Many budget models of Android smartphones and tablets are equipped with small capacity batteries. And this means that even with not the most intensive use of the device, you cannot do without additional recharging during the day. And if there is no way to constantly "sit near the outlet"? There are several ways out of this situation: carry an extra battery with you, buy a docking station with a recharging function, or try to improve the power saving of Android OS devices by turning off unnecessary functions by software. Since the latter method does not require money, we will consider it in more detail.
App logos: Battery Calibration and Battery Doctor
10 ways to save battery power
- The display consumes the most energy - the larger its diagonal, the more capacious the battery should be. To reduce its power consumption - reduce the screen brightness to an acceptable minimum or turn on the function of its automatic adjustment. Some Android applications support work in "dark" or "negative" mode - they allow you to switch the background from white to black (dark background - light text). This also reduces battery consumption.
- Disable features you are not currently using. Such as Wi-Fi, cellular, BlueTooth and GPS, since the constant search for networks and exchange data with them also requires a lot of energy. To do this, it is most convenient to switch to flight mode from time to time.
- Turn off vibration and auto-rotate screen. Internal elements that are responsible for this are in third place in terms of electricity consumption.
- Do not turn off your mobile device with the power button unnecessarily - turning it on and off consumes energy a lot.
- Do not leave running applications that you are not working with. Don't wait for the system to complete them - do it yourself.
- Do not use animations and videos as screensavers and wallpapers - choose a static picture for the background of the screen.
- It is not advisable to store it for a long time, and especially to use the device in extremely low and high temperatures. The battery quickly degrades from this and its capacity ceases to correspond to the nominal one.
- If you use the Internet, disable the synchronization function with other devices when it is not needed, and prevent automatic updates of installed programs. Make sure that your system is free of viruses that, among other things, harm, secretly increase the load on the battery.
- Calibrate the battery from time to time - with the device turned off, carry out a full charge cycle, then turn on the device and use without additional recharging until all the energy is consumed. It can also be done using special calibration programs.
- And if there is no desire to constantly monitor what the battery is draining from, the Android application that controls energy consumption will do it for you.
Programs for extending the battery life of Android devices
Easy Battery Saver
An intelligent program that flexibly manages the charge consumption by interacting with the software and hardware resources of the device. The Easy Battery Saver mode has 8 parameters that are adjusted depending on the load on the device. Can work on automatic and custom settings. The app monitors the power consumption of network systems, manages sleep patterns, screen brightness, and monitors the impact of running applications and services.
Easy Battery Saver Benefits
- free;
- efficiency - allows you to save up to 50% energy;
- ease of use and customization;
- selection of several energy saving modes;
- displaying the charge level and its main "consumers" on the main screen;
- recommendations on how to reduce energy consumption at the moment;
- video tutorial on using the program.
Battery Doctor
Convenient multifunctional application with great capabilities. When installed, it takes full control of the device's energy management. Using a unique three-stage technology, it regulates the charging process, prevents rapid energy consumption and precisely determines the time when it is necessary or, on the contrary, does not need to be connected to the power source. The Battery Doctor complex includes a Task Killer module that allows you to complete unused offers that are running in the background.
Program features
- with high accuracy determines the level of charge and the remaining battery life;
- automatically terminates unnecessary programs, positively affecting the performance of the device;
- provides data about hardware resources and software;
- monitors the processes of charging and discharging the battery, helping to prevent its rapid deterioration and extend its service life;
- informs the user about how much the battery life will increase when disconnecting network devices, games and other things;
- supports automatic and custom settings of power saving modes, quickly switches between them;
- supports connection of network management widgets, GPS, etc.
- the program is completely free.
Battery master
Another application for controlling power consumption and increasing the standby time of the device. Has a simple and convenient user interface, several design options, clear settings.
The advantages of Battery Master
- russian language support;
- three-stage charging technology;
- built-in notification system about the remaining operating time in different modes: calls, music, video, Internet, and more.
- management of systems that affect energy consumption through the application interface.
Battery Calibration

App logos: Easy Battery Saver and Battery Master
Battery calibration software, which is important for extending battery life. Battery Calibration removes the batterystats.bin file from the Android system, which contains the charge level data used by the battery controller, and creates a clean one instead. These actions allow you to achieve a deeper level of charge and extend the life of the battery. The calibration procedure is recommended to be done after updating the device firmware, as well as once every 1 - 2 months for prevention.
Battery Calibration Specifications
- ease of use - operated by pressing one button;
- notifies about the current state of the battery;
- has a built-in voltmeter;
- can notify with a sound signal about the opportunity to start calibration (at a charge level of 100%)
- distributed free of charge.
Using docking stations and portable batteries
Docking station for Android devices - a device for stationary connection of tablet computers and phones to peripherals. Allows you to charge the device, connect to computer networks, TVs, multimedia centers, printers, etc. Docking stations are available both for specific models of gadgets and universal. It is certainly convenient to use them: while the tablet or smartphone is idle, the docking station will provide it with charging, not to mention other possibilities. However, this option is only suitable for home, office or car - you will not constantly carry the docking station in your pocket.
There is another means of extending the "life" of the battery - portable batteries. These are small devices that can transfer energy to a mobile device through a cable. The portable battery is charged from the mains. Due to its compactness, it can be carried with you in your pocket or bag, and is especially convenient to take on the road. This gadget will give you the opportunity to use your mobile device 2 - 4 times longer during normal operation, without using other energy-saving "tricks".
P. S.
There is no dispute about the relevance of energy saving tools for mobile devices today, since for most owners of budget phones and tablets this issue is quite acute. The electronics industry has not yet reached a level where the user will not worry about his gadget turning off at the most inopportune moment. Therefore, almost everyone is looking for something that is most suitable for themselves - a program or an adaptation, good, there is a lot of both. And what is the best - everyone decides for himself, based on personal preferences and capabilities of his mobile technology.
A modern smartphone is a real communication center and assistant that performs many useful functions.
Our life is now completely tied to the phone. When we are on the move and see a small remainder of the battery charge, which is rapidly decreasing, we try to maintain it in all available ways.
The Android operating system gives the user a lot of possibilities through its services and applications, and a smartphone with decent characteristics ensures fast programs and high performance. The price to pay for this is significant energy consumption. With active use of the gadget, few people have enough full battery charge for the whole day - it is. Fortunately, there are many ways to avoid being left with your smartphone turned off at the most inopportune moment.
Any Android device can enable power saving mode. When switching to this mode, the work is limited or the main energy consumers are turned off in the operating system.
Display. It is he who consumes most of the battery charge. The degree of brightness, backlight timeout and screen resolution directly affect battery life.
Installed applications invisibly, but regularly update their content for the user, and messengers and email clients notify us of new messages and letters using Internet traffic and battery power.
CPU performance... This metric measures how the device copes with multitasking and how fast applications are running. High performance requires significant energy resources. When switching to power saving mode and reducing the processor speed while performing standard tasks, you may notice a deterioration in smartphone performance.

The power saving mode in Android can be activated both automatically (when a small remaining battery charge is reached) and manually - through the device settings. After that, the smartphone will tell you how many hours without recharging the user can expect. Of course, these are estimates.
Some smartphone manufacturers are adding yet another mode - "extreme / maximum power saving". In this case, many applications become unavailable to the user, except for SMS, phone calls and some basic functions.

For more economical use of battery power, you can use not only the standard modes of the smartphone, but also some parameters of its operation. Often the device activates functions that are not currently used, but continue to consume battery power:
- auto-rotation of the screen, the position sensor of which is in constant working mode;
- live wallpapers and numerous widgets;
- active synchronization of accounts and contacts;
- running wireless connections: Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, GPS and mobile internet (especially 4G).

It is important to pay attention to the number of applications running simultaneously. When actively working with a smartphone, many programs are launched that remain open for a long time, quickly reducing the battery power. It is recommended to close especially voracious processes manually.
As you know, Google does not hesitate to sometimes borrow for its Android operating system some useful but missing functions from the proprietary firmware for smartphones and tablets that manufacturers equip them with.
One of these features is the power saving mode, which appeared in the new version of the Google operating system: Android 5Lollipop and which can be very, very useful to those who unexpectedly low battery discharge of a smartphone or tablet is found far from external power sources. If, of course, you know how to enable and configure this mode.
Fortunately, this is fairly easy to do. So where to find it, how does it work, and how to use it to extend the battery life of your smartphone or tablet?
How it works: According to Google, "Power saving mode will decrease performance and limit vibration and background data to extend battery life."
In other words: your tablet or smartphone will not work as fast, but it will take a long time and some applications will not synchronize data on the Web all the time, but only when you launch them.
Where to find and how to set up power saving mode.
The easiest way to get to the power saving menu is to slide the quick settings menu curtain from under the top edge of the tablet or smartphone screen with two fingers, click on the battery icon and press the menu button (three vertical dots) in the battery usage statistics window that opens.

Then, in the menu that opens, select "Power saving mode".

Here you will be able to turn it on manually (just by clicking on the On / Off switch), or set the automatic activation of the power saving mode by clicking on the "Turn on automatically" item, after which you will have a choice of three options:

When you select one of the automatic modes, when the battery reaches the specified level, you will see a prompt asking you to turn on the power saving mode.
At the same time, so that you do not forget that the mode that slows down your device was enabled, the lower and upper navigation and notification bars on the tablet or smartphone screen will turn bright orange.
Modern smartphones and tablets are much more like a full-fledged PC than a simple device for communicating and receiving information. Now they are equipped with 2 GHz quad-core processors, gigabytes of RAM and Full HD screens. The only problem is that to power all these powers, not a cable from the outlet is used, but a small battery, the capacity of which rarely lasts more than a day. Well, let's see how to fix this.
In this article I will try to figure out whether modern smartphones really consume too much energy and in fact they need much less. First, let's look at the energy conservation methods that are already in use in the Android operating system and how much they can reduce overall energy consumption. Then we will try to apply the popular energy saving methods, which are often talked about on forums and blogs, and see the result. In the end, we will apply heavy artillery in the form of methods such as undervolting and downlocking. Go.
Standard Energy Savers
There is a myth among smartphone users that in fact mobile devices should live much longer than they are now, and the real problem is not in the capacity, but in the buzz of Android and iOS developers - they just do not want to optimize the OS due to laziness or collusion with hardware manufacturers who need to sell gigahertz and gigabytes. OK, let's spend our time reading the documentation and try to figure it out. So, here are four myths about why Android eats up so much energy.
- Java is a brake on CPU and memory. The first thing to remember is that there is no Java in Android. It uses the Dalvik registry virtual machine, designed specifically for embedded devices. The Plan9 / Inferno developers have already written about the advantage of a registered VM, and a link to their article is at the end. In short, the register VM differs from the classic Java stack in less RAM requirements and less redundancy, that is, it allows you to execute code quickly without wasting memory. Second: most of the "heavy" code (multimedia codecs, graphics processing algorithms, cryptography, etc.) in Android is written in C, which allows it to be executed as quickly as in any other OS. Dalvik code is mainly used to define application logic, and thanks to HotSpot JIT, the code inside Dalvik is not much slower than the C code.
- Android does not know how to work effectively with equipment. This is complete nonsense. Android is based on the Linux kernel, where the hardware support code has been polished, if not brilliantly, then close to that. The OS implements many techniques for optimizing work with equipment and energy saving, such as deferred flushing of buffers to disk with merging, a competent task scheduler and a processor power saving algorithm, effective energy saving algorithms for Wi-Fi, 3G, LTE and Bluetooth (4.0 Low Energy) modules, batch method for polling sensors (implemented in 4.4 KitKat). Without all this, an Android smartphone would not have survived even five hours.
- The Linux kernel is redundant in mobile technology. The Linux kernel has a very flexible build system that allows you to include in the resulting image only what is really needed in a particular device. The key subsystems of the kernel from this, of course, will not become simpler (at least the base layer), in many ways they are too redundant for the conditions of mobile technology, but this is the price that you have to pay for Android to exist at all.
- ** Android is too complicated and heavy. ** Probably, many OS components can be seriously optimized or even removed altogether (there is a lot of duplicate code in the source code), and Google did this work with the 4.4 release, but you should not expect that all these optimizations are - will seriously prolong the life of a smartphone. After all, one day of the life of a gadget was a reality in the days of the very simple and light version 1.5.
The main "problem" not only of Android, but of all modern mobile operating systems is not at all in their severity and unoptimization, but in the fact that a modern smartphone is no longer a static gadget like Nokia N95, which allows you to run ICQ and play Sokoban, but the system living her own life. Regardless of whether the device is asleep or not, it continues to collect mail, receive notifications from the calendar, Facebook, Instagram, wait for Skype calls and sync files with the cloud (as, for example, does the Dropsync application). All this work cannot but affect the battery life, and this is the direction that should be looked at when talking about extending battery life.
Automation
To conserve battery power, it is highly recommended to use automation apps such as Tasker or Locale. With their help, you can configure the automatic activation of airplane mode at night, turn off data transmission when a certain battery level is reached, reduce the brightness to a minimum in the evening, and much more. Almost any energy saving software from the market can be replaced with these tools, while you will have complete control over what is happening.
Insomnia
Before moving on to the stories about optimization techniques, I must pour some more water and talk about what wakelock and suspend are. Like any mobile OS, Android works on the principle of "conserve as much energy as possible" and therefore at any time seeks to put the processor and other components of the device in a power-saving mode. This mechanism of operation allows the device to give processor resources to applications as needed, and the rest of the time to be in a low power consumption mode. When the user presses the shutdown button and the screen turns off, Android puts the smartphone into suspend mode, turning off the processor and leaving the voltage only on the RAM (analogous to ACPI S3). In this way, even greater savings can be achieved, which under certain conditions can reach 99%.
To prevent already running applications that should continue to work even after the screen is turned off (music player, file synchronization, etc.), they do not freeze when they go to suspend, a mechanism called "partial wakelock" is used. It works very simply: as long as there are applications that have installed wakelock, the device will not go into suspend and applications will be able to work normally. In addition, applications can use the AlarmManager, which allows you to remove a device from suspend at the right time in order to perform a specific job (this is how widgets do, for example). AlarmManager also uses wakelock to keep the processor awake.
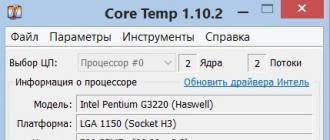
Overuse of these mechanisms can lead to excess energy consumption, regardless of which operating mode the gadget is in. Fortunately, having root, information about wakelock usage statistics is pretty easy to get. The most convenient way is with Wakelock Detector. This is a free application that shows the total number of wakelocks sorted by application.
Let's take a look, for example, what the Wakelock Detector shows on my Nexus 4 (screenshot of the Wakelock Detector). The very first line of the screen is the total wake time of the device for one day and six hours (since the moment it was fully charged). The five most voracious apps are Dropsync, OnLive, Google Search, Gmail, and Carbon. Together they kept the smartphone awake for almost an hour, which is a lot.

Unfortunately, I do not want to uninstall any of these applications, and therefore I will have to find out for what specific purposes they used wakelock and try to fix this problem using the settings of the applications themselves. Click on Dropsync and see that he set wakelock with the DropsyncWakeLock tag 15 times (which resulted in a total of 32 minutes of wakefulness) and once AlarmManager (2 seconds). We already know what AlarmManager is, but DropsyncWakelock is more interesting. The programmer has the right to give arbitrary names to wakelocks, but it's easy to assume that this one is used to perform automatic synchronization with Dropbox (Dropsync is designed for this). I don't really need constant synchronization, and I can start it myself. So I just go to Dropsync settings and disable automatic syncing. Voila, the phone wakes up less often and not for such long periods of time.

OnLive can be skipped, since 18 minutes of wakefulness were caused by incorrect closing of the application (you must exit it according to all the rules). Next up is Google Search, an app that includes Google Now, among other things. We tap on it and see that the two most actively used wakelocks are NlpWakeLock and EntriesRefresh_wakelock. This is already more difficult, and it is rather difficult to figure out what actually happens when installing them. Therefore, we hold our finger on the wakelock's name for a long time, select "Search" and see what the browser has found. Already on the second page found there is an explanation that NlpWakeLock is installed at the moment when the position of the smartphone relative to the network (3G, Wi-Fi) changes, after which Google Now sends location information to the server. The second wakelock appears to be used to update cards in Google Now. At the same time, you can solve the problem of gluttony in both cases by simply disabling "Google Search" in "Settings -\u003e Applications -\u003e All". The first solution is to turn off location detection in Android settings.
Gmail keeps the smartphone awake with a wakelock with a telling name sync/gmail-ls/com.google/ [email protected] Obviously, it is installed at the time of automatic mail synchronization, so you can reduce energy costs by simply disabling Gmail synchronization in "Settings -\u003e Accounts -\u003e Google -\u003e [email protected]". On the other hand, I do not want to do this and would rather tolerate three minutes of wakefulness in a day and a half.

After going through the list of the most power-hungry apps with Wakelock Detector, it's easy to see that the main reasons for waking up a device are different types of synchronization and regular location updates. This means that by disabling these features completely, you can get rid of most wakeups and seriously save battery.
I would recommend that you first go to your Google account settings ("Settings -\u003e Accounts -\u003e Google -\u003e [email protected]») And accounts of other applications and disable all unnecessary types of synchronization. For example, I don't need to sync my calendar, standard browser, Google+ contacts, and app data, so I can safely get rid of them. The same should be done with all other accounts registered on the smartphone, and turn off automatic synchronization in the settings of third-party applications (do you really need Twitter and RSS auto-sync?). Rarely used applications are best removed entirely.
The latest versions of Android do not allow you to turn off location detection completely, but they can use a very conservative and almost not affecting the life of a smartphone called (surprise!) "Battery saving" mode, which updates information only when there is a connection to Wi-Fi. networks or moving to another cell tower.
If the application runs out of battery, but you cannot delete it and there are no synchronization or auto-update options in the settings, then you can simply freeze it. This is done using a great app called Greenify. It suppresses the application's ability to wake up on its own and makes it work only when you want it. It's very easy to use. Launch Greenify, click on the + button in the lower left corner and see which applications work the longest in the background. The screenshot shows that the most gluttonous are the OTransfer Target, used to remotely enable redirection (it is generally constantly awake), as well as Beautiful Widgets and Carbon, which periodically wake up for all sorts of synchronizations. I set the OTransfer Target for the test, so I can safely remove it (by the way, it is also among the "leaders" in the Wakelock Detector). Beautiful Widgets wakes up to update the desktop widget, so I'll leave it alone. But Carbon, which took the fifth place according to the Wakelock Detector, can be frozen. To do this, just tap on the name and click the checkmark in the upper right corner.

- Killing background processes with a task killer. One of the stupidest ideas you can think of. You just need to remember: background processes do not consume energy, usually it is consumed by the services they run, which either are not killed by task killers at all, or have the ability to self-resurrect. But the killing of the background applications themselves leads to the need to restart them, for which energy is still wasted.
- Disable Wi-Fi at home. In energy-saving mode (when the smartphone is sleeping), the Wi-Fi module consumes very little energy, so little that much more is often spent on turning the module on and off. It makes sense only on a tablet, which you take in your hands two or three times a day to read a news or a book.
- Automatic switching between 2G and 3G. A similar story. When jumping between the types of networks, the towers are searched again and the connection is repeated, and at this time the radio module is operating at full power. Apps that automatically turn on 2G while sleeping almost always consume more power.
- Apps with names like Ultimate Battery Saver. In 99% (if not a hundred) of cases, this is either a placebo, or the same task killer equipped with a mechanism that turns off various components of the smartphone when a certain charge level is reached. First, there is a transfer to 2G and the GPS is turned off, then the Internet is turned off, and at the very end the phone is put into flight mode. The problem here is that the described mechanism of operation rather interferes and it is more convenient to do all this yourself at the right time.
- Battery calibration using recovery. There has long been a myth that deleting the /data/system/batterystats.bin file using CWM resets the battery settings, so that it starts to show a "more correct" charge level. The myth has become so ingrained in the minds that some individuals have begun to "calibrate" daily, claiming that this can extend the life of the battery and even increase its capacity. In fact, the file is needed to save energy usage statistics (the same information from "Settings -\u003e Battery") between reboots and does not affect anything.
Underwolting
Now let's talk about heavy artillery. It's no secret that one of the most power hungry components of a smartphone is the processor. Its power consumption may be even higher than that of the screen (or rather, its backlight), and this is all because it operates at very high frequencies that require high voltages. At first, it may seem that you can save battery life in this case simply by lowering the maximum processor frequency and turning off the "extra" cores. However, this most likely will not lead to anything: despite the reduced power consumption, the processor will execute code for longer, and ultimately the power consumption may even increase.

Instead, an undervolting operation should be performed, that is, simply to lower the maximum supplied voltage for all possible frequencies. To do this, you need to install a custom kernel that supports this function. I talked about how to do this and which kernel to choose in all the details in one of the previous issues of the magazine, so I will not repeat myself, but simply say that if you have one of the nexus, then it is enough to install franco.Kernel updater and with it help download and install the kernel. Everything happens automatically.
Next, install the paid version of Trickster MOD (free does not save voltage settings) or CPU Adjuster; for franco kernels, the paid franco.Kernel updater is also suitable. Go to the voltage adjustment page (in Trickster MOD, the required settings are at the bottom of the fourth page) and begin to carefully decrease 25 mV for each of the possible processor frequencies. After decreasing, we minimize the application and test the smartphone for a while, launching heavy applications, then we decrease it again and test it again.

In 90% of cases, the processor will withstand a drop of 100 mV without any consequences, and this will give us an additional hour or two in active use mode. If you are lucky, the processor will be able to withstand –150, and in especially happy cases even –200, it all depends on the batch of the processor and the specific instance. Too much underestimation of the voltage will lead to a reboot, after which it will be enough to raise the voltage by 25 mV and save the value in the default profile (in Trickster MOD, this is the "Profile" button immediately above the values).
INFO
A smartphone with an AMOLED screen will last longer if you use apps with a black background. To make system apps dark, one can use the AOKP firmware or one of the Xposed modules.
Often, the automatic screen brightness adjustment mechanism sets too high values. If you manually control the brightness, you can extend the life of your smartphone by another couple of hours.
Advanced firmware features of some smartphone manufacturers, such as gesture control, voice control, or automatic screen activation, drain the battery. Disable them if possible.
Instead of conclusions
In general, the methods described in the article can extend the battery life by at least half a day (with an average intensity of use), and even more if you turn off all types of synchronization and remove unnecessary applications. It is not difficult to implement the recommendations, and the effect is significant.
“Before you have time to charge the tablet, it’s already discharged!” - you can often hear from the happy owners of gadgets.
There can be two reasons affecting the energy saving of Android:
1) inability to use the battery correctly and
2) factory defect.
We will consider the first reason in this article.
Mobile laptops have faded into the background with the advent of portable gadgets: tablets and smartphones. The latest technological wonder is much more pleasant to use and costs less. If, apart from surfing the Internet, music and games, nothing else is required, then a tablet is what you need! Almost everyone is satisfied with such a convenient purchase, and they use it to the fullest with joy.
However, very soon the joy gives way to surprised disappointment from the question that arose: "Why is the battery draining so quickly?" Yes, the battery really rarely pleases anyone with its work, or maybe just the expectations of consumers are somewhat overestimated. Be that as it may, there are several secrets to energy conservation.
1. Brightness
The lion's share of the charge goes to the backlight of the screen, so it is worth setting the minimum brightness at which the convenience of work is maintained. You can even do a little test and find out how many minutes it takes 1% of the charge at maximum brightness and at minimum brightness. The test results are impressive.
2. Auto rotate
Disable auto-rotate the screen, just like any other sensors. It will also reduce power consumption.
3. Wallpapers and widgets
Give up live wallpapers and working widgets, they also consume the power of the tablet (or smartphone) battery.
4. Wireless connections
Turn off unnecessary wireless connections. Working wireless connections consume battery power. It means that it is extremely important to disable Wi-Fi, GPS, Bluetooth as unnecessary.
It is also worth turning the "My Location" section slider off.
By the way, in order to put all wireless connections, which waste battery charge, in one fell swoop, you can use "Airplane mode".
5. Synchronization
This is a necessary thing, often replacing information carriers, as well as other methods of data transmission. However, its constant work in the background is highly undesirable. Sync settings, disable sync can be found in Account Management.
6. Work in the background
The stock Android firmware is weighed down by a multitude of applications that are often not needed. However, in order to somehow change or completely stop their work, it will take some experience.
You need to stop running applications carefully, having previously figured out what this application does and what it is for. Otherwise, the operation of the tablet (gadget) may deteriorate, or even as a result of such ill-considered activity, a reboot may be required. In general, you only need to stop running background applications if you are sufficiently prepared to do so.
What should be done to stop running background applications? For this purpose, you can use the "Application Manager", which is in the standard "Settings" menu (Fig. 1).

Figure: 1. Launching application manager
Selecting the "Running" tab (1 in Fig. 2), you can see which of these applications are constantly "spinning" in the device's memory and "devour" its resources, including battery life.

Figure: 2. Application manager. The Running tab is open
By clicking on any of the running applications, for example, on the Settings application (3 in Fig. 2), we get to the “Application Information” window, which contains the “Stop” button of interest to us (Fig. 3).

Figure: 3. The "Stop" button in the Active application window
On the "Running" tab, you can see the "cached processes" (2 in Fig. 2), which can also be stopped in the same way using the Stop button (Fig. 4).

Figure: 4. The Stop button in the Active application window of the cached process
As a rule, the operating system provides minimal information about each application and about each cached process. This information may include, for example, messages:
- "Application may crash when stopping service",
- "This process usually does not need to be stopped" or
- “When the application stops, some data may be lost”, etc.
These messages must be carefully treated, these recommendations must be adhered to, it is not in vain that they are written to us, users of tablets (gadgets).
To be honest, I myself do not touch background applications and processes, I try not to stop them unnecessarily. Perhaps this leads to a faster discharge of the battery, but I feel so much safer than waiting for some "adventure" due to mistakenly or incorrectly disabled applications and processes. Let them work, since the operating system needs it.
7.Bluetooth keyboard
It consumes relatively little energy. However, if you often deal with documents that require a lot of printing, then it is best to purchase a USB keyboard. A Bluetooth keyboard may be more convenient, but not beneficial in terms of energy consumption.
8. Extreme Power Saving Android
It is impossible not to mention the standard Android option "Extreme energy saving". You can use the battery to conserve battery power. True, they mainly use it if there is no way to charge a fairly discharged battery of a tablet or gadget.
Turns on "Extreme energy saving" in "Settings". The option of interest is called “Extreme energy saving” (Fig. 5).

Figure: 5. Enabling extreme power saving Android
When this option is enabled, the use of applications is limited, they are downloaded only from the list of main applications, which you need to select yourself. Also, the transmission of mobile data is turned off, if the tablet or smartphone "knows how" to do this, WiFi and Bluetooth are turned off. However, you must remember that after turning off the extreme power saving mode on the screen of your device, the location of the application icons may change, the picture will become unusual, although nothing will get worse from this.
9. Battery
Finally, it is impossible not to say about the control of the use of battery resources and the optimization of the use of battery resources provided by the Android operating system. To do this, in the "Settings" menu there is an option "Battery". It allows you to:

Figure: 7. Optimizing apps to save battery life
So, if you click on the Facebook application, which consumes most of the electricity of our gadget (Fig. 8),

Figure: 8. Options for optimizing applications on the example of Facebook
... then, in particular, it can be seen that when the optimization option “Automatic optimization (Optimization of applications not used for 3 days)” is installed for the Facebook application, optimization of energy consumption is not enough (Fig. 8). You should choose the option "Always optimize".
But the option "Disable" energy saving on Android turns off optimization, and the application consumes the most electricity for its work.
so
These 9 tips will help you extend battery life.
But it is worth remembering that its capacity decreases over time, even with proper use of the gadget, simply because the battery is periodically charged and discharged. And its resource is precisely calculated by the number of possible charge-discharge cycles.
The more cycles, the more the battery of our tablet (gadget) wears out, and nothing can be done about it. Everything is not forever ...
Get the latest computer literacy articles straight to your inbox.
Already more 3.000 subscribers