If you open the catalog of an online store on the page with RAM, you can see hundreds of different memory models with completely different characteristics. Such a wide choice is often confusing, especially for inexperienced users who want to choose RAM for their computer. If you are also confused by the variety of choices, then our step-by-step guide should help you.
Step number 1. We select RAM by type and connector.
The first thing to do when choosing RAM for your computer is to decide on the type of memory that you need. Modern computers use four types of memory:
- DDR is the very first DDR variant, now it is extremely rare;
- DDR2 is the second generation of DDR, found in older computers;
- DDR3 is the third generation of DDR, the most common variant at the moment;
- DDR4 is the most modern version of DDR memory found only in new computers;
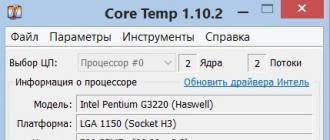
In order to determine which of these types of RAM is used in your computer, run the CPU-Z program and open the "Memory" tab. The memory type, size, frequency and timings will be indicated here.
If you want to get more detailed information about each of the ramps installed in your RAM, then go to the "SPD" tab.

In addition to the type of memory itself (DDR, DDR2, DDR3 and DDR4), it should be borne in mind that different connectors are used for desktops and laptops. Desktop computers use DIMM slots, while laptops use SO-DIMM slots. SO-DIMMs can also be used in compact desktop PCs.
Therefore, in order to be sure that the selected RAM will fit into the memory slot in the motherboard, it is necessary that the memory matches not only the type, but also the connector.
Step number 2. We select the required frequency of the RAM.
After you have decided on the type and connector of RAM, you need to decide on the memory frequency that you need. There are several important points here:
- The memory frequency must be supported. This is usually not a problem. Since modern motherboards support a wide range of RAM frequencies. However, this needs to be checked. To do this, enter the name of your motherboard into the search engine and go to the website of its manufacturer. It will indicate what memory frequencies this board supports.
- Also the memory frequency must be supported. This is checked in the same way. Enter the processor name into the search and see the technical specifications on the manufacturer's official website. Processors are usually more severely limited in their maximum memory frequency.
- After that, determine the maximum frequency of RAM with which the motherboard and processor can work. This is the frequency you can use;
It should be noted that:
- You are not required to buy RAM with the maximum supported frequency. In order to save money, you can use lower frequencies and everything will work. The main thing is that these frequencies are supported by the motherboard and processor.
- If the memory type is the same, then you can install the memory with higher frequencies. But, it will still work at the maximum allowable frequency for the motherboard and processor.
- You can install RAM with different frequencies, but it will work at the frequency of the slowest memory strip. Although it is not advisable to install different memory.
You also need to pay attention to the timings. There are no restrictions from the motherboard or processor, but timings do affect performance. The lower the timings, the faster the memory.
Step number 3. Check the maximum amount of RAM and the availability of free slots on the motherboard.
Another important point to pay attention to when selecting RAM is the maximum amount that the motherboard and processor can support. On the website of the motherboard and processor manufacturer (in the same place where you looked at the frequencies), you need to see the maximum amount of RAM. Obviously, this volume cannot be exceeded.
You also need to check for free slots on the motherboard. To do this, you need to remove the side cover of the computer and inspect the board. The main thing is not to forget to completely disconnect the computer before doing this.
Step number 4. The final stage of selecting RAM for your computer.
It is advisable to always set the same RAM sticks. This avoids compatibility issues that, although very rare, do occur. Therefore, if possible, it is better to install the memory at once as a whole set.
If you cannot install the entire set of memory at once, then you need to choose the most similar memory. Find memory sticks with exactly the same characteristics as those installed in yours (compare the volume of one stick, frequencies, timings).
The set of basic computer components also includes RAM. It is used to store information while performing various tasks. The stability and speed of games and software depends on the type and main characteristics of RAM. Therefore, you must carefully choose this component, having previously studied the recommendations.
There is nothing difficult in choosing RAM, you just need to know its most important characteristics and consider only proven options, since fakes are increasingly found in stores. Let's take a look at a few parameters to watch out for before purchasing.
Optimal amount of RAM
Different tasks require different amounts of memory. A PC for office work is enough 4 GB, which will also allow you to comfortably work on 64-bit OS. If you are using boards with a total capacity of less than 4 GB, then only 32-bit operating systems should be installed on your computer.

Modern games require at least 8 GB of memory, so at the moment this value is optimal, but over time you will have to buy a second die if you are going to play new items. If you plan to work with complex programs or are building a powerful gaming machine, then it is recommended to use from 16 to 32 GB of memory. More than 32 GB is extremely rare, only for very complex tasks.
RAM type
Nowadays, computer memory of the DDR SDRAM type is being produced, and it is divided into several specifications. DDR and DDR2 are outdated, new motherboards do not work with this type, and it becomes difficult to find this type of memory in stores. DDR3 is still actively used and works on many new motherboard models. DDR4 is the most relevant option, we recommend purchasing this type of RAM.
RAM size
It is very important to pay attention to the overall dimensions of the component, so as not to accidentally acquire the wrong form factor. A typical computer has a typical DIMM size, where the contacts are located on both sides of the bracket. And if you see the SO prefix, then the plate has other sizes and is most often used in laptops, but sometimes it can be found in monoblocks or small computers, since the system size does not allow installing DIMMs.

Specified frequency
The frequency of the RAM affects its performance, but it is worth paying attention to whether your motherboard and processor can support the frequencies you need. If not, then the frequency will drop to the one that will be compatible with the components, and you will simply overpay for the module.
At the moment, the most common on the market are models with frequencies of 2133 MHz and 2400 MHz, but their prices practically do not differ, so you should not buy the first option. If you see bars with a frequency higher than 2400 MHz, then you need to take into account that this frequency is achieved thanks to its automatic increase using XMP technology (eXtreme Memory Profile). Not all motherboards support it, so you should be careful when choosing and buying.
Time between operations
The shorter the execution time between operations (Timings), the faster the memory will work. The characteristics indicate four main timings, of which the main one is the latency value (CL). DDR3 has a latency of 9-11, while DDR 4 has a latency of 15-16. The value increases along with the frequency of the RAM.

Multichannel
RAM is capable of operating in single-channel and multi-channel modes (two, three or four channels). In the second mode, information is recorded simultaneously in each module, this provides an increase in performance. DDR2 and DDR motherboards do not support multichannel. Buy only the same modules to enable this mode, normal operation with dies from different manufacturers is not guaranteed.

To enable dual-channel mode, you need 2 or 4 strips of RAM, three-channel - 3 or 6, four-channel - 4 or 8 strips. As for the two-channel operation mode, it is supported by almost all modern motherboards, while the other two are supported only by expensive models. When installing the dies, take a closer look at the connectors. The inclusion of the two-channel mode is carried out by installing the brackets through one (often the connectors have a different color, this will help to connect correctly).

Presence of a heat exchanger
The presence of this component is not always necessary. Only DDR3 memory with a high frequency is very hot. Modern DDR4 is cold, and heatsinks are used only as decoration. Themselves as manufacturers well so inflate the price of models with such an addition. This is what we recommend to save on when choosing a board. Radiators can also interfere with installation and quickly become clogged with dust, which will complicate the process of cleaning the system unit.

Pay attention to the illuminated modules on the heat exchangers if it is important for you to have a beautiful assembly with lighting of everything that is possible. However, the prices for such models are very high, so you will have to overpay if you nevertheless decided to acquire an original solution.
System board connectors
Each type of memory listed has its own type of connector on the motherboard. Be sure to compare these two specifications when purchasing accessories. Let us remind you once again that motherboards for DDR2 are no longer produced, the only solution is to pick up an outdated model in a store or choose from used options.
Top manufacturers
There are not so many RAM manufacturers on the market now, so it will not be difficult to select the best ones. Crucial manufactures optimal modules. Each user will be able to choose the ideal option, the price will also pleasantly surprise.

The most popular and recognizable brand is Corsair. They produce good memory, however the price can be a little overpriced and most models have a built-in heatsink.

Also worth noting are Goodram, AMD and Transcend. They produce inexpensive models that perform well, work stably and for a long time. It is worth noting that AMD most often conflicts with other modules when trying to enable multi-channel mode. We do not recommend purchasing Samsung because of the frequent counterfeits and Kingston because of poor assembly and poor quality.
We examined the main characteristics that you should pay attention to when choosing RAM. Check them out and you will definitely make the right purchase. Once again, I would like to draw your attention to the compatibility of modules with motherboards, be sure to take this into account.
RAM is used for temporary storage of data necessary for the operation of the operating system and all programs. RAM should be enough, if it is not enough, the computer starts to slow down.
A board with memory chips is called a memory module (or strip). Memory for a laptop, except for the size of the brackets, does not differ in any way from memory for a computer, so when choosing, follow the same recommendations.
For an office computer, one 4 GB DDR4 bracket with a frequency of 2400 or 2666 MHz is enough (it costs almost the same).
RAM Crucial CT4G4DFS824A
For a multimedia computer (movies, simple games), it is better to take two DDR4 strips with a frequency of 2666 MHz, 4 GB each, then the memory will work in a faster dual-channel mode.
Ballistix RAM BLS2C4G4D240FSB
For a mid-range gaming computer, you can take one 8 GB DDR4 strip with a frequency of 2666 MHz so that in the future you can add one more and better if it is a simpler running model.
RAM Crucial CT8G4DFS824A
And for a powerful gaming or professional PC, you need to immediately take a set of 2 DDR4 8 GB strips, while the frequency of 2666 MHz will be quite enough.
2. How much memory is needed
For an office computer designed for working with documents and accessing the Internet, one 4 GB memory strip is enough with a head.
For a multimedia computer that can be used to watch videos in high quality and undemanding games, 8 GB of memory is enough.
For a mid-range gaming computer, the minimum option is 8 GB of RAM.
A powerful gaming or professional computer requires 16GB of memory.
More memory may be needed only for very demanding professional programs and is not needed by ordinary users.
Memory for old PCs
If you decide to increase the memory on your old computer, please note that 32-bit versions of Windows do not support more than 3 GB of RAM. That is, if you install 4 GB of RAM, then the operating system will see and use only 3 GB.
As for 64-bit versions of Windows, they will be able to use all the installed memory, but if you have an old computer or have an old printer, then they may not have drivers for these operating systems. In this case, before purchasing memory, install a 64-bit version of Windows and check if everything works for you. I also recommend that you look at the motherboard manufacturer's website and see how much modules and total memory it supports.
Note also that 64-bit operating systems consume 2 times more memory, for example, Windows 7 x64 takes about 800 MB for your needs. Therefore, 2 GB of memory for such a system will not be enough, preferably at least 4 GB.
Practice shows that modern operating systems Windows 7,8,10 are fully disclosed with 8 GB of memory. The system becomes more responsive, programs open faster, and jerks (freezes) disappear in games.
3. Types of memory
Modern memory is of the DDR SDRAM type and is constantly being improved. So DDR and DDR2 memory is already obsolete and can only be used on older computers. DDR3 memory is no longer advisable to use on new PCs, it has been replaced by the faster and more promising DDR4.
Please note that the selected memory type must be supported by the processor and motherboard.
Also, new processors, for compatibility reasons, can support DDR3L memory, which differs from the usual DDR3 by a reduced voltage from 1.5 to 1.35 V. Such processors can work with ordinary DDR3 memory if you already have it, but processor manufacturers do not recommend this from - due to the increased degradation of memory controllers designed for DDR4 with an even lower voltage of 1.2 V.
Memory type for old PCs
Legacy DDR2 memory costs several times more than more modern memory. A 2 GB DDR2 strip costs 2 times more, and a 4 GB DDR2 strip is 4 times more expensive than a DDR3 or DDR4 strip of the same size.
Therefore, if you want to significantly increase the memory on an old computer, then perhaps a better option would be to switch to a more modern platform with a replacement motherboard and, if necessary, a processor that will support DDR4 memory.
Calculate how much it will cost you, perhaps a profitable solution would be to sell an old motherboard with old memory and purchase new, albeit not the most expensive, but more modern components.
The motherboard connectors for installing memory are called slots.

Each type of memory (DDR, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4) has its own slot. DDR3 memory can only be installed in a motherboard with DDR3 slots, DDR4 - with DDR4 slots. Motherboards supporting the old DDR2 memory are no longer manufactured.
5. Memory characteristics
The main characteristics of memory, on which its performance depends, are frequency and timings. Memory speed does not affect the overall performance of a computer as much as a processor does. However, you can often get faster memory for little more. Fast memory is needed primarily for powerful professional computers.
5.1. Memory frequency
Frequency has the greatest impact on memory speed. But before buying it, you need to make sure that the processor and motherboard also support the required frequency. Otherwise, the real memory frequency will be lower and you will simply overpay for something that will not be used.
Inexpensive motherboards support a lower maximum memory frequency, for example 2400 MHz for DDR4. Mid-range and high-end motherboards can support higher frequency memory (3400-3600 MHz).
But with processors, the situation is different. Older processors that support DDR3 memory can support memory with a maximum frequency of 1333, 1600, or 1866 MHz (depending on the model). For modern processors that support DDR4 memory, the maximum supported memory frequency can be 2400 MHz or higher.
Intel 6th Gen processors and above and AMD Ryzen processors support DDR4 2400 MHz or above. Moreover, their lineup includes not only powerful expensive processors, but also processors of the middle and budget class. Thus, you can build a computer on the most modern platform with an inexpensive processor and DDR4 memory, and in the future you can change the processor and get the highest performance.
The main memory for today is DDR4 2400 MHz memory, which is supported by the most modern processors, motherboards and costs the same as DDR4 2133 MHz. Therefore, it makes no sense to purchase DDR4 memory with a frequency of 2133 MHz today.
What memory frequency is supported by a particular processor can be found on the manufacturers' websites:
By model number or serial number, it is very easy to find all the characteristics of any processor on the site:
Or just enter your model number in a Google or Yandex search engine (for example, "Ryzen 7 1800X").
5.2. High frequency memory
Now I want to touch upon another interesting point. On sale you can find RAM of a much higher frequency than any modern processor (3000-3600 MHz and higher) supports. Accordingly, many users are wondering how can this be?
It's all about the technology developed by Intel, eXtreme Memory Profile (XMP). XMP allows memory to run at a higher frequency than the processor officially supports. XMP must be supported by both the memory itself and the motherboard. Memory with a high frequency simply cannot exist without support for this technology, but not all motherboards can boast of its support. These are mainly more expensive models above the middle class.
The essence of XMP technology is that the motherboard automatically increases the frequency of the memory bus, so that the memory starts to work at its higher frequency.
AMD has a similar technology called AMD Memory Profile (AMP), which was supported by older AMD processor motherboards. These motherboards usually supported XMP modules as well.
It makes sense to purchase more expensive memory with a very high frequency and a motherboard with XMP support for very powerful professional computers equipped with a top processor. In a middle-class computer, this will be a waste of money, since everything rests on the performance of other components.
In games, the memory frequency has little effect and there is no point in overpaying, it will be enough to take it at 2400 MHz, or at 2666 MHz if the price difference is small.
For professional applications, you can take memory with a higher frequency - 2666 MHz, or, if you want, and allow 3000 MHz funds. The difference in performance here is greater than in games, but not dramatic, so it makes little sense to drive with the memory frequency.
Let me remind you again that your motherboard must support the memory of the required frequency. In addition, sometimes Intel processors start to work unstable at memory frequencies above 3000 MHz, while Ryzen has this limit around 2900 MHz.
Timings are called delays between read / write / copy operations of data in RAM. Accordingly, the less these delays, the better. But timings have a much smaller impact on memory speed than memory frequency.
There are only 4 main timings that are indicated in the characteristics of memory modules.

Of these, the most important is the first digit, which is called latency (CL).
Typical latency for 1333 MHz DDR3 memory is CL 9, for higher frequency DDR3 memory CL 11.
Typical latency for DDR4 2133MHz memory is CL 15, for higher frequency DDR4 memory CL 16.
You should not buy memory with a latency higher than the indicated one, as this indicates an overall low level of its technical characteristics.
Usually, memory with lower timings is more expensive, but if the difference in price is not significant, then memory with lower latency should be preferred.
5.4. Supply voltage
The memory can be supplied with different voltage. It can be either standard (generally accepted for a certain type of memory), or increased (for enthusiasts), or vice versa, decreased.
This is especially important if you want to add more memory to your computer or laptop. In this case, the tension of the new planks should be the same as that of the existing ones. Otherwise, problems are possible, since most motherboards cannot set different voltages for different modules.
If the voltage is set at a bar with a lower voltage, then the others may not have enough power and the system will not work stably. If the voltage is set at a bar with a higher voltage, then the memory designed for a lower voltage may fail.
If you are assembling a new computer, then this is not so important, but in order to avoid possible compatibility problems with the motherboard and replacement or expansion of memory in the future, it is better to choose brackets with a standard supply voltage.
The memory, depending on the type, has the following standard supply voltages:
- DDR - 2.5V
- DDR2 - 1.8V
- DDR3 - 1.5V
- DDR3L - 1.35V
- DDR4 - 1.2V
I think you noticed that there is DDR3L memory on the list. This is not a new type of memory, but ordinary DDR3, but with a reduced supply voltage (Low). This is the kind of memory required for 6th Gen and higher Intel processors that support both DDR4 and DDR3 memory. But in this case, it is better to build the system on new DDR4 memory.
6. Marking of memory modules
Memory modules are labeled according to the type of memory and its frequency. DDR memory modules are labeled with PC followed by a number indicating generation and speed in megabytes per second (Mb / s).
This marking is inconvenient to navigate, it is enough to know the type of memory (DDR, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4), its frequency and latency. But sometimes, for example on ad sites, you can see the markings rewritten from the bar. Therefore, so that you can navigate in this case, I will give the marking in the classical form, indicating the type of memory, its frequency and typical latency.
DDR - Obsolete
- PC-2100 (DDR 266 MHz) - CL 2.5
- PC-2700 (DDR 333 MHz) - CL 2.5
- PC-3200 (DDR 400 MHz) - CL 2.5
DDR2 - obsolete
- PC2-4200 (DDR2 533 MHz) - CL 5
- PC2-5300 (DDR2 667 MHz) - CL 5
- PC2-6400 (DDR2 800 MHz) - CL 5
- PC2-8500 (DDR2 1066 MHz) - CL 5
DDR3 - Obsolete
- PC3-10600 (DDR3 1333 MHz) - CL 9
- PC3-12800 (DDR3 1600 MHz) - CL 11
- PC3-14400 (DDR3 1866 MHz) - CL 11
- PC3-16000 (DDR3 2000 MHz) - CL 11
- PC4-17000 (DDR4 2133 MHz) - CL 15
- PC4-19200 (DDR4 2400 MHz) - CL 16
- PC4-21300 (DDR4 2666 MHz) - CL 16
- PC4-24000 (DDR4 3000 MHz) - CL 16
- PC4-25600 (DDR4 3200 MHz) - CL 16
DDR3 and DDR4 memory can be at a higher frequency, but only top-end processors and more expensive motherboards can work with it.
7. Design of memory modules
Memory strips can be single-sided, double-sided, with or without heatsinks.
7.1. Chip placement
Chips on memory modules can be placed on one side of the board (single-sided) and on both sides (double-sided).
It doesn't matter if you are purchasing memory for a new computer. If you want to add memory to an old PC, then it is desirable that the location of the chips on the new strip is the same as on the old one. This will help avoid compatibility issues and increase the likelihood of memory working in dual channel mode, which we will discuss later in this article.
Now on sale you can find many memory modules with aluminum heat sinks of various colors and shapes.

The presence of heatsinks can be justified on DDR3 memory with a high frequency (1866 MHz and more), since it gets hotter. At the same time, ventilation must be well organized in the case.
Modern DDR4 RAM with a frequency of 2400, 2666 MHz practically does not heat up and the radiators on it will be purely decorative. They can even get in the way, as after a while they become clogged with dust, which is difficult to clean out of them. Besides, such memory will cost a little more. So, if you want, you can save on this, for example, by taking Crucial's excellent 2400 MHz memory without heatsinks.
Memory with a frequency of 3000 MHz and more also has an increased supply voltage, but it also does not heat up much and in any case there will be radiators on it.
8. Memory for laptops
Notebook memory differs from desktop memory only in the size of the memory module and is marked with SO-DIMM DDR. As well as for stationary computers, memory for laptops has the types DDR, DDR2, DDR3, DDR3L, DDR4.

In terms of frequency, timings and supply voltage, memory for laptops does not differ from memory for computers. But laptops only come with 1 or 2 memory slots and have stricter maximum capacity limits. Be sure to check these parameters before choosing memory for a specific laptop model.
9. Modes of memory operation
The memory can operate in Single Channel, Dual Channel, Triple Channel or Quad Channel.
In single-channel mode, data is written sequentially to each module. In multichannel modes, data is written in parallel to all modules, which leads to a significant increase in the speed of the memory subsystem.
Only hopelessly outdated motherboards with DDR memory and the first models with DDR2 are limited to single-channel memory operation.
All modern motherboards support dual-channel memory operation, while three-channel and four-channel modes are supported only by a few single models of very expensive motherboards.
The main condition for dual-channel operation is the presence of 2 or 4 memory strips. For a three-channel mode, 3 or 6 memory strips are required, and for a four-channel mode, 4 or 8 strips.
It is desirable that all memory modules are the same. Otherwise, dual channel operation is not guaranteed.
If you want to add memory to an old computer and your motherboard supports dual-channel mode, try to choose the most identical bar in all respects. It is best to sell the old one and buy 2 new identical strips.
In modern computers, memory controllers have been moved from the motherboard to the processor. Now it is not so important that the memory modules are the same, as the processor in most cases will still be able to activate dual-channel mode. This means that if in the future you want to add memory to a modern computer, you will not have to look for exactly the same module, it is enough to choose the most similar in characteristics. But still, I recommend that the memory modules are the same. This will give you the guarantee of its fast and stable operation.
With the transfer of memory controllers to the processor, 2 more modes of dual-channel memory operation appeared - Ganged (paired) and Unganged (unpaired). If the memory modules are the same, then the processor can work with them in Ganged mode, as before. If the modules differ in characteristics, the processor can activate the Unganged mode to eliminate distortions in working with memory. On the whole, the memory speed in these modes is practically the same and does not make any difference.
The only drawback of dual channel mode is that multiple memory modules are more expensive than one of the same size. But if you are not very tightly constrained in funds, then buy 2 strips, the memory speed will be much higher.
If you need, say, 16 GB of RAM, but you cannot afford it yet, then you can purchase one 8 GB bar to add another one of the same in the future. But still, it is better to purchase two identical strips at once, since later you may not be able to find the same one and you will face a compatibility problem.
10. Manufacturers of memory modules
One of the best price / quality ratios today has the memory of the impeccably proven brand Crucial, which has modules from budget to gaming (Ballistix).
Along with it, the well-deserved popularity of the Corsair brand competes, the memory of which is somewhat more expensive.
As an inexpensive but high-quality alternative, I especially recommend the Polish brand Goodram, which has bars with low timings for a low price (Play line).
For an inexpensive office computer, a simple and reliable memory from AMD or Transcend will suffice. They have proven themselves perfectly and there are practically no problems with them.
In general, the Korean companies Hynix and Samsung are considered the leaders in memory production. But now modules of these brands are mass-produced in cheap Chinese factories and there are a lot of fakes among them. Therefore, I do not recommend purchasing memory from these brands.
An exception may be Hynix Original and Samsung Original memory modules that are manufactured in Korea. These strips are usually blue, their quality is considered better than the ones made in China and the warranty on them is slightly higher. But in terms of speed characteristics, they are inferior to memory with lower timings of other high-quality brands.
Well, for enthusiasts and mod lovers, there are available overclocking brands GeIL, G.Skill, Team. Their memory is distinguished by low timings, high overclocking potential, unusual appearance and is slightly cheaper than the promoted Corsair brand.
There is also a wide range of memory modules on sale from the very popular manufacturer Kingston. The memory sold under the budget Kingston brand has never been of high quality. But they do have a top-end HyperX series that is well-deservedly popular, which can be recommended for purchase, but it is often overpriced.
11. Packing memory
It is better to purchase individually wrapped memory.

It is usually of a higher quality and the likelihood of damage in transit is much lower than that of a memory that comes unpackaged.
12. Increase memory
If you are planning to add memory to your existing computer or laptop, then first find out what the maximum amount of brackets and the total amount of memory your motherboard or laptop supports.
Also check how many memory slots are on the motherboard or laptop, how many of them are occupied and what brackets are installed in them. Better to do it visually. Open the case, take out the memory sticks, examine them and rewrite all the specifications (or take a photo).
If for some reason you do not want to go into the case, then you can see the memory parameters in the program on the SPD tab. Thus, you will not recognize a one-sided strip or a double-sided one, but you can know the memory characteristics if there is no sticker on the strip.
There is a base and effective memory frequency. The CPU-Z program and many similar ones show the base frequency, it needs to be multiplied by 2.
After you know how much memory you can expand, how many free slots and what memory you have installed, you can start exploring the possibilities for increasing memory.
If all the memory slots are occupied, then the only way to increase the memory is to replace the existing strips with new larger ones. And the old planks can be sold on the ad site or handed over for exchange to a computer store when buying new ones.
If there are free slots, then you can add new ones to the existing memory strips. In this case, it is desirable that the new strips are as close as possible in terms of the characteristics already established. In this case, you can avoid various compatibility issues and increase the chances that the memory will operate in dual channel mode. To do this, the following conditions must be met, in order of importance.
- The memory type must match (DDR, DDR2, DDR3, DDR3L, DDR4).
- The supply voltage for all strips must be the same.
- All planks must be single-sided or double-sided.
- The frequency of all bars must be the same.
- All strips must be of the same size (for two-channel mode).
- The number of strips must be even: 2, 4 (for two-channel mode).
- It is desirable that the latency (CL) matches.
- It is desirable that the slats are from the same manufacturer.
The easiest way to start choosing a manufacturer. Choose in the catalog of the online store the bars of the same manufacturer, volume and frequency as you have set. Make sure the supply voltage matches and check with your consultant if they are one-way or two-way. If the latency still matches, then it's generally good.
If you did not manage to find slats of the same manufacturer, similar in characteristics, then choose all the others from the list of recommended ones. Then again look for the bars of the required volume and frequency, check the supply voltage and specify whether they are one-sided or two-sided. If you can't find similar trims, then look in another store, catalog or classifieds site.
Always the best option is to sell all the old memory and buy 2 new identical strips. If the motherboard does not support the required amount of strips, you may need to buy 4 of the same strips.
13. Setting up filters in the online store
- Go to the "RAM" section on the seller's website.
- Select the recommended manufacturers.
- Select the form factor (DIMM for PC, SO-DIMM for laptop).
- Select the memory type (DDR3, DDR3L, DDR4).
- Select the required amount of strips (2, 4, 8 GB).
- Select the maximum frequency supported by the processor (1600, 1866, 2133, 2400 MHz).
- If your motherboard supports XMP, add higher frequency memory (2666, 3000 MHz) to the sample.
- Sort the sample by price.
- View all positions in sequence, starting with the cheapest ones.
- Select several planks that are suitable for the frequency.
- If the difference in price is acceptable for you, take the bars with higher frequency and lower latency (CL).
Thus, you will get the memory that is optimal in terms of price / quality / speed ratio at the lowest possible cost.
14. Links
RAM Corsair CMK16GX4M2A2400C16
RAM Corsair CMK8GX4M2A2400C16
RAM Crucial CT2K4G4DFS824A
When faced with the problem of optimizing the operation of a computer and increasing its performance, the first step towards solving the problem, which is easiest to do, is to increase rAM size or optimize it by increasing performance. The most optimal option from the proposed ones is to purchase an additional strip of random access memory (RAM) or replace the existing memory strips with those that have a large capacity.
The difficulty of choosing when replacing a Windows RAM module lies in the particular effect of its parameters on the computer's performance. It should be remembered that the RAM communicates with the central processor. The stronger the interconnection of these components, the faster the necessary calculations are carried out in the system. Therefore, the choice of memory must be approached on the basis of the above, and then, RAM, will work with maximum efficiency.
But before going to the store for new planks, you need to install:
- How much memory is currently installed and what is the maximum amount supported by the board?
- What type of memory is supported by the motherboard and processor?
- How many memory slots are there and in what mode do they work?
- What is the memory frequency supported by the processor?
Let's start in order. In general, what is RAM for? In order to temporarily store data to perform current processor operations. The larger it is, the easier it is for the processor to simultaneously perform several tasks.
RAM is volatile, that is, after the computer is turned off, all data on it will be deleted, in contrast to the data that is stored on the hard disk.
How can I find out the current amount of RAM?
To do this, it is not even necessary to open the computer lid - we launch the Speccy utility already known to us and find the current characteristics in it in the corresponding section. In principle, all the main characteristics are already presented here, which we will consider in detail below.
At the moment we are interested in the volume - I have 2 slots on my laptop, both of which are occupied. The total size is 2000 MB (2GB), that is, there are 2 strips of 1 GB on the laptop.
This is quite enough for normal daily work of Windows, but if you plan to play games with complex graphics or use heavy graphics or video programs, then it is advisable to put more.
By the way, each version of the operating system has minimum RAM requirements, without which it simply will not work.
- For Windows XP - At least 64 MB of RAM (at least 128 MB is recommended)
- Windows 10, 7 and 8 - 1 gigabyte (GB) (32-bit) or 2 GB (64-bit) random access memory (RAM).
Even when planning for a larger size, you should check the motherboard or processor specifications for the maximum size supported. This is indicated in the detailed description in the memory section. So, in the Intel Core i54430 model, the maximum size is 32 GB.
For an office PC, which will only work with office documents, 1 GB of memory is enough.
For home, for watching videos, photos, using various applications, it is recommended to use 2 GB or more.
For a powerful gaming computer - 8GB and above.
However, keep in mind that 4 GB or more will only work fully on a 64-bit OS, Windows from 32 will see no more than 3 GB.
Supported RAM type
The next indicator that characterizes the RAM is its type. Let's list them as technologies develop - SDRAMM DIMM, DDR (or PC), DDR2 (PC-2) and DDR3 (PC-3).
As you can see from the above screen from the Speccy program, DDR3 memory is supported on my laptop, although today the latest modern standard is DDR4.
All modern processors work with this standard, however, older boards can also be found on older boards. If your computer is already many years old, then it is likely that it uses an outdated type and the memory module needs to be selected exactly of this standard. Different types of memory modules are incompatible with "foreign" slots on the motherboard.
You can also find out the type of supported RAM from the characteristics of the processor (CPU) or motherboard model on the manufacturer's official website - it is also easy to find out these models in the Speccy program or its analogues.
If you have spare RAM strips in stock, it is also sometimes difficult to determine which type it belongs to. Usually they have a sticker indicating the type - PC, PC-2, PC-3 or DDR, DDR2, DDR3. But if there is no sticker, then we will define it as follows.
DDR and DDR2 strips look very similar and have 1 key (cutout) located almost in the center. But DDR has 180 contacts - 92 on each side. And on DDR2 - 240 - 120 on each side, and they are visually narrower than DDR2. It is easy to count them as they are numbered.
DDR3 modules have the same number of pins as PC-2, but the key is not in the middle, but shifted to the edge.

The memory module of the very old SDRAM standard is distinguished by the presence of two keys.

The number of slots for memory strips and their mode of operation
We also saw the number of slots for mounting brackets in the program - I have 2. If you open the lid of the computer case, you can see several characteristic one- or multi-colored connectors on the board. This is where the memory bars are placed. There are 4 of them in the picture below.

The multicolor tells us that the memory on this board can operate in two-channel mode - that is, data is simultaneously transmitted to the controller to the processor or the north bridge (depending on) via two channels, which increases the data processing speed.
To activate this mode, you must purchase at least 2 strips and, as a rule, insert them into two single-color connectors. Which ones? This is written in the instructions for the board and colors may differ in different models. If you buy 4 modules at once, then use all the slots at once.
It should also be borne in mind that if you currently have a total memory of 2 GB, like mine, and you plan to increase it to 4 GB, then it is optimal to purchase 2 2 GB modules than one 4 GB, since you can use them to the maximum in in two-channel mode.
It should also be noted here that when buying several modules, it is advisable to choose one manufacturer, or even better to take a ready-made kit (KIT), consisting of several strips at once - such a set is guaranteed to work without problems.

Clock frequency
Another important indicator of memory is its clock speed, which is measured in megahertz (MHz). The speed of information processing depends on it. When choosing a module, be sure to check what frequency your processor officially supports. The model shown in the screenshot above works with PC3-12800 (DDR3 1600 MHz), PC3-10600 (DDR3 1333 MHz), PC3-8500 (DDR3 1066 MHz) memory. The same characteristics can be seen on the websites of online stores in the detailed description of memory modules. For example, let's look at a gaming set of 4 4 gig sticks Corsair XMS3 DDR-III DIMM 32Gb KIT 4 * 8Gb:

RAM bandwidth
The frequency also depends on such a parameter as throughput, which shows how much data can be transmitted as much as possible in a certain time. It is measured in megabytes per second (Mb / s) and is calculated by multiplying the frequency by 8. That is, in our example, the memory has a frequency of 1333 MHz * 8 \u003d 10667 Mb / s, which is also seen in the description.
The higher the bandwidth, the higher the speed of the RAM module. However, we take into account the fact that
modern processors support work with memory, which has a maximum frequency of 1600 MHz.
If you buy an expensive bar with a higher frequency, it will work the same as the cheaper one at 1600 MHz.
Timing
Here we can also say about such characteristics as timing. This is the time of delays in processing operations inside the chips of the RAM module. Timing is recorded as a sequence of several digits - in our example, it is 9-9-9-24. The last 4th two-digit parameter characterizes the speed of the entire microcircuit as a whole.
Also, the timing can be indicated by the letters CL and a number that denotes the first value in the detailed sequence. In our example, the short version would be CL9.
The lower the timings, the better, but such modules are also more expensive. However, this only matters for high-performance, high-speed PCs - for home and office, this parameter can be ignored.
Gamers, on the other hand, can use the BIOS settings and manually play with changing timings downward, but this must be done carefully, otherwise you risk spoiling the modules.
RAM for a laptop or desktop computer?
In theory, this is the first question that we should ask ourselves, but essentially not the most important one, since it is simply impossible to confuse the form factor. For a laptop, the modules are wide and short, for a PC, long and narrow.
On sites in the characteristics they are indicated as follows:
- DIMM - for PC,
- SODIMM - for the laptop.

Cooling type for memory strips
If you purchase a RAM module for a powerful gaming computer, then you should pay attention to the type of cooling. With intensive work or "overclocking" by decreasing the timings, they may heat up, so the work of the in-case fans to cool them may not be enough.
On simple strips, there is no cooling at all - you will see open soldered chips of microcircuits. On more expensive models, the most common type of cooling is installed - a metal radiator.

For the most inveterate gamers, they even invented such a thing as water cooling - such modules, together with the system, can significantly exceed the cost of both the motherboard and the processor combined.

Decryption of the RAM module
Now let's decipher the name of the memory module presented in one of the popular online stores:
Crucial Ballistix Sport XT BLS2C4G3D18ADS3CEU DDR-III DIMM 8Gb KIT 2 * 4Gb PC3-14900 CL10
- So, the manufacturer Cruisal, the kit consists of 2 modules of 4 Gb each.
- DDR-III memory and DIMM form factor, that is, for a desktop PC.
- Bandwidth - 14900 Mb / s
- Timing - CL10
- In this case, you need to look at the frequency in the detailed characteristics of the product, or calculate it yourself, dividing the bandwidth (14900) by 8.
Tips to Follow When Buying RAM
- Buy RAM from trusted manufacturers. The price of brand names is much higher, but the quality assurance and stable computer performance are worth it. Here is a list of trusted firms: Corsair, Kingston, Kingmax, Transcend, OCZ, Hynix, Hyundai, Samsung.
- RAM paired with a good quality chipset is the guarantee of maximum performance, considering that the former has a maximum operating frequency.
- Remember that RAM should always be paired. It is necessary that the modules coincide in frequency of operation, the bars installed with different frequencies work at the memory frequency, which is the slowest one that you have installed, or do not work together at all. For example, if you have two channels for RAM and in one of the slots there is a 2GB bar, then you need to purchase another module with the same capacity, timings and from the same manufacturer.
And the best option is to buy a set of modules (Kit), which is guaranteed by the manufacturer that these strips are compatible. - For gaming computers, preference should be given to RAM with the lowest time delays. Even at low frequencies, the memory always performs at its best.
- Remember to make sure your motherboard, processor, and operating system are compatible with the amount of memory you choose. If your computer system is 32-bit, then it is worth purchasing a bar of no more than 4GB, since a 32-bit system sees up to 3GB of RAM.
- When purchasing memory to increase the available RAM, it will be better to purchase a model that has characteristics similar to those installed in your computer. Buying a better or worse bar in terms of characteristics will lead to a deterioration in computer performance.
In conclusion - a detailed video on installing a memory module into a computer.
Good day, dear visitors.
When buying RAM, you need to pay attention to its frequency. Do you know why? If not, I suggest that you read this article, from which you will find out what the frequency of RAM affects. The information can also be useful to those who already know a little about this topic: what if you still don't know something?
Answers on questions
The frequency of the RAM is more correctly called the data transmission frequency. It shows how many of them the device can transmit in one second through the selected channel. Simply put, the performance of the RAM depends on this parameter. The higher it is, the faster it works.
What is measured?
The frequency is calculated in gigatransfers (GT / s), megatransfers (MT / s) or megahertz (MHz). Usually the number is indicated with a hyphen in the device name, for example, DDR3-1333.
However, you should not delude yourself and confuse this number with the real clock frequency, which is half of that stated in the name. This is indicated by the decoding of the abbreviation DDR - Double Data Rate, which translates as double data transfer rate. Therefore, for example, DDR-800 actually operates at 400 MHz.

Maximum possibilities
The fact is that the maximum frequency is written on the device. But this does not mean that all resources will always be used. For this to be possible, the memory needs a corresponding bus and slot on the motherboard with the same bandwidth.
Let's say you decided to install 2 RAMs in order to speed up your computer: DDR3-2400 and 1333. This is a pointless waste of money, because the system can only operate at the maximum capabilities of the weakest module, that is, the second. Also, if you install a DDR3-1800 board in a socket on a motherboard with a bandwidth of 1600 MHz, you will actually get the last figure.

In view of the fact that the device is not intended to constantly operate at maximum, and the motherboard does not meet such requirements, the bandwidth will not increase, but, on the contrary, will decrease. Because of this, errors in the loading and operation of the operating system may occur.
But the parameters of the motherboard and the bus are not all that affect the speed of the RAM, taking into account its frequency. What else? We read further.
Device operating modes
To achieve the most efficiency in the work of RAM, take into account the modes that the motherboard sets for it. They are of several types:
- Single chanell mode (single channel or asymmetric). Works when installing one module or several, but with different characteristics. In the second case, the capabilities of the weakest device are taken into account. An example was given above.
- Dual Mode (two-channel mode or balanced). It comes into effect when two RAMs with the same volume are installed in the motherboard, as a result of which the RAM capacity is theoretically doubled. It is advisable to install devices in slots 1 and 3, or in 2 and 4.
- Triple Mode (three-channel). The same principle as in the previous version, but this does not mean 2, but 3 modules. In practice, the effectiveness of this regime is inferior to the previous one.
- Flex Mode (flexible). It makes it possible to increase memory productivity by installing 2 modules of different sizes, but with the same frequency. As in the symmetrical version, it is necessary to put them in the slots of the same name on different channels.

Timings
In the process of transferring information from the RAM to the processor, timings are of great importance. They determine how many clock cycles of RAM will cause a delay in the return of data that the CPU requests. In simple terms, this parameter specifies the memory delay time.
The measurement is performed in nanoseconds and is written in the device characteristics under the abbreviation CL (CAS Latency). Timings are set in the range from 2 to 9. Let's take an example: a module with CL 9 will delay 9 clock cycles when transmitting information that requires a percentage, and CL 7, as you understand, will delay 7 cycles. Moreover, both boards have the same memory size and clock speed. However, the second will run faster.
From this we draw a simple conclusion: the fewer the number of timings, the higher the speed of the RAM.
That's all.
Armed with the information in this article, you will be able to choose and install the correct RAM according to your needs.