. Such data transmission is most effective in situations where a high exchange rate is required for a large amount of information. The corresponding signals are used to initiate the direct access process on the system bus.
In computers compatible with IBM PC and PC / XT, one 4-channel DMA i8237 chip is used to provide direct memory access, channel 0 of which is intended for dynamic memory regeneration. Channels 2 and 3 are used to control high-speed data transfer between floppy drives, hard drive and RAM, respectively.
IBM PC / AT-compatible computers have 7 DMA channels. In the first computers, this was achieved by cascading two i8237 microcircuits, as in the case of interrupt controllers.
Computer memory
All personal computers use three types of memory: operational, permanent, and external (various storage devices). The random access memory is intended for storing variable information, since it allows its contents to be changed during the corresponding operations by the microprocessor. Since at any moment of time access can be carried out to an arbitrarily selected cell, this type of memory is also called random access memory - RAM (Random Access Memory).
All programs, including games, are executed in RAM. Permanent memory usually contains information that should not change over time. Permanent memory has its own name - ROM (Read Only Memory), which indicates that it only provides read and storage modes.
Logical memory organization
As you know, used in the IBM PC, the PC / XT microprocessor i8088 through its 20 address buses provides access to only 1 MB of memory space. The first 640 KB of addressable space in IBM PC-compatible computers is usually called conventional memory. The remaining 384 Kbytes are reserved for system use and are called memory in the upper addresses (UMB, Upper Memory Blocks, High DOS Memory or UM Area - UMA). This memory area is reserved for the location of the system ROM BIOS (Read Only Memory Basic Input Output System), for video memory and ROM memory of additional adapters.
Expanded memory
On almost all personal computers, the UMB is rarely full. As a rule, the area for expanding the system ROM BIOS or part of the video memory and areas for additional ROM modules is empty. This is the basis of the EMS (Expanded Memory Specification) specification, first developed by Lotus Development, Intel and Microsoft (therefore sometimes referred to as the LIM-specification). This specification allows the use of memory in excess of the standard 640KB for application programs. The principle of using additional memory is based on switching blocks (pages) of memory. In the UMB area, between the video buffer and the system RGM BIOS, an unoccupied 64 KB "window" is allocated, which is divided into pages. Software and hardware allow mapping any segment of additional memory to any of the allocated "window (TM) pages. Although the microprocessor always accesses the data stored in the" window "(address below 1 MB), the addresses of this data may be offset in the additional memory relative to "windows" for several megabytes (see Fig. 1).
It should not be forgotten that although IBM PCs are compatible computers and are the most popular, occupying the lion's share of the market, there exist and are dynamically developing cosplayers that do not have x86 processors. In particular, computers that are not compatible with IBM PC - laptops and personal digital assistants (PDAs) with processors developed by Motorola and IBM, Playstation brand game consoles, have a completely different internal architecture and are assembled on chips that are developed specifically for them. Although outwardly, for example, it is almost impossible to distinguish a laptop on an Intel processor from an Apple branded laptop, which uses a Motorola processor.
In addition, the Playstation 3 game console should be mentioned, which appeared in large quantities in the fall of 2007. Its design uses a 9-core Cell processor developed by IBM Corporation. With a modest price and dimensions, its ability to create a virtual world on a monitor or TV screen is much higher than that of the most sophisticated personal computers with x86 processors.
Microprocessor block diagram
The block diagram of the basic model of the microprocessor is shown in Fig. 1.
Figure: 1. Block diagram of the microprocessor
The microprocessor can be conventionally divided into two parts: the Execution Unit (EU) and the Bus Interface Unit (BIU).
The executive block contains: arithmetic block and registers. The arithmetic unit includes an arithmetic logic unit, auxiliary registers for storing operands, and a flag register.
Eight registers of the MP execution unit (AX, BX, CX, DX, SP, BP, SI, DI), having a length equal to the machine word, are divided into two groups. The first group consists of general purpose registers: AX, BX, CX and DX, each of which is a register pair composed of two registers 0.5 machine word long.
The accumulator, or register AX, consists of registers AH and AL. Base Register BX consists of BH and BL registers. The CX Count Register includes the CH and CL registers. The Data Register DX contains the DH and DL registers. Each of the short registers can be used alone or as part of a register pair. Conventional names (accumulator, base register, counter, data register) do not restrict the use of these registers - these names speak about their most frequent use or about the peculiarities of using one or another register in a particular command.
The second group is made up of SP, BP, SI and DI address registers (in older models the number of address registers is increased). These registers are actively used for their functional purpose and for other purposes they are not recommended. Their main purpose is to store numeric values, which are realized when forming addresses of operands.
The device for interfacing with the system backbone contains control registers, a command pipeline, ALU commands, a control device for the MP executive unit and a memory interface (connecting the internal backbone of the MP with the computer system backbone).
BIU control registers: CS (command segment pointer), DS data segment pointer), SS (stack segment pointer), ES (additional segment pointer), etc. are used to determine the physical addresses of the OP - operands and commands. The IP register (Instruction Pointer) is the address indicator of the command that will be selected into the command pipeline as the next command (in Russian literature, such a device is called an command counter). The pipeline of MP commands stores several commands, which allows, when executing linear programs, to combine the preparation of the next command with the execution of the current one.
The flags register also belongs to the control registers of the MP, each bit of which has a strictly defined purpose. Usually, the bits of the flags register are set by hardware when performing the next operation, depending on the result obtained in the ALU. In this case, such properties of the result obtained as a zero result, negative number, overflow of the ALU bit grid, etc. are recorded. But some bits of the flags register can be set by special commands. Some bits have a purely service purpose (for example, they store a bit dropped from the ALU during the shift, or are reserved (i.e., not used).
IBM is a large corporation today engaged in the development and supply of software and other high-tech products. Over its more than 100-year history, it has brought many new products to the market. It was thanks to IBM that computers appeared in almost every home.
Start
IBM appeared at a time when the personal computer was difficult to imagine. In 1896 it was founded by the name of the company then received TMC and was engaged in the production of calculating machines, which were sold mainly to government organizations.
At the beginning of its history, the company received a huge order from the Ministry of Statistics, and thanks to this, it immediately took a significant position in the market. However, due to health problems, the founder and owner still had to sell the company to the famous financial genius Charles Flint. The millionaire paid a whopping $ 2.3 billion for the company at the time.
The emergence of IBM
After taking control of TMC, Charles Flint immediately began merging with other assets such as ITRC and CSC. As a result, the prototype of the modern "blue giant" was created - the CTR corporation.
The formed company started producing a wide variety of equipment corresponding to that time. Among them were scales, time tracking systems and, most importantly, punch card equipment. It was the latter that played a big role in the company's transition to the production of computers.
The IBM brand first appeared in the Canadian market in 1917. This is how the company decided to show that it had become an international corporation. After the sufficient success of the new name, the American division also changed its name to IBM in 1924.
For the next several years, the company actively continues to improve its own technologies, creating a new type of punched cards called the IBM Card. Also, the corporation again gains access to large government orders, which allows it to practically not carry out reductions even during the Great Depression.
IBM and World War II
The IBM company actively cooperated with the fascist regime in Germany. In 1933, after the corporation even launched its own plant in Germany. However, the company, like most other American firms, only announces the sale of cars and does not consider this to be support for the regime.
On the territory of the United States during the war years, the corporation was mainly engaged in supplying the front on a government order. She was engaged in the production of sights for throwing bombs, rifles, engine parts and other items necessary for the military. At the same time, the head of the corporation then set a nominal profit of 1%, which was sent not to shareholders, but to the needs of aid funds.
The beginning of the era of computers
The first IBM computer was released in 1941-1943 and was named "Mark-I". The car weighed an impressive 4.5 tons. After testing, its official launch took place only in 1944, after being transferred to Harvard University.
In fact, "Mark-I" was a very much improved adding machine, but due to its automation and programmability, it is the first electronic computer.

The collaboration between the international corporation and the main developer was extremely unsuccessful. IBM computers continued to develop without him. As a result, in 1952, the company released the first tube computer.
In the late 1950s, the first transistor-based IBM computers were created. It was thanks to this improvement that it was possible to increase the reliability of computers and create on their basis the first defense system against missile strike. At the same time, the first mass-produced IBM computer with a hard disk appeared. True, the drive, shown to the Soviet leader in 1958, occupied two large cabinets and was 5 MB in size. IBM set prices for it, too, rather big. The first hard drive prototype cost about $ 50,000 at the prices of the time. But that was only the beginning.
First appearance of the IBM System
In 1964, new IBM computers were introduced. They have changed significantly and set the standard for many years to come. The family was named IBM System / 360. These were the first machines that allowed you to gradually increase computing power by changing the model without changing the software. It was in these mainframes that microcode technology was first introduced.

The computers created by IBM received a very successful architecture that became the de facto standard for many years. And today the System Z series, which is a logical continuation of the System / 360 line, is very actively used.
First PC
IBM did not see personal computers as a promising market. However, in 1976, the first desktop computer of the IBM 5100 series was introduced. It was intended more for engineers and was not suitable for office work or personal use.

The first mass personal computer "blue giant" presented only in 1981. In fact, the company did not really hope for his success. That is why most of its components were purchased from other companies. The new computer was included in the IBM 5150 family and received the name PC.
The popularity of the IBM PC
A new processor from Intel demanded and which was very successfully proposed by a young company founded by Bill Gates.
The biggest factor that made the PC popular was its open architecture. For the first time, the corporation abandoned long-term principles and did not license the components or BIOS used. This allowed many third-party firms to quickly build "clones" based on the published specifications.

The open architecture provided other advantages, such as the ability to repair and self-upgrade computers. In the future, this gave rise to the development of personal computers.
However, IBM itself practically did not hit the home computer market. The original IBM PC was quite expensive. In addition to this basic kit, it was required to purchase a floppy disk controller and the drives themselves. The competitors looked more promising against this background.
Nevertheless, the company tried to launch a number of models for home users as well. One of them, called the IBM PCjr, was ranked among the 25 worst computing devices. But the production of this model was quickly discontinued.
In the business segment, IBM traditionally felt excellent, including in the personal computer market. This was achieved by high brand awareness and thoughtful marketing. Success has resulted in the IBM PC / XT and IBM PC / AT.
First laptop
Despite the rather bad initial attitude towards personal computers, the giant was forced to think. First of all, this was influenced by the overwhelming success of the IBM PC. By the way, the six-month sales target for the first personal computer was completed in less than 30 days.

The IBM Convertible went on sale in early 1986 and, despite its rather modest characteristics, was produced until 1991. Among the innovations, this device was the first PC from the giant corporation equipped with a 3.5 ”floppy drive.
90s
By the 90s, the giant corporation was rapidly losing its position in the personal computer market, but for a long time it continued to produce new models of stationary and mobile computers.
First, in 1990, IBM introduced a new computer to the market that had a completely new architecture and was incompatible in hardware and software with previous generations.

The new computer received a modern data bus, and many of the components were changed in such a way that it was almost impossible to reproduce them by small companies from Asia for technological and licensing reasons. But the architecture was a failure. Although some of the innovations applied to these PCs have been around for a long time, for example, PS / 2 mouse and keyboard connectors are sometimes used even in modern machines.
At the same time, the company produced a series of computers compatible with the previous generation called PS / 1, and later - Aptiva.
These were the last personal computers produced by the blue giant. By 1996-1997, the production of cars for this market segment was phased out.
2000s and the final exit from the PC market
IBM, despite the termination of the development and production of desktop PCs, continued to produce and quite successfully sell on the market laptops. Some users even continued to regard IBM computers as benchmarks.
In 2004, the corporation made a difficult decision, as a result of which the entire business of manufacturing personal computers and laptops was sold to the Chinese company Lenovo. The company itself has focused on a much more interesting server and support market for the giant. Later, IBM sold other divisions that linked it to the production of PCs, for example, the division that was engaged in the production of hard drives came under the control of HITACHI.
The long history of IBM has allowed the company to accumulate vast experience in the creation of computer hardware and software. Today, even despite the withdrawal from the PC market, the company has a fairly strong influence on the development of the entire industry.
Computer compatibility
| Parameter name | Value |
| Topic of the article: | Computer compatibility |
| Category (thematic category) | Technology |
Classification of computers.
E generation (mid 40s - mid 50s).
Computer generations
The division of computer technology into generations is a very conditional, non-strict classification of computer systems according to the degree of development of hardware and software, as well as ways of communicating with a computer
The idea of \u200b\u200bdividing machines into generations is due to the fact that during the short history of its development, computer technology has undergone a great evolution, both in the sense of the element base ( lamps, transistors, microcircuits and others), and in the sense of changing its structure, the emergence of new opportunities, expanding the scope and nature of use.
The development of computers has gone through several stages associated with generations of computers. Each generation of computers is distinguished by its element base, architecture, scope, interfaces, and software for solving problems.
Element base - vacuum tubes, resistors, capacitors; the architecture is the simplest; application - scientific calculations; methods of communication - direct manual control of computer devices, programming in the language of the machine.
1945-1950 Prominent scientist J. von Neumann (USA) developed the concept and design of the EDVAC computer. The main provisions of the von Neumann concept are still used today.
1946 ᴦ. American engineers D. Eckert and D. Moachley at the University of Pennsylvania built the first operating computer ENtAC.
1947-1950 A group of engineers led by Acad. S. A. Lebedeva develops and puts into operation the first small electronic calculating machine (MESM) in the USSR.
1948 ᴦ. A group of American physicists have constructed a transistor - the main element of the 2nd generation computer.
1949 ᴦ. In England, under the leadership of M. Wilkes, the first computer with the stored program EDSAK was created.
The beginning of the 50s. In several countries, the serial production of 1st generation computers begins, the main element base of which was vacuum tubes. RAMs were built on mercury delay lines, CRTs, and later on ferrite rings.
In the USSR, after MESM, the following were produced: in Moscow, a large electronic calculating machine BESM-1, BESM-2 (S.A. Lebedev) and the fastest computer in Europe at that time, M-10 (L. Lebedev and Yu. A. Bazilevsky), Penza -ʼʼUralʼʼ (V.I.Rameev), in Minsk-ʼʼMinsk-1, ʼʼMinsk-14ʼʼ (V.V. Przhislovsky), in Kiev - Kievʼʼ (V.M. Glushkov), in Yerevan - Rozdanʼʼ (F.T. Sargsyan).
The introduction of the first computers could not take place without the advanced development of numerical methods for solving problems and the basics of programming. This work in the USSR was headed by academicians A.A. Markov, A.N. Kolmogorov, I.V. Kurchatov, M.A. Lavrent'eva, A.A. Dorodnitsyn, M.V. Keldysh.
1942-1953 Soviet scientists A.A. Lyapunov and M.R. Shura-Pura proposed an operator programming method.
1943-1955 A group of mathematicians led by D. Beycus (USA) developed the Fortran algorithmic language.
2nd generation (mid 50s-mid 60s): semiconductor transistors and diodes, resistors, capacitors; more complex architecture; solution of scientific, technical and national economic problems; the use of operating systems; creation of computing systems; collective use; development of algorithmic languages.
1954-1957 The first computer based on the NCR 304 transistor will be created in the USA.
End of the 50s. At the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the algorithmic language LISP has been developed, works on the problems of artificial intelligence in the applied plan - for expert systems).
The beginning of the 60s. Serial production in the USSR of computers of the 2nd generation on transistors: M-220, BESM-3, BESG 4, "Ural-11", "Ural-14", "Ural-16", "Minsk-22", "Minsk-32", "Razdan-2", "Razdan-3" , ʼʼDnipro-1ʼʼ, ʼʼDnepr-3ʼʼ, etc.
1961 ᴦ. Intel (USA) launched the first integrated circuits (ICs).
1966 ᴦ. In the USSR, the world's fastest (for that time) large EVG BESM-6 (S.A. Lsbsdv) was put into operation. The high-speed performance of BESM-6 was determined for the first time by the multiprogrammed operation mode and the pipeline procedure for data processing, which are used in almost all modern computers.
3rd generation (mid 60s - mid 70s) integrated circuits; the architecture is associated with multiprocessor, multicomputer and multichannel complexes; solution of a wide range of tasks of automation of control, design and planning; efficient operating systems, applications and programming languages; the appearance of the first computer networks.
1965 ᴦ. In the USA, the production of the 3rd generation computers of the 360 \u200b\u200bseries on integrated circuits has begun.
1966 ᴦ. The algorithmic language COBOL (USA) has been developed for processing commercial information.
1986 ᴦ. DEC (USA) has developed a mini-computer of the PDP family with a wide range of applications: scientific research, process control, processing of experimental data in real time, automation of engineering, economic and management work, etc.
The beginning of the 70s. In the USSR, together with specialists from the People's Republic of Belarus, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, and the GDR, third-generation computers of the unified system (ES computers) have been developed and are being produced in the required quantity. These computers, compatible with the IBM 360, served as the basis for organizing shared computing centers and automated control systems in large organizations and enterprises.
1971 ᴦ. Intel (USA) has released a microprocessor based on IC technology.
1971 ᴦ. The Office of Advanced Study of the US Department of Defense announced the deployment of the first part of the global information and computing network ARPANET. In 1982 ᴦ. ARPANET was integrated with other networks and this community of networks became known as the Internet.
70s - early 80s. In the USA, England and the USSR supercomputers come into operation: ILLIAC-IV, STATAN-100, Sgau-1 (2, 3, MX), Cyber-205, DAP, Phenix, Connection machine, Elbrus.
1973-1976. Experts from the USSR, Bulgaria, Hungary, Poland, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Mongolia and Cuba have developed a series of mini-computers compatible with PDP (USA).
4th generation (mid 70s - 2000 ᴦ.): large integrated circuits; complex architecture; solving various problems in all areas of human activity; multitasking and multiuser operating systems; ʼʼPersonal type manipulators; speech input and output devices; multimedia tools; effective applications and languages \u200b\u200bthat support artificial intelligence; development of the infrastructure of computer networks.
1977 ᴦ. In the United States, young entrepreneurs S. Jobson and S. Voznyak organized a firm to manufacture inexpensive PCs designed for a wide range of users. These PCs, called APPLE ("Apple"), served as the basis for the widespread distribution of PCs around the world.
1979-1980. Japanese specialists have developed and launched the first electronic translation dictionaries.
1981 ᴦ. A group of leading experts from several electronic firms in Japan announced the creation of a 5th generation computer ("Japanese challenge to the world") in the 90s.
1982 ᴦ. The company IBM (USA), which occupied a leading position in the production of mainframe computers, began production of the IBM PC. Many firms in the world started out with IBM - joint PCs.
Mid 80s. A group of scientists led by K. Sagan (USA) and V.V. Aleksandrova (USSR) developed mathematical models of the consequences of a "nuclear winter" and a "nuclear night". These conclusions have played a huge role in shaping the policy of the countries that hold atomic weapons.
1988 ᴦ. In the USSR, the mass production of school PCs ("Corvette", UKNTs, "Nemiga", etc.) and household PCs (BK 0010, "Partner", "Vector", "Byte", etc.) has begun.
Today, a large number of electronic firms in the world produce various classes of computers from household to supercomputers in stationary and portable versions. The number of computers in the world today is approximately: 2.5 ‣‣‣ 10 8 PCs; mini-computer-10 6 pcs .; manframes - 2 * 10 4 pcs. supercomputer - 100 pcs.
5th generation (early XXI century). Now it is difficult to predict what the 6th generation computers will look like, but it is possible to indicate the general trends in the development of computer technology and their impact on society.
Development is also on the way "intellectualization" computers, removing the barrier between man and computer. Computers will be able to perceive information from handwritten or printed text͵ from forms, from a human voice, recognize the user by voice, translate from one language to another.
Sixth generation computers will make a quantum leap from processing data to processing knowledge.
Creation of a family of computers with fundamentally new capabilities that will provide:
effective use of all available resources of the country: material, energy, human information;
improvement of affairs in areas with low labor productivity;
inclusion of the country in international cooperation;
improving the use of the intellectual potential of society;
increasing the competitiveness of goods in the international market;
increasing the productivity of the population;
promoting a high level of education.
The elemental base of the computer is supposed to:
reaching the maximum packing density of elements in silicon-based VLSI;
production of VLSI based on gallium arsenide;
use of cryogenic technology based on the Josephson effect.
Computer architectures are being improved in the following areas:
· Creation of a computer system of various capacities, balanced in architecture, which will allow the user to quickly, simply and efficiently use the huge potential of such a system;
· Development of single-processor computers with command control, on a new high-speed element base; these directions are developed by those companies that want to maintain software compatibility of new PCs with existing ones;
· Development of computers based on several fast processors with command control, some of which are universal, and the other part - pipelined or parallel with a small number of processing elements;
· Development of high-performance multiprocessor computers with pipeline, parallel or matrix processing of information.
In addition to the well-known methods of information processing, computers are focused on pattern recognition and processing structured knowledge and making intelligent decisions.
Improving intelligent interfaces:
hardware and software for input / output of various types of information;
communication in a problem-oriented natural spoken language;
the use of text documents, both printed and handwritten, and images;
all the development of well-known and new algorithmic programming languages;
application of artificial intelligence languages: Lisp Prolog, PS, FRL, VALID, OCCAM, etc.
The implementation of programs for creating computers of the 5th generation will make it possible in a number of countries to build the so-called information society.
There are various classifications of computer technology:
by stages of development (by generations);
on architecture;
by performance;
by operating conditions;
by the number of processors;
by consumer properties, etc.
There are no clear boundaries between classes of computers... As the structures and technologies of production improve, new classes of computers appear, the boundaries of existing classes change significantly.
According to the operating conditions, computers are divided into two types:
office (universal);
special.
Office is designed to solve a wide class of tasks under normal operating conditions.
Special computers are used to solve a narrower class of tasks or even one task that requires multiple solutions, and operate under special operating conditions.
The machine resources of special computers are often limited. Moreover, their narrow orientation makes it possible to implement a given class of tasks most efficiently.
Special computers control technological installations, work in operating rooms or ambulances, on missiles, airplanes and helicopters, near high-voltage transmission lines or in the area of \u200b\u200boperation of radars, radio transmitters, in unheated rooms, under water at a depth, in dusty, muddy conditions, vibrations, explosive gases, etc. There are many models of such computers. Let's get acquainted with one of them.
Ergotouch computer
The Ergotouch computer is housed in a fully sealed die-cast aluminum case that is easy to open for service.
Computer walls absorb virtually all electromagnetic radiation from both the inside and the outside. The machine is equipped with a touch-sensitive screen.
The computer can be cleaned from a hose, disinfected, decontaminated, degreased without turning off.
The highest reliability allows it to be used as a tool for real-time control and monitoring of technological processes. The computer is easily included in the local network of the enterprise.
An important direction in the creation of industrial computers is the development "operator interface" - control panels, displays, keyboards and pointing devices in all possible designs. The comfort and efficiency of the operators' work directly depends on these products.
By performance and nature of use, computers can be roughly divided into:
microcomputers, incl. - personal computers;
minicomputers;
mainframes (general purpose computers);
supercomputers.
Microcomputers are computers in which the central processing unit is designed as a microprocessor.
Advanced microcomputer models have multiple microprocessors. The performance of a computer is determined not only by the characteristics of the microprocessor used, but also by the capacity of the RAM, types of peripheral devices, the quality of design solutions, etc.
Microcomputers are tools for solving a variety of complex tasks. Their microprocessors increase power every year, and their peripherals increase efficiency. High-speed performance - about 1 - 10 million operations per second.
A kind of microcomputer is a microcontroller.
Posted on ref.rf
It is a microprocessor-based specialized device built into a control system or production line.
Modern computer hardware is classified as follows:
· Personal computers;
· Corporate computers;
· Supercomputers.
Personal computers (PCs) are general purpose microcomputers designed for one user and operated by one person.
The class of personal computers includes various machines - from cheap home and gaming machines with small RAM, with program memory on cassette tape and a conventional TV set as a display, to ultra-complex machines with a powerful processor, hard drive with a capacity of tens of Gigabytes, with high-definition color graphics devices, multimedia and other additional devices.
Personal computers are computational systems, all resources of which are completely aimed at supporting the activities of one employee.
The most famous are computers of the IBM PC and Macintosh families. These are two different directions of PC development, incompatible with each other in terms of hardware and software. It just so happens that computers of the Macintosh family are very easy to use, have wide graphic capabilities and are widely used among professional artists, designers, in publishing and in education.
In the family of IBM-compatible PCs, there are also several types of computers that differ significantly from each other in their characteristics and appearance, and, nevertheless, they are all personal computers. These are, first of all, desktop and laptop PCs, which, despite significant external differences, have approximately the same characteristics and capabilities.
Laptop PCs - expensive products, but they are compact and transportable. Essentially different from desktop and laptop - pocket computers - so-called organizers, or "portable secretaries". These PC notebooks do not have any peripherals or keyboard, the choice of commands is carried out directly on the miniature screen using a pointer - stylus.
Laptop computers usually needed by heads of enterprises, managers, scientists, journalists who have to work outside the office - at home, at presentations or during business trips.
The main types of laptop computers:
Laptop (knee pad, from lap - knee and top - on top). It is similar in size to a regular portfolio. In terms of the main characteristics (speed, memory), it roughly corresponds to a desktop PC. Now computers of this type are giving way to even smaller ones.
Notebook (notepad, notebook). It is closer in size to a large format book. It has a weight of about 3 kg. Fits in a briefcase-diplomat. It is important to note that for communication with the office, it is usually equipped with modem... Laptops often provide cD-ROM drives.
Many modern laptops include interchangeable blocks with standard connectors... These modules are designed for very different functions. The same slot can be used to insert a CD drive, magnetic disk drive, spare battery, or removable hard drive as needed.
Posted on ref.rf
Laptop resistant to power outages... Even if it receives energy from a conventional power grid, in the event of any failure, it instantly switches to battery power.
Personal digital assistant
Palmtop (handheld) - the smallest modern personal computers. Fits in the palm of your hand. The magnetic disks in them are replaced by non-volatile electronic memory. There are no storage devices on disks either - information exchange with ordinary computers goes through communication lines. If Palmtop is supplemented with a set of business programs recorded in its permanent memory, it will turn out personal digital assistant (Personal Digital Assistant).
Corporate computers (sometimes called minicomputers or main fram) are computing systems that ensure the joint activities of many employees within one organization, one project ͵ one sphere of information activity using the same information and computing resources. These are multi-user systems with a central unit with a large computing power and significant information resources, to which a large number of workplaces with minimal equipment (video terminal, keyboard, mouse positioning device and, possibly, a printing device) are connected. In principle, personal computers are also used as workstations connected to the central unit of a corporate computer. The area of \u200b\u200bapplication of corporate computers is the implementation of information technologies for ensuring management activities in large financial and industrial organizations, government agencies, the creation of information systems serving a large number of users within one function (exchange and banking systems, booking and selling tickets, etc.) ).
Features of corporate computers:
Exceptional reliability;
High performance;
Large I / O bandwidth.
The cost of such computers is millions of dollars. The demand is high.
Advantages - Centralized storage and processing of data is less expensive than maintaining distributed data processing systems consisting of hundreds or thousands of PCs.
Supercomputers are computing systems with extreme characteristics of computing power and information resources. Οʜᴎ are used in military and space activities, in basic scientific research, global weather forecasting, military industry, geology, etc. For example, forecasting the weather or simulating a nuclear explosion.
Supercomputer architecture is based on ideas parallelism and pipelining computation.
In these machines, in parallel, that is, simultaneously, many similar operations are performed (this is usually called multiprocessing). Τᴀᴋᴎᴍ ᴏϬᴩᴀᴈᴏᴍ, ultra-fast performance is ensured not for all tasks, but only for tasks, amenable to parallelization.
A distinctive feature of supercomputers are vector processors equipped with equipment for parallel execution of operations with multidimensional digital objects - vectors and matrices. They have built-in vector registers and a parallel pipelined processing engine. If on a regular processor the programmer performs operations on each component of a vector in turn, then on a vector processor he immediately issues vector commands.
Vector hardware is very expensive, in part because it requires a lot of ultra-fast memory for vector registers.
The most common supercomputers are massively parallel computer systems. Οʜᴎ have tens of thousands of processors interacting through a complex, hierarchically organized memory system.
As an example, consider the characteristics intel Pentium Pro 200 multipurpose mass-parallel supercomputer... This computer contains 9,200 200 MHz Pentium Pro processors for a total (theoretical) performance 1.34 Teraflops (1 Teraflop is equal to 10 12 floating point operations per second), has 537 GB of memory and disks with a capacity of 2.25 Terabytes. The system weighs 44 tons (air conditioners for it - as much as 300 tons) and consumes 850 kW.
Super-computers are used to solve complex and large scientific problems (meteorology, hydrodynamics, etc.), in control, intelligence, as centralized storage of information, etc.
Element base - microcircuits of ultra-high degree of integration.
The cost is tens of millions of dollars.
Purpose - solving those tasks for which PC performance is not enough;
Providing centralized storage and processing of data.
Features: the ability to connect dozens and hundreds of terminals or PCs for user work; availability of special hardware for three-dimensional modeling and animation, in this regard, it is on them that a large number of films are created.
Mainframes are designed to solve a wide class of scientific and technical problems and are complex and expensive machines. It is advisable to use them in large systems with at least 200 - 300 jobs.
Centralized processing on a mainframe is about 5 to 6 times less expensive than distributed processing in a client-server approach.
Famous mainframe S / 390 from IBM is usually equipped with at least three processors. The maximum amount of operational storage reaches 342 Terabytes.
The performance of its processors, bandwidth of channels, and the amount of operational storage allow to increase the number of workplaces in the range from 20 to 200,000 by simply adding processor boards, RAM modules and disk drives.
Dozens of mainframes can work together under a single operating system to complete a single task.
This classification is rather arbitrary, since the intensive development of technologies for the production of electronic components, significant progress in the improvement of computers and their most important constituent elements lead to a blurring of the boundaries between the indicated classes of computer technology.
At the same time, the above classification takes into account only the autonomous use of computer technology. Today, the prevailing trend is to integrate them into computer networks, which makes it possible to integrate information and computing resources for the most efficient implementation of information technologies.
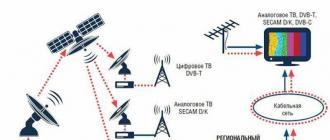
ІВМ РС - compatible computers - about 90% of all modern computers.
Compatibility is:
Software Compatibility - All IBM PC software will run on all IBM PC compatible computers.
Hardware compatibility - most devices (except five or ten years old) for computers ІВМ РС and newer versions of ІВМ РС ХТ, ІВМ РС АТ and others are suitable for ІВМ РС - compatible computers.
Advantages of ІВМ РС - compatible computers:
1) full compatibility has caused the emergence of hundreds of thousands of programs for all areas of human activity;
2) the openness of the market of ІВМ РС - compatible computers has caused intense competition among manufacturers of computers and their components, which ensured high reliability, relatively low price and the fastest possible introduction of technical innovations;
3) modular design and integration of ІВМ РС components - compatible computers providing compactness, high reliability, ease of repair ͵ the possibility of easy upgrading and increasing the computer's power (more powerful processor or more capacious HDD).
The wide capabilities of the ІВМ РС - compatible computers allow using them in various industries and for solving various problems.
Questions for self-control
1. On what grounds can computers be divided into classes and types?
7. How has the element base of computers evolved from generation to generation?
8. When did microcomputers become available for general home use?
9. Can you connect the concepts of "apple", "garage" and "computer"?
10. On the basis of what technical elements were the computers of the first generation created?
11. What is the main problem for developers and users raised by the experience of operating first generation computers?
12. What element base is typical for the second generation of computers?
13. What is the function of the operating system while the computer is running?
14. On what element base are the third generation machines designed?
15. What generations of computers are characterized by widespread use of integrated circuits?
16. What speed is typical for the fourth generation machines?
17. What is meant by "intelligence" of computers?
18. What task should the "smart interface" solve in the fifth generation machines?
19. What features should industrial computers have?
20. What is a computer operator interface?
21. What are the main features that distinguish mainframes from other modern computers?
22. How many users are mainframes for?
23. What are the ideas behind supercomputer architecture?
24. On what types of tasks are the capabilities of supercomputers maximized?
Topic 5 ... PC AS A BASIS OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES
1. PC architecture
2. PC structure
3. PC functional characteristics
Computer compatibility - concept and types. Classification and features of the category "Computer compatibility" 2017, 2018.