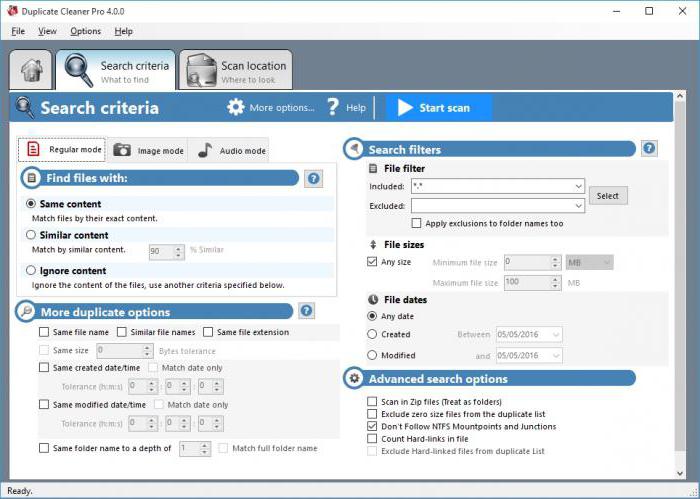
A solid-state drive has a rather high service life due to the technology of leveling wear and reservation of a certain space for the needs of the controller. However, during prolonged use, in order to avoid data loss, it is necessary to periodically evaluate the performance of the disk. This is true for those cases when you need to check after acquiring a second-hand SSD.
Checking the status of the solid state drive is performed using special utilities based on S.M.A.R.T. In turn, this abbreviation stands for Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology, and translated from English means technology of self-monitoring, analysis and reporting. It contains many attributes, but here more emphasis will be placed on the parameters characterizing the wear and tear of the SSD.
If the SSD was in operation, make sure that it is detected in the BIOS and directly by the system itself after it is connected to the computer.
Method 1: SSDlife Pro
SSDlife Pro is a popular utility for assessing the "health" of solid state drives.

Erase fail count shows the number of failed attempts to clear memory cells. In fact, this indicates the presence of broken blocks. The higher this value, the higher the likelihood that the disk will soon become inoperative.
Unexpected Power Loss Count - parameter showing the number of sudden power outages. It is important because NAND memory is vulnerable to such phenomena. If a high value is found, it is recommended to check all the connections between the board and the drive, and then re-check. If the number does not change, the SDS most likely needs to be replaced.
Initial Bad Blocks Count displays the number of failed cells; therefore, it is a critical parameter on which the further performance of the disk depends. Here it is recommended to look at the change in value for some time. If the value remains unchanged, then most likely with the SSD everything is in order.

For some drive models, the option SSD Life Left, which shows the remaining resource as a percentage. The lower the value, the worse the condition of the SSD. The disadvantage of the program is that viewing S.M.A.R.T. Available only in the paid Pro version.
Method 2: CrystalDiskInfo
Method 3: HDDScan
HDDScan is a program that is designed to test drives for performance.


If any parameter exceeds the permissible value, its status will be marked with "Attention".
Method 4: SSDReady
SSDReady is a software tool that is designed to evaluate the life of an SSD.


Method 5: SanDisk SSD Dashboard
Unlike the software discussed above, SanDisk SSD Dashboard is a proprietary Russian-language utility designed to work with solid-state drives of the same manufacturer.


Conclusion
Thus, all the above methods are suitable for assessing the overall health of the SSD. In most cases, you will have to deal with SMART disk data. For an accurate assessment of the health and residual life of the drive, it is better to use proprietary software from the manufacturer, which has the appropriate functions.
Diagnosing the state of an SSD drive is a must, because the resource of such media is limited. Although the creators write the approximate date of model development, you can extend the life of the device if you regularly check it.
SSD speed test
There are no moving parts in the design of solid state bodies, and DDR DRAM transmits information. SSD works by analogy. Data recording is carried out in parallel. It is not necessary to transfer files for further reading to reading heads, as is the case with HDD. Ssd does not have such heads at all, which increases productivity.
For comparison: the average speed of modern HDDs with average characteristics is 60 MB / s, the solid state drive, all other things being equal, during the test shows the result 4-5 times higher. The same story with the launch: in HDD, this process from zero to full readiness will take 30-60 seconds, while an SSD will cope twice as fast.

Drive speed indicators are determined by various testers (benchmarks), which, as mentioned above, consume SSD resources. In order not to waste the power of the ssd disk, it is better not to abuse such software. But sometimes you need to do this, because how else to find out if the disk is in order. The following are programs designed to check such media for errors, as well as speed tests that do not exhaust disk resources.
Programs for monitoring the status of SSDs on Windows:
How to test SSD? Below are six utilities that will help with this.
The software enables knowledgeable users not only to identify a problem, but also to quickly fix it. The option is also suitable for monitoring hard drives.
Key software features:
- Temperature control and health check device.
- Auto power control in emergency situations, as well as creating backup copies of data.
- Browse and configure S.M.A.R.T. attributes.
- Timelines.
- Creating reports on the status of the device.
- Troubleshoot caused by system errors.
- This utility for checking ssd also allows you to protect information on it with a password.
- Support for hot keys.

Software has more than enough pluses, but alas, there are also disadvantages. First of all, these are certain difficulties in work. It’s not so easy for beginners with program features and function management to figure it out. And the second significant drawback is the consumption of system resources, namely RAM and the central processor, even in standby mode. If the computer is not enough - during the diagnosis it will “slow down”.
Another suitable software for diagnosing the state of solid-state drives, which may well be applied to the HDD. The program interacts comfortably with all versions: from XP to the "top ten."

3 main features of the program:
- The software is suitable for personal PCs or laptops as well as for corporate networks.
- The utility analyzes the drive and provides a lot of useful data, including an approximate date of mining, as well as operating modes supported by a particular model.
- It’s convenient to work with Active SMART, because a very detailed guide is attached to it. In addition, you can choose the Russian language, which makes the interface intuitive.
The program was created to monitor the state of a data warehouse with support for S.M.A.R.T. The utility is shareware. The software trial period is two weeks. Testing SDD for errors with this program is easy: it can report problems in time. In addition, for beginners, developers have introduced a simplified mode.
What HDI can do:
- show the basic characteristics of the disk;
- check for errors, test performance;
- describe the current state of the drive in text form;
- make recommendations;
- test the temperature;
- predict date T.E.C. (Threshold Exceed Condition) - the approximate term for the termination of work.

There is also an advanced mode for experienced ones, which makes it possible to learn more about your SSD.
|
Additional program features / advanced mode |
|
|---|---|
| Technical information | firmware; |
| "geometry"; | |
| buffer volume | |
| supported data transfer modes. | |
| Information about S.M.A.R.T. table attributes | name and description, current status, value and flags. |
| Chart S.M.A.R.T | graphical representation of the T.E.C. prediction algorithm |
|
A brief description of the interface and basic features |
|
|---|---|
| View | What shows |
| A panel that displays all drives detected by software in the system | Through it, you can switch between existing devices. Also in the program are the media characteristics: manufacturer, full name of the model, volume, total operating time, etc. |
| Two indicators | display the general status of the disk. The program independently evaluates the values \u200b\u200bof all monitored parameters and issues an opinion on the status and temperature of the device. Blue color means that the drive is in good condition. Yellow - a warning that one of the parameters is close to critical. Red - poor technical condition. Gray - the program cannot determine the parameters of the device. |
| The largest part of the main window | shows data on basic parameters, based on which CrystallDiskInfo concludes the status of the disk. |

It’s convenient that you don’t need to know specific parameter values. The program performs all actions automatically, after which it sends a corresponding signal with a color indicator.
A tool that helps you find problems in the drive. With it, you can save time and save information. You don’t have to pay to download the program. It is suitable for different versions of Windows, including XP (SP2), Vista, Seven, as well as 2003 (SP2), Server 2008
6 main software skills:
- checks the status of disks automatically;
- monitors event logs
- instantly reports a problem;
- reports once a week;
- supports RAID;
- checks using S.M.A.R.T. technology or user script.

Like other utilities, this one has its drawbacks. So, the system indicates an error, but does not give hints on its solution. You can easily receive messages from the program by mail if you are using an SMTP server. But if the Exchange server is available to the user, then you will have to tinker with the notification settings.
Important: not all software versions are designed for SSD.
Programs for monitoring the status of SSDs on Mac:
The utility shows everything that is happening with the disk, well, in great detail. The tab - the namesake of the installed SSD - will tell you a lot of useful things. In particular, it reflects:
- basic information;
- problem reports
- health indicator.
Note: to display all the indicator icons, you need to go to the appropriate tab.

The statistical section deserves special attention. Entering it, you can see:
- how many logical sectors the disk wrote and read;
- are there any errors in the interface;
- information regarding forced reboots, etc.
All errors are recorded, which will establish the cause of the problem and eliminate it in time. Testing is performed automatically when the system starts. It is available in two modes - fast or long.
Software works efficiently. Easy to use and quite simple, only here is the free version, alas, no.
A decent product from the developers of the once popular Trim Enabler. The creators did a great job. This is evident both in design and in functions. Now this is not just the software needed to run Trim, but a complete product for monitoring the SSD.

Dashboard shows:
- company-creator and serial of the disk;
- the amount that the medium recorded or read;
- capacity (this concept also includes free and filled volume);
- "thermometer";
- "Health" in general.
Everything is comfortable: just the facts and nothing more.
Visual section- data on the content that is stored on the drive. They are sorted by sector, which allows you to immediately track large files.
Health, as it already becomes clear from the name of the section, it provides detailed information about the technical condition of the device, allowing the user to evaluate its status.
Tip: when buying an SSD, you need to pay attention to the form factor, because not every option fits in a laptop or is suitable for a stationary PC.
Also in the program, you can track the path to a specific file and clear the cache. A free week is given to evaluate the capabilities of Disk Sensei, then you will have to spend money on a license.
When working with PCs with hard drives, a lot of things connect us. We often copy and transfer a lot of information, install programs. In this regard, there are many overwrites, the disk is constantly working, which means that over time its condition will worsen.
In this article I want to tell you about tools that will help you find out the status of your hard drive or. To start, let's start with the tools that are built into Windows, because some are outraged by the fact that many blogs often describe third-party programs for this matter.
How to check the status of the hard drive using Windows 10?
Below I will discuss how to use the tool to check the status, but before starting, I will say a few words about this method.
When using this method, you will be shown two states: All disks are working normally, or working badly. Encouraging, right?
How good or how bad the disk is unknown, since the system takes information from S.M.A.R.T - analysis or self-monitoring of the hard disk. If a value is displayed Good, then the drive is working properly, if Bad, then something is wrong with the disk. You will not learn more information about the disc using this tool. Output? So-so tool, it is better to use third-party applications, as if you did not want it.
Who wants to try it all, here is the instruction:
- Press the Win + X keys and select "Control Panel";
- We pass to the section "System and Security";
- Security and Service Center;
- Open the “Service” tab;
- We are looking for an item.
We will use the program and see what information it will show us.
Information about the disk, as we see, abound. If the condition is bad, the program will say this. I am fine with both discs.

You can also use the program. There the information can be indicated in English, but I think you’ll figure it out, all the more Yandex and Google translators are available.

Useful articles:
CHKDSK Disk Checker
Actually, the built-in utility chkdsk is not designed to check the status of a hard disk; it is needed to fix errors related to a file system, such as NTFS. Also, the utility is unable to fix bad blocks.
In our case, we will do the following. Let's run the chkdsk utility, which will generate a report for us about the file system, but not about the state of the hard drive.
Go to "Computer" and right-click on the disk you are interested in, say (C :). Select item "Properties".
Go to the tab "Service" and click on the button "Verify" section "Checking for errors."

A window appears in which we click on the "Check disk" button. We are waiting for some time.


As soon as the process is completed, the tool will notify you of this. To find out more information, click on the button. Show Details. A window immediately opens in which you need to double-click on the specified item "Intelligence".

The General tab will show basic information about the file system, I hope you have no problems there. If you wish, you can copy this information.

How to start chkdsk using the command line?
Very simple. Open the command line and enter the command with the following key.
/ f - checking the disk for file system errors and fixing them.
If you check the drive “E:”, the command will look like this:
chkdsk e: / f

Articles where the chkdsk command applies:
-
I think that Victoria needs to be sorted out, since it is very useful and provides not only useful information, but also allows various software manipulations on disks, for example, fixing bad sectors.
And that’s all, don’t forget to subscribe to the social. network and monitor the appearance of relevant information.
HDDScan
The program is designed to check hard drives and SSDs for bad sectors, view S.M.A.R.T. attributes, changes to special settings, such as: power management, start / stop of the spindle, adjustment of the acoustic mode, etc. It is possible to output the temperature of the drive to the taskbar.
Features and requirements
Supported drive types:- HDD with ATA / SATA interface.
- HDD with SCSI interface.
- USB HDD (see Appendix A).
- HDD with FireWire or IEEE 1394 interface (see Appendix A).
- RAID arrays with ATA / SATA / SCSI interface (tests only).
- USB flash drives (tests only).
- SSD with ATA / SATA interface.
- Test in linear verification mode.
- Test in linear reading mode.
- Test in linear recording mode.
- Butterfly reading test (artificial random reading test)
- Reading and analysis S.M.A.R.T. parameters from disks with the ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire interface.
- Reading and analyzing log tables from SCSI drives.
- Launch S.M.A.R.T. tests on drives with ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire interface.
- Temperature monitor on drives with ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire / SCSI interface.
- Reading and analysis of identification information from ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire / SCSI drives.
- Changing AAM, APM, PM parameters on ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire drives.
- View defect information on a SCSI drive.
- Spindle start / stop on ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire / SCSI drives.
- Saving reports in MHT format.
- Printing reports.
- Support for "skins".
- Command line support.
- Support for SSD drives.
- Operating System: Windows XP SP3, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10 (NEW).
- The program should not be launched from a drive that is in read-only mode.
User interface
The main view of the program at startup
Fig. 1 Main view of the program
Main window controls:
- Select Drive - a drop-down list that contains all the supported drives in the system. The drive model and serial number are displayed. Nearby is an icon identifying the alleged type of drive.
- S.M.A.R.T. Button - allows you to get a report on the status of the drive, made on the basis of the attributes S.M.A.R.T.
- TESTS button - shows a pop-up menu with a choice of read and write tests (see. Fig. 2).
- TOOLS button - shows a pop-up menu for selecting available controls and disk functions (see Fig. 3).
- Button More - shows a drop-down menu with program controls.
When you press the TESTS button, a pop-up menu offers you one of the tests. If you select a test, the test dialog box will open (see Figure 4).
Fig. 2 Test menu

When you press the TOOLS button, a pop-up menu will prompt you to select one of the following options:
Fig. 3 Function Menu

- DRIVE ID - Generates an identity information report.
- FEATURES - opens a window of additional features of the program.
- S.M.A.R.T. TEST - opens the window S.M.A.R.T. tests: Short, Extended, Conveyance.
- TEMP MON - launches a temperature monitoring task.
- COMMAND - opens a command line build window.
Test Dialog Box
Fig. 4 Test dialog

Controls:
- FIRST SECTOR field - initial logical sector number for testing.
- SIZE field - the number of logical sector numbers for testing.
- BLOCK SIZE field - block size in sectors for testing.
- Button Previous - returns to the main program window.
- Next button - adds a test to the task queue.
- Only one surface test can be run at a time. This is due to the fact that the author of the program has not yet been able to obtain stable qualitative results when running 2 or more tests at the same time (on different drives).
- A test in Verify mode may have a block size limit of 256, 16384, or 65536 sectors. This is due to the features of Windows.
- Test in Verify mode may not work correctly on USB / Flash drives.
- When testing in Verify mode, the drive reads the data block into the internal buffer and checks its integrity; data transfer via the interface does not occur. The program measures the drive ready time after performing this operation after each block and displays the results. Blocks are tested sequentially - from minimum to maximum.
- When testing in Read mode, the drive reads data into the internal buffer, after which the data is transmitted via the interface and stored in the program’s temporary buffer. The program measures the total readiness of the drive and data transfer after each block and displays the results. Blocks are tested sequentially - from minimum to maximum.
- When testing in Erase mode, the program prepares a block of data filled with a special pattern with a sector number and transfers data to the drive, the drive writes the received block information in the block is irretrievably lost!) The program measures the total transmission and recording time of the block and the readiness of the drive after each block and displays the results. Blocks are tested sequentially - from minimum to maximum.
- Testing in Butterfly Read mode is similar to testing in Read mode. The difference is in the order of testing the blocks. Blocks are processed in pairs. The first block in the first pair will be Block 0. The second block in the first pair will be Block N, where N is the last block of a given section. The next pair will be Block 1, Block N-1, etc. Testing ends in the middle of a given section. This test measures reading time and positioning.
Task management window
Fig. 5 Task Manager

This window contains the task queue. This includes all the tests that the program launches, as well as the temperature monitor. The manager allows you to remove tests from the queue. Some tasks can be paused or stopped.
Double-clicking on the entries in the queue brings up a window with information about the current task.
Tests info window
The window contains information about the test, allows you to pause or stop the test, and also generates a report.
Graph Tab:
It contains information on the dependence of the test speed on the block number, which is presented in the form of a graph.
Fig. 6 Graph Tab

Map Tab:
It contains information about the dependence of testing time on the block number, which is presented in the form of a map.
Fig. 7 Map Tab

You can select “Block Processing Time” in milliseconds. Each tested block that takes longer than “Block Processing Time” will be logged on the “Report” tab.
Report Tab:
Contains information about the test and all blocks whose testing time is longer than the "Block Processing Time".
Fig. 8 Report Tab
Identification information
The report contains information about the main physical and logical parameters of the drive.
The report can be printed and saved to an MHT file.
Fig. 9 Example identity window

S.M.A.R.T. report
The report contains information about the performance and “health” of the drive in the form of attributes. If, according to the program, the attribute is normal, then the green icon is next to it. Yellow indicates the attributes that you should pay particular attention to, as a rule, they indicate any malfunction of the drive. Red indicates attributes that are outside the normal range.
Reports can be printed or saved to a file of type MHT.
Fig. 10 Sample Report S.M.A.R.T.

Temperature monitor
Allows you to estimate the temperature of the drive. Information is displayed in the taskbar, as well as in a special window for information about the test. Fig. 11 contains readings for two drives.
Fig. 11 Taskbar temperature monitor

For ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire drives, the information window contains 2 values. The second value is displayed in the taskbar.
The first value is taken from the Airflow Temperature attribute, the second value is taken from the HDA Temperature attribute.
Fig. 12 Temperature monitor for ATA / SATA drive

For SCSI drives, the information window contains 2 values. The second value is displayed in the taskbar.
The first value contains the maximum allowable temperature for the drive, the second shows the current temperature.
Fig. 13 Temperature Monitor for SCSI Disk

S.M.A.R.T. tests
The program allows you to run three types of S.M.A.R.T. tests:
- Short test - usually lasts 1-2 minutes. Checks the main nodes of the drive, and also scans a small portion of the drive surface and sectors located in the Pending-List (sectors that may contain read errors). The test is recommended for a quick assessment of the state of the drive.
- Extended test - usually lasts from 0.5 to 60 hours. Checks the main components of the drive, and also completely scans the surface of the drive.
- Conveyance test - usually lasts a few minutes. Checks the nodes and logs of the drive, which may indicate improper storage or transportation of the drive.
The SMART test can be selected from the SMART Tests dialog box, called up by pressing the SMART TESTS button.
Fig. 14 SMART Tests Dialog Box

Once selected, the test will be added to the Tasks queue. Information window S.M.A.R.T. The test can display the status of the completion and completion of the task.
Fig. 15 Information window S.M.A.R.T. test

Additional features
For ATA / SATA / USB / FireWire drives, the program allows you to change some parameters.
- AAM - function controls the noise of the drive. Enabling this function allows you to reduce drive noise due to smoother head positioning. At the same time, the drive loses a little in performance with random access.
- APM - the function allows saving drive power by temporarily reducing the rotation speed (or complete stop) of the drive spindle at the time of inactivity.
- PM - the function allows you to set the spindle stop timer for a specific time. When this is achieved, the spindle will be stopped, provided that the drive is in idle mode. Any program accessing the drive causes the spindle to spin up and reset the timer to zero.
- The program also allows you to stop or start the drive spindle forcibly. Accessing the drive by any program forces the spindle to spin up.
Fig. 16 Information window for additional features of ATA / SATA drive

For SCSI drives, the program allows you to view defect lists and start / stop the spindle.
Fig. 17 Information window for additional SCSI drive capabilities

Command line usage
The program can build a command line to control some parameters of the drive and save this line in a .bat or .cmd file. When such a file is launched, the program is called in the background, changes the drive parameters in accordance with the settings and automatically closes.
Fig. 18 Command line build window

Appendix A: USB / FireWire Drives
If the drive is supported by the program, then tests are available for it, S.M.A.R.T. features and additional features.
If the drive is not supported by the program, then only tests are available for it.
USB / FireWire Drives Supported by the Program:
| Storage device | Controller chip |
| StarTeck IDECase35U2 | Cypress CY7C68001 |
| Wd passpopt | Unknown |
| Iomega PB-10391 | Unknown |
| Seagate ST9000U2 (PN: 9W3638-556) | Cypress CY7C68300B |
| Seagate External Drive (PN: 9W286D) | Cypress CY7C68300B |
| Seagate FreeAgentPro | Oxford |
| CASE SWEXX ST010 | Cypress AT2LP RC7 |
| Vantec CB-ISATAU2 (adapter) | JMicron JM20337 |
| Beyond Micro Mobile Disk 3.5 "120GB | Prolific PL3507 (USB only) |
| Maxtor Personal Storage 3100 | Prolific PL2507 |
| In-System ISD300A | |
| SunPlus SPIF215A | |
| Toshiba USB Mini Hard Drive | Unknown |
| USB Teac HD-15 PUK-B-S | Unknown |
| Transcend StoreJet 35 Ultra (TS1TSJ35U-EU) | Unknown |
| AGEStar FUBCP | JMicron JM20337 |
| USB Teac HD-15 PUK-B-S | Unknown |
| Prolific 2571 | |
| All Drives That Support SAT Protocol | Majority of Modern USB controllers |
USB / FireWire drives that the program possibly supports:
| Storage device | Controller chip |
| AGEStar IUB3A | Cypress |
| AGEStar ICB3RA | Cypress |
| AGEStar IUB3A4 | Cypress |
| AGEStar IUB5A | Cypress |
| AGEStar IUB5P | Cypress |
| AGEStar IUB5S | Cypress |
| AGEStar NUB3AR | Cypress |
| AGEStar IBP2A2 | Cypress |
| AGEStar SCB3AH | JMicron JM2033x |
| AGEStar SCB3AHR | JMicron JM2033x |
| AGEStar CCB3A | JMicron JM2033x |
| AGEStar CCB3AT | JMicron JM2033x |
| AGEStar IUB2A3 | JMicron JM2033x |
| AGEStar SCBP | JMicron JM2033x |
| AGEStar FUBCP | JMicron JM2033x |
| Noontec SU25 | Prolific PL2507 |
| Transcend TS80GHDC2 | Prolific PL2507 |
| Transcend TS40GHDC2 | Prolific PL2507 |
| I-O Data HDP-U series | Unknown |
| I-O Data HDC-U series | Unknown |
| Enermax Vanguard EB206U-B | Unknown |
| Thermaltake Max4 A2295 | Unknown |
| Spire GigaPod SP222 | Unknown |
| Cooler Master - RX-3SB | Unknown |
| MegaDrive200 | Unknown |
| RaidSonic Icy Box IB-250U | Unknown |
| Logitech USB | Unknown |
USB / FireWire drives that the program does not support:
| Storage device | Controller chip |
| Matrix | Genesis Logic GL811E |
| Pine | Genesis Logic GL811E |
| Iomega LDHD250-U | Cypress CY7C68300A |
| Iomega DHD160-U | Prolific PL-2507 (modified firmware) |
| Iomega | |
| Maxtor Personal Storage 3200 | Prolific PL-3507 (modified firmware) |
| Maxtor one-touch | Cypress CY7C68013 |
| Seagate External Drive (PN-9W2063) | Cypress CY7C68013 |
| Seagate Pocket HDD | Unknown |
| SympleTech SympleDrive 9000-40479-002 | CY7C68300A |
| Myson Century CS8818 | |
| Myson Century CS8813 |
Appendix B: SSDs
Support for a particular drive to a large extent depends on the controller installed on it.
SSD drives supported by the program:
| Storage device | Controller chip |
| OCZ Vertex, Vertex Turbo, Agility, Solid 2 | Indilinx IDX110M00 |
| Super Talent STT_FTM28GX25H | Indilinx IDX110M00 |
| Corsair extreme series | Indilinx IDX110M00 |
| Kingston SSDNow M-Series | Intel PC29AS21AA0 G1 |
| Intel X25-M G2 | Intel PC29AS21BA0 G2 |
| OCZ Throttle | JMicron JMF601 |
| Corsair performance series | Samsung S3C29RBB01 |
| Samsung SSDs | Samsung Controllers |
| Crucial and Micron SSDs | Some marvell controllers |
SSD drives that the program possibly supports:
Additional Information
Version HDDScan 3.3 can be downloaded version 2.8
| Support: |
Epigraph
“Never trust a computer that you cannot throw out of a window”
Steve Wozniak
Two months ago I installed an SSD drive in my laptop. He worked great, but last week he suddenly died due to depletion of cells (as I believe). This article is about how this happened and what I did wrong.
Description of the environment
- User: Web developer. That is, things like virtual machines, eclipse, frequent updates of repositories are in use.
- OS: Gentoo. That is, the world is often "rebuilt."
- FS: ext4. That is, a journal is being written.
So, the story begins in April, when, finally, I got a hand to copy the sections on the 64GB SSD broom, bought back in September. I deliberately do not inform the manufacturer and the model, because while I have not yet figured out what happened, it does not really matter.
What have I done to make it work longer
Of course, I studied numerous publications on how to protect SSDs. And here is what I did:- Put noatime for partitions, so that when accessing the file, the record about the last access time is not updated.
- Increased the RAM to the maximum and disabled the swap.
S.M.A.R.T.
Three days before the fall, I became preoccupied with the question: how can I find out if I have enough happiness? I tried the utility smartmontoolsbut she was displaying incorrect information. I had to download the datasheet and write a patch for them.After writing the patch, I dig one interesting parameter: average_number_of erasures / maximum_number_ of erasures \u003d 35000/45000. But after reading that the MLC cells withstand only 10,000 cycles, I decided that these parameters do not mean exactly what I think and scored on them.
Chronicle of the fall
Suddenly, inexplicable things began to happen during work, for example, new programs did not start. For the sake of interest I looked at the very S.M.A.R.T. parameter, it was already 37000/50000 (+2000/5000 for three days). It was already not possible to restart, the file system of the main partition was not read.I started from the compact and started checking. Check showed a lot of broken nodes. During the repair process, the utility began testing for bad sectors and marking them. It all ended the next day with the following result: 60GB of 64GB were marked as bad.
Note: In SSD hard drives, a cell is considered a bat if new information cannot be written there. Reading from such a cell will still be possible. On this aly run utility badblocks in read-only mode, it is unlikely that she will find anything.
I decided to start the flashing utility, because it not only reflashes, but also reformatted the disk. The utility began to format, groaned and showed that a reasonable allowable number of bad sectors had been exceeded, and also that there were failures, so it was not possible to complete the formatting.
After that, the disk began to be defined as a disk with a very strange name, model number and size of 4GB. And, in the future, except for specialized utilities, no one sees it.
I wrote a letter in support of the manufacturer. They recommended me to reflash, if it does not work out, then return it to the seller. Warranty 2 more years, so I’ll try.
I end this section with thanks to Steve Wozniak, who taught me how to make periodic backups.
What happened
Honestly, I myself do not know. I assume the following: S.M.A.R.T. I didn’t lie and the cells really wore out (this indirectly confirms the backup that I did two days before the fall, when unpacking it showed that the creation dates of some files were reset). And when checking for sector troubles, the disk controller simply allowed to mark all cells as broken, in which the permissible number of write cycles was exceeded.What to do if you have an SSD
Windows
Put Windows 7 in it as much as possible optimized for such drives. Also put a lot of RAM.Macos
Most likely, only those computers that will be immediately sold with SSDs are optimized.Freebsd
Put 9.0. Read Linux tips, think about what you can make of them.Linux
- Install the 2.6.33 kernel, in which there is optimization for such disks in the form of the TRIM command.
- Increase memory so that you can safely disable the swap.
- Set for mounted partitions noatime.
- Used a file system made on the principle of copy-on-write or a non-journaled file system (for example ext2).
Currently, copy-on-write FS is rather difficult to use. ZFS so far only works through FUSE. But nilfs and btrfs, when mounting, swear that their format is not finally finalized yet.
- Enable NOOP IO Scheduler, it will allow you to not perform unnecessary useless actions for SSD.
- Conceptually true, but not much help to the drive - transferring temporary files to tmpfs.
- For systems that write intensively to the log, you need to store it in another place. This is mainly true for servers for which the log server is raised without problems.
- Get S.M.A.R.T.-utilities that correctly display the status of the SSD, so that you can periodically monitor the drive.
- Just spare the drive. And for gentushniks, this additionally means not "reassembling the world."
Questions to the habrasociety
- Is it really possible to kill MLC cells in 2 months? Of course, I understand that I did not spare the disc, but I did not do anything supernatural, it just worked as usual.
- Is this a warranty case?
UPD: I had a drive Transcend TS64GSSD25S-M.
UPD2: In the comments, very good reviews about Intel SSDs and SAMSUNG. In addition, people wonder how you can kill an SSD broom so quickly. Believe me, I was perplexed in the same way. Nevertheless, it is possible that this is a hastily tailored SSD series and can be quickly killed.
UPD3: In the comments and