In lithium polymer batteries (Li-po), they differ from lithium-ion batteries in that they do not have separators and liquid electrolyte. Lithium polymers use a homogeneous electrolyte with lithium salts in the form of a gel, or a composite polymer with lithium salts in a dry state (often polyethylene oxide is the basis). Also, lithium polymer batteries can consist of a non-aqueous solution of lithium salts. Read more about the differences.
Advantages of lithium polymer batteries.
The main advantages of lithium polymers over batteries is that they have a fairly low self-discharge and have 4 and a half times greater energy consumption than Ni-CD batteries of the same mass.
Lithium polymers typically have a life of 300 to 600 charge / discharge cycles, but are sometimes found with 1000 recharge cycles.
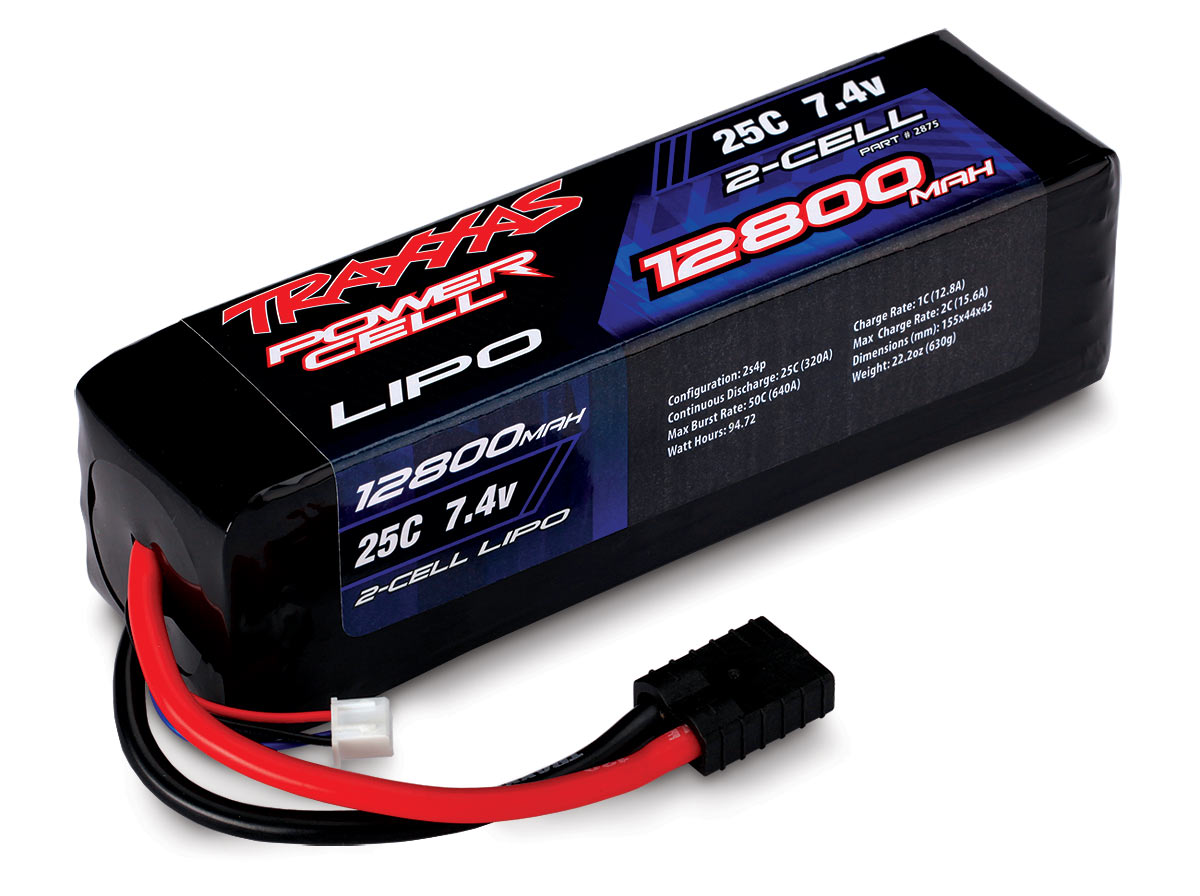
Very often lithium-polymer batteries are common in the form of a button, only 1 mm thick. (tablet). Also, these batteries have the smallest mass relative to lithium-ion, nickel-cadmium batteries and non-rechargeable batteries, provided the same capacity.
Application
Small-sized lithium-polymer button-shaped batteries with a thickness of only 1 mm are widespread. In addition, these batteries have the smallest mass relative to the above batteries and non-rechargeable batteries with the same energy consumption. This factor determined further niches for the use of lithium-polymer batteries:
- mobile phones
- dVRs and navigators
- radio controlled models
- various gadgets and devices.
Disadvantages of lithium polymer batteries:
■ Energy density lower than that of;
■ The high internal resistance of lithium polymers cannot provide high discharge currents. Consequently, lithium polymers cannot be used in screwdrivers and other highly powerful equipment.
■ Rapid degradation, so lithium polymer batteries lose most of their capacity after a couple of years, even during storage.
These batteries are very sensitive to the temperature conditions under which they operate. So lithium polymers cannot work normally at negative ambient temperatures. Surely you often noticed how quickly a mobile phone discharges in the cold. Lithium polymers can explode at temperatures above 70 ° C and cause a fire.
Lithium polymer batteries can lose their properties over time, even if they are not used. Therefore, you should not buy lithium polymers in reserve. lithium polymers, like lithium-ion batteries, do not possess, nevertheless, it is recommended to adhere to some rules regarding these batteries:
- Fully charge on first use.
- Complete several full recharge cycles using a voltage stabilizer.
- Store lithium-polymer batteries in a cool place, but not at sub-zero temperatures.
- Do not allow full discharge
- Frequent short-term recharges should be avoided.
- The most optimal temperature for the battery is from + 10 ° C to plus 25 ° C.

Almost all modern electronic gadgets are equipped with lithium-polymer batteries. They found wide application on flying radio-controlled models, quadrocopters, helicopters and airplanes. Lithium-polymer batteries have many advantages, including a high energy density, low self-discharge and the absence of the so-called "memory effect".
As a result, for models with Li Pol power generators, there is practically no decent alternative to the battery. It should be expected that they will be applied more and more widely, especially in areas such as unmanned aerial vehicles, electric cars, etc.
Despite all the advantages, LiPol batteries have a reputation for being capricious, dangerous and low-living power supplies. In fact, these shortcomings are somewhat exaggerated. If used correctly, problems will be minimized.

Charging rules
In order to avoid problems in the operation of the power supply, it is necessary to properly charge the LiPo batteries. Otherwise, there is a high risk of damage and even spontaneous combustion. Consider how to properly charge a lithium polymer battery to avoid possible problems:

- It will not work to charge the LiPo battery with any charger, this requires special chargers. This is due to the features of the two-phase charging process.
- Charging Li Pol batteries takes place in two phases (CC-CV method). At the first stage, the voltage on all banks of the battery increases. By the end of the phase, it reaches 4.2 volts. In fact, by this time, charging Li Pol batteries reaches 95%. Then the second phase begins. To prevent overcharging, which is detrimental to a lithium polymer battery, current is reduced. If the voltage exceeds 4.25 volts, the risk of spontaneous combustion increases.
- It is not recommended to allow a complete discharge of the power source, before recharging it should remain about 10-20%, otherwise it will quickly fail.
- It is important to ensure that the voltage does not fall below 3 volts on each bank. With such a decrease in voltage indicators, there is a high risk that the battery may swell. At the same time, a swollen LiPo battery will lose more than 50% of its capacity. If the LiPo battery is swollen, it remains only to throw it away - the loss of capacity is irreversible.
The fact that lithium-polymer power sources are swollen is one of the serious problems of their operation. All cans should be charged and discharged evenly. At the same time, the charger for lithium-polymer batteries only monitors the total voltage, but with a wide range of indicators, the likelihood that the LiPo battery is swollen increases significantly. It also leads to overcharging individual cans, increasing the risk of spontaneous combustion.

To solve this problem, Li Pol batteries must be charged using a balancer that can monitor the voltage on each bank, or a charger with a built-in balancer. Do not charge the charger power source with a timer. If the current is insufficient, the charger will turn off without fully charging it. The charge current should not exceed 1C and be less than 0.5C. You also need to remember that the larger the LiPo capacity of the battery, the longer it will charge.
Exploitation
In order to extend the life of Li Pol devices or at least not shorten it, the proper operation of the batteries is important. When we charge the power source, we must not allow it to heat above 60 degrees. If heating does occur before using the battery, allow it to cool. Also, it is impossible to put an overheated drive on charging.
Do not leave a fully discharged battery in storage. Be sure to charge it. The most optimal indicators are 60%. In general, subject to these simple rules, problems with the use of lithium-polymer batteries do not arise.
Lithium-polymer batteries represent an advanced design of world-famous lithium-ion batteries. It is planned that precisely these devices will soon completely displace nickel-metal hydride and nickel-cadmium from the market. batteries . Lithium-polymer cells are increasingly being used in a wide variety of electronic devices as a power source. With the same weight in energy capacity, they are several times superior to nickel-metal hydride and nickel-cadmium structures.
Potentially lithium-polymer cells will cost less than lithium-ion batteries. However, at the moment it is still quite expensive. At the moment, only a few large firms are engaged in their production. They are similar in design to lithium-ion cells, but they use helium electrolyte. As a result, they are distinguished by a low discharge current, a significant energy density, and a significant number of charge and discharge cycles. Their shape can be very different, and they themselves stand out with light weight and compactness.
Kinds
At the moment, lithium-polymer batteries can be of several types, which differ in the structure of the electrolyte:
- Elements having gel homogeneous electrolyte , which is created by the introduction of lithium polymer salts.
- Elements having dry polymer electrolyte . This type is based on polyethylene oxide using a variety of lithium salts.
- Having polymer matrix electrolyte having a microporous structure. It contains non-aqueous components of lithium salts.
Due to the fact that a liquid electrolyte is used in the polymer cell, their operational safety is an order of magnitude higher. In addition, they can be made in various shapes and configurations.
Some lithium polymer cells are made of metal polymer. However, at low temperatures, the parameters of such batteries are significantly reduced due to crystallization of the polymer.
There are developments in polymer batteries where a metal anode is used. Some companies managed to obtain a significant expansion of the operating temperature range and current density. Similar types of batteries can be used in various household appliances and electronics.
Moreover, different manufacturers use different electrode materials, electrolyte structure and assembly technology. As a result, the produced batteries can have completely different parameters. But all companies producing such batteries note that the stability of lithium-polymer batteries ensures the uniformity of the polymer electrolyte. This in turn depends on the number of components, as well as the polymerization temperature.
Already available in battery options having a thickness of only 1 millimeter. Thanks to this, manufacturers can produce very compact mobile devices.
Also, lithium-polymer batteries that are commercially available are divided into:
- Ordinary.
- Fast bit.
Device
Lithium-polymer batteries operate on the principle of moving a number of polymer elements into semiconductor materials, provided that they include electrolyte ions. As a result, a substantial increase in conductivity occurs. According to the device, these batteries are allocated by electrolytic composition.

The essence of polymer technology is that the electrolyte is applied to a plastic film. It does not allow the conduct of electricity, but makes it possible to exchange ions. In other words, a polymer electrolyte replaces a standard porous separator impregnated with a liquid electrolyte. Thanks to the dry polymer construction, it is possible to ensure a minimum cell thickness of the order of 1 mm, safe use and ease of production. Thanks to this design, developers have the opportunity to introduce such batteries in shoes, clothes, miniature equipment and other devices.
But a dry polymer battery has drawbacks in the form of reduced conductivity and internal resistance of polymers, which is unacceptable for a number of powerful mobile devices. To make the small polymer battery more advanced, a certain percentage of gel elements is added to the electrolyte. Most commercial batteries currently in use in cell phones are polymer and gel hybrids. Hybrid batteries are currently the most popular.
Operating principle
Lithium-polymer batteries have an operating principle similar to lithium-ion cells, that is, they operate on the reversibility of a chemical reaction. Here the anode is carbon material, where lithium ions are introduced. Vanadium, manganese or cobalt oxides are used in the cathode. The operation of such a battery is based on the ability of polymers to transition to a semiconductor state due to the inclusion of electrolytic ions in them.

As the chemical base of the electrolyte, lithium salts are still used here. However, they are located in the corresponding polymer gasket, which is located between the cathode and the anode. Due to this, lithium-polymer batteries can be made in any arbitrary form. They can be placed in various inaccessible places, which opens up new opportunities for electronics manufacturers.
Application
Lithium polymer batteries are increasingly used. Such batteries can significantly increase the operating time of the device with a reduced battery weight. Thanks to this, you can get an energy carrier that will be several times larger capacity. Using fast-discharge batteries will provide even greater performance. Therefore, such batteries are becoming an excellent option for radio-controlled models of airplanes and helicopters, including other radio-controlled devices.

Application Li-Pol batteries makes it possible to reduce the weight of the battery and increase the period of operation of the devices. Lithium-polymer batteries have proven excellent when used in small helicopters, for example, Piccolo. Such devices are capable of flying on such batteries for 30 minutes or more. These elements are a good option for small flying structures.
Typical lithium polymer batteries are used as power sources, which are necessary for electronic devices that consume a relatively small current. It can be laptops, smartphones and so on. High-speed batteries are used in devices where high current consumption is required. Such batteries are used in modern, portable electric tools and radio-controlled devices.
Application limitations
These batteries can be used everywhere in the automotive industry in the future. Today they are used to create new technologies and test electric vehicles. However, there are certain restrictions that prevent the use of these batteries everywhere.
- Lithium polymer batteries require a special charging mode. In principle, this is not difficult, but the usual cannot be used for this. This is caused by the fact that they are allocated by fire hazard during the period of overdischarge. To combat this phenomenon, all such batteries have an electronic system that prevents over-discharge and overheating.
- If the lithium polymer battery is not used correctly, it may cause a fire.
- The lithium polymer battery should not be used immediately after charging. First, it should be cooled to ambient temperature. Otherwise, the battery may malfunction.
- Short circuit inadmissible.
- Depressurization of the battery is not allowed.
- Battery discharge below 3 volts.
- Do not heat above 60 degrees.
- Batteries should not be exposed to microwaves or pressure. This can lead to smoke, fire and more serious consequences.
- It is necessary to protect the battery from integrity and shock. Strong mechanical stress can lead to disruption of the internal structure.
However, these disadvantages do not interfere with their use in a wide variety of areas. In the future, all these shortcomings will be offset by the introduction of new technologies and developments.
Benefits of lithium polymer batteries
- Quite high energy density.
- A small parameter of self-discharge.
- There is no memory effect.
- Lithium-polymer batteries are slightly superior to lithium counterparts in battery capacity and duration of use.
- Making batteries just one millimeter thick.
- Applications in a fairly wide temperature range: from minus 20 to plus 40 degrees Celsius.
- The ability to give the battery a different shape.
- Slight voltage drop during discharge.
Portable chargers have become an integral element of modern everyday life. The quality of batteries is the main condition for their performance, efficiency and safety. Manufacturers of chargers use two types of batteries in their design - lithium-ion and lithium-polymer. For an ordinary consumer unfamiliar with the features of different types, it often becomes a problem to choose one or another type of battery.
What is the difference between these varieties, which one will be more correct to choose - all these questions require detailed knowledge about each type. In this article, we will reveal the features of lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries, introduce them to their technical properties, charging methods, and service life.
Differences between lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries
Models of batteries manufactured using different technologies perform the same energy supply function. Design features of each type affect the reported power, durability, degree of protection against explosion. It cannot be stated unequivocally that a more modern type of battery is better than an outdated one. Both technologies have practical advantages and disadvantages. The Li-pol and Li-ion models have similar operation schemes, but differ in configuration and technical parameters.
To understand which is better - Li-polymer or Li-ion, we will examine in detail each species separately. Compare the types of batteries and make a choice in the direction of a particular type should be based on the following indicators:
- price;
- weight to capacity ratio;
- security;
- intended use in a device for a specific purpose;
- temperature mode of operation.
When choosing one of two types, consider the scope and financial possibilities.
Lithium-ion batteries: features and specifications
Initially, lithium-based models were produced using manganese and cobalt as the main element (active electrolyte). Modern lithium-ion batteries have undergone design changes. Their productivity does not depend on the substance used, but on the arrangement of the elements in the block. The components of a modern Li-Ion battery are electrodes and a separator. Materials - aluminum and copper (copper anodes and aluminum foil as the cathode base).
Special current collector terminals provide an internal connection of the anode and cathode, and the electrolyte impregnation of the separator mass creates a favorable environment for charge maintenance. The positive charges of lithium ions trigger chemical reactions, form bonds and provide energy output. The principle of operation of a power source based on a lithium-ion base resembles the operation of a full-size gel battery.
Lithium polymer batteries
Since lithium-ion models cannot cope with many modern tasks, polymer elements gradually began to displace them. Li-ion batteries did not have a high level of safety and were quite expensive. To eliminate these shortcomings and operation problems, to make the batteries more efficient, the developers decided to change the electrolyte. Instead of impregnating the porous separator, polymer electrolytes were used in the battery design.
The lithium-polymer cell has a thickness of 1 mm, which makes the battery compact. Replacing liquid electrolytes with polymer films eliminated the high risk of battery ignition and made it safe. The comparison table below will help you visually determine how Li-ion differs from Li-Pol.
| Specifications | Li-ion | Li-Pol |
| Energy intensity | low, the number of charge and discharge cycles is less |
|
| Size | small choice | high selection, independent of the standard cell format |
| slightly heavier | ||
| almost two times higher at the same size |
||
| Life time | about the same | about the same |
| Explosion and fire hazard | higher | built-in protection against electrolyte leakage and overcharging |
| Charging time | ||
| up to 0.1% monthly | less active |
|
The design of polymer-lithium battery devices completely eliminates the presence of electrolyte in the form of a liquid or gel. You can clearly see the difference in technology when considering the principle of operation of modern automotive power supplies. Safety interests have led to the exclusion of liquid electrolytes from everyday practice. But in automobile batteries until recently porous structures with impregnation were used.
The introduction of lithium polymer elements already implied a solid state basis. A characteristic difference from lithium-ion batteries is the contact action of the plate of the active substance with lithium and the prevention of the formation of dendrites during cycling. It is this feature that protects battery cells from fire or explosion.
Life time

Both lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries are prone to intense aging. They provide about nine hundred full charge cycles, after which they become unusable. It does not matter how active the operation of the device was. If the battery has not been used for a long time at all, a reduction in battery life will nevertheless take place.
After a year, the capacities become significantly reduced in resource, and after two or three years it can be stated that the battery is completely out of order. This is a common drawback of lithium batteries, and choosing a more durable model is only depending on the reputation of the manufacturer and reviews on specific models.
Additional protection
If you consider the question of what is the difference between Li-ion and Li-Pol batteries, it is worth paying attention to the built-in protective systems. Polymer-lithium-based models require additional internal protection features. They are characterized by cases of burnout due to overheating of the elements. Such consequences are caused by the internal stress of various work sites.
In order to protect the device from unauthorized overcharges, from overheating of parts and burnout, the design uses a special stabilizing system and a current limiting mechanism. This increases the safety of lithium-polymer models, but significantly increases the cost of the battery through the use of protective elements.
Partially in the design, electrolytic components in the gel formation are involved. Combined batteries are used in many portable devices. They are extremely sensitive to temperature changes and require strict adherence to operating rules. The polymer-based battery can be used in devices with heating in the range of 60-100 degrees.
Manufacturers enclose the inner part in a case with heat-insulating properties - it is convenient to use such batteries in hot climates. In conditions where the temperature regime does not meet the requirements of operation, elements with a polymer component are used as backup.
Battery Charging Features
To recharge a lithium polymer battery, it will take at least three hours to charge. In this case, the unit does not heat up. There are two stages of filling. The first proceeds until the peak mode is set, which is maintained until charging reaches 70%. Under normal voltage conditions, a residual charge of 30% is gained. Recharging must be done on a strict schedule, waiting for a full discharge and carrying out the procedure every 500 hours of using the device. This mode maintains a constant volume of filling. 
It is only necessary to connect the battery to a stable operating power supply network, without any voltage surges or interference. Only appropriate chargers that match the specifications stated in the description should be operated. An important point: during charging, all connectors must be connected correctly, you must not allow opening. Li-Pol cells are extremely sensitive to all kinds of overloads, excessive currents, mechanical shocks, and subcooling. The tightness of solid elements should be monitored.
Li-ion cells are charged in approximately the same way as polymer cells, but are more sensitive and less reliable in terms of safety. Charging time for both types is approximately the same, but the polymer element is “more capricious" to the quality of the energy supply point.
Better lithium-ion battery
Lithium-ion batteries are more familiar to consumers, they have a number of operational advantages:
- price below lithium polymer battery;
- standardized sizes allow you to make no mistake when choosing a model;
- widespread scope.
Powerful lithium batteries are effectively used for devices requiring short-term high current consumption. The temperature regime, as with polymer-based devices, is of key importance during operation.
The average user does not feel any tangible difference, but, from the point of view of rationality of the scope, this type of battery is convenient in chargers for the following equipment:
- cordless tools (screwdrivers, saws, grinders);
- laptops;
- mobile phones;
- electric cars;
- home robots;
- wheelchairs.
Before choosing the optimal type of charging, you need to know exactly for which device it will be used. This is especially important if you plan to universal use and maintenance of several portable devices.
Lithium polymer batteries can be used where weight and temperature are important factors. They are “afraid” of frost and are not very convenient for portable tools and gadgets. Therefore, the main area of \u200b\u200buse:
- quadrocopters;
- airsoft guns;
- toys
- cCTV Cameras.
When choosing the appropriate type of charger, pay attention to the scope, cost and level of security. Read user reviews about products from different manufacturers and make a choice.
Among the most common types of batteries are lithium-polymer and lithium-ion. What are their features?
Facts About Li-Polymer Batteries
AT lithium polymer batteries solid polymer electrolyte is activated. In the very first samples of the batteries of this type, created in the 70s, it was present mainly in the dry modification. This electrolyte actually did not conduct electric current, however, it could exchange ions formed by lithium compounds. In modern devices - laptops, mobile phones, gadgets - batteries are used, in which there is also a certain amount of electrolyte in the form of a gel.
Lithium-polymer batteries are capable of providing a high level of energy density based on their size and weight. They are characterized by a rather low self-discharge, do not have the so-called memory effect - when a charged battery in use is sometimes discharged only to a level that corresponds to the moment the battery is charged (that is, not necessarily to zero), and can also operate at a wide temperature range.
However, lithium-polymer batteries are not always safe - especially when overheating or charging too long. The batteries of this type have about 800-900 operating cycles, at which the level of capacity loss does not exceed 20%. The battery loses the same 20% of its performance after 2 years of operation, even if it is not used, but is stored.
Lithium-polymer batteries are often very small - theoretically possible to produce batteries with a thickness of the order of a millimeter. The use of a metal case in their design is optional.
Facts About Li-ion Batteries
Design lithium ion battery consists of electrodes and separators, usually impregnated with liquid electrolyte. The former are represented by aluminum cathodes and copper anodes. The electric charge in the batteries of this type is transferred by a positively charged lithium ion, which has the ability to integrate into the crystal lattices of other substances and thus form new compounds. Cathodes in modern lithium-ion batteries, as a rule, are represented by lithium compounds with cobalt, nickel, manganese, and iron phosphate.
The batteries of this type are characterized, like lithium-polymer products, by low self-discharge, but somewhat exceed them in energy intensity. Lithium-ion batteries do not need to be periodically charged and discharged in order to maintain functionality.
Outdated models of lithium-ion batteries are considered unsafe in operation, but those that include elements from a compound of lithium with iron phosphate are recognized as quite reliable. Like lithium polymer devices, batteries of this type lose capacity over time - even if they are not used.
Comparison
The main difference between a lithium polymer and a lithium-ion battery is the use of a predominantly dry electrolyte (with a small percentage of gel) in the structure of the former, while the latter uses, as a rule, liquid electrolyte. This makes it possible, first of all, not to use a metal shell in the design of lithium-polymer batteries and to produce a battery of small size and thickness. In lithium-ion batteries, in turn, it is necessary - otherwise the electrolyte will leak. The importance of using a metal casing may make it difficult to reduce the size of batteries manufactured by manufacturers.
Having determined the difference between the lithium-polymer and lithium-ion batteries, we reflect the findings in a small table.
Table
| Lithium polymer batteries | Lithium ion batteries |
| What do they have in common? | |
| They have general principles of electric charge transfer - using lithium compounds | |
| Characterized by low self-discharge | |
| No memory effect | |
| There is a common drawback in the form of a decrease in capacity over time | |
| What is the difference between the two? | |
| They have a solid electrolyte in their structure (with the addition of gel) | They have a liquid electrolyte in their structure |
| They do not require a metal sheath and may be small | They require a metal shell, which determines their larger size in comparison with lithium-polymer batteries |
| Have a slightly lower energy intensity | They have a slightly greater energy intensity |