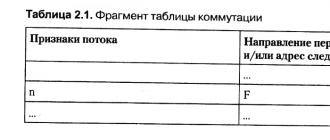
10. Information systems
1. Information systems: definition, purpose of creation, structure.
2. Basic principles of IP development
3. Classification of information systems.
4. Systems of classification and coding of economic information.
IP classes: MR I, MRP II, ERP
1. Information systems: definition, purpose of creation, structure.
Information- this is some information, knowledge about objects and processes of the real world. Economic information is usually displayed in the form of documents.
Document is a material carrier of information that has legal force and is executed in accordance with the established procedure.
System is a complex of interrelated means that act as a whole. Each system is characterized by structure, input and output flows, purpose and restrictions, and a law of functioning.
System covers a complex of interrelated elements that act as a whole in achieving the goals set.
Each system includes components
1. The structure of the system is a set of elements of the system and the relationships between them.
2. Functions of each element of the system
3. Input and output of each element and the system as a whole.
4. Objectives and limitations of the system and its individual elements (achieving cost reduction and increasing profits)
Each system has properties of divisibility and integrity.
IP provides collection, storage, processing of information about the facility supplying workers of various ranks with information for the implementation of management functions.
EIS is system, functioning which is the collection, storage, processing and dissemination of information about the activities of any economic entity in the real world.
EIS are intended for solving problems of processing data of office automation, performing information search and individual tasks based on artificial intelligence methods (from lectures).
Information System (IS) is a software and hardware complex designed for automated collection, storage, processing and delivery of information. Typically, ISs deal with large amounts of information that has a rather complex structure. The classic examples of information systems are banking systems, transport ticketing systems, etc.
IP always specializes in information from a certain area of \u200b\u200bthe real world: economics, technology, medicine, etc. The part of the real world displayed in the IS is called subject area ... Therefore, economic IP is an IP whose subject area is economics. In this sense, it acts as an information model of the subject area.
Any system of management of an economic object has its own information system, called an economic information system.
Economic Information System (EIS) - a set of internal and external flows of direct and feedback information communication of an economic object, methods, means, specialists involved in the process of information processing and the development of management decisions.
The information system is information service system for employees of management services and performs technological functions for the accumulation, storage, transmission and processing of information. It is formed, formed and functions in the regulations determined by the methods and structure of management activities adopted at a specific economic facility, realizes the goals and objectives facing it.
IP structure
The most common division of EIS subsystems is the separation of the supporting and functional parts. The functional part is actually a model of the object management system. As applied to control systems, the feature of structuring can be the object control functions, in accordance with which the EIS consists of functional subsystems. The supporting part of the EIS consists of information, technical, software, organizational, legal and other types of support.
Regardless of the features, any EIS consists of functional and supporting parts. The functional part is determined by the totality of tasks to be solved, identified for certain types of activities of various economic objects (by function).
The supporting part is a complex of interconnected means of a certain type that ensure the functioning of the system as a whole or its individual elements. The supporting subsystems include: information support for IO, technical support for maintenance, software for MO, legal support for Legal A, software software, organizational support for Organizational A, technological support for Tech.
IO is a set of a unified system of classification and coding of information of unified documentation systems, schemes of information flows circulating in organizations, as well as the methodology for constructing an IO database is subdivided into out-of-machine and intra-machine.
Out-of-machine unified documentation system, as well as a classification system for coding accounting information.
Intra-machine - documents and arrays of documents stored in the computer memory in the form of libraries, archives, databases, knowledge bases.
TO - a set of technical means intended for the operation of the IS, as well as the corresponding documentation for these means and technological processes.
Tech.O - focused on the selected information technology for entering the registration of transmission, processing and issuance of effective information. (centralized, distributed, decentralized)
Software - includes: general system and special software products, as well as technical documentation (OS, shells, programs ....)
Mat.O. - a set of mathematical methods, models, algorithms for the implementation of the goals and objectives of the IS, as well as the functioning of the complex of technical means.
Org.O - a set of methods and means that regulate the interaction of workers with technical means and among themselves in the process of developing and operating IS.
Right. - a set of legal norms that determine the creation of the legal status and functioning of IP, governing the procedure for obtaining the transformation and use of information. (from lectures)
The structure of information includes in its totality the following concepts: information space, subject area, object, object instance, object properties, object interaction and interaction properties. To describe a subject area means to enumerate objects and relationships between them, and then describe them with attributes and constituent units of information.
The structure of economic information is quite complex and may include various combinations of information aggregates with a certain content. An information set is understood as a group of data characterizing an object, process, operation. By structural composition, information aggregates can be divided into:
- Performing one or more functions in relation to information;
- Unity of the system, implying the presence of a common file base, uniform standards and protocols, uniform management, and more;
- The ability to perform the specified functions to create compositions and decomposition of system objects.
- Efficiency;
- Functioning quality: consistency with standards, accuracy, security;
- Reliability. The system should not fail on the following thresholds: information quality, access time, performance,
- Safety.
- Documentary. In such information retrieval systems, all stored documents are indexed in a special way. Each individual document is given an individual code, which makes up the search image. That is, the search will be conducted by search images, and not by the documents themselves. Thus, one usually searches for literature in large libraries. The required book is searched for by the number indicated in the catalog card.
- Factographic. These information retrieval systems store facts, not documents; these facts relate to any subject area. The search is carried out on the basis of the fact.
- DB is the database itself;
- DBMS is a database management system.
- Increased resistance to external influences, flexibility and internal control.
- Increasing the competitiveness and efficiency of the company.
- Reducing the cost of goods and services.
- Decrease in warehouse stock.
- Increase in sales of goods and services.
- Improving the interaction with suppliers.
- Reducing the lead time.
- transaction processing;
- decision support;
- knowledge or learning management;
- database management.
- data storage;
- enterprise resource planning schemes;
- expert;
- search engines;
- geographic information;
- global information system;
- office automation.
- A piece of hardware that includes a monitor, processor, printer, and keyboard that work together to receive, process, display data and information.
- Software - programs that enable hardware to process data.
- Databases, which are a repository of related files or tables containing relevant data.
- Networks, which are a nexus system that allows a variety of computers to allocate resources.
- Procedures, which are a set of commands designed to combine the above components in order to process information.
- Recognition and specification problems.
- Collection of information.
- Specification requirements for the new system.
- System design.
- System architecture.
- Implementation.
- Review and maintenance.
requisites,
indicators,
It is worth considering this issue from different points of view, which will create a big picture. Experts say that it is an interconnected set of tools, personnel and methods used to store, process and issue information necessary to solve any specific tasks.
Highlights
Considering, it must be said that it can have a different scale and purpose. There are other features as well. The systems can differ in the degree of coverage of different areas of the company's activities, they can be designed not only for warehouse or accounting, but also for finance, production accounting and control of enterprise document flow.
Regardless of their purpose, they all have a whole set of properties that have become common to them. As the main ones for information processing in any modern system, the use of computers is required. They are tools and technical base in conjunction with specialized programs installed on them. If we talk about what an information system is, then it should be noted that its basis can be called the means developed for storing and accessing data. They are herewith intended for use by the end user, who does not need to be a computer expert. This includes client applications designed to provide an intuitive interface.

IC types
Such systems are divided into documentary and factual. The first are focused on solving problems related to production management, accounting and others like them. The latter are focused on finding unambiguous answers to queries, as well as on solving the problem in only one way. These can be heterogeneous reference systems, search systems, as well as those engaged in operational data processing. Documentary IS are designed to solve problems that do not provide unambiguous answers to questions. Here we can cite as an example which is becoming more and more popular in enterprises lately. Mixed type of IC is allowed.

The scale
Speaking about what an information system is, it is worth touching on such an important issue as its scale. It is customary to distinguish between individual or desktop IS, network, which includes several users, as well as the largest - enterprise scale. It is quite difficult to imagine a modern company without using such a system. It does not matter in which area the activity of the enterprise is concentrated, its size is not so important, its IP in any case serves as a core that ensures effective management of production, trade or timely high-quality services. With its help, it simplifies the solution of managerial tasks, it is possible to free some employees from solving various routine matters, the probability of errors decreases, the number of paper documents decreases, and also there are opportunities for a significant reduction in costs. For this reason, any modern enterprise is distinguished by the fact that everything related to the information system and ensuring its uninterrupted functioning has become the subject of special control by the management personnel.

City information system of cadastral registration
IS of the city cadastre is one of the ways to ensure the information transformation of cadastral data on objects of different types of property in a settlement. It is a complex of technical means and software, material and labor resources, which are aimed at creating information about real estate objects and its full presentation in the form of tangible documents.
The city information system plays a very important role in providing data, since it serves as an effective means of forming an information space, which is used to manage social, economic, economic and other activities in it. In the current socio-economic conditions, the creation of such a space becomes possible only on the basis of absolute automation of such processes as collection, processing, storage and updating of cadastral data on real estate objects. In addition, the provision of information systems provides access to all specified data, operational exchange between government and commercial structures of various kinds, services and organizations of the city.

The need for such a structure
At the moment, certain state, commercial and municipal organizations (land markets, mortgage banks, real estate privatization committees, tax inspectorates, insurance companies and others) can hardly fulfill their direct responsibilities without organizing a timely exchange of cadastral information that is reliable during this period of time. That is why the development of an information system of this kind allows solving not only the problems of protecting property rights and taxation, but also other issues.
Non-cadastral tasks
Prompt, complete and high-quality information support of the authorities that manage the city, commercial, economic and other structures and individual citizens with full and reliable information about the physical condition of real estate objects of different forms of ownership and other elements of the urban environment;
Analysis of the use of infrastructure, natural, labor, material, technical means and resources of the city, their distribution by forms of ownership, etc.
Works on the preparation of urban planning and architectural projects, on the design of utilities and others.

Difficulties in work
The design of information systems of this kind became necessary due to the fact that until recently there were no analogues on the domestic market capable of solving such complex problems. There are no such solutions abroad either, but in recent years, the intensification of work in this area is simply amazing. The first Russian development in this area was the AIS GK, created by the Novosibirsk branch of RosNITs "Earth". It is focused on providing a variety of structures with reliable cadastral information: administration, privatization committee, insurance bureaus, tax inspections, institutions and enterprises, mortgage, land and investment banks, as well as individuals who own real estate.
Features of data accounting
It is important to understand that certain services and organizations of the city are able to be not only passive consumers of cadastral information, but also to form it, having a huge impact on the formation of the urban information space. It is for this reason that the development of the AIS GK was carried out taking into account the possibility of using software products of such users, and also provided for the safety of their fleet of technical measuring instruments. The unified information system was developed taking into account all these features.

Construction principles used
Modularity in terms of construction, which allows to ensure the normal functioning of each individual element, and hence their entire set as a whole;
They have a very flexible software architecture that allows you to include new subscribers in the network and exclude them from it without reducing the operability, reliability and productivity of the entire structure, and does not require any reconfiguration;
Data is fully protected from loss in case of failures or unauthorized access to the IS;
Classification and coding of data on the elements of the urban environment is uniform;
Information is entered in a single format, which became possible due to the use of system configuration tools provided by the operating system and network DBMS;
The results of geodetic changes are processed in a fully automated mode, regardless of what methods were used to collect them;
Information in the database is presented in topological integrity, there is an opportunity for editing all types of cadastral data;
Operational control of the reliability and correctness of data during all operations with them.
Such a unified information system is capable of solving not only directly cadastral problems, but also many others associated with the development of plans for the development of territories and their reorganization, environmental protection, rational placement of housing facilities, modeling traffic flows, property management and much more. In addition, such a system easily absorbs user devices, instruments and computers.
Alternative options
The school information system is a completely new approach to education. Timely data provision is achieved with the help of important elements. For example, an element such as an electronic diary is used to post information about grades and homework, allowing teachers to quickly interact with their students. This includes a student portfolio that demonstrates student activity in and out of school. The school information system supports the use of personal privacy settings through a personal account. Parents can quickly receive reliable information not only about academic performance, but also about homework.
So, all this allows you to understand what an information system is, how it helps in solving many important issues.
The set of software, hardware, organizational support and personnel, which is designed to provide the right people with the information they need in a timely manner, is called an information system. In this article we will talk in more detail about what an information system is, we will give information about some types of existing systems.
Information system
In the second article of the Law on Information, the following definition of IP is given: an information system is a set of information contained in databases and technical means and information technologies that ensure its processing.
IP signs:
Basic requirements for IP:
What is an automated information system
An automated information system is an interconnected set of software, data, standards, equipment, procedures and personnel, which is designed to process and collect, store, distribute and issue information and meets the requirements that arise from the goals of a particular organization.
In essence, AIS is a man-machine system based on an automated technology for obtaining information, which is used to optimize the management process and information support of personnel in specific activities.
Due to the formalization of processing processes and the complexity of structuring information, the automation of information procedures is difficult. The degree of automation of information processes can range from ten to twenty percent.
What is an information retrieval system
The definition of the ISS is as follows: an information retrieval system is an applied computer environment designed to search, collect, process, sort, store and filter large-scale arrays of information in a structured form.
ISS, information retrieval systems are designed to solve certain types of problems, characterized by their own set of objects and their attributes.
IPS, information retrieval systems are subdivided into:
Information retrieval systems, IPS include 2 parts of the database:
DB is a set of structured data that relate to a specific subject area.
DBMS is a set of language and software tools that are necessary for creating a database, keeping them up to date, and organizing the search for the necessary information in them.
The most famous are such DBMS as Microsoft Access, Dbase, FoxPro, Clipper, Paradox.
What is a corporate information system
Any large company, moreover a rapidly developing one, will sooner or later face the problem of organizing information and automation processes that will participate in processing this information.
At the beginning of the development of an organization, it is possible for employees to use standard office applications, but over time, the constant growth of information volumes will set the company the task of organizing a Corporate Information System (CIS).
KIS, Corporate Information System is a scalable system that is designed for the complex automation of economic activities of organizations, corporations, companies that require unified management.
The introduction of the corporate information system, the corporate information system, will give the following results:
All this will contribute to the implementation of the main goal of the corporate information system, the corporate information system, which is to increase the profitability of the organization through the most efficient use of all the company's resources and improve the quality of management decisions made by the management.
We hope that everyone who was interested in the question of what an information system is, could find an answer to it in this article.
Information system (IS) is any organized system for collecting, storing and transmitting information. More deeply, it is the creation of additional sources that people use to obtain, filter and disseminate data.
The definition of "information systems" is associated with computer technology. In other words, it is a kind of complex, implying the work of people and computers, as a result of which information is processed or interpreted. This term is sometimes used in a more limited sense - to refer to the software required to run a computer database, or as a definition of a computer component.
But the emphasis is usually on information systems, the definition of which includes the final surface layer - users, processors, inputs, outputs and the aforementioned communication networks. Any specific IS is aimed at supporting operations, management and decision making.
The definition of an information system can be reduced to the fact that it is information and communication technologies (ICT) that are used by various organizations, as well as the way people interact with these technologies in support of business processes. Some researchers make a clear distinction between information and computer systems and business processes. ICs typically include, but are not directly related to, a computer component. 
Information systems, the definition of which we will consider later in the article, differ from business processes in that they only help control the effectiveness of the latter.
Some scholars have argued for the benefits of IP as a specific type of workflow. However, it is a system in which people or machines perform certain functions and activities using resources to produce specific products or services for customers. While the information system is, as already mentioned, an intellectual complex whose activities are devoted to the collection, transmission, storage, search, processing and display of information.
Information system - what is it?
Thus, ICs are closely related to data transmission systems on the one hand and workflow on the other. They represent a form of interconnection in which data is presented and processed as a form of social memory. The information system (the basic concepts, definitions associated with it, we consider in the article) can also appear as a semi-official language that supports the creation of human decisions and actions. It is a major area of \u200b\u200bresearch for organizational informatics.

Basic concepts, definitions, classification of information systems
There are different types of ICs, for example:
Of decisive importance for most information systems are information technologies, usually designed to perform tasks for which the human brain is not very well suited. For example, processing large amounts of information, performing complex calculations, and managing numerous concurrent processes.
Information technology is a very important and flexible resource available to leaders. Many companies are now recruiting a Chief Executive Officer for these issues. The CTO can also act in this role.

Equipment
The definition of "the essence of an information system" implies the presence of six components that must be combined to create it. And the first is hardware.
This term refers to technology. And it means the computer itself, which is often referred to as a central processing unit (CPU), and all the hardware associated with it to support the operation. Among the auxiliary equipment required for the creation of ICs, one can mention input and output devices, data storage and communication devices.
Software
The next component is software. This term refers to the computer programs and manuals (if any) that support them. There are computer applications, machine-readable instructions, that direct electrical circuitry within the hardware of a system and cause it to function in such a way as to produce useful information from the received data.
Programs are usually stored on some machines, sometimes on removable media.
Data
Another component is data - facts, which are used by programs to obtain useful information. Like programs, data is usually stored in machine-readable form on disk or other storage device until the computer needs it.
Definition of the concept of "information systems" is not possible without taking into account the presence of facts that are processed and systematized.

Procedures
Another component that defines the essence of the described definition is procedures. This term refers to the policy that governs the operation of a computer system. These can be certain requirements and rules on the basis of which the IS functions and develops.
People
Every system also needs people if it is to be useful in some way. Moreover, people are often the most significant element. And this is probably the component that most affects the success or failure of information systems. This item includes not only users, but also those who operate and maintain computers, maintain data and networks, etc.
Feedback
Another component of the IS is feedback (although it is not necessary for functioning).
As noted, data is a kind of bridge between hardware and people. This means that the information we collect is only scattered information until it is systematized. At this stage, the data becomes information and falls into the definition of an information system.

The use of information systems directly depends on their types.
Pyramid
Thus, the classical type of IP is often described in various textbooks. In the 80s, it was presented as a pyramid that reflected the hierarchy of the organization.
As a rule, transaction processing systems were at the bottom of the pyramid, the management of information systems, making decisions to support the system, was located just above, and the executive IS model ended at the top.
This pyramid model remains useful today, since it was the first to formulate a number of new technologies, but some of its components may not be relevant, although they fall under modern information systems, the definition of which we are trying to formulate. Examples of such ICs can be as follows:
Computer ICs
A computer information system is created using computer technology to perform some or all of the scheduled tasks. Its main components are:
Information systems, the definition of which is presented in the article, includes the first four components (hardware, software, databases and networks) into one complex, which is known as an information technology platform.
IT workers can then use them to create ICs that monitor security, risk, and data management. These activities are known as information technology services.

Information systems development
Information technology departments in large organizations tend to greatly influence the development, use and application of information technology. A number of techniques and processes can be used to develop and use IP. Many developers now use an engineering approach such as the Software Life Cycle (SDLC), which is a systematic order of developing an information system through stages that occur in a specific sequence.
IP can be developed internally or externally. This agreement can be achieved by outsourcing specific components or the entire system. A technologically implemented environment for recording, storing and distributing linguistic expressions, for drawing conclusions from such expressions - all this includes the concept of "information systems".
Terms and definitions related to IP are rather complex and do not have a narrow focus, so they can be used in almost any field. But there are also specific areas of their application.
Geographic Information Systems: Definition
Examples of narrower classifications are geographic information systems (GIS) and earth information systems. They allow collecting, storing and analyzing and graphically visualizing spatial data. Their development is carried out in several stages, which include:
Academic discipline
The field of research on the concept of IP covers a variety of topics, including systems analysis and design, computer networks, information security, database management and decision support systems.
The definition of "classification of information systems" currently does not have a unified interpretation. It involves some data management operations, with a practical and theoretical solution to the problems of data collection and analysis. Depending on the field of activity, this can be tools for increasing the productivity of business applications, programming and software implementation, e-commerce, the use of electronic media, data mining and decision support.
Information systems (the definition of this concept was given earlier), serve to unite economics and informatics. They are a field for the study of computers and algorithmic processes, including their principles, software and hardware designs, applications, and their impact on society. Many modern scientists have discussed the nature and foundations of information systems, which have their roots in other reference disciplines - for example, computer science, engineering, mathematics, management, cybernetics, etc.
IC can also be defined as the collection of hardware, software, data, people and procedures that work together to produce quality information. They are directly related to information technology, computer science and business. The study of theory and practice related to social and technological phenomena that determine their development, use and impact on human life is the area of \u200b\u200binterest of those who study information systems.
The definition that the article was devoted to is also used to describe the organizational function that applies this knowledge to industry, government agencies, and non-profit organizations. They often boil down to interactions between algorithmic processes and technologies.
The field of IP study includes the study of theory and practice related to social and technological phenomena that determine the development, use and impact of information systems in an organization and society. In a broad sense, the term "information systems" means a scientific direction of research that considers the strategic, managerial and operational activities to participate in the collection, processing, storage, dissemination and use of information and related technologies in society and organizations.
The term information systems is also used to describe the organizational function that applies this knowledge to industry, government agencies, and non-profit organizations. IP is often limited to interactions between algorithmic processes and technologies. These interactions can occur within or outside organizational boundaries. An information system is a technology that various organizations use for their own purposes.
Information System (IS) is a communication system for the collection, transmission, processing of information about an object, providing an employee of any profession with information for the implementation of the management function.
PROPERTIES OF INFORMATION SYSTEMS:
1. complexity (depends on the components included in it, their structural interaction);
2. divisibility (means that the system can be represented from various independent constituent parts - subsystems);
3. integrity (means that the functioning of many elements of the system is subordinated to one goal);
4. the variety of elements and the difference in their nature (associated with their functional specificity and autonomy);
5. structuredness (determines the presence of established links and relationships between elements within the system, the distribution of elements across the levels of the hierarchy).
Types of systems:
Automatic system (AC) -it is a set of a controlled object and automatic control devices, functioning independently, without human intervention.
Automated system -it is a set of a controlled object and automatic control devices, in which part of the control functions is performed by a human operator. An automated system is a complex of technical, software and other tools and personnel designed to automate various processes, and cannot function without human participation.
Computing system (ВС) -it is a set of computers and software tools designed to perform computational processes.
An open system is a computing system that meets standards. Basic principles of building open systems:
· Portability, allowing you to easily transfer data and software between different platforms;
· Interaction, ensuring the joint operation of devices from different manufacturers;
· Scalability to ensure that your information and software investment is maintained when moving to a more powerful hardware platform.
Database Management System (DBMS) - an integral part of any information system. The type of DBMS used is usually determined by the scale of the IS - small ISs can use local DBMSs, corporate ISs will require a powerful client-server DBMS that supports multi-user work.
IP classification by purpose:
Information management system -it is a system for collecting and processing information necessary to manage an organization, enterprise, industry.
Decision support system -are intended for the accumulation and analysis of data necessary for making decisions in various fields of human activity.
Information retrieval systems -these are systems, the main purpose of which is the search for information contained in various databases, various computer systems located at a considerable distance from each other.
Information and reference systems - provide the user with the necessary information in an interactive mode.
Data processing systems -function of systems processing and archiving large amounts of data.
Automated system (AS) Is a system consisting of personnel and a complex of means for automating their activities, the implementation of information technologies for performing established functions. Depending on the type of activity, the following AS are distinguished:
1. Automated control system (ACS).
2. Computer-aided design system (CAD).
3. Automated scientific research systems (ASNI).
IN expanded meaning ACS is a complex of software, technical, informational, linguistic, organizational and technological tools and personnel, designed to control various objects. IN special The meaning of ACS is a man-machine system based on the complex use of economic and mathematical methods (EMM) and technical means of information processing for solving problems of planning and managing various objects of production and economic activity. The main purpose of the ACS and, accordingly, the principles of their construction are the processes of collecting, storing, processing, as well as issuing significant amounts of information.
Automated Information System (AIS) Is a collection of information, economic and mathematical methods and models, technical, software, technological tools and specialists intended for processing information and making management decisions.
AIS provision.
Organizational support -this is a set of documents that establish the organizational structure, rights and obligations of users and operational personnel of AIS in the conditions of functioning, testing and ensuring the operability of automated information systems.
Organizational support implements the following functions:
· Analysis of the existing enterprise (organization) management system to identify tasks to be automated;
· Preparation of tasks for automation, including the development of technical specifications and feasibility studies of efficiency;
· Development of management decisions to change the structure of the organization and methodologies for solving problems aimed at improving the efficiency of the management system.
Organizational support includes:
· Methodological materials regulating the process of creation and functioning of IS;
· A set of tools for effective design and operation of IS;
· Technical documentation obtained in the course of enterprise survey, design, implementation and maintenance of the system;
· Personnel (organizational and staff structures of the enterprise), designing, implementing, maintaining and using IS.
Methodological support Is a set of documents describing the technology of AIS functioning, methods of selection and application of technological methods by users to obtain specific results in the operation of automated information systems.
Technical support Is a set of all technical means used in the functioning of the AIS.
The technical means include:
Computing equipment for various purposes (servers, workstations);
Special devices for collecting, accumulating, processing, transmitting and outputting information;
Data transmission devices and communication lines;
Automatic information retrieval devices;
Office equipment, operating materials, etc.
Mathematical software Is a set of mathematical methods, models and algorithms used in AIS.
The software includes:
Mathematical support (tools for modeling typical control problems, methods of multicriteria optimization, mathematical statistics, queuing theory, etc.);
Technical documentation (description of tasks, algorithms for solving problems, economic and mathematical models);
Methods for choosing software (methods for determining the types of problems, assessing the computational complexity of algorithms, methods for assessing the reliability of results).
Software Is a set of programs on data carriers and program documents intended for postponing, functioning and testing the AIS performance.
AIS software includes:
Software specially developed within the framework of automation, which implements the developed models of varying degrees of adequacy, reflecting the functioning of a real object;
General-purpose software designed for solving typical information processing tasks.
Information Support Is a set of forms of documents, classifiers, regulatory framework and implemented information used in the AIS during its operation.
Information support includes:
· Description of technological processes;
· Description of the organization of the information base;
· Description of input streams;
· Description of output messages;
· Description of classification and coding systems;
· Forms of documents;
· Description of the structure of arrays.
Linguistic support Is a set of tools and rules for formalizing a natural language used when communicating between users and AIS operating personnel with a set of automation tools in the operation of an automated information system.
Language means of linguistic support are divided into two groups: traditional languages \u200b\u200b(natural, mathematical, algorithmic languages, modeling languages) and languages \u200b\u200bintended for dialogue with computers.
Legal support Is a set of legal norms governing legal relations in the functioning of the AIS and the legal status of the results of its functioning.
(Legal support is implemented in the organizational support of AIS.)
The legal framework includes laws, decrees, decisions of state authorities, orders, instructions and other normative documents of ministries, departments, organizations, local authorities. In legal support, one can distinguish a general part that regulates the functioning of any information system, and a local part that regulates the functioning of a specific system.
The legal support for the development of an information system includes regulations related to the contractual relationship between the developer and the customer and the legal regulation of deviations from the contract.
Legal support for the functioning of IP includes:
· IP status;
· Rights, duties and responsibilities of personnel;
· Legal provisions of certain types of management process;
· The procedure for the creation and use of information.
Ergonomic support Is a set of implemented solutions in automated information systems for the coordination of psychological, psychophysiological, anthropometric, physiological characteristics and capabilities of AIS users with the technical characteristics of the AIS automation complex and the parameters of the working environment at the workplaces of the automated information systems personnel.
Protecting the health of workers, ensuring the safety of working conditions, eliminating occupational diseases and industrial injuries are one of the main concerns of the human society.