The electrical equipment of any car includes a generator - a device that converts mechanical energy received from the engine into electrical energy. Together with a voltage regulator, it is called a generator set. On modern cars, alternators are installed. They most meet the requirements.
What is a generator voltage regulator?
Maintains the voltage of the on-board network within specified limits in all operating modes when changing the frequency of rotation of the rotor of the generator, electrical load, and ambient temperature. In addition, it can perform additional functions - to protect the elements of the generator set from emergency conditions and overload, to automatically include the field circuit or the alarm system of emergency operation of the generator set in the on-board network.
The principle of operation of the voltage regulator
 Currently, all generating sets are equipped with semiconductor electronic voltage regulators, usually built into the generator. The schemes of their execution and design may be different, but the principle of operation of all regulators is the same. The voltage of the generator without a regulator depends on the frequency of rotation of its rotor, the magnetic flux generated by the excitation winding, and, therefore, on the current strength in this winding and the magnitude of the current given by the generator to consumers. The higher the rotation frequency and the current intensity of the excitation, the greater the voltage of the generator, the greater the current strength of its load - the lower this voltage.
Currently, all generating sets are equipped with semiconductor electronic voltage regulators, usually built into the generator. The schemes of their execution and design may be different, but the principle of operation of all regulators is the same. The voltage of the generator without a regulator depends on the frequency of rotation of its rotor, the magnetic flux generated by the excitation winding, and, therefore, on the current strength in this winding and the magnitude of the current given by the generator to consumers. The higher the rotation frequency and the current intensity of the excitation, the greater the voltage of the generator, the greater the current strength of its load - the lower this voltage.
The function of the voltage regulator is to stabilize the voltage when changing the speed and load due to the impact on the excitation current. Of course, you can change the current in the excitation circuit by introducing an additional resistor into this circuit, as was done in previous vibrational voltage regulators, but this method is associated with power loss in this resistor and is not used in electronic regulators. Electronic controllers change the excitation current by turning on and off the field winding from the supply network, while the relative length of the time that the field winding is turned on changes. If, to stabilize the voltage, it is necessary to reduce the strength of the field current, the turn-on time of the field coil is reduced, and if necessary, it increases.
Voltage Regulator Test
Before checking the voltage regulator, you need to make sure that the problem lies in it, and not in other elements of the generator (the belt is tight, the mass is oxidized, etc.), for this you need to check the generator itself (How to check the generator?). After that you need to remove the voltage regulator. The process of dismantling the regulator is described in the article "How to remove the voltage regulator?" In a nutshell, I will say that you first need to remove the negative terminal, remove all wires from the generator, remove the plastic casing from the generator, then unscrew and remove the voltage regulator assembly along with the brushes.
 Let's go directly to checking the voltage regulator. The voltage regulator must be checked together with the brush holders - as in the event of an open circuit of the brushes and voltage regulator, we immediately notice this. Before checking, pay attention to the condition of the brushes: if they are broken off or their length is shorter than 5mm, they are motionless and do not spring, then they need to be replaced. For verification we need:
Let's go directly to checking the voltage regulator. The voltage regulator must be checked together with the brush holders - as in the event of an open circuit of the brushes and voltage regulator, we immediately notice this. Before checking, pay attention to the condition of the brushes: if they are broken off or their length is shorter than 5mm, they are motionless and do not spring, then they need to be replaced. For verification we need:
- wires;
- car battery;
- a bulb on 12v 1-3vt;
- two ordinary finger batteries.
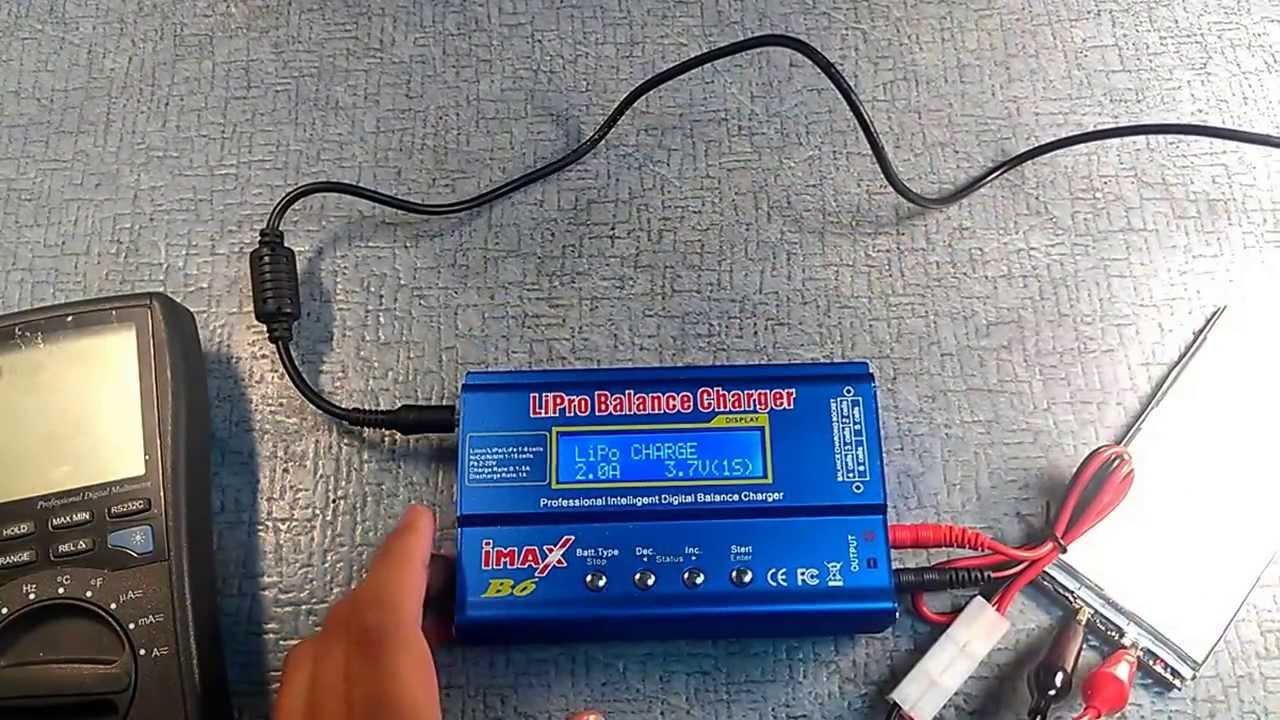
To check the voltage regulator, we will need to build two circuits: We connect a light bulb to the brushes, we connect “+” from the battery to terminals B and C, we fix the battery “-” to the regulator ground. We make the same circuit, but add two finger batteries in series. The conclusion from the foregoing is as follows. Serviceable voltage regulator: in the first circuit, the lamp is on, in the second circuit the lamp is off, because voltage is higher than 14.7V and voltage supply to the brushes should be stopped. Faulty voltage regulator: in both cases, the lamp is on, which means a breakdown in the regulator. The lamp does not light at all - it means that there is no contact between the brushes and the regulator or an open circuit in the regulator.
Three-Level Voltage Regulators
First we find out why this regulator is needed. The car generator must energize the battery while driving and running the engine. Thereby, the battery capacity is restored when it is discharged during parking. If we drive every day, the battery is almost not discharged, if it is in good condition.
 It is worse for the battery when the car stands idle for a long time, because its energy is gradually spent on maintaining the operation of the car alarm. Things are even worse in winter, when at low temperatures the battery discharges very quickly. And if you drive slowly and not often, then the battery does not fully charge while driving and may completely discharge one morning.
It is worse for the battery when the car stands idle for a long time, because its energy is gradually spent on maintaining the operation of the car alarm. Things are even worse in winter, when at low temperatures the battery discharges very quickly. And if you drive slowly and not often, then the battery does not fully charge while driving and may completely discharge one morning.
To cope with the above problem, a three-level voltage regulator is designed. He has three positions of work:this is the maximum(generates voltage on the generator 14.0-14.2 V), normal (13.6-13.8 V) and the minimum (13.0-13.2 V). As we know from the article about checking the battery’s performance, the normal voltage with the engine running should be between 13.2-13.6 V. This means that the generator is operating in normal mode and the battery is fully charged.
This corresponds to the average (normal) position of the voltage regulator. But in winter, it is advisable to increase the voltage to 13.8-14.0 V, because the battery discharges faster at low temperatures. This is done by simply moving the lever on the voltage regulator. This will ensure the best battery charge in winter with the engine running.
In summer, especially when the heat exceeds +25 degrees and above, it is advisable to lower the voltage of the generator to 13.0-13.2 V. Charging will not suffer from this, but the generator will not “boil away”, i.e. will not lose its nominal capacity and does not reduce the resource.
How to remove or replace the voltage regulator?
Before replacing the voltage regulator, be sure to check the generator as a whole (How to check the generator?). The voltage regulator needs to be changed if the voltage under the load of the on-board network (long-range included, mirror heating, stove) is less than 13v. Also, the voltage regulator can cause high voltage (above 14.7v). But, as mentioned above, before removing the regulator, you need to check the generator itself, familiarize yourself with other possible malfunctions (for example, the generator belt is slightly tightened), and only then proceed with the replacement of the voltage regulator. You will also need this article to replace the generator brushes, as brushes and voltage regulator are installed on the generator assembly.
 So, how to remove the voltage regulator? Open the hood, remove the negative terminal of the battery, find the generator, disconnect the wiring block “D”.
So, how to remove the voltage regulator? Open the hood, remove the negative terminal of the battery, find the generator, disconnect the wiring block “D”.
- Remove the protective rubber cap from the terminals of the “+” output wires. Unscrew the nut securing these wires, remove them from the generator unit.
We find the voltage regulator, and use a Phillips screwdriver to unscrew its fasteners.
We take out the voltage regulator assembly with brushes, and disconnect the wiring block from it.
We install the voltage regulator strictly in the reverse order. It is worth noting that recently, many motorists began to use a three-level voltage regulator in order to get rid of voltage drops in the on-board network.
Subscribe to our feeds in
Currently, voltage control tasks have received a material basis in the form of regulating and compensating devices. The constancy of voltage at each point of the network can be ensured by the use of local regulators in electrical circuits. Thus, the question arises of creating local systems of automatic voltage regulation in the electric network.
Share your work on social networks.
If this work does not fit you at the bottom of the page there is a list of similar works. You can also use the search button.
INTRODUCTION 3
Product Description 4
Main purpose and scope 5
Types of voltage regulators 6
thyristor-based ac voltage regulators 7
amplifiers based on magnetic amplifiers 8
transistor-based ac voltage regulators 9
synchronous compensator: purpose, principle of operation 10
The principle of operation of the voltage regulator 13
Conclusion 1 4
References 15
Introduction: Voltage regulation allows not only improving the quality of electricity, but also improving the course of production processes at industrial enterprises: reducing product rejects, increasing their quality, increasing people's labor productivity and machinery productivity, and also in some cases, reducing energy losses. Currently, voltage control tasks have received a material basis in the form of regulating and compensating devices. Calculations show that, as a rule, the additional costs associated with the use of control devices and their automation are paid off by the savings that are achieved by improving the voltage regimes in electric networks and systems. The constancy of voltage at each point of the network can be ensured by the use of local regulators in electrical circuits. Thus, the question arises of creating local systems for automatic voltage regulation in the electric network. It seems appropriate to build a local automatic control system using transistors.
Purpose of the study: To study the principle of operation and application of voltage regulators to improve the functioning of electrical devices.
Research Objectives:
- Find out the scope and application of the voltage regulator.
- Identify the types of voltage regulators.
- To study the principle of operation of voltage regulators.
- Draw conclusions about the work done.
1. Description of the device:
The voltage regulator is an electric device that regulates the voltage produced by an alternator or a direct current generator in the range from 14 to 14.4 V at a rated voltage of 12 V and from 7 to 7.2 V at a rated voltage of 6 V.
The voltage regulated in the indicated interval ensures the correct operation of the battery and the protection of devices from destruction. A prerequisite for proper operation is to prevent the possibility of overloading the regulator's electrical power. For example: The regulator has a maximum electric power of 200 watts. This means that the power of the alternator must be P alt<= 200 Вт. Далее, суммарное электропотребление приборов в сети транспортного средства не должно превышать 200 Вт. When overloaded, the regulator may be destroyed, or the battery may be discharged and destroyed.
The AC voltage regulator provides an average voltage value over a specified interval. This means that, for example, the voltage measured by the oscilloscope changes periodically by a larger amount than the rated voltage. For example, from + - 20 to 30 V. This average value ensures that appliances such as light bulbs will not collapse. However, there is such a rule that the sum of power consumption of devices should be Ps [W]<= Preg[Вт]. То есть, регулятор необходимо выбирать согласно номинальному напряжению [В] и макс. электропотреблению [Вт].
2. The main purpose and scope:
Voltage regulation allows not only improving the quality of electricity, but also improving the course of production processes at industrial enterprises: reducing product rejects, increasing their quality, increasing people's labor productivity and machinery productivity, and also in some cases, reducing energy losses. There are various ways to regulate voltage. A variety of solutions is due to the requirements for stability, the necessary accuracy of regulation, load parameters, economic and other factors.
Regulation in secondary power supplies
The magnitude of the rectified voltage in some cases needs to be changed. Such a need may arise when turning on powerful engines, the glow of the generator lamps, to reduce the inrush current when turned on. Regulation of the rectified voltage can be done on the AC side (input), on the DC side (output) and in the rectifier itself using adjustable valves.
As voltage regulators on the AC side are used:
adjustable transformers or autotransformers.
regulating chokes (magnetic amplifiers).
In an adjustable transformer or autotransformer, the primary or secondary windings are made with several leads. Using the switch, the number of turns of the winding and, therefore, the output voltage of the transformer or autotransformer is changed. When switching the windings, part of the turns can be short-circuited by the switch engine, which will lead to the creation of excessively high currents in closed turns and to failure of the transformer. Therefore, such switching is recommended to be done after disconnecting the transformer from the network. This is a big disadvantage..
3. Types of voltage regulators.
1. By the number of nodes in one housing:
- voltage regulator only
- voltage regulator together with an electric current rectifier
- combined regulator for AC voltage and DC voltage with a rectifier
2. According to the rated voltage in the vehicle network and voltage change:
- rated voltage 6 or 12 V
- aC voltage or DC voltage
3. According to the electric power (load) of the regulator
4. According to the number of phases per 1-phase and 3-phase
5. As an adjustable DC generator - for generators with independent excitation and generators with permanent magnets.
3.1. Thyristor-based ac voltage regulators:
Thyristor regulators can significantly reduce the physical dimensions of the device, reduce its cost and reduce energy losses, but they have significant disadvantages that limit their capabilities. Firstly, they introduce quite noticeable interference into the electric network, which often negatively affects the operation of televisions, radios, tape recorders. Thyristor AC voltage regulators are widely used in electric drives, also for powering electrothermal installations. The use of thyristors for switching stator circuits of asynchronous motors with a squirrel-cage rotor allows us to solve the problem of creating a simple and reliable non-contact asynchronous electric drive. It is possible to effectively influence the processes of acceleration, deceleration, to carry out intensive braking and precise stop. Sparkless switching, the absence of moving parts, a high degree of reliability allow the use of thyristor controllers in explosive and aggressive environments.
A generalized circuit of a thyristor AC voltage regulator is shown in Fig. one:
3.2. Magnetic amplifier based AC voltage regulators:
Consider AC voltage regulators based on magnetic amplifiers, thyristors and transistors. Magnetic amplifier (MU) is a static electromagnetic apparatus that allows using a control signal of direct current of small power to control significant powers in the circuitalternating current. The control choke (or magnetic amplifier) \u200b\u200bis switched on at the input of the rectifier. If the alternating current windings of the magnetic amplifier are switched on in series with the load and the current in the control winding is changed, the inductance of the inductor windings and the voltage drop across these windings will change. Consequently, will change. With increase, decreases, decreases, decreases and grows.
Voltage regulators, built on the basis of magnetic amplifiers, have several advantages: almost unlimited service life, ease of operation, high temperature and temporary stability of characteristics, high efficiency. Despite a number of advantages, regulators based on magnetic amplifiers are rarely used in modern control systems, since a significant drawback of such devices is their large size and weight, caused by the design features of magnetic amplifiers.
3.3. Transistor-based AC voltage regulators:
The transistor voltage regulator does not interfere with the electrical network and can be used to control the load, both with active and inductive resistance. The regulator can be used to adjust the brightness of the glow of a chandelier or table lamp, the heating temperature of a soldering iron or electric stove, the speed of rotation of the fan motor or drill, and the voltage on the transformer winding.
A generalized diagram of transistor AC voltage regulators is shown in Figure 2:

3.4. Synchronous compensator purpose, principle of operation:
Understanding how important the quality of electricity (the ratio of its active and reactive components is the power factor) is constantly growing, and with it the application of power factor compensation (CMC) will also grow. Improving the quality of electricity by increasing its power factor reduces costs and ensures a quick return on capital spent. In power distribution in networks with low and medium voltage, KKM focuses on the ratio of active and reactive power components (cosφ) and optimization of voltage stability by generating reactive power in order to increase the quality and stability of voltage at the distribution level.
Compensator synchronous, synchronous electric motor, operating without an active load, designed to improve power factor and voltage regulation in power lines and electric networks Depending on changes in the magnitude and nature of the load (inductive or capacitive) of the electric network, the voltage at the consumer (at the receiving ends of the line power transmission). If the load of the electric network is large and has an inductive nature, they connect a C. with., Working in an overexcited mode, which is equivalent to connecting a capacitive load. When electric power is transmitted through a long-distance line with a small load, the network operation mode is noticeably affected by the distributed capacity in the line. In this case, to compensate for the capacitive current in the network, a C. s., Operating in an unexcited mode, is connected to the line. The constancy of the voltage in the line is maintained by regulating the excitation current from the voltage of the regulator. Start K. s. carried out as well as conventional synchronous motors; inrush current K. s. makes up 30-100% of its nominal value. K. p. manufactured with a capacity of up to 100 kVA or more; powerful C. s. have hydrogen or water cooling. They are mainly used in electrical substations.
Any electrical equipment using magnetic fields (motors, inductors, transformers, induction heating equipment, generators for arc welding) is subject to a certain delay when the current changes, which is called inductance. This delay in electrical equipment preserves the current direction for a certain time, despite the fact that the negative voltage is trying to change it. As long as this phase shift is maintained, the current and voltage have opposite signs. The negative power that has been produced all this time is given back to the network. When the current and voltage sign equalize again, the same energy is needed to restore the magnetic fields of the induction equipment. This magnetic reversal energy is called reactive power. In networks with alternating current voltage (50/60 Hz), this process is repeated 50-60 times per second. The obvious way out of this situation is the accumulation of reverse magnetic energy in capacitors in order to free the network (power line). That is why automatic reactive power compensation systems (detuned / standard) are installed on a powerful load, for example, in factories. Such systems consist of several capacitor units, which can be connected and disconnected as required, and are controlled by the KKM controller based on the data of the current transformer.
Low power factor (cosφ) leads to: increased costs and energy consumption, reduced power transmitted through the network, power losses in the network, increased transformer losses, increased voltage drop in distributed power networks. An increase in power factor can be achieved by: compensation of reactive power with capacitors, active compensation - the use of semiconductors, overexcitation of synchronous machines (engine / generator)
In the power supply system, losses in networks are 8–12% of the production volume. To reduce these losses, it is necessary: \u200b\u200bcorrectly aboutp distribute electrical loads; rationally transmit and distribute electrical energy; provide the necessary degree of reliability; provide the necessary quality of electricity; provide electricabout receiver magnetic compatibility with the network; save energy. Activities that can ensure the above tasksbut high-speed reactive power compensationh awesome quality; loss reduction is achieved by compensating reactive power, increasing the load of transformers, reducing losses in them, bringing the transformers closer to the load, using savingsh equipment and optimization of its operating modes. The operating mode of the power system is characterized by three parameters: voltage, current and active power. An auxiliary parameter is reactive power. Reactive power and energy degrade energy system performanceand reads fuel consumption; losses in supply networks and receivers increase; the voltage drop in the networks increases. Reactive mou such elements as mains transformers consume powerto trostanes; the main step-down power plants, power lines - this accounts for 42% of the reactive power of the generator, of which 22%about outgoing transformers; 6.5% on district power lineswith topics; 12.5% \u200b\u200bfor step-down transformers. The main consumers of reactive power are asynchronous electricabout engines that consume 40% of all power in conjunction with domestic and personal needs. In other words, there are power receivers that need reactive power. One reactive power provided by the generator is clearly not enough. Took awayand it is inexpedient to reactive power generated by the generator due to the above reasons, i.e. need to issue reactive mou it’s exactly where it is most needed.
4. The principle of operation of the voltage regulator:
Currently, all generating sets are equipped with semiconductor electronic voltage regulators, usually built into the generator. The schemes of their execution and design may be different, but the principle of operation of all regulators is the same. When connecting the regulator to the mains, it is not allowed to change the + and - poles of the battery. The regulator may collapse.
The voltage of the generator without a regulator depends on the frequency of rotation of its rotor, the magnetic flux generated by the excitation winding, and, therefore, on the current strength in this winding and the magnitude of the current given by the generator to consumers. The higher the rotation frequency and the current intensity of the excitation, the greater the voltage of the generator, the greater the current strength of its load - the lower this voltage.
The function of the voltage regulator is to stabilize the voltage when changing the speed and load due to the impact on the excitation current. Of course, you can change the current in the excitation circuit by introducing an additional resistor into this circuit, as was done in previous vibrational voltage regulators, but this method is associated with power loss in this resistor and is not used in electronic regulators. Electronic controllers change the excitation current by turning on and off the field winding from the supply network, while the relative length of the time that the field winding is turned on changes. If, to stabilize the voltage, it is necessary to reduce the strength of the field current, the turn-on time of the field coil decreases, if it is necessary to increase, it increases.
Conclusion:
Voltage regulation allows not only improving the quality of electricity, but also improving the course of production processes at industrial enterprises: reducing product rejects, increasing their quality, increasing people's labor productivity and machinery productivity, and also in some cases, reducing energy losses. Having made conclusions about the device and the use of an AC voltage regulator, we can say with confidence that this device can sufficiently facilitate the work of both the radio technician and the average person in its use to improve the quality of electricity consumed.
Bibliography:
- Butov A. “Protection device for low-power incandescent bulbs”, Radio magazine No. 2, 2004
- Chekarov A. “No-noise voltage regulator” “Radio” magazine, No. 11, 1999
- Fundamentals of Radio Engineering [Text] / N. M. Izyumov, D. P. Linde. - 4th ed., Revised. and add. - M.: Radio and communications, 1983 .-- 376 p. : ill. - (Mass Radio Library; issue 1059). - B. c.
- Radio engineering [Text]: to the study of discipline / I. P. Zherebtsov. - 4th ed., Revised. and add. - M.: [b. and.], 1958. - 495 p. - B. c.
- Workshop on Electrical and Radio Engineering [Text]: a manual for students. ped in-to / Ed. N.N. Malova. - M.: Uchpedgiz, 1958.- 166 p. - B. c.
- Electrical and Radio Engineering Course [Text]: study guide: for ped. in-to / N.N. Malov. - M.: Gosfismat, 1959.- 424 p. - B. c.
PAGE \\ * MERGEFORMAT 2
Other similar works that might interest you. |
|||
| 11466. | Strategic management as the basis for increasing the efficiency of the enterprise in a crisis | 32.6 KB | |
| In the past, enterprises could function successfully, focusing mainly on daily work on internal problems associated with improving the efficiency of resource use in current activities. Now, although the task of rational use of potential in current activities is not being removed, it is extremely important to implement such a management that ensures the adaptation of the enterprise to rapidly changing environmental conditions. Strategic decisions are those that have ... | |||
| 16837. | The problem of using the replacement rate as the main indicator of the effectiveness of the functioning of the pension system in Russia | 8.8 KB | |
| Basically, from the position of the insured person, it is possible to judge the effectiveness of the functioning of pension insurance schemes in which financing of payments is carried out by paying insurance premiums by the level of replacement of the employee's lost earnings with a pension. Such an indicator in the theory of pension insurance is called the replacement rate. So in the draft Strategy for the long-term development of the pension system of the Russian Federation it is said that the objectives of the development of the pension system are to ensure the replacement rate for a retirement pension ... | |||
| 2542. | Familiarity with practical circuits of automatic voltage regulators SG | 306.51 KB | |
| Schematic diagram of the AVR generators of the TMV series Automatic voltage regulation of the SG of the TMV series is provided with an accuracy of 57 AFK system. In addition, the regulator has a voltage corrector that brings the voltage stabilization accuracy to 12. A three-phase inductor Dr included in each phase of the voltage winding of the excitation transformer is used as a compounding resistance. | |||
| 948. | Ways to increase the efficiency of commercial work in a retail trade organization | 100.41 KB | |
| The theoretical basis of the study of the effectiveness of commercial activities of a trading company. Functions of the goal of the task of the commercial activity of a retail trade organization. Commercial activity is one of the most important areas of human activity arising from the division of labor. However, such a broad interpretation of commercial activity is not consistent with the previously outlined approach to commerce as trading processes for the implementation of acts of sale of goods. | |||
| 5380. | Development of a training stand. The device and principle of the printer as a means of improving the quality of training of students in the specialty. Maintenance of computer equipment and computer networks | 243.46 KB | |
| Printers are classified according to five main positions: the principle of the printing mechanism, the maximum paper size, the use of color printing, the presence or absence of PostScript language hardware support, and the recommended monthly load. | |||
| 19917. | Directions for improving staff training and improving the efficiency of JSC SB Bank of China in Kazakhstan | 146.22 KB | |
| The role of staff training in organization development strategies. The process of vocational training and evaluation of its effectiveness. Management of the process of training and the formation of effective personnel of the organization. Methods for improving staff training. | |||
| 15626. | Ways to improve the organization of socio-pedagogical work with pedagogically neglected adolescents in a general educational institution | 68.85 KB | |
| Analysis of socio-pedagogical work with pedagogically neglected adolescents as a research problem. The study of foreign and domestic experience in the study of the problem of pedagogical neglect. The state of the organization of socio-pedagogical work with pedagogically neglected adolescents in a general educational institution. Justification of the model of socio-pedagogical work with pedagogically neglected adolescents in a comprehensive school. | |||
| 598. | The concept of protective grounding and the principle of its action. Types of grounding devices | 8.92 KB | |
| The concept of protective grounding and the principle of its action. The purpose of grounding is to eliminate the danger of electric shock in case of contact with the housing. The calculation of grounding is carried out according to the permissible voltage of touch and step or the permissible resistance to spreading current of the ground electrode. The calculation of grounding aims to establish the main parameters of grounding - the number of vertical grounding conductors and their sizes, the arrangement of grounding conductors of the length of grounding conductors and their cross-section. | |||
| 6655. | Field effect transistors, the principle of their work | 48.85 KB | |
| When the negative value of voltage U increases, the width of the pn junction increases due to a decrease in the width of the n channel, see. Thus, the flow of working charge carriers in the field effect transistor is controlled by changing the channel resistance when the gate voltage changes. Obviously, the degree of reduction of the channel width and therefore its resistance will increase with increasing voltage U. For small values \u200b\u200bof voltage U, the decrease in channel width caused by this voltage is not significant and ... | |||
| 14245. | Appointment, device and principle of operation of the radio | 68.26 KB | |
| The main functional units of the tape recorder are the tape drive mechanism of the LPM block of magnetic heads BMG BVG for recording playback and erasure of signals and electronic devices for the operation of the BMG. The characteristics of the CVL to the greatest extent affect the sound quality of the apparatus as a whole because the distortions that the non-ideal CVL introduces into the signal cannot be corrected by any correction in the analog electronic path ... | |||
The failure of the relay-regulator is the most common cause of malfunction of automobile generators. That is why, with a check of the regulator, they usually begin monitoring the operability of the generator nodes.
In most cases, this can be done independently even without removing it.
The principle of operation of the generator voltage regulator
The generator is one of the most conservative car components. The circuit developed in the mid-60s has remained virtually unchanged up to the present day with the exception of the element base.
Scheme
In general, the diagram of a car generator can be represented as follows:
It contains the following main nodes:
- rectifier bridge 5 and 6;
- rectifier bridge power relay-regulator 7;
- field winding brushes 10;
- field winding (armature) 9;
- stator winding 8;
- indicator lamp 4;
- rechargeable battery 3;
- contact group ignition 1;
- capacitor 2 (may be absent).
The general principle of operation of alternators was invented by the ingenious Tesla. Direct current through the field winding induces a magnetic field. During rotation of the excitation coil (armature), an alternating voltage is generated inside the stator winding in the latter.
This voltage is converted to constant by a rectifier made on the diode bridge 5 and 6. The rectified voltage.
The higher the current in the field winding, the higher the voltage of the generator.
What function does the relay regulator perform? Essentially, it is a feedback amplifier. That is, as soon as the voltage rises, its circuit reduces the current through the field winding.
Accordingly, the voltage of the generator decreases. Then it increases the winding current, the voltage of the generator increases. And so on to infinity. Ultimately, the voltage of the generator stabilizes at a certain level. This whole stabilization process lasts a split second.
Kinds
Relay regulators classify on the element base of execution:
- relay;
- transistor-relay;
- transistor (in cars until the 90s);
- integral (in modern cars);
- microprocessor controlled (Audi, BMW).

By design:
- external fixed to body elements;
- built-in;
- built-in, combined with brushes.

In modern cars, devices that are combined with brushes are most often used. This has its drawback: when the brushes wear out, you have to change the relay regulator. Conversely, failure of the relay controller can lead to the replacement of healthy brushes.
Some experts change only the brushes located together with the relay regulator. This is not the best option for reasons of reliability, especially since the cost of relay controllers of common cars is not so great and may even be lower than the cost of replacing brushes.
Possible causes of malfunction
The main causes of malfunctions of the voltage regulators of generators are:
- inter-turn circuit of the field winding. The most dangerous cause of the malfunction. After replacing the relay controller, the generator runs for a certain time without problems. But the regulator works at high currents and burns out again after a couple of months. In this case, it is necessary to remove the generator and take it for testing;
- failure of the rectifier bridge (breakdown of diodes). Less dangerous, especially since this malfunction causes the generator to overheat, and the diodes change in the first place;
- polarity reversal or reversal of battery poles. In this case, rectifier diodes also fail;
- destruction of brushes;
- short circuit on the control terminal of the relay-regulator;
- natural wear.
The consequences of a faulty relay controller can be significant:
- increased voltage of the generator can lead to failure of the electronic components of the car, therefore it is impossible with the engine running;
- internal circuit of the relay-regulator leads to overheating of the field winding and, ultimately, more expensive repairs;
- the destruction of the brushes of the relay-regulator can cause the final breakdown of the generator, its jamming, breakage of the belt and more serious consequences.
Key Symptoms
The very first symptom of a malfunction is the absence of a glow of the control lamp (indicator) on the dashboard when the ignition is turned on.
In age-old cars, where the battery charge pattern is similar to that shown in the first figure, it is too early for motorists to panic. Perhaps it was just a blown out bulb or a broken contact, and these cases are quite common. Car owners remove the generator, driven for testing, but in vain.
The second sign - the “battery” indicator does not go out after starting the engine. This already indicates a violation of the charge process and a possible malfunction of the generator.
Another sign of malfunction - the brightness of the dipped-high beam depends on the engine speed. By the way, such a check is recommended to be done regularly. To do this, it is necessary to stop in the dark at night in an uninhabited place opposite a building and to neutralize at the neutral by switching on the main beam. A change in brightness indicates possible problems with the charge system.
The smell of a burned winding in the cabin is also a sign of a generator malfunction, but you can not feel it.
How to independently check the generator relay relay with a multimeter or a lamp
In case of suspicion of a malfunction of the battery charge system, the test should begin with monitoring the voltage on the battery with the engine running. It should be between 13.3 - 14.5 volts. A voltage of more than 15 volts is a sure sign of a malfunction of the relay regulator.
Video - how to check the relay-regulator without an adjustable power supply:
Sometimes there is another for controlling the tachometer. You should ring the control wire to ground. Resistance below 10 ohms will also indicate a malfunction of the relay regulator.
The following checks should be carried out on a relay-controller removed from the generator. In most cases, this can and should be done without dismantling the generator. The control relay is usually mounted on the generator with two or three bolts or screws.

After that, you need to assemble a simple scheme.

or its other variant

As a light bulb, you can take an ordinary salon lamp. Its glow will indicate the serviceability of the relay regulator. On the removed relay, the condition of the brushes should also be checked.
On the Internet, you can find verification schemes for almost any type of relay-voltage regulator generators.
In the event that the results of the test turned out to be negative, the regulator should be changed. Usually its cost does not exceed 2000 rubles for common brands.
At the slightest suspicion of a malfunction of the battery charge system (a change in the brightness of the lamp, blinking of the indicator lamp, difficulty starting the engine, overheating of the device and others), the generator should be checked immediately, especially in the cold season.
In order for the generator to last longer, follow the following simple rules:
- do not allow excessive pollution of the generator (it has technological holes for ventilation, dirt can get there), clean its surface;
- periodically check the belt tension;
- watch the state of the stator windings, this can be done through the technological holes, they should not be darkened;
- poor contact of the control wire can lead to failure of the relay controller;
- to prevent overcharging the battery and damage to the electronic systems of the car, periodically check the voltage on the battery with the engine running (charge voltage).
And let your generator last longer!
Video - how to check the VALEO generator voltage regulator in Renault cars:
May interest:
Unique car scanner Scan Tool Pro
Electromechanical, in which, using vibrating contacts, the current in the excitation winding of the alternator is changed. The operation of the vibrating contacts is ensured in such a way that, with an increase in the voltage of the on-board network, the current in the field winding decreases. However, vibrational voltage regulators maintain voltage with an accuracy of 5-10%, because of this, the durability of the battery and car light bulbs is significantly reduced.
Electronic voltage regulators on-board network type Ya112, which the people call "chocolate." The disadvantages of this controller are known to everyone - low reliability due to the low switching current of 5A and the installation location directly on the generator, which leads to overheating of the controller and its failure. Despite the electronic circuit, the accuracy of voltage maintenance remains very low and amounts to 5% of the rated voltage.
That's why I decided to make a device that is free from the above disadvantages. The regulator is easy to configure, the accuracy of voltage maintenance is 1% of the rated voltage. The circuit shown in Fig. 1 was tested on many cars, including trucks for 2 years, and showed very good results.

Fig. 1.
Principle of operation
When the ignition switch is turned on, a voltage of + 12V is applied to the electronic regulator circuit. If the voltage supplied to the Zener diode VD1 from the voltage divider R1R2 is not enough for its breakdown, then the transistors VT1, VT2 are in the closed state, and VT3 is in the open state. The maximum current flows through the excitation winding, the output voltage of the generator begins to increase, and upon reaching 13.5 - 14.2 V, a zener diode breakdown occurs.
Due to this, transistors VT1, VT2 open, respectively, the transistor VT3 closes, the field current decreases and the output voltage of the generator decreases. Reducing the output voltage by about 0.05 - 0.12 V is enough for the zener diode to go into a locked state, after which the transistors VT1, VT2 are closed, and the transistor VT3 opens and current flows through the field winding again. This process is continuously repeated with a frequency of 200 - 300 Hz, which is determined by the inertia of the magnetic flux.
Design
In the manufacture of an electronic controller, special attention should be paid to the heat dissipation from the VT3 transistor. On this transistor, operating in key mode, significant power is allocated at least 1, so it should be mounted on a radiator. The remaining parts can be placed on a printed circuit board attached to the radiator.
Thus, a very compact design is obtained. Resistor R6 must be at least 2W. The VD2 diode should have a direct current of about 2A and a reverse voltage of at least 400V, KD202ZH is best suited, but other options are possible. It is advisable to use transistors that are indicated on the circuit diagram, especially VT3. Transistor VT2 can be replaced by KT814 with any letter indices. It is desirable to install the Zener diode VD1 series KS with a stabilization voltage of 5.6-9V (type KS156A, KS358A, KS172A), while the accuracy of voltage maintenance will increase.
Customization
A correctly assembled voltage regulator does not need special adjustment and ensures voltage stability of the on-board network of about 0.1 - 0.12 V, when the engine speed changes from 800 to 5500 rpm. The easiest way to set up is on a stand consisting of an adjustable power supply 0-17V and an incandescent lamp 12V 5-10W. The positive output of the power supply is connected to the “+” terminal of the regulator, the negative output of the power supply is connected to the “Common” terminal, and the incandescent lamp is connected to the “Ш” terminal and the “General” terminal of the regulator.
The setup is reduced to the selection of the resistor R2, which is changed within 1-5 kOhm, and the threshold is reached at the level of 14.2V. This is the supported voltage of the on-board network. It is impossible to increase it above 14.5V, since this will drastically reduce the battery life.
The generator set is designed to provide power to consumers included in the electrical system, and charge the battery when the car engine is running. The output parameters of the generator must be such that progressive discharge of the battery does not occur in any modes of vehicle movement. In addition, the voltage in the vehicle’s on-board network, powered by the generator set, must be stable over a wide range of changes in speed and loads.
The generator set is a fairly reliable device that can withstand increased engine vibrations, high engine compartment temperatures, exposure to a humid environment, dirt and other factors.
Generator Specifications
Features of the device and principle of operation
Generator type 37.3701 - alternating current, three-phase, with built-in rectifier unit and electronic voltage regulator, clockwise rotation (on the drive side), with a fan on the drive pulley and ventilation windows in the end part. To protect against dirt, the back cover of the generator is covered with a protective cover.
The generator is based on the effect of electromagnetic induction. If the coil, for example, from a copper wire, penetrates the magnetic flux, then when it is changed, an alternating voltage appears on the terminals of the coil. Such coils, placed in the grooves of the magnetic circuit (iron bag), are the stator windings - the most important stationary part of the generator - they generate alternating electric current.
The magnetic flux in the generator is created by the rotor. It also represents a coil (field winding) through which a direct current (field current) is passed. This winding is laid in the grooves of its magnetic circuit (pole system). The rotor, the most important moving part of the generator, also includes a shaft and slip rings. When the rotor rotates opposite the coils of the stator winding, the "north" and "south" poles of the rotor appear alternately, that is, the direction of the magnetic flux penetrating the stator windings changes, which causes the appearance of an alternating voltage in them.
A permanent magnet could be used as a rotor, but the creation of a magnetic flux by an electromagnet makes it easy to regulate the output voltage of the generator in wide ranges of rotation speeds and load current by changing the excitation current.
In order to obtain a constant voltage from an alternating voltage, six power semiconductor diodes are used, which make up a rectifier unit installed inside the generator housing.

The excitation winding is supplied from the generator itself and fed to it through brushes and slip rings.
To ensure the initial excitation of the generator, after ignition is turned on, a current is supplied to terminal “B” of the voltage regulator in two circuits.
- Plus, the battery - contact 30 of the generator - contacts 30/1 and 15 of the ignition switch - contact 86 and 85 of the ignition relay coil - minus the battery. The relay turned on, and the current went along the second circuit:
- Plus, battery - contact 30 of the generator - contacts 30 and 87 of the ignition relay - fuse No. 2 in the fuse box - contact 4 of the white connector in the instrument cluster - 36 ohm resistor in the instrument cluster - battery charge warning lamp - contact 12 of the white connector in the instrument cluster - contact 61 - terminal "B" of the voltage regulator - field winding - terminal "W" of the voltage regulator - output transistor of the voltage regulator - minus the battery.
After starting the engine, the field winding is powered from the common output of three additional diodes mounted on the rectifier unit, and the voltage in the vehicle’s electrical system is controlled by an LED or a lamp in a combination of devices. When the generator is working properly, after turning on the ignition, the LED or lamp should be on, and after starting the engine should go out. The voltage at the 30th pin and the common terminal of 61 additional diodes becomes the same. Therefore, the current through the control lamp (LED) does not flow, and it does not light.
If the lamp (LED) is on after starting the engine, this means that the generator set is faulty, i.e. it does not produce voltage at all, or it is lower than the battery voltage. In this case, the voltage at terminal 61 is lower than the voltage at terminal 30. Therefore, current flows through the LED through the LED / lamp in the circuit between them. He / she lights up to warn of a generator malfunction.

Voltage regulator: purpose and principle of operation
The generator set is equipped with a semiconductor electronic voltage regulator built into the generator. The voltage of the generator without a regulator depends on the frequency of rotation of its rotor, the magnetic flux generated by the excitation winding, and, therefore, on the current strength in this winding and on the magnitude of the current given by the generator to consumers. The higher the rotation frequency and the current intensity of the excitation, the greater the voltage of the generator, the greater the current strength of its load, the lower this voltage.
The function of the voltage regulator is to stabilize the voltage when changing the speed and load due to the control of the excitation current.
Electronic controllers change the excitation current by turning on and off the field winding from the mains (additional diodes).
With increasing rotor speed, the voltage of the generator rises. When it begins to exceed the level of 13.5 ... 14.2 V, the output transistor in the voltage regulator is locked, and the current through the field winding is interrupted. The voltage of the generator drops, the transistor in the controller is unlocked and again passes current through the field winding.
The higher the frequency of rotation of the rotor of the generator, the longer the locked state of the transistor in the controller, therefore, the more the voltage of the generator decreases. This process of locking and unlocking the controller occurs at a high frequency. Therefore, the voltage fluctuations at the generator output are invisible, and in practice it can be considered constant, maintained at a level of 13.5 ... 14.2 V.
Drive the generator and mount it to the engine
The generator is driven from the crankshaft by a belt drive with a V-belt. Accordingly, for this belt the drive pulley of the generator is performed with one handle.
To cool the generator, plates are welded from the back of the pulley by spot welding. On the pulley, they are almost perpendicular and perform the function of a fan.
The lower mounting of the generator on the engine is made on two mounting legs, articulated with the engine bracket with one long bolt and nut. Upper - through the pin to the tension bar.
Precautionary measures
The operation of the generator set requires compliance with certain rules, mainly related to the presence of electronic elements in them.
- The generator set must not be operated with the battery disconnected. Even a brief disconnection of the battery with the generator running can lead to the failure of the elements of the voltage regulator.
With a fully discharged battery, it is impossible to start the car, even if it is towed: the battery does not give an excitation current, and the voltage in the on-board network remains close to zero. It helps to install a working charged battery, which then, when the engine is running, changes to the previous, discharged one. To avoid failure of the voltage regulator elements (and connected consumers) due to an increase in voltage, powerful consumers of electricity, such as heating the rear window or headlights, must be turned on for the duration of the battery shift. Subsequently, within half an hour or an hour of engine operation at 1500-2000 rpm, the discharged battery (if it is working) will be charged sufficiently to start the engine. - It is not allowed to connect reverse polarity power sources to the on-board network (plus on the ground), which can happen, for example, when starting the engine from an external battery.
- Any checks in the generator set circuit with the connection of high voltage sources (above 14 V) are not allowed.
- When carrying out electric welding work on a car, the mass terminal of the welding machine must be connected to the part to be welded. Wires to the generator and voltage regulator should be disconnected.
Generator Service
Maintenance of the generator set is minimized and does not require any special knowledge and skills; each motorist can carry out these works.
Start generator maintenance by cleaning the exterior. Check the mounting of the generator to the engine, the reliability of the wires connecting to the generator and voltage regulator, as well as the tension of the fan drive belt. If the tension is weak, then the generator is unstable, if strong, the belt and bearings wear out quickly.
Also check the condition of the drive belt. There should be no cracks and delaminations on it.
The condition of the bearings can be checked by rotating the generator rotor by hand with the drive belt removed. In the normal condition of the bearings, the rotation of the shaft should occur smoothly, without jamming, strong play, noise and clicks. 
In principle, these works can be limited to until any malfunctions appear.
Verification check
Before leaving, it is recommended to check the operability of the generator set by the control lamp installed on the instrument panel. After the ignition is switched on, before the engine starts, the control lamp is on, which allows you to check its performance. During normal operation of the generator set, the indicator lamp goes off after starting the engine.
For a normally working generator set, at medium engine speeds, the voltage should be between 13.5 ... 14.2 V. The value of this voltage is measured with a voltmeter at the battery terminals.
Pre-Repair Diagnosis
A flashing battery charge warning lamp does not always indicate a malfunction inside the generator. Often the malfunction is commonplace and lies on the surface. Therefore, you should not immediately climb into the generator and change your head-relay relay headlong, maybe it will help. See the pre-diagnosis chart. To conduct it, you may need a voltmeter with a scale of at least 15 V. Everyone can do these checks and, thereby, protect themselves from unnecessary, incorrect actions and loss of valuable time.
If preliminary diagnostics showed that the field winding circuit is operational and the malfunction is in the generator, then after removing it, it is advisable to check all the circuits, including the relay controller, according to the schemes described in section
Removal and installation of the generator
- Disconnect the negative wire from the battery terminal (key 10).
- Remove plastic tape clamps from a branch pipe of an inlet and a plait of wires of a starter and the generator.
- Disconnect the generator field coil connector.
- Unscrew the nut from the 30th terminal of the generator (key 10).
- Turn away a nut of fastening of the generator to a tension level (a key on 17).
- Using the mounting blade, drive the generator to the engine and remove the drive belt.
- Turn away three bolts of protection of a case (a head on 13) and remove it.
- Remove the right mudguard of the engine, having turned off five self-tapping screws with a turnkey head on 8.
- Unscrew the nut 19 from the bottom bolt securing the generator to the bracket.
- Remove the generator along with the air intake pipe. To do this, slightly tilt it so that it goes down between the spar and the lower bracket for mounting the generator.
- Install the generator in the reverse order.
Disassembly and replacement of the voltage regulator
Start the preparation by cleaning the exterior of the generator.
- Remove the back cover along with the air inlet.
- Disconnect the wire from the relay controller, unscrew the two M4 screws and remove the relay controller. To remove the old-type relay-regulator, unscrew the wire fixed under the output extension cable "30" of the generator. Insert a screwdriver blade between the relay control housing and the brush holder. Using a screwdriver as a lever, slide out the relay control and pull out the brushes.
- Blow out the internal cavity of the generator from dust and dirt with compressed air using a compressor or pump.
- If the rotor contact rings are severely burned or worn, clean them with a fine sandpaper.
- Install a new relay control in the reverse order of removal.
If after checking the old relay-controller turns out to be working (the verification method is described in the next section), then:
- clean the contact connections of the generator and the relay-regulator from dirt and oil with a cloth moistened with gasoline or solvent. Oil and dirt increases the resistance at the contact points, which reduces the current given by the generator and increases the wear of the brushes.
- check the minimum permissible protrusion of the brushes from the brush holder - 5 mm. If the brushes in the brush holder seize, replace the relay regulator assembly. (For old-style relay controllers, it is sufficient to replace only the brush assembly.)
- put it in place.
Troubleshooting components and parts of the generator set
To troubleshoot the electrical circuits of the generator set, it is enough to have an ohmmeter. A more accurate check of the winding nodes requires the use of special devices, such as PDO-1, with its help, a fault is searched for in the windings by comparing their parameters. To check the relay-regulator, you need DC sources of 12 ... 14 V and 16 ... 22 V. All checks are more convenient to carry out on a generator taken from the car.
Voltage Regulator Test
Voltage regulators are not repaired, but replaced with new ones. However, before replacing, it must be precisely established that it was he who failed.
Check on the car
For verification, it is necessary to have a DC voltmeter with a scale of up to 15 ... 30 volts.
With the engine running at medium speed and the headlights on, measure the voltage at the battery terminals. It should be within 13.5 ... 14.2 V.
In the event that there is a systematic undercharging or overcharging of the battery and the regulated voltage does not fall within the specified limits, it is possible that the voltage regulator is faulty and must be replaced. In order to find out whether the regulator is working or not, we will check it according to the figure below.
Checking the removed regulator
The regulator taken from the generator is checked according to the following schemes (old model on the left, new one on the right):


It is better to check the relay-regulator assembly with the brush holder, as this can immediately detect breakage of the brush leads and poor contact between the terminals of the voltage regulator and the brush holder.
Between the brushes, turn on the lamp 1 ... 3 W, 12 V. To the terminals "B", "C" and to the mass of the regulator, connect the power source first with a voltage of 12 ... 14 V, and then with a voltage of 16 ... 22 V.
If the regulator is working, then in the first case the lamp should light up, and in the second it should go out.
If the lamp is lit in both cases, then there is a breakdown in the regulator, and if it is not lit in both cases, the regulator has an open or not contact between the brushes and the terminals of the voltage regulator.
Checking the rotor winding (field)
 To check the winding, an ohmmeter should be turned on to measure the resistance and bring its conclusions to the rotor rings. A working rotor must have a winding resistance of 1.8 ... 5 Ohms. If the ohmmeter shows an infinitely large resistance, this means that the field winding circuit is broken.
To check the winding, an ohmmeter should be turned on to measure the resistance and bring its conclusions to the rotor rings. A working rotor must have a winding resistance of 1.8 ... 5 Ohms. If the ohmmeter shows an infinitely large resistance, this means that the field winding circuit is broken.
The gap most often occurs at the site of soldering the winding leads to the rings. Carefully check the quality of this solder. Checking can be done with a needle, moving the winding leads in place of their soldering. The burning of the winding is indicated by the darkening and shedding of its insulation, which can be detected visually. The combustion of the windings leads to a break or inter-turn circuit in the winding with a decrease in its total resistance. A partial inter-turn circuit, in which the resistance of the winding changes little, can be detected by the PDO-1 device, by comparing this winding with a known good one. After checking the resistance of the winding, you should check if it has a short to ground. For this, one output of the ohmmeter is brought to any ring of the rotor, and the other to its beak. In a healthy winding, an ohmmeter will show infinitely large resistance. A defective rotor must be replaced.
Stator winding test
The stator is checked separately after disassembling the generator. The findings of its windings must be disconnected from the rectifier valves.


First of all, check with an ohmmeter for breaks in the stator winding (a). Then by connecting the ends of the ohmmeter to one of the terminals of the winding and the uninsulated portion of the stator iron, check if its turns are closed to the “mass” (b). An ohmmeter should show an open circuit in a working winding. Checking the inter-turn circuit in the stator windings can be carried out with sufficient accuracy using the PDO-1 device. An open circuit can also be checked with an ohmmeter, connecting it to the zero point and alternately to the output of each phase. An external inspection should ensure that there is no cracking of the insulation and burning of the winding that occurs during a short circuit in the valves of the rectifier unit. Replace the stator with such a damaged winding.
Checking the valves (diodes) of the rectifier unit
The rectifier block diodes are checked after disconnecting it from the stator winding with an ohmmeter. A serviceable valve passes current in only one direction. Faulty - it can either not pass current at all (open circuit), or pass current in both directions (short circuit). If one of the rectifier valves is damaged, the entire rectifier block must be replaced.
The short circuit of the valves of the rectifier unit can be checked without disassembling the generator, but only by removing the protective cover. Also disconnects terminal “B” of the regulator from terminal “30” of the generator and the wire from terminal “B” of the voltage regulator. You can check with an ohmmeter or with a lamp (1 ... 5 W, 12 V) and a battery.
In order to simplify the mounting of the rectifier parts, three valves (with a red mark) create a rectified voltage on the plus case. These valves are "positive" and they are pressed into one plate of the rectifier unit connected to the terminal "30" of the generator. The other three gates ("negative" with a black mark) have a rectified voltage on the minus case. They are pressed into another plate of the rectifier unit, connected to the "mass".
First check for a short in the “positive” and “negative” valves at the same time. To do this, connect the “plus” of the battery through the lamp to the terminal “30” of the generator, and the “minus” to the generator housing:

If the lamp is on, the “negative” and “positive” valves have a short circuit.
The short circuit of the "negative" valves can be checked by connecting the "plus" of the battery through the lamp with one of the bolts of the rectifier unit, and the "minus" with the generator housing:

Lamp burning means a short circuit in one or more "negative" valves. It should be remembered that in this case, the burning of the lamp may also be a consequence of the closure of the turns of the stator winding to the generator housing. However, such a malfunction is less common than a short circuit in the valves.
To check the short circuit in the "positive" valves "plus" of the battery through the lamp, connect to the clamp 30 of the generator, and the "minus" - with one of the bolts of the rectifier unit:

A burning lamp indicates a short circuit in one or more “positive” valves.
An open in the valves without disassembling the generator can be detected either by an oscilloscope, or when checking the generator at the bench for a significant decrease (by 20-30%) in the magnitude of the output current compared to the nominal one. If the windings, additional diodes and the generator voltage regulator are operational, and there is no short circuit in the valves, then the cause of the decrease in the output current is an open in the valves.
Checking Additional Diodes
A short circuit of additional diodes can be checked according to the scheme:

Connect the “Plus” of the battery through the lamp (1 ... 3 W, 12 V) to the “61” terminal of the generator, and the “minus” to one of the bolts securing the rectifier unit.
If the lamp lights up, then in some of the additional diodes there is a short circuit. You can find a damaged diode only by removing the rectifier unit and checking each diode individually.
An open in the additional diodes can be detected by the oscilloscope by distorting the voltage curve at plug "61", as well as by low voltage (below 14 V) at plug "61" at an average rotor speed of the generator.
Capacitor check
The capacitor serves to protect the vehicle’s electronic equipment from voltage pulses in the ignition system, and also to reduce radio interference.
Damage to the capacitor or the weakening of its fastening on the generator (deterioration of contact with the ground) is detected by an increase in radio interference when the engine is running.
Tentatively, the health of the capacitor can be checked with a megohmmeter or tester (on a scale of 1 ... 10 MΩ). If there is no break in the capacitor, then at the time of connecting the probe to the terminals of the capacitor, the arrow should deviate in the direction of decreasing resistance, and then gradually return back.
Capacitor capacitance measured with a special device should be 2.2 μF + 20%.
Checking and replacing bearings
Check the bearings with an external inspection, detecting cracks in the cages, wrapping or chipping the metal, the presence of corrosion, etc. Check the ease of rotation and the absence of strong play and noise. If the bearing is heavily worn or damaged, it must be replaced.
The procedure for replacing bearings (the generator is removed from the car).
- Remove the back cover along with the air intake pipe.
- Remove the voltage regulator.
- Unscrew the alternator pulley and pull out the key.
- Unscrew the 4 nuts of the coupling bolts and remove the front cover of the generator along with the rotor and bearings.
- Remove the defective bearing from the cover on the drive side. Unscrew the nuts of the screws that tighten the bearing washers, remove the washers with screws and press out the bearing on a hand press. If the screw nuts do not loosen (the ends of the screws are open), cut off the ends of the screws.
- Press in a new bearing. To do this, put the new bearing on the seat, and on top of it - the old one. With gentle hammer blows, against the old bearing, upset the new bearing in the seat. If the bearing comes with a tight fit, spray WD-40 liquid onto its outer ring.
- Using a puller, compress the second bearing on the back of the rotor.
- Press in a new bearing (see item 6).
- Reassemble in the reverse order.
Lid check
An external inspection determines the absence of cracks passing through the bearing housing, broken parts of the generator mounting paws, and severe damage to the seats. If there is such damage, the cover must be replaced. If there is strong wear on the bearing seats, replace the covers.
Generator troubleshooting by schemes
Typical generator malfunctions
|
Reasons for the malfunction |
Remedy |
|
The LED (lamp) of the voltmeter does not light up when the ignition is turned on. Control devices do not work |
|
|
1. The LED (lamp) of the voltmeter is damaged |
Replace the LED (lamp) of the voltmeter |
|
2. Blown No. 2 fuse in the fuse box |
Replace fuse |
|
3. An open in the power circuit of the instrument cluster: |
|
|
no voltage is supplied from plug “B” of the fuse box to the instrument cluster |
check wire “O” and its connections from the fuse box to the instrument cluster |
|
no voltage is supplied from the ignition relay to plug “B” of the fuse box |
check the "warhead" wire and its connections from the fuse box to the ignition relay |
|
open or broken contact in the wire connecting the instrument cluster to the ground |
check wire "H" and its connections from the instrument cluster to ground |
|
4. The switch or ignition relay does not work: |
|
|
malfunctioning contact part or ignition relay |
check, replace the contact part of the switch or ignition relay |
|
no voltage is supplied from the switch to the ignition relay |
check wire "H" and its connections between the switch and the ignition relay |
|
open or broken contact in the wire connecting to the "ground" ignition relay |
check the wire "H" and its connections from the ignition relay to the "mass" |
|
5. Damaged voltage regulator in the instrument cluster |
Replace voltage regulator |
|
When the ignition is turned on and after the engine is started, the LED / lamp of the voltmeter does not light, the battery is discharged |
|
|
Faulty generator field circuit: |
|
|
1. Blown No. 2 fuse |
Replace fuse |
|
2. Open circuit in the circuit: fuse No. 2 - instrument cluster; a combination of devices - the relay regulator. |
Find and repair a cliff |
|
3. In the dashboard; burned out LED / lamp; open circuit of conductors; faulty quenching resistance or poor soldering of its terminals |
Replace LED / lamp; repair open circuit of conductors; replace or solder the resistance. |
|
4. There is no "mass" between the housing and the relay-regulator |
Clean oxides and dirt from the junction of the relay regulator to the generator |
|
5. Faulty relay controller |
Replace regulator relay |
|
6. Open rotor winding |
Replace rotor |
|
The voltmeter LED is on when the engine is running. The battery is low |
|
|
1. Belt drive belt slippage |
Adjust belt tension |
|
2. There is no contact between the terminals "H" and "W" of the voltage regulator and the terminals of the brushes |
Strip the terminals "H" and "W" of the voltage regulator and brushes, bend the terminals of the regulator |
|
3. An open in the circuit between the instrument cluster and the generator plug "61" |
Check the "KB" wire and its connections from the generator to the instrument cluster |
|
4. Worn or stuck brushes, oxidation of slip rings |
Replace the brush holder with brushes, wipe the rings with a cloth soaked in gasoline |
|
5. The voltage regulator is damaged |
Replace voltage regulator |
|
6. Damaged rectifier block valves |
Replace the rectifier unit |
|
7. Damaged field winding power diodes |
Replace diodes or rectifier unit |
|
8. Soldering the conclusions of the field winding from the contact rings |
Solder leads or replace alternator rotor |
|
9. Open or short circuit in the stator winding, shorting it to ground |
Replace the generator stator |
|
The battery discharges during operation, but there are no external signs of abnormal operation of the generator |
|
|
1. Faulty battery: oxidation of wires or battery terminals; not enough electrolyte; closure of one or several cans |
Clean wires / terminals; add distilled water; replace battery |
|
2. Dirt, oiling, oxidation of rotor slip rings |
Clean contact rings with a cloth dampened with gasoline and fine sandpaper. |
|
3. Dirt, oiling the brushes of the relay-regulator or poor contact due to excessive wear |
Clean the brushes from dirt with a rag dipped in gasoline. Replace the relay controller assembly. (For relays-regulators of the old model, it is enough to replace only the brushes) |
|
4. Overexpenditure of energy by powerful / additional consumers |
Replace the generator with another, more powerful (VAZ-2108 - 955.3701; GAZ-3102) |
|
5. Inter-turn circuit or break of one of the phases of the stator winding |
Replace the stator winding. |
|
The voltmeter LED flashes when the engine is running. The battery is being recharged. |
|
|
The voltage regulator is damaged (short circuit between terminal "Ш" and "ground") |
Replace voltage regulator |
|
The control lamp lights up at full speed when the engine is running |
|
|
Defective additional and / or rectifier diodes |
Replace diodes or rectifier assembly |
|
Increased generator noise |
|
|
1. The pulley nut of the generator is loosened |
Tighten the nut |
|
2. Damaged rotor bearings or their seats |
Replace bearings, generator cover / covers |
|
3. Inter-turn circuit or short circuit to the "mass" of the stator winding (howling generator) |
Replace stator |
|
4. Short circuit in one of the generator valves |
Replace the rectifier unit |
|
5. Squeaking brushes |
Wipe the brushes and slip rings with a cotton dampened cloth |
|
6. Impact of the rotor at the stator poles |
Replace rotor, stator. Pay attention to bearings |
|
Quick wear of brushes and slip rings |
|
|
1. Oil or dirt entering contact rings |
Clean the slip rings with a cloth dampened with gasoline and fine sandpaper. |
|
2. Increased runout of slip rings |
Replace rotor |
Attention! The "minus" of the battery must always be connected to ground, and the "plus" - is connected to the terminal "30" of the generator. Erroneous reverse switching of the battery will immediately cause increased current through the generator valves, and they will fail.
The generator is not allowed to work with the battery disconnected. This will cause the occurrence of short-term overvoltages at the terminal "30" of the generator, which can damage the voltage regulator of the generator and electronic devices in the on-board network of the car.
It is forbidden to check the generator’s operability "for spark" even by short-term connection of the generator clamp "30" to the "mass". At the same time, a significant current flows through the valves and they are damaged. The generator can only be checked with an ammeter or voltmeter.
It is not allowed to check the generator valves with a voltage of more than 12 V or a megger, since it has a voltage too high for the valves and they will be broken during the test (short circuit will occur).
It is forbidden to check the electrical wiring of the car with a megger or a lamp powered by a voltage of more than 12 V. If such a check is necessary, you must first disconnect the wires from the generator.
Check the insulation resistance of the stator winding of the generator with high voltage should only be on the stand and always with the outputs of the phase windings disconnected from the valves.
When welding units and parts of the car body, disconnect the wires from all terminals of the generator and the battery terminals.