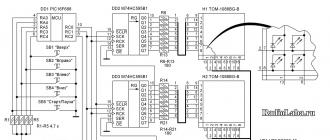
Storing keys on hardware keys (Kaztoken, eToken) increases the security of storing and using the organization’s digital signature:
- It is more difficult to secretly copy stored digital signatures from these devices than from a PC
- If the token is lost, the use of the digital signature is password protected
To use eToken devices, an organization must have valid EDS keys.
In the article:
Installing EDS keys on the eToken device (video lesson)
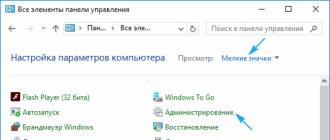
Installing an electronic digital signature on eToken media has some nuances (tested as of September 2015).
When using the eToken device for the first time, before writing keys to it, it is necessary to change the default password (1234567890) to a more complex one, only after which is it possible to write EDS keys to the device. Therefore, if you simply insert a new eToken device into your PC and try to install certificates through the NCA website, after the installation is complete, you will receive a certificate installation error message.
Therefore, you will have to download the control program to the eToken device, reinitialize the device, unchecking the box to require a password change before use.
And since the NCA website can write keys to a token only if the password for eToken is 1234567890 (with other passwords, again after installation we get a key writing error), in the control program we force the password to be 1234567890, having first unchecked the box requiring a complex password.
After the completed operations, you can successfully write the digital signature keys onto the eToken media.
Cleaning eToken media (video tutorial)
Fixing the error More than one RSA key detected
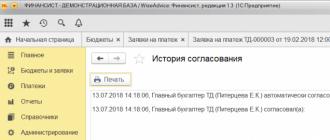
If you do not clear the eToken media before installing new keys, the installation through the NCA website will be successful, but when you try to log into the Treasury Client IS portal, you will encounter the following error: More than one RSA key detected:
The solution to this problem is to download the InfoToken() utility and use it to format the device. After which you will have to re-write the keys to the token.
Advice from our reader: you can try removing unnecessary keys using TumarCSP.
From the author:
If the problem is solved, one of the ways to say “Thank you” to the author is indicated - .
If the problem could not be resolved or additional questions arise, you can ask them on our website, in our group.
Or, use our “” service and entrust the problem to a specialist.
The main task of enterprise management is to ensure solvency, liquidity and financial potential. Control over budget execution is an important component of the budget process. Treasury budget execution ensures control of the operational and strategic development plans of the enterprise.
Treasury automation allows you to quickly manage the financial flows of an enterprise and control budget execution. A modern treasury accounting system should be aimed at up-to-date identification of emerging imbalances and internal reserves, which allows timely development of measures to eliminate cash gaps and increase solvency. The effectiveness of the functioning of the enterprise as a whole depends on the effectiveness of treasury control. Treasury automation makes it easy to handle these tasks.
A methodology for monitoring budget execution should be developed before the start of its execution and may include procedures and a set of reporting forms for comparison with plan indicators:
1. Acceptance of requests for payment within the approved budget
For example, the head of a business area accepts all requests for payment in his financial center and is responsible for implementing the budget, and a financial service employee monitors the compliance of requests with budget limits and the implementation of regulatory procedures of the payment system. At the same time, control over compliance with the budget can be carried out automatically - this procedure can be provided by an automated treasury system.

Figure 1. Monitoring expense requests for compliance with the budget using the example of the software product “WA: Financier: Cash Management”.
2. Formation of a payment calendar for the planned period
A payment calendar is a financial planning tool/document that makes it possible to manage the receipt and expenditure of funds in a company on a daily basis. The composition of the payment calendar may be different (this depends on the specifics of the business and the preferences of responsible employees). At the same time, the payment calendar must necessarily include data on receipts and payments, as well as planned cash balances, usually broken down by day and source (or place of storage of funds).
3. Coordination of the payment register
By the register of payments we mean a list of justified applications that have been accepted and monitored for compliance with the budget, and are subject to execution on a certain date. Coordination of the payment register by responsible persons is also more convenient and faster using automated systems.
4. Adjustment of the operational plan
It often becomes necessary to adjust some of the payments included in the final and approved version of the payment register. This kind of adjustment may even be required several times during one operational period. This task is also easier to solve when using automated treasury systems.
5. Plan-actual analysis of cash flows
Plan-fact analysis allows you to monitor deviations in the implementation of the plan in absolute and relative terms (in percentage) and make appropriate management decisions.
6. Cash flow report
The cash flow statement summarizes information about the company's cash inflows and outflows. It is one of the main forms of financial reporting.
7. Cash flow analysis
Cash flow analysis can be carried out by calculating various indicators, for example, cash turnover ratios, calculating turnover periods, etc.
8. Analysis of the ratio of cash reserves taking into account the budget
In this report, you can compare the amount of actual and reserved payments (accepted and included in the payment calendar, register) with the amount of payments planned in the budget.
This list of procedures can be expanded or reduced, depending on the needs of the company’s financial management. For example, a company may not use a payment register, but make payments directly based on the payment calendar.
Treasury Information Systems
Treasury automation is of great importance for treasury budget execution, as a tool for monitoring and comparing indicators in various combinations and sections.
The most convenient way to calculate and control financial flows is using the software product “WA: Financier” (Cash Management subsystem). Treasury information systems already include a set of necessary techniques and procedures for monitoring cash flows. The reliability of information obtained on the basis of “WA: Financier Cash Management” allows you to avoid technical errors and, as a result, distorted reports and decisions.
WA: The UDS financier consists of the following subsystems:
- Planning – formation, approval and adjustment of cash flow budgets
- Operational planning – formation, control and approval of documents for operational planning of cash flows
- Accounting for payment schedules under contracts.
- Interaction with client-bank systems, reflection of actual data in accounting systems.
- Reporting
The program increases transparency and availability of information, both at the level of company managers and at the level of senior management. The blocks of the software product "WA: Financier" - Cash Management and Budgeting - calculate alternative options taking into account the strategic and tactical plans of the company, and allow you to adapt the enterprise model to changes in the shortest possible time. Automation of treasury and budgeting provides stakeholders with operational information for decision-making in conditions of uncertainty.
Thus, treasury budget execution is most optimally carried out on the basis of a specialized software product designed to automate treasury/cash management.
Information system "Treasury-client" (hereinafter referred to as IS KK, System) is an information system of the Treasury Committee of the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Kazakhstan and its territorial divisions (hereinafter referred to as the Treasury), providing automation of functions for receiving and processing documents .
IS QC is a set of functional qualities that ensure effective and efficient management of the Government's financial resources and control over budget execution. The system covers all levels of the Treasury, and ensures functional interaction with government organizations, the National Bank, payment systems, ministries, akimats, budget program administrators and government agencies.
Clients of IS QC are government agencies, administrators of budget programs, and entities of the quasi-public sector.
Target
Increasing the efficiency of interaction between the Treasury and government agencies served by providing a modern, integrated and highly efficient information environment. It is a component of the Treasury Information Integrated System.
Tasks
- ensures effective and efficient management of the Government's financial resources and control over budget execution;
- increasing the speed of service to government agencies;
- effective management of public finances;
- monitoring the status of electronic documents submitted by government agencies to the Treasury;
System advantages
Connected to the CC IS 12 856 government agencies, including 315 quasi-public sector entities. 35 134 active users carry out operations in real time in the Treasury information system, performing procedures for crediting and spending state budget funds.
Data: Number of processed (paid) documents through the “Treasury - Client” IS system as of 01/01/2017:
29 184 110
accounts payable;
2 146 141
applications for registration of civil transactions ;
658 375
plans and certificates of changes;
152 071
payment orders of quasi-public sector entities;
235 806
payment orders of Territorial Tax Authorities, etc.
Conducted daily on average 30 thousand payments from the Kazakhstan Center for Interbank Settlements and on average 40 thousand budget revenues. At the end of the month, these indicators double, because during this period the main payments by government agencies (salaries, benefits, taxes, etc.) are made.
Since the main task of IS QC is the timely execution of financial transactions, even in conditions of increasing load on system performance, IS “Treasury - Client” provides the opportunity to collaborate in a unified information environment of the Treasury Committee. In self-service mode, government agencies fill out electronic document forms. After verification, approval and approval, these documents automatically become available in the integrated Treasury information system.
Thanks to the “Treasury - Client” IS:
- the speed of servicing government institutions has increased;
- administrative barriers have decreased;
- the “human factor” is minimized;
- reduced paper consumption
- time and transportation costs for government agencies have also been reduced.
Integration
In order to eliminate the repeated entry of electronic documents in State institutions, integration with the subsystem “Accounting”, “Budget Application” of the IAIS “e-MINFIN” has been implemented.
In 2016, the integration of the “Treasury - Client” Information System with the Automated Integrated Information System “Electronic Public Procurement” (AIIS “EGP”) was put into trial operation.
Integration of AIIS "EGZ" with the Information System "Treasury - Client" made it possible to structure data on each transaction completed within the framework of public procurement and ensure prompt receipt of data on payments under contracts. Thus, significantly expanding the possibilities for analyzing transactions.
Integration with the Information System for the receipt and processing of electronic invoices, and the Information System “Centralized Unified Personal Account (IS CULS of the Tax Committee of the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Kazakhstan)” allows you to quickly accept invoices from the IS ESF and payment orders from the IS CULS for execution in the Treasury.
By providing government agencies with reliable and timely financial information for decision-making, the Treasury Information System is the basis for effective public financial management.
IS "Treasury - Client" will provide control over the implementation of budget procedures at all budget levels and stages of the budget process, including local budgets and executive bodies.
IT infrastructure
- Support for the IT infrastructure of the Federal Treasury of Russia
Import substitution of information systems in the Federal Treasury
Chronicle of informatization
2018
* Deputy Head of the Treasury Alexander Albychev on TAdviser SummIT - about the mega-project of moving government agencies to cloud accounting
Creation of IT infrastructure based on data centers of the Federal Tax Service
In July 2016, the structure of the Federal Tax Service of Russia "Nalog-Service" announced an auction for the creation of a hardware and software complex for the Federal Treasury in a reserve data center located in Gorodets in the Nizhny Novgorod region (RDDC No. 1). More details about the project can be found at the link.
2015: OTR-2000 and Lanit are the largest IT suppliers of the year
Every year, the Federal Treasury spends 7-8 billion rubles on informatization, occupying one of the leading positions among federal government agencies in terms of this indicator.
In September 2015, TAdviser analyzed the purchases of the Federal Treasury in order to determine its largest suppliers of IT products and services. Tenders from 2010-2015 were taken into account, the amount of which exceeds 50 million rubles.
Top 5 suppliers of IT products and services for the Federal Treasury| № | Company | Amount of contracts in rubles. | Number of tenders won | Years of winning tenders | Types of jobs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | OTR-2000 | 6.76 billion | 12 | 2010-2015 | |
| 2 | Lanit (including Onlanta contracts) | 5.25 billion | 21 | 2010-2015 | Development services, support, equipment supply |
| 3 | I-Teco (including Servionics contracts) | 3.59 billion | 6 | 2010-2014 | Development services, support, equipment supply |
| 4 | NKK (Systematics, TopC) | 2.82 billion | 4 | 2011,2013-2014 | Equipment supply |
| 5 | Computerel | 2.79 billion | 7 | 2011-2015 | Delivery of equipment and software, support |
Data: TAdviser analytical center, September 2015
The main IT contractors of the Treasury - OTR and Lanit companies, in addition to supplying ready-made equipment and software, are developing and maintaining the main information system
The Federal Treasury is a special government body created to manage federal budget revenues and expenditures, control the receipt and execution of extra-budgetary funds, manage and service jointly with authorized banks Russia’s internal and external debt, etc.Presidential Decree No. 1556 of December 8, 1992 “On the Federal Treasury” created a unified centralized system of Federal Treasury bodies, including the Main Directorate of the Federal Treasury of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and territorial bodies for the republics of the Russian Federation, territories, regions, autonomous entities, the cities of Moscow and St. Petersburg, other cities (except for cities of regional subordination), districts and districts in cities.
The “Regulations on the Federal Treasury of the Russian Federation” was approved by the Government in April 1993. Since then, payments of federal budget funds began to be made through the Treasury.
The organizational and functional structure of the Federal Treasury of the Russian Federation has three levels:
Main Directorate of the Federal Treasury (GUFK);
regional departments of the Federal Treasury (UFK);
district branches of the Federal Treasury (OFC).
Treasury bodies interact with government bodies of the republics within the Russian Federation, territories, regions, autonomous entities, the cities of Moscow and St. Petersburg in the process of crediting revenues and offsets between budgets, as well as coordinating work to create an information base on the state of the Russian Federation.
The tasks facing the treasury can be fully resolved by creating an automated information system for financial settlements using modern information technologies.
As a result of the creation and implementation of a unified automated system of the Federal Treasury, the following should be achieved:
reducing paperwork and the amount of manual labor when processing information and at the same time increasing the total volume of information processed, its completeness and reliability;
increasing the efficiency of processing information received at various levels of the financial system hierarchy;
standardization of the information base (regulatory, reference and legal information, input and output documents, descriptions of information objects and assignment rules and provision of their details) to ensure unified processing of financial information as a single interconnected system;
increasing the reliability of data on accounting for budgetary funds and effective control over their receipt and use;
in-depth automated analysis of the dynamics of tax receipts and the ability to forecast these dynamics;
increasing the efficiency and completeness of information exchange with external systems - with tax services, banks, financial authorities, customs authorities, etc.;
increasing the efficiency and completeness of obtaining data on budget income and expenses (by type) upon request for any accounting date;
in-depth analytical analysis of the dynamics of budget expenditure and revenue items at any hierarchical levels of the budget execution system;
efficiency of transfer of information on budget revenues and expenditures between different levels of the budget execution hierarchy (methodological and instructional materials - from top to bottom, generalized and analytical information - from bottom to top).
The presence of a unified Treasury AIS allows, on the basis of clearly defined objects of need, to most realistically selectively optimize budget flows, reduce the likelihood of serious problems in financing, and make the budget execution process smoother.
The main purpose of the system is to coordinate and ensure interaction between Federal Treasury bodies of all levels, their operational information support, automation of basic operations, organization of a communication and data transmission system.
The creation of a treasury automated information system is based on the principles of forming a unified information base, protecting data from unauthorized access and the ability to adapt the software package to the conditions of a specific treasury body.
All operations carried out in the treasury are documented.
Since the federal budget consists of revenue and expenditure parts, there are two relatively independent flows of documents on income and budget expenditures.
Treasury authorities control the movement of money through budget accounts and expenditure items of budgets at different levels. The AIS of the Federal Treasury includes three main software packages. 1.
“TREASURE”, which takes into account federal budget revenues and the distribution of regulatory taxes between budgets of different levels. 2.
“SMETA-W”, “SMETA-F”, taking into account expenses from the federal budget and financing of budget recipients organized by the Federal Treasury. 3.
Internal treasury accounting and reporting. In particular, the accounting department of the district treasury branch solves the following sets of tasks: “Personnel”, “Office work”, “Warehouse”, “Accounting for material assets”, “Wages”, “Reporting”, as well as generating reports on the execution of cost estimates for treasury departments .
The system of Russian treasury bodies was created very dynamically. Over the years of development of the treasury system, Federal Treasury bodies were organized in regional structures, and they began to be equipped with household supplies and office equipment, including computer equipment, communications and information transmission. The methodology of the treasury authorities has undergone significant changes in a short period of development and continues to develop dynamically. The set of measures taken during the creation of the system made it possible to bring this structure to a leading position in the field of government institutions and organizations in the financial sector, both in terms of technical equipment and the dynamics of development of methodological and technological support.
The information complex of treasury authorities is capable of not only functionally ensuring, in combination with the banking system, the execution by treasury authorities of the federal budget, but also organizing effective dynamic interaction between financial authorities of different levels and departmental affiliations, as well as the banking and tax systems. The creation of such a complex is based on the technology of centralized and distributed solutions based on the use of high-tech operating systems and database management systems (DBMS) and noise-resistant telecommunication systems protected from unauthorized access. The development and application of such a unified technology with the creation of corporate (departmental) systems on its basis makes it possible to solve the problem of interdepartmental interaction of complex secure information technology systems.
The functions of the Federal Treasury include:
organization, implementation and control over the execution of the federal budget, management of income and expenses of this budget in treasury accounts, in banks based on the principle of a single cash desk;
regulation of financial relations between the federal budget and extra-budgetary funds, financial execution of these funds, control over the receipt and use of extra-budgetary funds;
implementation of short-term forecasting of volumes of government financial resources, as well as operational management of these resources within the limits established for the corresponding period of government spending;
collection, processing and analysis of information on the state of public finances, submission to the highest legislative and executive bodies of reporting on financial transactions of the Government of the Russian Federation on the federal budget, on extra-budgetary funds, as well as on the state of the budget system of the Russian Federation;
management and servicing, together with the Central Bank of the Russian Federation and other authorized banks, of the state internal and external debt of Russia;
development of methodological and instructional materials, procedures for conducting accounting operations on issues within the competence of the treasury, mandatory for public authorities and management, enterprises, institutions and organizations, including organizations managing public funds of state (federal) extra-budgetary funds, etc.
To perform these functions, a complex multi-level system has been created with developed functional and information connections not only between the hierarchical levels of the treasury authorities, but also with the banking payment system, the Federal Tax Service system, the system for the formation and execution of budgets at all levels, recipients of budget funds and taxpayers.
The complexity of the system is aggravated by the fact that it is deployed over large areas, covering a large number of participants from different departments. The flow diagram of information flows of funds and documents when financing enterprises from the federal budget through the system of treasury authorities is shown in Fig. 9.3.
According to the priority of solving problems of the development of the treasury system, two main directions are distinguished: 1)
creation of an automated unified system for accounting for the execution of income and expenses of the federal budget and integration of this system with the payment and settlement system of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation and the information system of the tax service; 2)
creation of an automated unified depository system of the Federal Treasury and its integration with the securities market.
Both areas are associated not only with the creation of the necessary software and hardware in treasury bodies, but also with the improvement of related systems.
Thus, the coordinated development of the interbank payment and settlement system and the information complex of treasury authorities allows, in order to increase the efficiency of execution and accounting, to change the existing scheme for collecting budget revenues and bringing federal budget funds to recipients.
The use of an effective electronic payment system with a single settlement center makes it possible to organize a full cycle of crediting and accounting for budget revenues with completed interbudgetary settlements within one business day. At the same time, accounting for revenue receipts is carried out automatically with a full analytical breakdown by budget classification, territories, taxpayers, etc.
The distribution of regulatory revenues and the transfer of funds to regional budgets is also carried out from a single settlement center using electronic payments, and these operations are included in the full cycle of crediting and accounting for federal budget revenues. This organization makes it possible to increase the efficiency of execution of revenues of the federal budget and budgets of other levels, as well as the efficiency and accuracy of information about funds received by budgets of all levels. Registers for transfer of funds
Operational report, financing report, budget execution report Approved cost estimates, monthly, quarterly and annual reporting
Register, copy ^ Approved cost estimate
payment order expenses
lg Registry,
copy of payment order
Main Directorate of the Federal Treasury
Operational report, financing report, budget execution report
Stewards
1st level
Federal Treasury Department
Approved cost estimates, monthly, quarterly and annual reporting
Copy of the register for transfer
Rice. 9.3. Movement of information flows, funds and documents when financed from the federal budget through the treasury system
The main goal of creating an information complex for the Federal Treasury is to significantly increase the efficiency of federal budget execution. This allows the Federal Treasury authorities to quickly, accurately and effectively solve the entire scope of tasks assigned to the system:
prompt and accurate accounting of federal budget revenues;
interaction between the federal budget, the budget of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local budgets of all levels;
quick and accurate delivery of federal budget funds to final recipients;
current full operational and strict control over the rational and targeted use of budget funds;
prompt and objective analysis of the execution of the federal budget and forecasting the receipt of revenues into the budget and upcoming expenses for any given period;
management and servicing of public internal debt, etc.
Based on the formulation of the main goal of creating automated information technology in treasury bodies, the following requirements are imposed on the treasury information system:
promptly, accurately and reliably solve problems related to accounting for federal budget revenues;
organize interaction between the federal budget, the budget of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local budgets of all levels;
quickly and accurately deliver federal budget funds to final recipients;
ensure current, complete, operational and strict control over the rational and targeted use of budget funds;
provide prompt and objective analysis of the execution of the federal budget and forecasting the receipt of revenues into the budget and upcoming expenses for any given period;
manage and service public internal debt;
comply with the current legislative practice in Russia and the regulatory requirements of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation;
maintain confidential and classified information in accordance with the requirements of the competent authorities;
ensure legal continuity of the primary document and its electronic copy, as well as its safety in
during the entire period of their regulatory existence, determined by instructions and regulations on office work, etc.
Achieving the main goals of building automated information technology for treasury bodies is possible if a number of conditions are met in the process of its creation. 1.
The information system serving the execution of the federal budget should be built on the basis of automated accounting with an equivalent level of detail in setting up charts of accounts. Accounting for the execution of the federal budget should be carried out in an analytical aspect to the full depth of the budget classification, including in the context of the final recipients of budget funds. This principle will make it possible to have in the accounting registers of the information complex a prompt and reliable reflection of the actual state of the federal budget at any level. 2.
The treasury information system must be adapted to work with both traditional banking operations and electronic banking settlement systems and maintain active interaction with information systems for the execution of federal and regional budgets. Such systems related to the complex should be based on full-scale, automated and operational accounting of budget execution and provide for one-time generation of information when processing primary documents, including payment documents in the banking system. 3.
The main budget execution processes must be coordinated and synchronized throughout the operating day, week, month, quarter, and year. 4.
It is necessary to organize a unified technological information communication system for bodies executing budgets at various levels. 5.
Information included in one or another related departmental system during their interaction must be reliable, which requires the use of a unified technology for protecting information from unauthorized access and protecting an electronic signature. 6.
When organizing and implementing automated treasury information technology, it is necessary to use technological and methodological solutions that allow modification of both the entire system or its core, and only individual workstations and individual tasks at workplaces, without affecting the current operation of the rest of the system as a whole, etc. .
Hardware and software treasury system. Based on the listed requirements for treasury AIS and the conditions for building this system, two automated information technology architectures are used: 1)
“terminal” - based on the use of a high-performance central computing complex - a mainframe (mainframe) and a system of localized and remote terminals, including intelligent ones; 2)
“client-server” - based on the organization of collective high-performance work with databases in the local computer networks of the organization.
The creation of information systems in terminal architecture using mainframes4 has significant historical traditions. Such complexes based on high-performance computers have recently been widely used abroad and in Russia.
The advantage of such systems is centralized multi-threaded and multi-tasking processing of all information located in the information system. This allows you to optimize the use of expensive high-performance computing resources of the central machine. When the mainframe operates, each user and each process is allocated a set of information resources that allows them to solve assigned tasks. The user can communicate with the machine both using high-speed input-output devices that are part of a mainframe-based computer complex, and by working on terminals connected to the central machine of the complex.
Mainframe operating systems are distinguished by their stability, security, and efficient use of memory resources, a central processor (one or more), and peripheral input/output devices.
This architecture was initially focused on effectively solving several (or many) different tasks simultaneously in a time-sharing mode, and therefore has developed means of information protection and protection against failures. The design of operating systems to accommodate a large number (up to several thousand) of users determined the creation of developed and high-speed telecommunications tools built into operating systems and mainframe hardware.
The hardware of the system, created for conditions of many years of non-stop operation in intense information processing mode, is highly reliable and fault-tolerant. Software products installed only on the central machine allow modification and replacement to be carried out fairly easily and quickly without harm to system users.
However, in recent years, world practice indicates a significant reorientation of the main consumers of mainframe-based systems to the use of cheaper solutions using new computer technologies. This happens for a number of reasons.
The creation of terminal systems most often leads to the monopolization by the initial system supplier of all services for their development.
The intensive development of personal computers and minicomputers based on high-performance processor systems and the saturation of the information technology market with them have led to the emergence of inexpensive competitive solutions.
Reduced prices for computing systems based on powerful microprocessors while increasing their performance and energy efficiency make these systems very attractive for widespread use in areas traditional for mainframes - banks, communications, financial activities, and complex corporate systems.
Improvements in the operating systems of personal computers and systems based on them are bringing them closer to mainframes in terms of performance and reliability, as well as in the area of support for multitasking and multithreading.
With the rise of both microcomputers and minicomputer systems, the importance of mainframes has declined. The cost of mainframes is relatively high: one computer with a package of application programs is estimated at at least a million dollars. Despite this, they are actively used in the financial sector and the defense complex, where they occupy from 20 to 30% of the computer park, since the use of mainframes for centralized storage and processing of a sufficiently large amount of information is cheaper than maintaining distributed data processing systems consisting of hundreds and thousands of personal computers.
The client-server system contains not only a common database, but also search programs. This allows you to request not all data, but only those that the user needs.
Many DBMSs divide their work into two levels using the client-server system. From an execution point of view, the program is divided into two parts - client and server. On the client side (computer) contact with the outside world occurs. The server computer contains data common to all clients and runs a special program - a database server that optimizes the execution of client requests.
The client is a processing program, it is also a user and application program. Usually deals with the user interface, and delegates all actual work with the database to the database server. The database server transmits information selected from the database via an interprocessor channel to the client.
Performance is the main factor in the feasibility of developing systems for the client-server architecture.
Work is constantly underway to improve the method of storing and processing information, and if its implementation (i.e., the database server) has changed, then it will not be necessary to recompile all developed programs with new libraries, but it will be enough to install a new database server to replace the old one and translate database into the format of the new server (by using the utility supplied with it).
By using many small computers, client-server system developers can emulate the processing power of mainframe computers by distributing an application task across different microcomputers and servers. Each of them takes on its part of the computing load, sharing information with other processors on the network. The essence of the idea is to increase the power of the system, not by increasing the performance of one computer, but by summing up the resources of many.
The client-server architecture gives software developers exceptional freedom to select and coordinate different types of components for the client, server, and everything in between.
Nowadays, most of the leading manufacturers of automated information technologies offer products of automated treasury systems based on client-server technology.
The main idea behind this technology is to minimize the amount of data transmitted over the network, since the main time losses and failures occur precisely because of insufficiently high network bandwidth.
Working on a LAN based on technologies for collective creation and use of documents allows treasury authorities to reduce the production of redundant or unnecessary paper documents. This technology makes it possible to organize paperless technology for the work of treasury bodies in electronic office mode.
In accordance with the organizational and functional structure of the Federal Treasury, the structure of the unified corporate network contains three levels: 1-
th level - local computer network of the Main Directorate of the Federal Treasury of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation; 2-
1st level - local computer networks in the departments of the Federal Treasury in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation; 3-
th level - local computer networks in branches of the Federal Treasury in cities, districts and districts in cities.
Deployment of subsystems of the RS-Treasury software package is carried out on the basis of client-server technology for Windows platforms (95/98/Me/NT/2000/XP/2003) in a three-level architecture with the construction of relational databases. It is planned to organize the interaction of workstations with the exchange of data in online/offline modes and the execution of distributed data processing transactions.
Possible DBMS of the RS-Treasury software package - MS SQL or Oracle. The software development platform is the most modern and progressive .NET platform, which provides the most universal, open and mobile architecture for the development of complex information and analytical applications.
Database servers are oriented on Microsoft Windows 2000, Microsoft Windows NT 4.0, Microsoft Windows 2003. Operation of client machines is guaranteed under Microsoft Windows 95, 98, NT, ME, 2000, 2003, XP.
The use of modern XML formats for data transfer and exchange is provided.
When organizing an automated workstation of any subsystem, precise individual configuration of the financial authority’s workplaces is carried out, the area of responsibility is assigned in the budget planning process, and access rights are determined for both individual employees and divisions (departments), and user groups.
Information interaction of budget subjects - automated workplaces is provided by special service components for receiving and transmitting data that are part of the subsystem. For security purposes and maintaining the integrity of information, the system uses certified cryptographic protection tools (encryption and digital signature).
In general, the automated information technology of treasury authorities, built on the basis of a “client-server” architecture, should contain workstations of administrators of office systems and information security services, administration of treasury authorities and treasurers performing specific functions in the execution of budgets at different levels. The organization of the work of the office as a whole and its technological parts related to work in banking payment systems, including electronic ones, and with the depository system for servicing the government securities market, is based on a single principle of collective work with objects - electronic documents, which are legally equivalent to paper documents. document adopted in traditional document flow. This approach complicates the operation of distributed systems, but ensures the legal integrity of information in the system and reliability during collective processing of information.
The workplaces of such an office must reliably reproduce all the regulatory conditions for the creation and processing of documents - from registration and organization of the processing route to recording the decision. Typically, such systems operate on the basis of strictly organized procedures at specific workstations, linked into routing flows for transferring information from one workstation to another through the transport of document files.
To organize automated information technology, a special communications system is organized in the treasury. Data transmission can be carried out via telephone and telegraph communication channels.
The most promising in terms of building corporate communication solutions for organizational structures distributed over a large territory of the country are the telephone system and regional computer network solutions with shared access, organized on its basis. Currently, the long-distance communication system is based on the use of relatively modern stations of the “Kvant” series, which allow dialing a subscriber’s number without the participation of operators using uniform long-distance codes. The use of these stations makes it possible to organize automated exchange of information over dial-up communication channels using computers equipped with telephone modems and corresponding application communication software. The exchange speed is very high - from 1200 to 28,000 baud or more (in dedicated communication channels, the data transfer rate can reach 1.5 Mbaud).
If there is significant traffic of information exchange between remote subscribers or if there is a technological need to have a short fixed time for establishing a connection between exchange participants, a dedicated communication line can be used when the communication line exists constantly, regardless of the presence or absence of information transfer. Long-distance and city (district) telephone operating organizations allocate channel capacities for permanent use under the terms of a lease agreement. Given the significant cost of renting such channels, they should be used only when necessary, confirmed by a feasibility study.
An option for operating a corporate communication system over dedicated communication channels is the participation of an organization and its remote branches in the operation of a regional or global public computer network.
When organizing information exchange over switched long-distance telephone channels, the quality of the physical communication channels automatically allocated by the system when connecting subscribers has a significant impact on the stability of transmission characteristics. However, it should be taken into account that the large length of communication lines, a significant number of intermediate connections on the line, physical deterioration of equipment and transmission lines in certain sections significantly reduce the reliability of telephone modem communications over dial-up channels. Currently, the Federal Treasury authorities, based on high-quality modems and specialized communication application software, have organized a departmental system for transmitting information to all regions. This system is used as an effective platform for organizing information technology of treasury authorities, operating in real time on routed virtual data transmission channels, including protecting information from unauthorized access, when transmitting data from remote terminals to a central data server.
Thus, the automated treasury information system is an integral part of an integrated hardware and software system that combines individual information technology hardware and software tools and systems of Federal Treasury bodies at various levels, including local computer networks, separate workstations and terminals, communication computer systems and tools available at the disposal of these institutions.
The automated treasury information system provides the opportunity to carry out prompt and effective exchange of information in agreed data formats between all participants in the budget process - both directly between the territorial bodies of the Federal Treasury, and between the bodies of the Federal Treasury and other organizations involved in the receipt, transfer and control of budget funds.
Today, the load on the treasury system has increased many times over, and this trend will only intensify in the near future.
The Federal Treasury is carrying out very complex work to create a unified automated system of the Federal Treasury, which will have to ensure the operation of the Treasury on the territory of Russia as a single integral organism
In principle, almost all tasks that arise during the work of the treasury structure are quite easy to automate. Fast and uninterrupted processing of significant flows of information is one of the main tasks of any large financial organization. In accordance with this, the need for a computer network that allows processing huge information flows is obvious.
Automated income accounting technology (Kazna system). The automated information system for the execution of part of the federal budget revenues is a software package that provides the following functions:
collection, registration, transmission, storage, processing and analysis of information on the revenue side of the federal budget;
obtaining timely and reliable information about the receipt of funds in the federal budget;
generation of accounting and payment documents, as well as regulated reporting;
issuance of reference, statistical and analytical information upon request.
Based on the information received, treasury departments solve the following tasks:
direct control over the dynamics of the flow of funds into the federal budget;
distribution of regulatory taxes between the federal budget and the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation;
exercising control over the movement of funds received in the form of taxes to the federal budget through banks;
transfer of information from lower divisions of the treasury to tax and financial authorities, as well as to higher authorities of the treasury;
forecasting the dynamics of the receipt of funds for the purpose of planning and adjusting allocations from the federal budget.
An automated income accounting system, depending on the scale of the tasks being solved, is created at three main levels of the Federal Treasury (see above).
A temporary automated system for the Federal Treasury of the ASFC of the Russian Federation was developed. Its main purpose was to coordinate and ensure interaction between Federal Treasury bodies of all levels, their operational information support, automation of basic operations, organization of a communication and data transmission system.
The creation of the ASFC of the Russian Federation was based on the principles of forming a unified information base, protecting data from unauthorized access and the ability to adapt the software package to the conditions of a specific Federal Treasury body.
In the Main Directorate of the Federal Treasury of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and its territorial bodies, individual components of the information system have been introduced and are being operated, there are no end-to-end data processing technologies, and some of the information technologies are outdated, the collection and processing of a significant part of the information is duplicated by different organizations (tax services, customs committee, financial authorities, regional and sectoral governing bodies, statistical bodies, etc.). At the same time, there is no regulatory framework that determines information interaction using communication channels (media) between economic departments.
All operations carried out in the treasury are documented. Since the federal budget consists of revenue and expenditure parts, there are two relatively independent flows of documents on federal budget revenues and on its expenses.
Therefore, there are mainly two software subsystems:
federal budget revenue accounting subsystem (Kazna system);
subsystem for accounting for expenses from the federal budget and financing recipients of budget funds from personal accounts opened for regional bodies of the Federal Treasury (Smeta-F system).
In addition, the accounting departments of treasury authorities solve internal tasks related to accounting for execution and reporting on the execution of cost estimates for treasury departments. In particular, the accounting department of the regional treasury department solves the following sets of tasks: “Personnel”, “Office work”, “Warehouse”, “Accounting for material assets”, “Wages”, “Reporting”.
The electronic document management technology for generating federal budget revenues is as follows. 1.
The taxpayer submits to the bank where his current accounts are opened a payment order for the payment of taxes from the federal budget in four copies. One copy of the payment order with a payment stamp is returned to the taxpayer, one copy remains in the taxpayer’s bank, two copies are sent to the bank in which the treasury current account is opened, one of them remains in the bank, and the other is sent to the treasury. 2.
The received amounts of taxes and other payments are transferred daily by electronic payment by taxpayer banks to the bank in which the Treasury income account is opened.
When transferring, copies of the payment document and a summary advice are transferred to the bank. 3.
The bank in which the treasury current account is opened credits taxes and payments to the specified account, after which it sends copies of received payment documents and an income statement to the treasury via electronic communication channels. 4.
The Treasury processes payment documents received from the bank within one business day, i.e. enters them into the database, taking into account the distribution of regulatory taxes in accordance with current legislation. 5.
The completion of accounting for income for the operating day of the Federal Treasury for account 40101 is the printing of payment orders to the federal budget revenue account and to the budget account of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation and local budgets.
The operating day for this account ends upon receipt of a bank statement with a mark on the passage of the prepared documents.
The “Kazna” system is constantly modified and improved in connection with changes in the regulatory framework, set and technology for executing operations, taking into account proposals, comments and wishes from the regions.
The development of implemented capabilities, experimental and industrial implementation, training, support, hotline support, and provision of consulting services are carried out.
The system is intended for users of four categories: 1)
administrator - a specialist in maintaining and supporting an automated system, in matters of office equipment and local computer network; 2)
financier (treasurer) - a specialist responsible for performing financial transactions; 3)
operator - a specialist responsible for entering information into the system; 4)
accountant - a specialist responsible for performing accounting operations and maintaining financial statements.
The system allows you to create new categories of jobs, works in multi-user network mode, in addition, you can work in local mode.
The functional content of the automated system today is represented by the following software systems:
“Analytical accounting and distribution of federal budget revenues in the conditions of maintaining a centralized balance sheet account 40101”;
“Analytical accounting and distribution of local budget revenues”;
“Accounting for budget execution”;
“Analytical accounting and distribution of federal budget revenues”;
“Accounting for customs payments on accounts opened with the Federal Treasury”;
“Information interaction with territorial bodies of the Ministry of Taxation, banks, Federal Treasury bodies at other levels”;
“Creation and maintenance of a database of regulatory and reference information.”
Service functions of AIS "Kazna". This system is equipped with the following tools:
control of the correctness and integrity of entered and processed information;
issuing messages about the progress of processes and errors made by the user;
automated copying and recovery of information on daily transactions;
archiving closed-period data to store it in a compressed form and the ability to unarchive it;
custom menu settings (menu design, functionality);
means of limiting the access rights of certain categories of users in order to prevent unauthorized access;
generating reports based on arbitrary queries created by the user.
expansion of the system (for example, through user functions it is possible to connect autonomous modules);
viewing databases based on selectable search and viewing criteria;
database integrity checks (several levels);
initialization of data from any intermediate date during the financial year.
When setting the operating parameters of the system for a specific user, the system provides: 1)
logical control of input and processed information; 2)
control over compliance of entered data with the contents of directories; 3)
blocking user actions in case of serious violations in the database.
Automated cost accounting (Smeta-F system). The software system "Smeta-F" is designed for automated accounting of financial transactions of financial treasury departments and allows you to perform the following functions:
maintain customer catalogs, their attributes and characteristics;
maintain a catalog of personal accounts of budget fund managers (RBS);
enter payment documents;
establish correspondence between the entered payment documents and statements from accounts of a certain treasury in the bank with automatic generation of account transactions;
post postings to the personal accounts of fund managers;
take into account the placement of payment documents on the card index;
increase the reliability of calculations when entering payment documents by connecting to the directory of managers of budget allocations of enterprises - correspondents in the bank;
generate and print reporting forms and documents;
maintain archives of payment documents;
configure attributes of Federal Treasury branches;
establish different levels of access to information for
system users.
The automated treasury system includes working tools:
system administrator (AS);
payment department;
operations department;
accounting department
Each workplace has certain functions that can be adjusted and supplemented.
As the starting point of the technological process, we will take the receipts from the register of the Federal Treasury Department for primary financing to the payments department. If the financed organization is not yet among those serviced by the Federal Treasury, then the payment department notifies this organization about the receipt of funding, prepares a package of documents that must be submitted to the organization to open a personal account (application, service agreement, cards with sample signatures, cash application and cost estimate ). Each organization served by the Federal Treasury is assigned a registration number, and all its documents are stored in a special folder with this number. Each serviced organization opens a personal account (one organization may have several personal accounts depending on the financing symbol).
The opening of personal accounts of the RBA is carried out by order of the accounting department on the basis of a set of documents provided by the RBA and OFK in the prescribed form. Along with the personal accounts of clients in the AS, a current OFC account is also opened in the bank and personal accounts of blocks of federal programs (block of FI managers).
A personal account is opened at the payment department workplace. If a financed organization is not in the RBA directory, then to open a personal account it is necessary to add it to this directory, located in the section of local directories of NSI (regulatory and reference information). When entering an organization, the registration number is checked (there cannot be two organizations with the same number). When entering a personal account, the registration number of the organization is monitored (it must be present in the reference data directory), subsection, symbol and personal article (according to the reference data).
Accounting and maintenance of RBA cost estimates are carried out at the workstation of the payments department, where the estimate provided by the RBA is entered into the database in the context of economic classifications. When estimates change, the operator enters these changes into the existing estimate database. Changes are introduced to adjust estimates and transfer amounts within financing based on transfer documents provided by the RBA. These estimates serve to control the transfer and expenditure of funds from RBA personal accounts.
Spending of funds from the personal accounts of the RBA and federal programs is carried out through the accounts of the Federal Treasury authorities opened in an authorized bank. Financing of expenses from the personal accounts of the RBA and federal programs is carried out under strict control over compliance with the cost estimates (limits) in the context of items of economic classification. If necessary, in the event of a lack of funds in one item of economic classification, but availability in another, it is possible to move funds within one personal account according to a letter from the RBA, with the obligatory restoration of the original data during the financial year in accordance with estimated assignments.
When payment orders are received to write off funds from personal accounts of the RBA, the payments department controls the targeted execution of budget funds, checks them with the cost estimate and formulates orders for the operational department to write off funds from accounts. The operational department enters payment orders into the database.
If there are no or insufficient funds in the personal accounts of the RBA, payment documents of the RBA or third-party collectors are placed in a card index. Subsequently, when funds are received into the corresponding personal account, the payments department will write off the funds in full or partially from the card index with the formation of an order and the subsequent execution of a memorial order.
Managers of budgetary allocations to receive cash from the bank submit applications to the Federal Treasury to receive cash. The payments department controls the intended use of budget funds, checking the cost estimate, checks the availability of obligatory payments to the budget and funds and generates a free application for transmission to the bank. On the day of receipt of cash, the accounting department of the Federal Treasury, based on the application and power of attorney of the RBA representative, issues checks for cash receipt.
Upon completion of the transaction with payment documents for debiting funds, the operations department prepares a register of payment documents for transferring them to the bank. After confirmation, the amounts of entered documents are taken into account in reporting forms and reflected in personal accounts.
When a bank statement arrives at the operational department, an automatic reconciliation with those already in the system and confirmation of payment documents are carried out, and then additional processing of missing documents. After confirming all documents on the bank statement, the system administrator closes the operating day, as a result of which operations are carried out on correspondent accounts of the Federal Treasury authorities opened in the bank. Then, in the operations department, an extract on personal accounts of the RBA and federal programs is generated for transfer to their clients, as well as a balance sheet.
Information security in automated treasury systems. An important characteristic of software is the safety of its use, i.e. the ability to ensure the legal significance of electronic documents and protect the system from unauthorized access.
Since confidential information is processed during budget execution, much attention is paid to protecting data from unauthorized access.
The main goals of information protection in automated systems of the Federal Treasury of the Russian Federation are:
prevention of leakage, theft, loss, unauthorized destruction or copying, modification (forgery), blocking of information;
maintaining the integrity and reliability of information in databases and processing programs;
ensuring the confidentiality of information in accordance with the law;
preventing illegal interference in information systems.
Information protection in automated systems of the Federal Treasury of the Russian Federation should be based on the following basic principles:
ensuring physical separation of areas intended for processing classified and unclassified information;
ensuring cryptographic protection of information;
ensuring authentication of subscribers and subscriber installations;
ensuring differentiation of access of subjects and their processes to information;
ensuring the establishment of the authenticity and integrity of documentary messages when they are transmitted via communication channels;
ensuring the protection of equipment and technical means of the system, the premises where they are located, from leakage of confidential information through technical channels;
ensuring the protection of encryption technology, equipment, hardware and software from information leakage through hardware and software bookmarks;
ensuring control of the integrity of the software and information part of the automated system;
using only domestic developments as protection mechanisms;
ensuring organizational and regime protection measures. It is advisable to use additional measures to ensure communication security in the system;
organizing the protection of information about the intensity, duration and schedules of information exchange;
the use of channels and methods for transmitting and processing information that make interception difficult;
implementation of secure administration of the financial system.
Mechanisms for ensuring information security in automated systems include:
access control to information resources;
data encryption (cryptographic protection);
electronic digital signature;
ensuring data integrity and reliability;
ensuring authentication (confirming the authenticity of the sender and recipient of information);
traffic masking (making it difficult to analyze information flows without opening it).
Automated information systems of customs authorities